14628fe6f0b8e804167a76d3fb693346.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 The Role of Technology Change in NEC’s Growth J. Travis Brooks New York University February 19, 2003 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
The Role of Technology Change in NEC’s Growth J. Travis Brooks New York University February 19, 2003 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Discussion Topics Ø Ø Historical IT Perspective: Technology Innovation Ø The Era of Consolidation: Back to Basics Ø Strategic Challenges to NEC Ø 2 Background to NEC Corporation March 18 th Visit to Japan Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Discussion Topics Ø Ø Historical IT Perspective: Technology Innovation Ø The Era of Consolidation: Back to Basics Ø Strategic Challenges to NEC Ø 2 Background to NEC Corporation March 18 th Visit to Japan Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 ØBackground on NEC Corporation 3 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
ØBackground on NEC Corporation 3 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
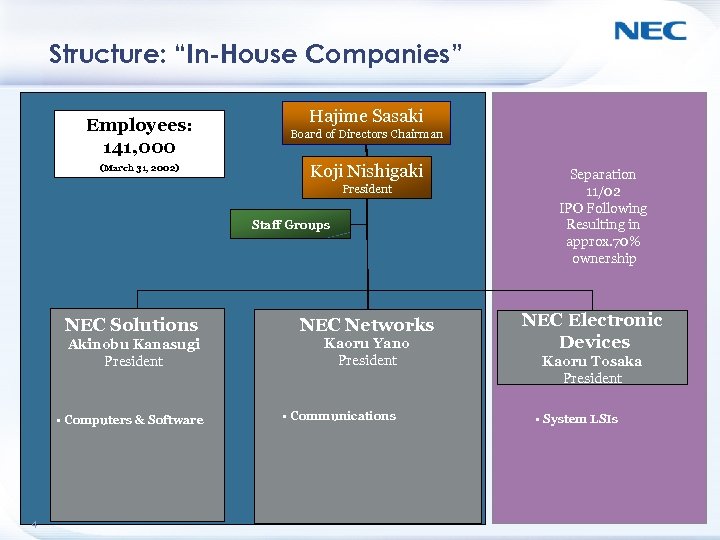 Structure: “In-House Companies” Hajime Sasaki Employees: 141, 000 Board of Directors Chairman (March 31, 2002) Koji Nishigaki President Staff Groups NEC Solutions NEC Networks Akinobu Kanasugi President Kaoru Yano President • Computers & Software 4 • Communications Separation 11/02 IPO Following Resulting in approx. 70% ownership NEC Electronic Devices Kaoru Tosaka President • System LSIs Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Structure: “In-House Companies” Hajime Sasaki Employees: 141, 000 Board of Directors Chairman (March 31, 2002) Koji Nishigaki President Staff Groups NEC Solutions NEC Networks Akinobu Kanasugi President Kaoru Yano President • Computers & Software 4 • Communications Separation 11/02 IPO Following Resulting in approx. 70% ownership NEC Electronic Devices Kaoru Tosaka President • System LSIs Corporate Strategy and Business Development
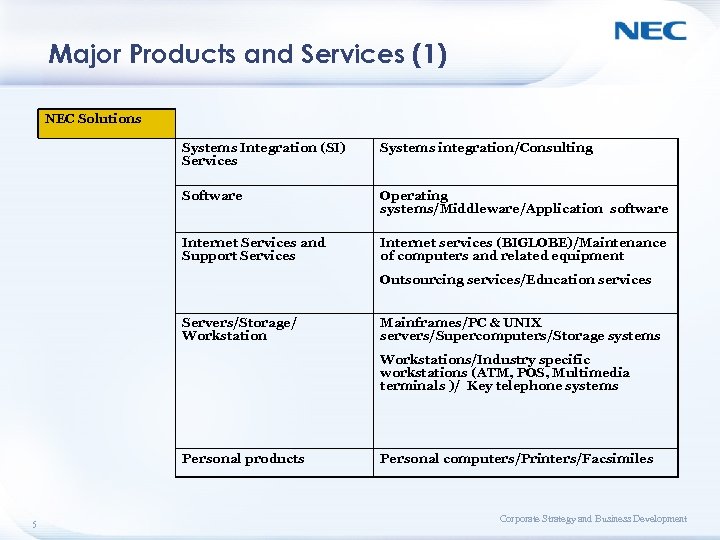 Major Products and Services (1) NEC Solutions Systems Integration (SI) Services Systems integration/Consulting Software Operating systems/Middleware/Application software Internet Services and Support Services Internet services (BIGLOBE)/Maintenance of computers and related equipment Outsourcing services/Education services Servers/Storage/ Workstation Mainframes/PC & UNIX servers/Supercomputers/Storage systems Workstations/Industry specific workstations (ATM, POS, Multimedia terminals )/ Key telephone systems Personal products 5 Personal computers/Printers/Facsimiles Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Major Products and Services (1) NEC Solutions Systems Integration (SI) Services Systems integration/Consulting Software Operating systems/Middleware/Application software Internet Services and Support Services Internet services (BIGLOBE)/Maintenance of computers and related equipment Outsourcing services/Education services Servers/Storage/ Workstation Mainframes/PC & UNIX servers/Supercomputers/Storage systems Workstations/Industry specific workstations (ATM, POS, Multimedia terminals )/ Key telephone systems Personal products 5 Personal computers/Printers/Facsimiles Corporate Strategy and Business Development
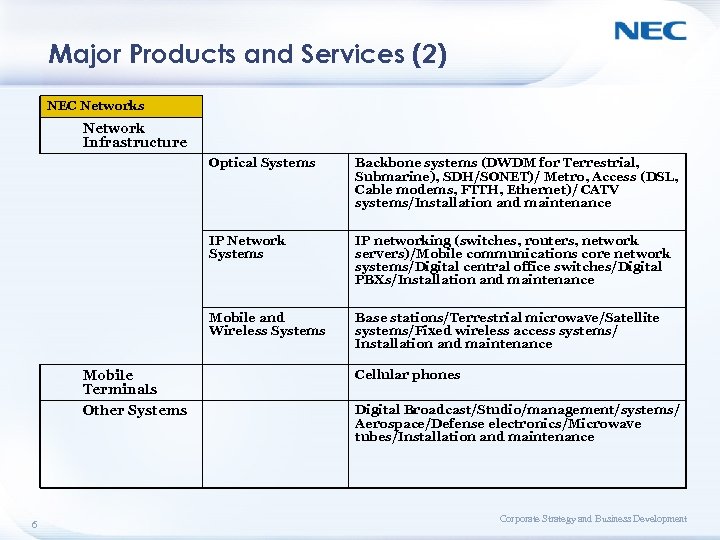 Major Products and Services (2) NEC Networks Network Infrastructure Optical Systems Backbone systems (DWDM for Terrestrial, Submarine), SDH/SONET)/ Metro, Access (DSL, Cable modems, FTTH, Ethernet)/ CATV systems/Installation and maintenance IP Network Systems IP networking (switches, routers, network servers)/Mobile communications core network systems/Digital central office switches/Digital PBXs/Installation and maintenance Mobile and Wireless Systems Base stations/Terrestrial microwave/Satellite systems/Fixed wireless access systems/ Installation and maintenance Mobile Terminals Other Systems 6 Cellular phones Digital Broadcast/Studio/management/systems/ Aerospace/Defense electronics/Microwave tubes/Installation and maintenance Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Major Products and Services (2) NEC Networks Network Infrastructure Optical Systems Backbone systems (DWDM for Terrestrial, Submarine), SDH/SONET)/ Metro, Access (DSL, Cable modems, FTTH, Ethernet)/ CATV systems/Installation and maintenance IP Network Systems IP networking (switches, routers, network servers)/Mobile communications core network systems/Digital central office switches/Digital PBXs/Installation and maintenance Mobile and Wireless Systems Base stations/Terrestrial microwave/Satellite systems/Fixed wireless access systems/ Installation and maintenance Mobile Terminals Other Systems 6 Cellular phones Digital Broadcast/Studio/management/systems/ Aerospace/Defense electronics/Microwave tubes/Installation and maintenance Corporate Strategy and Business Development
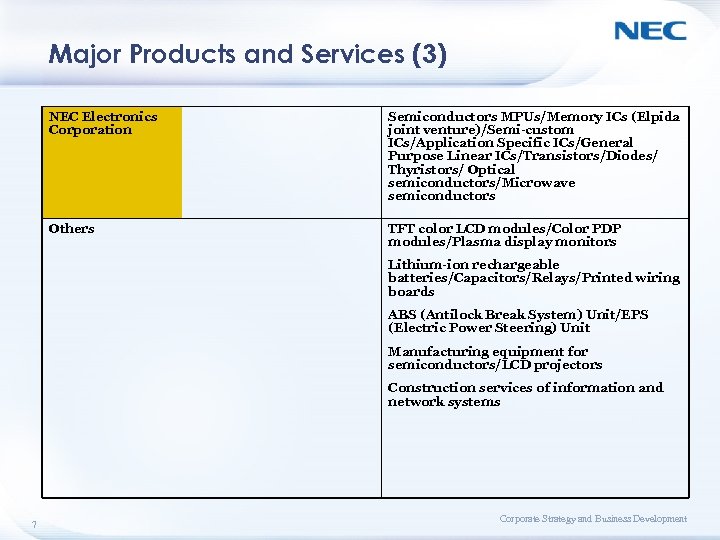 Major Products and Services (3) NEC Electronics Corporation Semiconductors MPUs/Memory ICs (Elpida joint venture)/Semi-custom ICs/Application Specific ICs/General Purpose Linear ICs/Transistors/Diodes/ Thyristors/ Optical semiconductors/Microwave semiconductors Others TFT color LCD modules/Color PDP modules/Plasma display monitors Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries/Capacitors/Relays/Printed wiring boards ABS (Antilock Break System) Unit/EPS (Electric Power Steering) Unit Manufacturing equipment for semiconductors/LCD projectors Construction services of information and network systems 7 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Major Products and Services (3) NEC Electronics Corporation Semiconductors MPUs/Memory ICs (Elpida joint venture)/Semi-custom ICs/Application Specific ICs/General Purpose Linear ICs/Transistors/Diodes/ Thyristors/ Optical semiconductors/Microwave semiconductors Others TFT color LCD modules/Color PDP modules/Plasma display monitors Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries/Capacitors/Relays/Printed wiring boards ABS (Antilock Break System) Unit/EPS (Electric Power Steering) Unit Manufacturing equipment for semiconductors/LCD projectors Construction services of information and network systems 7 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
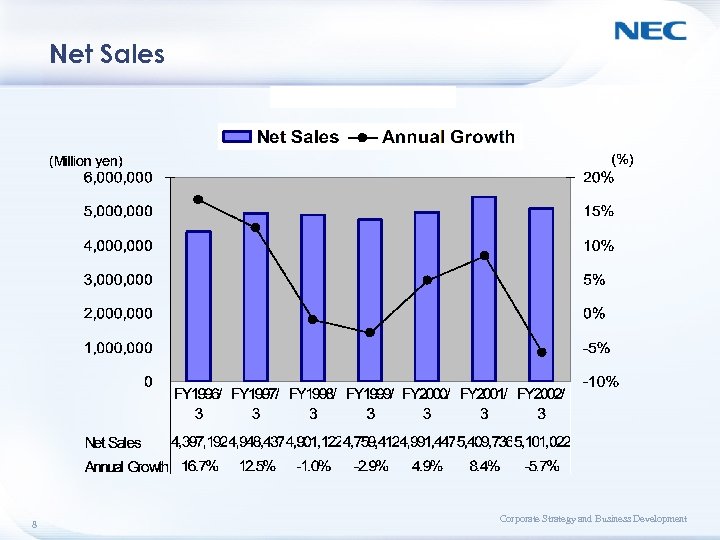 Net Sales 8 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Net Sales 8 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
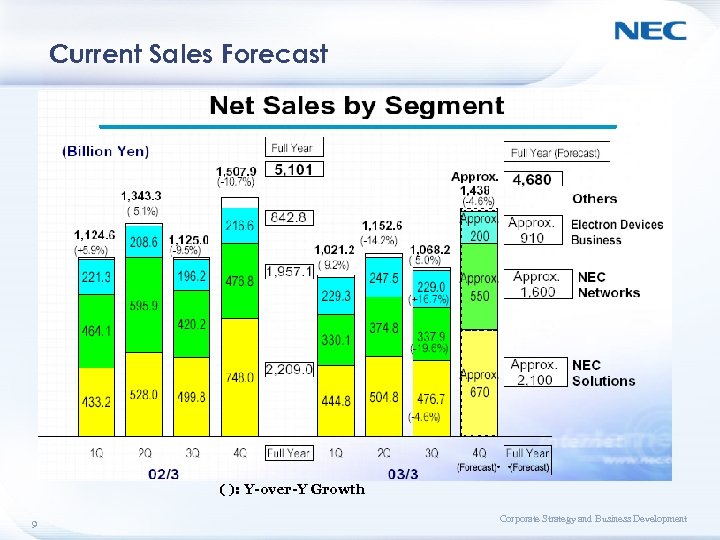 Current Sales Forecast ( ): Y-over-Y Growth 9 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Current Sales Forecast ( ): Y-over-Y Growth 9 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
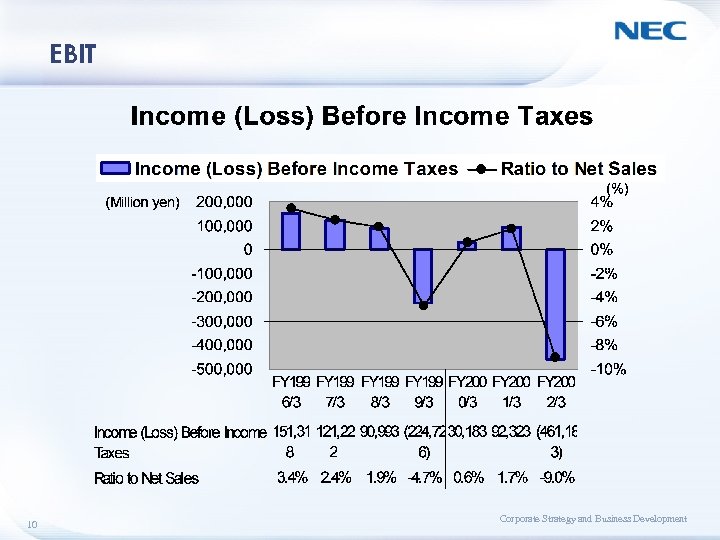 EBIT 10 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
EBIT 10 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
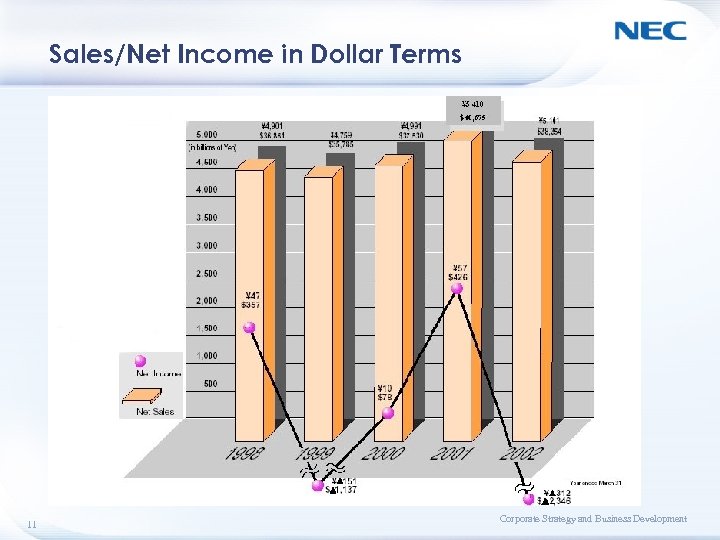 Sales/Net Income in Dollar Terms 11 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Sales/Net Income in Dollar Terms 11 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
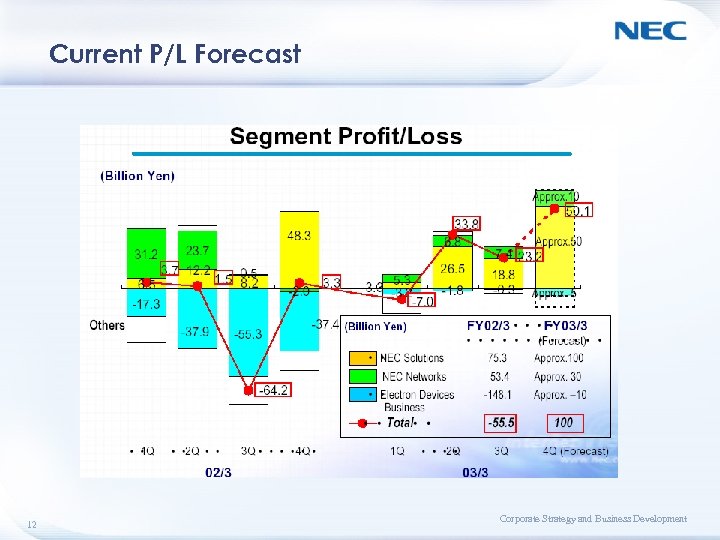 Current P/L Forecast 12 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Current P/L Forecast 12 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
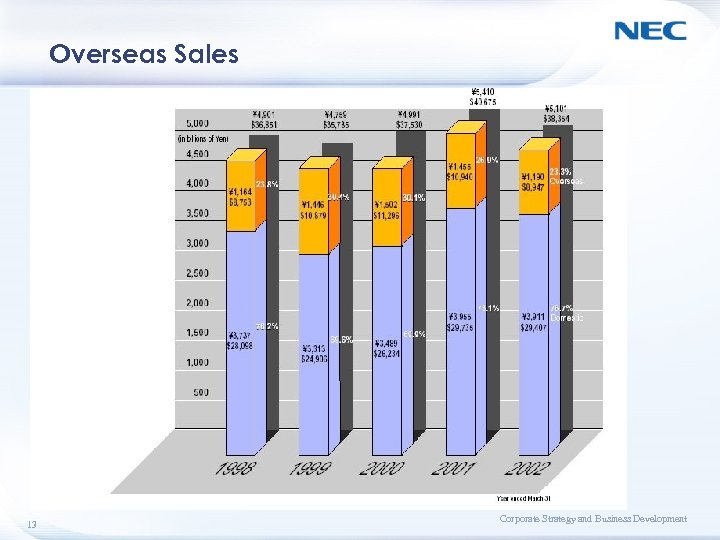 Overseas Sales 13 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Overseas Sales 13 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
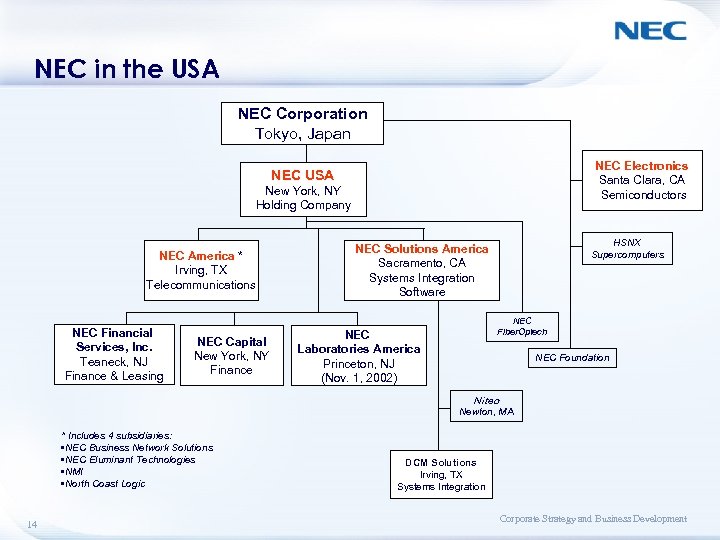 NEC in the USA NEC Corporation Tokyo, Japan NEC Electronics Santa Clara, CA Semiconductors NEC USA New York, NY Holding Company NEC America * Irving, TX Telecommunications NEC Financial Services, Inc. Teaneck, NJ Finance & Leasing NEC Capital New York, NY Finance HSNX Supercomputers NEC Solutions America Sacramento, CA Systems Integration Software NEC Fiber. Optech NEC Laboratories America Princeton, NJ (Nov. 1, 2002) NEC Foundation Niteo Newton, MA * Includes 4 subsidiaries: • NEC Business Network Solutions • NEC Eluminant Technologies • NMI • North Coast Logic 14 DCM Solutions Irving, TX Systems Integration Corporate Strategy and Business Development
NEC in the USA NEC Corporation Tokyo, Japan NEC Electronics Santa Clara, CA Semiconductors NEC USA New York, NY Holding Company NEC America * Irving, TX Telecommunications NEC Financial Services, Inc. Teaneck, NJ Finance & Leasing NEC Capital New York, NY Finance HSNX Supercomputers NEC Solutions America Sacramento, CA Systems Integration Software NEC Fiber. Optech NEC Laboratories America Princeton, NJ (Nov. 1, 2002) NEC Foundation Niteo Newton, MA * Includes 4 subsidiaries: • NEC Business Network Solutions • NEC Eluminant Technologies • NMI • North Coast Logic 14 DCM Solutions Irving, TX Systems Integration Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 ØHistorical IT Perspective: Technology Innovation 15 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
ØHistorical IT Perspective: Technology Innovation 15 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
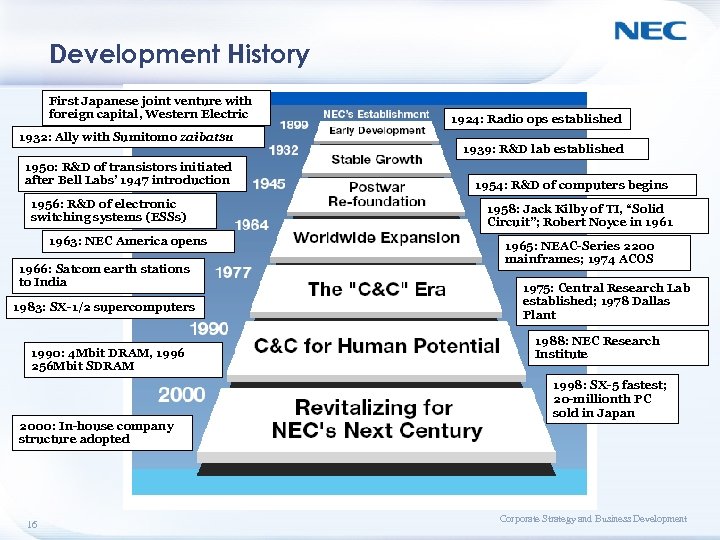 Development History First Japanese joint venture with foreign capital, Western Electric 1932: Ally with Sumitomo zaibatsu 1950: R&D of transistors initiated after Bell Labs’ 1947 introduction 1956: R&D of electronic switching systems (ESSs) 1963: NEC America opens 1966: Satcom earth stations to India 1983: SX-1/2 supercomputers 1990: 4 Mbit DRAM, 1996 256 Mbit SDRAM 2000: In-house company structure adopted 16 1924: Radio ops established 1939: R&D lab established 1954: R&D of computers begins 1958: Jack Kilby of TI, “Solid Circuit”; Robert Noyce in 1961 1965: NEAC-Series 2200 mainframes; 1974 ACOS 1975: Central Research Lab established; 1978 Dallas Plant 1988: NEC Research Institute 1998: SX-5 fastest; 20 -millionth PC sold in Japan Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Development History First Japanese joint venture with foreign capital, Western Electric 1932: Ally with Sumitomo zaibatsu 1950: R&D of transistors initiated after Bell Labs’ 1947 introduction 1956: R&D of electronic switching systems (ESSs) 1963: NEC America opens 1966: Satcom earth stations to India 1983: SX-1/2 supercomputers 1990: 4 Mbit DRAM, 1996 256 Mbit SDRAM 2000: In-house company structure adopted 16 1924: Radio ops established 1939: R&D lab established 1954: R&D of computers begins 1958: Jack Kilby of TI, “Solid Circuit”; Robert Noyce in 1961 1965: NEAC-Series 2200 mainframes; 1974 ACOS 1975: Central Research Lab established; 1978 Dallas Plant 1988: NEC Research Institute 1998: SX-5 fastest; 20 -millionth PC sold in Japan Corporate Strategy and Business Development
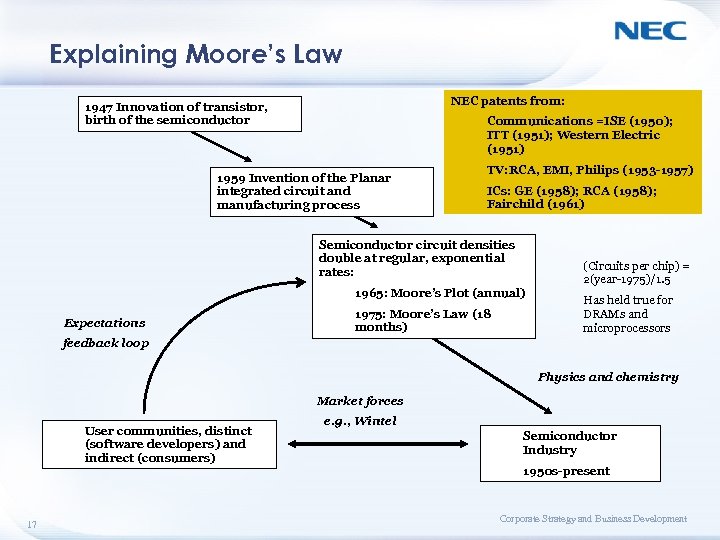 Explaining Moore’s Law NEC patents from: 1947 Innovation of transistor, birth of the semiconductor Communications =ISE (1950); ITT (1951); Western Electric (1951) 1959 Invention of the Planar integrated circuit and manufacturing process TV: RCA, EMI, Philips (1953 -1957) ICs: GE (1958); RCA (1958); Fairchild (1961) Semiconductor circuit densities double at regular, exponential rates: 1965: Moore’s Plot (annual) Expectations 1975: Moore’s Law (18 months) (Circuits per chip) = 2(year-1975)/1. 5 Has held true for DRAMs and microprocessors feedback loop Physics and chemistry Market forces User communities, distinct (software developers) and indirect (consumers) 17 e. g. , Wintel Semiconductor Industry 1950 s-present Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Explaining Moore’s Law NEC patents from: 1947 Innovation of transistor, birth of the semiconductor Communications =ISE (1950); ITT (1951); Western Electric (1951) 1959 Invention of the Planar integrated circuit and manufacturing process TV: RCA, EMI, Philips (1953 -1957) ICs: GE (1958); RCA (1958); Fairchild (1961) Semiconductor circuit densities double at regular, exponential rates: 1965: Moore’s Plot (annual) Expectations 1975: Moore’s Law (18 months) (Circuits per chip) = 2(year-1975)/1. 5 Has held true for DRAMs and microprocessors feedback loop Physics and chemistry Market forces User communities, distinct (software developers) and indirect (consumers) 17 e. g. , Wintel Semiconductor Industry 1950 s-present Corporate Strategy and Business Development
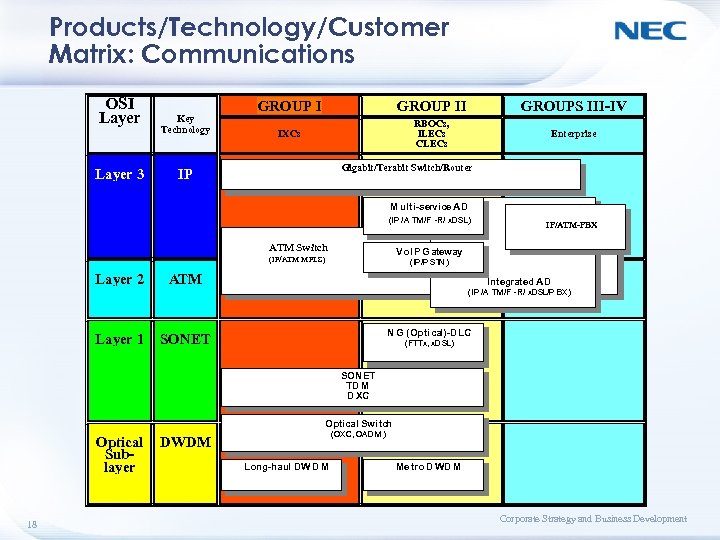 Products/Technology/Customer Matrix: Communications OSI Layer 3 Key Technology GROUP II GROUPS III-IV IXCs RBOCs, ILECs CLECs Enterprise Gigabit/Terabit Switch/Router IP M ulti-service AD (IP /A TM/F -R/ x. DSL) ATM Switch Vo. IP Gateway (IP/ATM MPLS) Layer 2 IP/ATM-PBX (IP/P STN ) ATM I ntegrated AD (IP /A TM/F -R/ x. DSL/P BX) Layer 1 N G (Optical)-D LC SONET (FTTx, x. DSL) SON ET TD M D XC Optical Swi tch Optical Sublayer 18 (OXC, OAD M ) DWDM Long-haul DW D M Me tro D WD M Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Products/Technology/Customer Matrix: Communications OSI Layer 3 Key Technology GROUP II GROUPS III-IV IXCs RBOCs, ILECs CLECs Enterprise Gigabit/Terabit Switch/Router IP M ulti-service AD (IP /A TM/F -R/ x. DSL) ATM Switch Vo. IP Gateway (IP/ATM MPLS) Layer 2 IP/ATM-PBX (IP/P STN ) ATM I ntegrated AD (IP /A TM/F -R/ x. DSL/P BX) Layer 1 N G (Optical)-D LC SONET (FTTx, x. DSL) SON ET TD M D XC Optical Swi tch Optical Sublayer 18 (OXC, OAD M ) DWDM Long-haul DW D M Me tro D WD M Corporate Strategy and Business Development
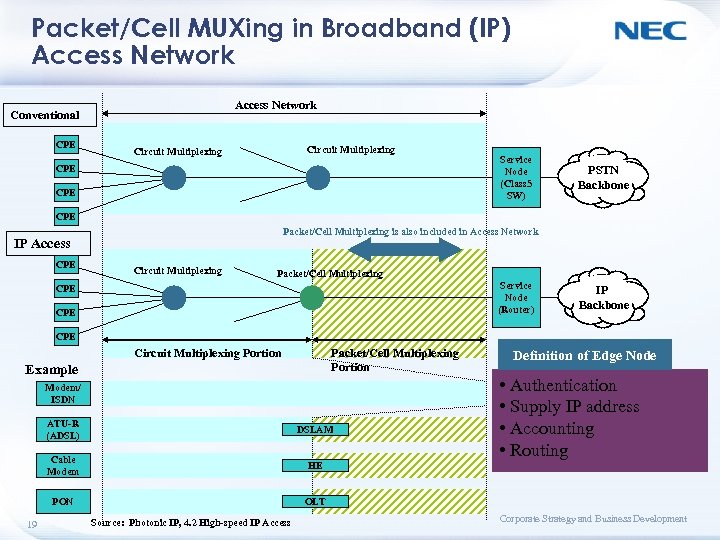 Packet/Cell MUXing in Broadband (IP) Access Network Conventional CPE Circuit Multiplexing CPE Service Node (Class 5 SW) PSTN Backbone CPE Packet/Cell Multiplexing is also included in Access Network IP Access CPE Circuit Multiplexing Packet/Cell Multiplexing Service Node (Router) CPE IP Backbone CPE Circuit Multiplexing Portion Packet/Cell Multiplexing Portion Example Modem/ ISDN ATU-R (ADSL) Cable Modem • Authentication • Supply IP address • Accounting • Routing HE PON 19 DSLAM Definition of Edge Node OLT Source: Photonic IP, 4. 2 High-speed IP Access Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Packet/Cell MUXing in Broadband (IP) Access Network Conventional CPE Circuit Multiplexing CPE Service Node (Class 5 SW) PSTN Backbone CPE Packet/Cell Multiplexing is also included in Access Network IP Access CPE Circuit Multiplexing Packet/Cell Multiplexing Service Node (Router) CPE IP Backbone CPE Circuit Multiplexing Portion Packet/Cell Multiplexing Portion Example Modem/ ISDN ATU-R (ADSL) Cable Modem • Authentication • Supply IP address • Accounting • Routing HE PON 19 DSLAM Definition of Edge Node OLT Source: Photonic IP, 4. 2 High-speed IP Access Corporate Strategy and Business Development
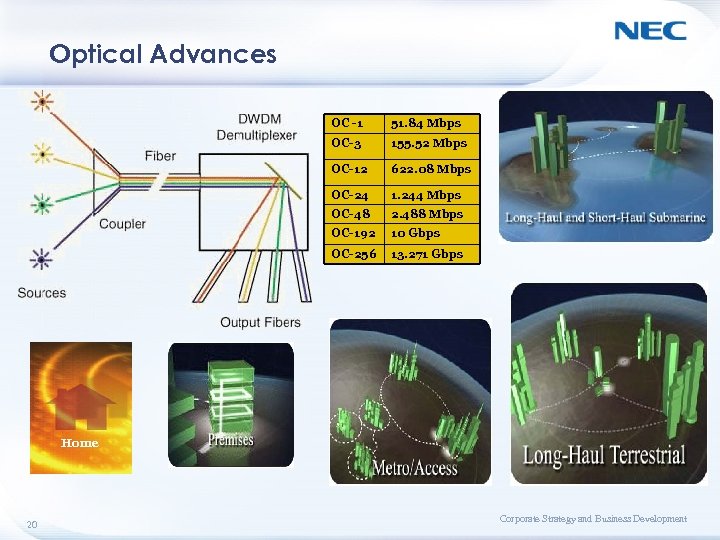 Optical Advances OC -1 51. 84 Mbps OC-3 155. 52 Mbps OC-12 622. 08 Mbps OC-24 1. 244 Mbps OC-48 2. 488 Mbps OC-192 10 Gbps OC-256 13. 271 Gbps Home 20 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Optical Advances OC -1 51. 84 Mbps OC-3 155. 52 Mbps OC-12 622. 08 Mbps OC-24 1. 244 Mbps OC-48 2. 488 Mbps OC-192 10 Gbps OC-256 13. 271 Gbps Home 20 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
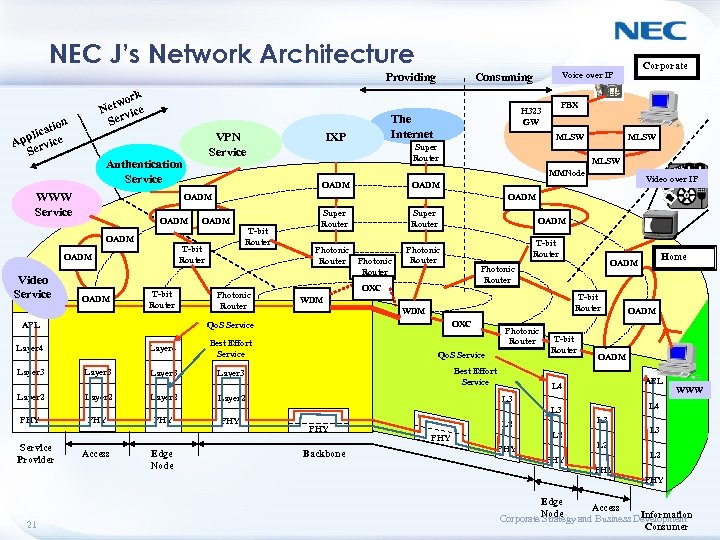 NEC J’s Network Architecture Providing ork etw ce N vi Ser tion lica e App rvic Se VPN Service Authentication Service WWW Service MLSW Super Router OADM T-bit Router Photonic Router Layer 4 Super Router Photonic Router OADM T-bit Router WDM OXC Layer 3 Layer 2 PHY PHY Qo. S Service Best Effort Service Layer 2 PHY 21 Photonic Router T-bit Router APL L 4 Edge Node Backbone L 3 L 2 PHY WWW L 4 L 3 L 2 OADM L 3 PHY Home OADM Photonic Router OXC Layer 3 T-bit Router Photonic Router WDM Best Effort Service Layer 3 Super Router Qo. S Service Access Video over IP OADM APL Service Provider MLSW OADM MLSW MMNode OADM Video Service IXP PBX H 323 GW The Internet Corporate Voice over IP Consuming PHY L 3 L 2 PHY Edge Access Node and Business Development Information Corporate Strategy Consumer
NEC J’s Network Architecture Providing ork etw ce N vi Ser tion lica e App rvic Se VPN Service Authentication Service WWW Service MLSW Super Router OADM T-bit Router Photonic Router Layer 4 Super Router Photonic Router OADM T-bit Router WDM OXC Layer 3 Layer 2 PHY PHY Qo. S Service Best Effort Service Layer 2 PHY 21 Photonic Router T-bit Router APL L 4 Edge Node Backbone L 3 L 2 PHY WWW L 4 L 3 L 2 OADM L 3 PHY Home OADM Photonic Router OXC Layer 3 T-bit Router Photonic Router WDM Best Effort Service Layer 3 Super Router Qo. S Service Access Video over IP OADM APL Service Provider MLSW OADM MLSW MMNode OADM Video Service IXP PBX H 323 GW The Internet Corporate Voice over IP Consuming PHY L 3 L 2 PHY Edge Access Node and Business Development Information Corporate Strategy Consumer
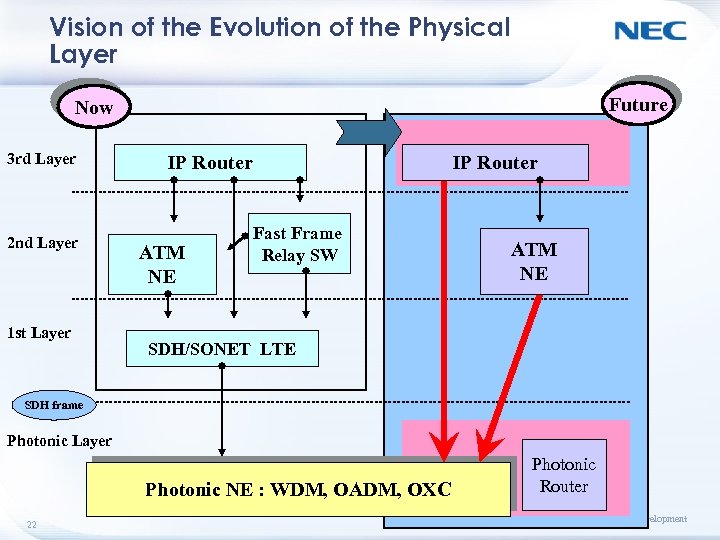 Vision of the Evolution of the Physical Layer Future Now 3 rd Layer 2 nd Layer 1 st Layer IP Router ATM NE IP Router Fast Frame Relay SW ATM NE SDH/SONET LTE SDH frame Photonic Layer Photonic NE : WDM, OADM, OXC 22 Photonic Router Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Vision of the Evolution of the Physical Layer Future Now 3 rd Layer 2 nd Layer 1 st Layer IP Router ATM NE IP Router Fast Frame Relay SW ATM NE SDH/SONET LTE SDH frame Photonic Layer Photonic NE : WDM, OADM, OXC 22 Photonic Router Corporate Strategy and Business Development
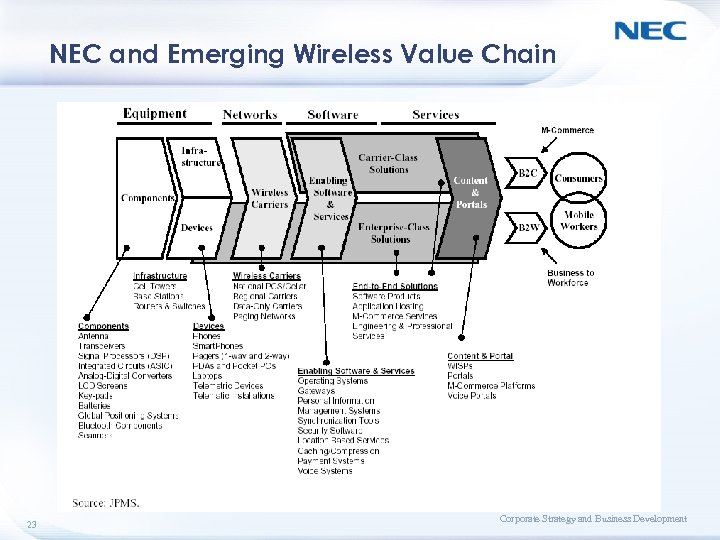 NEC and Emerging Wireless Value Chain 23 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
NEC and Emerging Wireless Value Chain 23 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Metcalf’s Law u Robert Metcalf's law states that the "value" or "power" of a network increases in proportion to the square of the number of nodes on the network. – In other words, if you have four nodes, or computers, on a network, say, an office intranet, its "value" would be four squared (4^2), or 16. – If you added on addition node, or PC, then the value would increase to 25 (5^2). – Holds for LANs and WANs (metro, the Internet) u One consequence of the network effect is that once a product is established in the market, demand for similar but incompatible products collapses. – Advantage of earlier drivers who come to dominate: Microsoft; Dell; Intel; Amazon; e. Bay. – A feedback phenomenon that says whenever it is in people's best interests to be where everyone else is, then that's where they'll be. 24 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Metcalf’s Law u Robert Metcalf's law states that the "value" or "power" of a network increases in proportion to the square of the number of nodes on the network. – In other words, if you have four nodes, or computers, on a network, say, an office intranet, its "value" would be four squared (4^2), or 16. – If you added on addition node, or PC, then the value would increase to 25 (5^2). – Holds for LANs and WANs (metro, the Internet) u One consequence of the network effect is that once a product is established in the market, demand for similar but incompatible products collapses. – Advantage of earlier drivers who come to dominate: Microsoft; Dell; Intel; Amazon; e. Bay. – A feedback phenomenon that says whenever it is in people's best interests to be where everyone else is, then that's where they'll be. 24 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
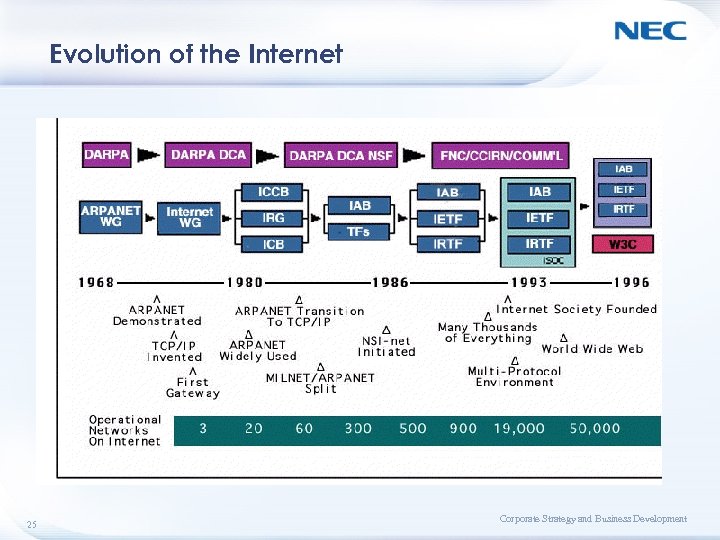 Evolution of the Internet 25 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Evolution of the Internet 25 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
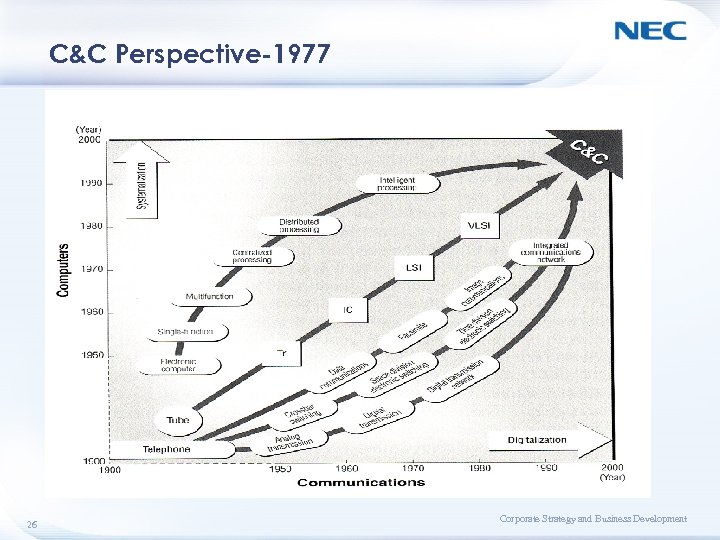 C&C Perspective-1977 26 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
C&C Perspective-1977 26 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 The Era of Consolidation: Back to Basics 27 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
The Era of Consolidation: Back to Basics 27 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
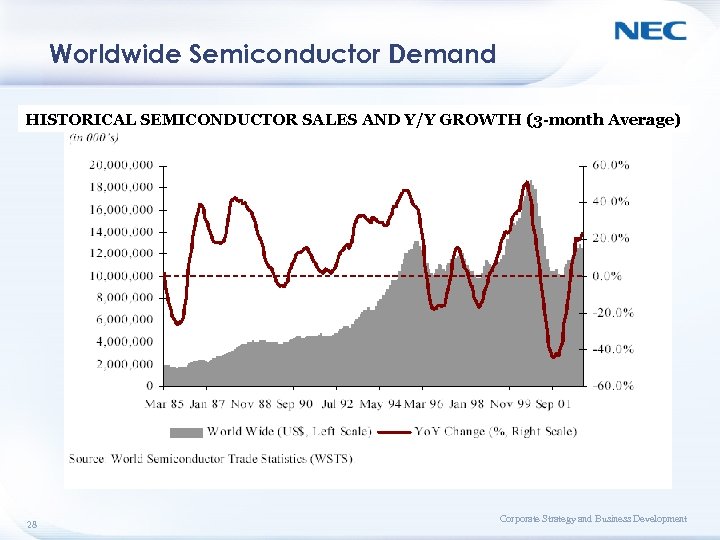 Worldwide Semiconductor Demand HISTORICAL SEMICONDUCTOR SALES AND Y/Y GROWTH (3 -month Average) 28 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Worldwide Semiconductor Demand HISTORICAL SEMICONDUCTOR SALES AND Y/Y GROWTH (3 -month Average) 28 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
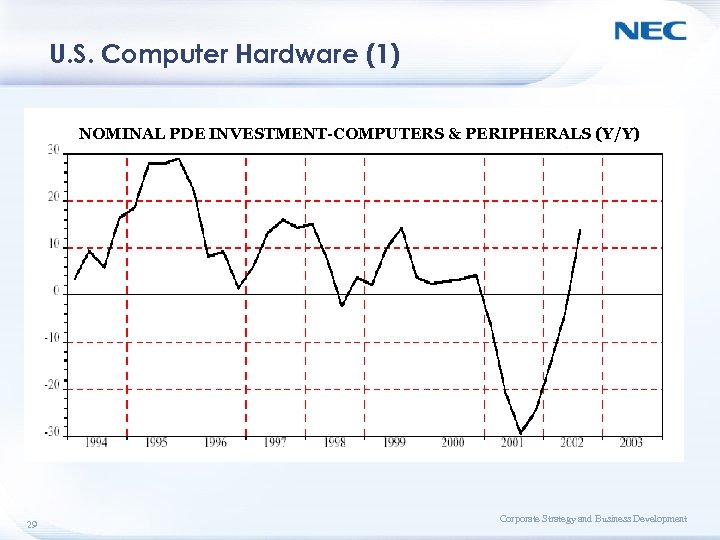 U. S. Computer Hardware (1) NOMINAL PDE INVESTMENT-COMPUTERS & PERIPHERALS (Y/Y) 29 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
U. S. Computer Hardware (1) NOMINAL PDE INVESTMENT-COMPUTERS & PERIPHERALS (Y/Y) 29 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
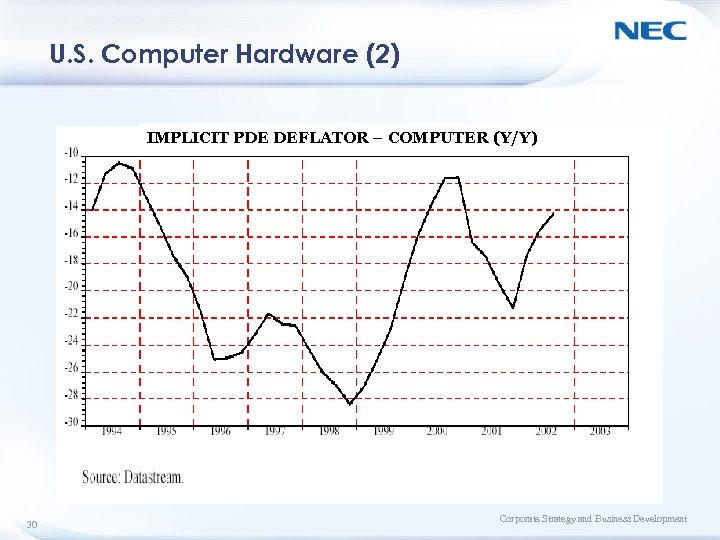 U. S. Computer Hardware (2) IMPLICIT PDE DEFLATOR – COMPUTER (Y/Y) 30 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
U. S. Computer Hardware (2) IMPLICIT PDE DEFLATOR – COMPUTER (Y/Y) 30 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
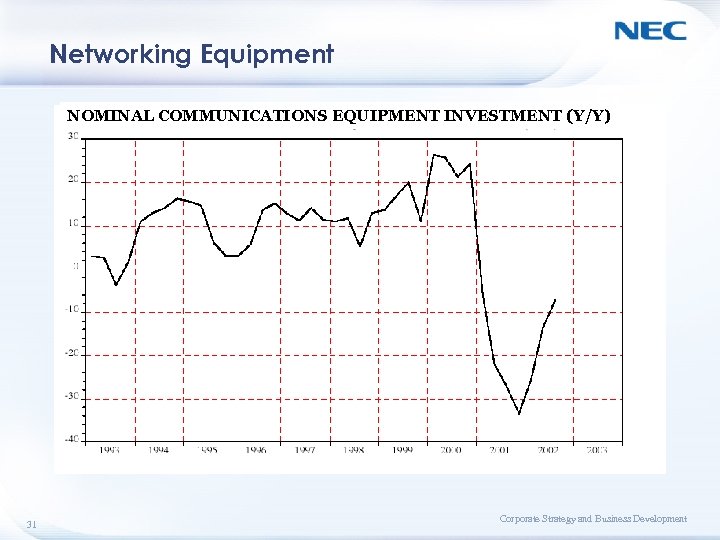 Networking Equipment NOMINAL COMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT INVESTMENT (Y/Y) 31 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Networking Equipment NOMINAL COMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT INVESTMENT (Y/Y) 31 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
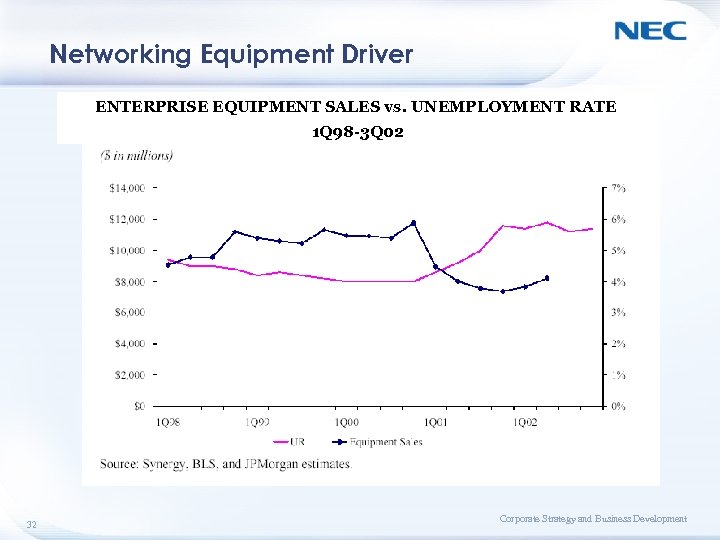 Networking Equipment Driver ENTERPRISE EQUIPMENT SALES vs. UNEMPLOYMENT RATE 1 Q 98 -3 Q 02 32 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Networking Equipment Driver ENTERPRISE EQUIPMENT SALES vs. UNEMPLOYMENT RATE 1 Q 98 -3 Q 02 32 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
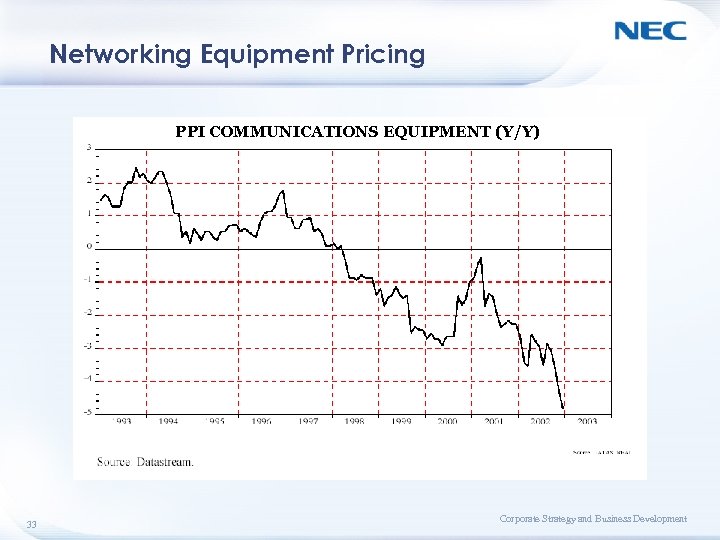 Networking Equipment Pricing PPI COMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT (Y/Y) 33 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Networking Equipment Pricing PPI COMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT (Y/Y) 33 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
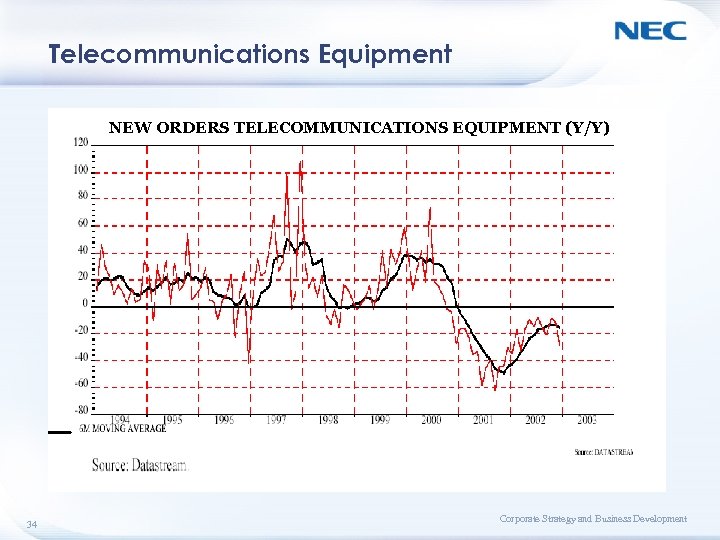 Telecommunications Equipment NEW ORDERS TELECOMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT (Y/Y) 34 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Telecommunications Equipment NEW ORDERS TELECOMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT (Y/Y) 34 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
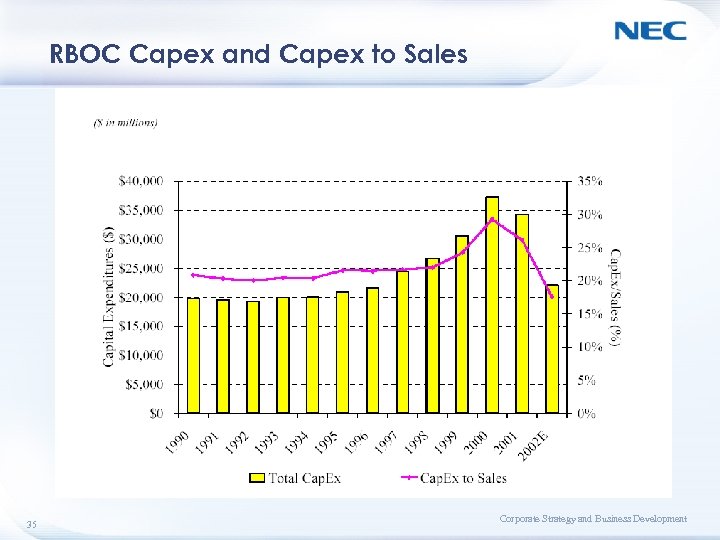 RBOC Capex and Capex to Sales 35 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
RBOC Capex and Capex to Sales 35 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Factors Leading to the Tech Bubble u The Telecom Act of 1996 u The Buildout of the Internet u The Buildout of Digital Wireless Networks u Rebuilding of U. S. Cable Networks 36 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Factors Leading to the Tech Bubble u The Telecom Act of 1996 u The Buildout of the Internet u The Buildout of Digital Wireless Networks u Rebuilding of U. S. Cable Networks 36 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
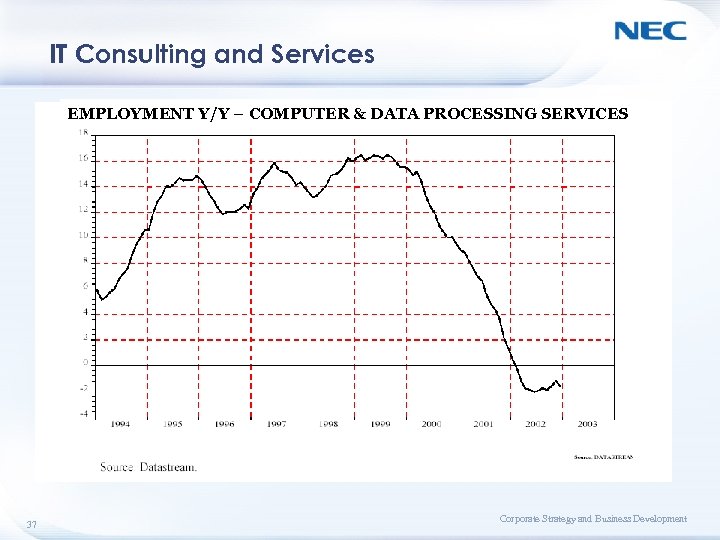 IT Consulting and Services EMPLOYMENT Y/Y – COMPUTER & DATA PROCESSING SERVICES 37 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
IT Consulting and Services EMPLOYMENT Y/Y – COMPUTER & DATA PROCESSING SERVICES 37 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Best Technology vs. Basic Business u From 1993 -2000, high R&D-to-sales ratios played best for companies with the fastest and latest equipment and strong revenue growth. u Now, operational factors more competitive: – Good cash management – Strong customer relationships – Control over both the supply and distribution sides of their businesses – Evolutionary, not revolutionary technology u Consolidation seemingly inevitable – Slower but more sustainable rate of technological development, more rational use of capital – Fewer players means more benign pricing pressures, allowing for improved gross margins and profitability 38 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Best Technology vs. Basic Business u From 1993 -2000, high R&D-to-sales ratios played best for companies with the fastest and latest equipment and strong revenue growth. u Now, operational factors more competitive: – Good cash management – Strong customer relationships – Control over both the supply and distribution sides of their businesses – Evolutionary, not revolutionary technology u Consolidation seemingly inevitable – Slower but more sustainable rate of technological development, more rational use of capital – Fewer players means more benign pricing pressures, allowing for improved gross margins and profitability 38 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Strategic Challenges to NEC 39 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Strategic Challenges to NEC 39 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Issues Areas Being Addressed by NEC u Creating a globally competitive corporate culture with new management skill sets – Ensuring strategy formulation and execution; marketing; financial u Should NEC remain in semiconductor, computers, and communications businesses u How best to survive and grow in consolidating IT sectors, particularly by integrating IT and network businesses u Aligning capital and costs structures to current and likely future market conditions; cash management u Identify/define core competencies needed in today’s hightech markets u Institutionalizing strong corporate governance 40 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Issues Areas Being Addressed by NEC u Creating a globally competitive corporate culture with new management skill sets – Ensuring strategy formulation and execution; marketing; financial u Should NEC remain in semiconductor, computers, and communications businesses u How best to survive and grow in consolidating IT sectors, particularly by integrating IT and network businesses u Aligning capital and costs structures to current and likely future market conditions; cash management u Identify/define core competencies needed in today’s hightech markets u Institutionalizing strong corporate governance 40 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
 Upcoming Visit to NEC March 18 (Mon) u at NEC Head Office – 9: 00 -9: 05 Opening Remark (Dr. H. Kaneko) – 9: 05 -10: 15 Presentation (S. Suzuki SVP) – 10: 15 -10: 30 Q&A u at NEC Saitama – 14: 00 -14: 30 Outline of NEC Saitama – 14: 30 -15: 30 Plant Tour, Q&A 41 Corporate Strategy and Business Development
Upcoming Visit to NEC March 18 (Mon) u at NEC Head Office – 9: 00 -9: 05 Opening Remark (Dr. H. Kaneko) – 9: 05 -10: 15 Presentation (S. Suzuki SVP) – 10: 15 -10: 30 Q&A u at NEC Saitama – 14: 00 -14: 30 Outline of NEC Saitama – 14: 30 -15: 30 Plant Tour, Q&A 41 Corporate Strategy and Business Development


