5f841921d52c5e695cbd664435dc1503.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 The role of simulation and modelling in health care Martin Utley, Clinical Operational Research Unit University College London
The role of simulation and modelling in health care Martin Utley, Clinical Operational Research Unit University College London
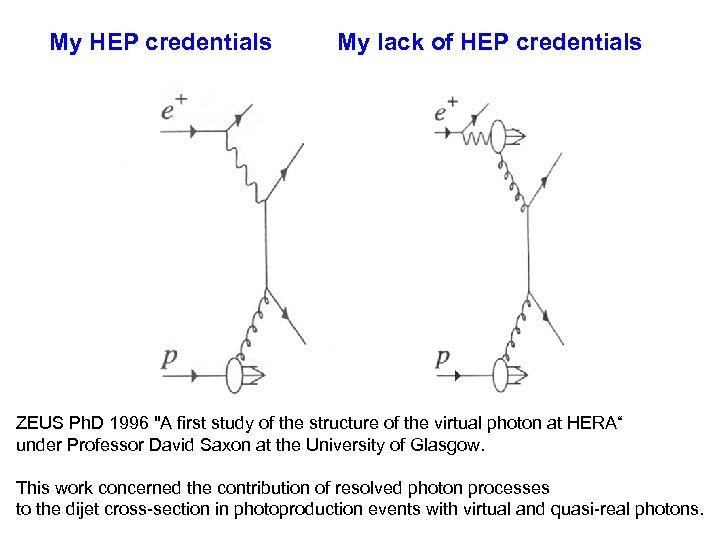 My HEP credentials My lack of HEP credentials ZEUS Ph. D 1996 "A first study of the structure of the virtual photon at HERA“ under Professor David Saxon at the University of Glasgow. This work concerned the contribution of resolved photon processes to the dijet cross-section in photoproduction events with virtual and quasi-real photons.
My HEP credentials My lack of HEP credentials ZEUS Ph. D 1996 "A first study of the structure of the virtual photon at HERA“ under Professor David Saxon at the University of Glasgow. This work concerned the contribution of resolved photon processes to the dijet cross-section in photoproduction events with virtual and quasi-real photons.
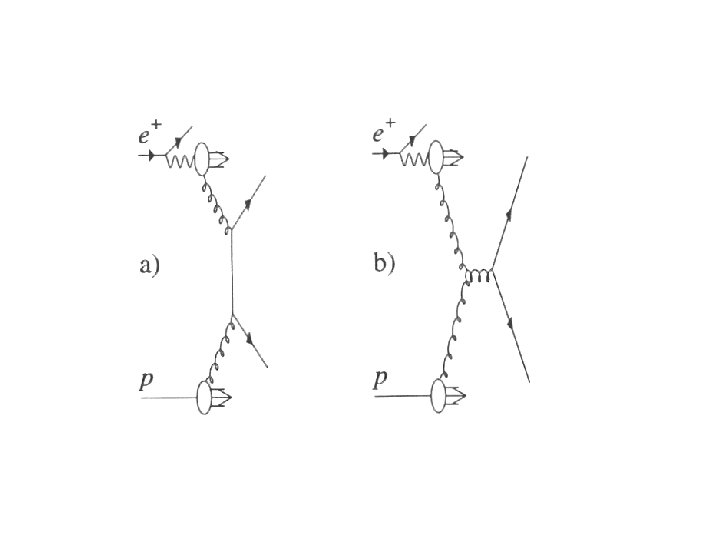
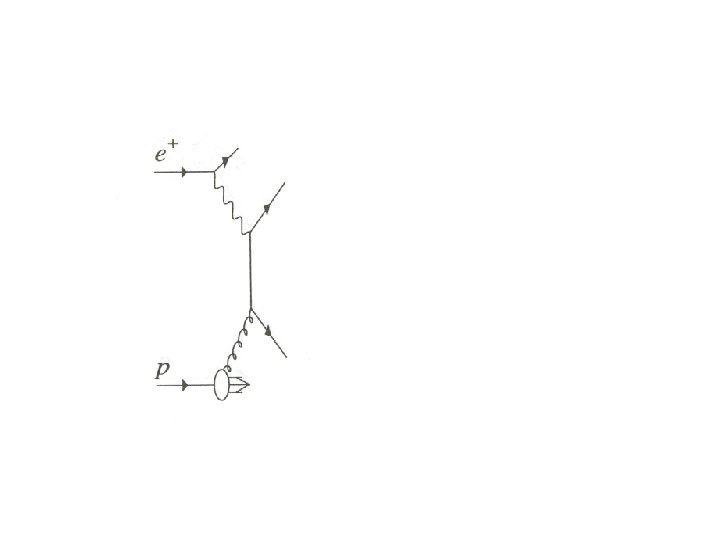
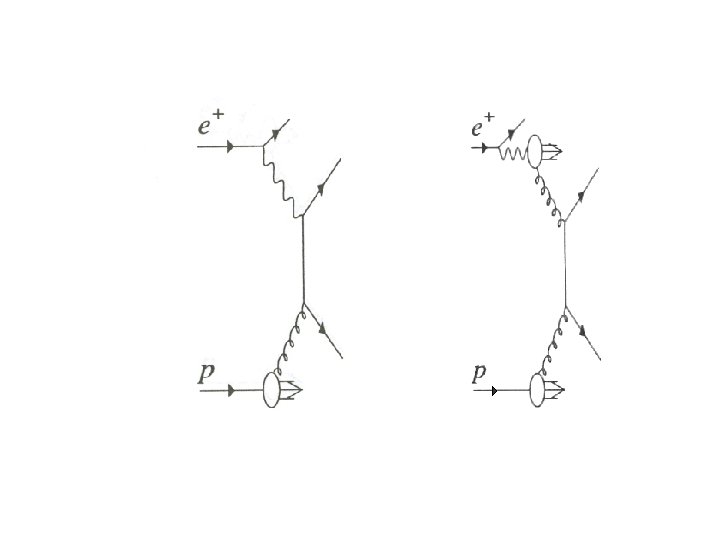
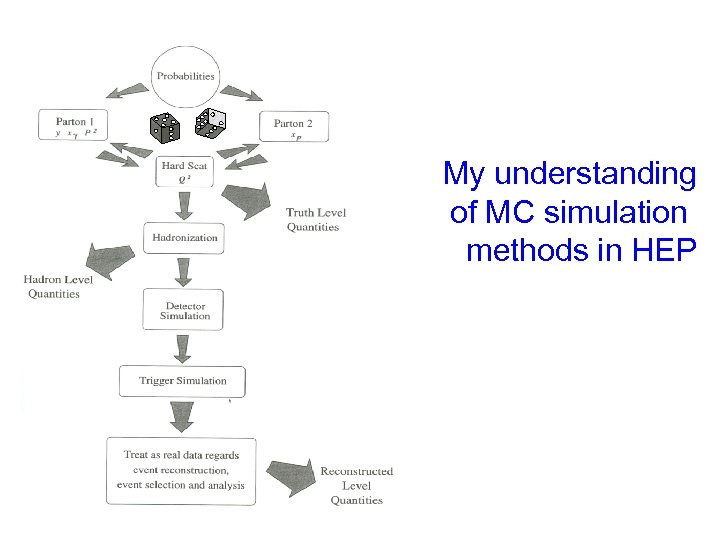 My understanding of MC simulation methods in HEP
My understanding of MC simulation methods in HEP
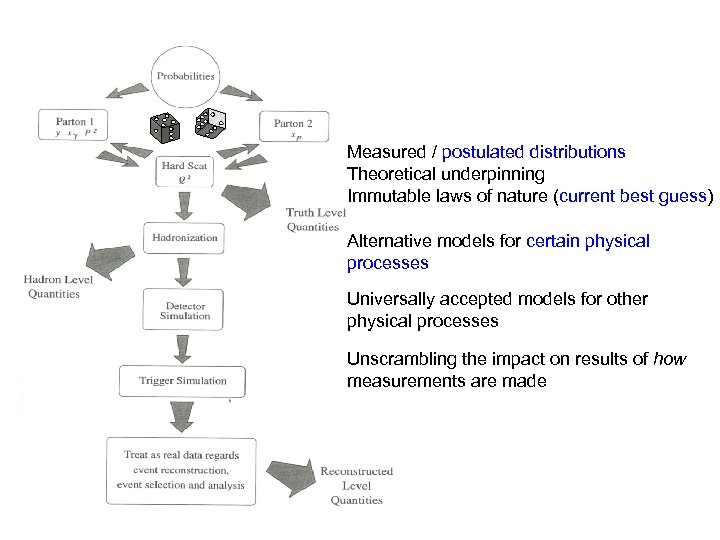 Measured / postulated distributions Theoretical underpinning Immutable laws of nature (current best guess) Alternative models for certain physical processes Universally accepted models for other physical processes Unscrambling the impact on results of how measurements are made
Measured / postulated distributions Theoretical underpinning Immutable laws of nature (current best guess) Alternative models for certain physical processes Universally accepted models for other physical processes Unscrambling the impact on results of how measurements are made
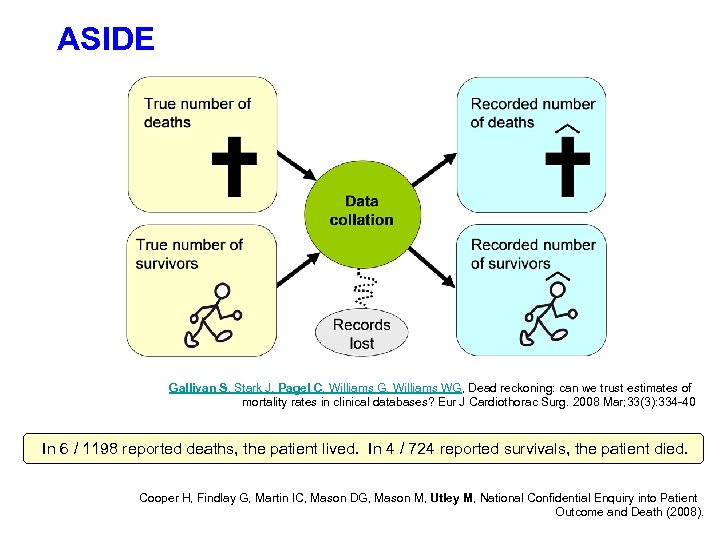 ASIDE Gallivan S, Stark J, Pagel C, Williams G, Williams WG, Dead reckoning: can we trust estimates of mortality rates in clinical databases? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008 Mar; 33(3): 334 -40 In 6 / 1198 reported deaths, the patient lived. In 4 / 724 reported survivals, the patient died. Cooper H, Findlay G, Martin IC, Mason DG, Mason M, Utley M, National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death (2008).
ASIDE Gallivan S, Stark J, Pagel C, Williams G, Williams WG, Dead reckoning: can we trust estimates of mortality rates in clinical databases? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008 Mar; 33(3): 334 -40 In 6 / 1198 reported deaths, the patient lived. In 4 / 724 reported survivals, the patient died. Cooper H, Findlay G, Martin IC, Mason DG, Mason M, Utley M, National Confidential Enquiry into Patient Outcome and Death (2008).
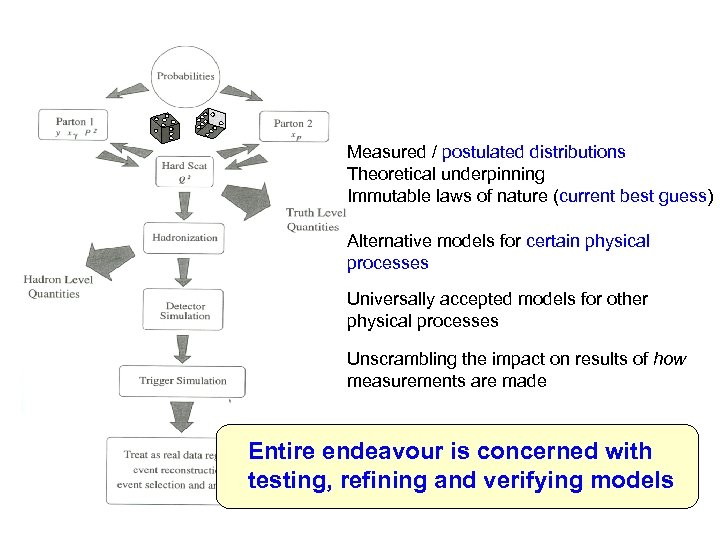 Measured / postulated distributions Theoretical underpinning Immutable laws of nature (current best guess) Alternative models for certain physical processes Universally accepted models for other physical processes Unscrambling the impact on results of how measurements are made Entire endeavour is concerned with testing, refining and verifying models
Measured / postulated distributions Theoretical underpinning Immutable laws of nature (current best guess) Alternative models for certain physical processes Universally accepted models for other physical processes Unscrambling the impact on results of how measurements are made Entire endeavour is concerned with testing, refining and verifying models
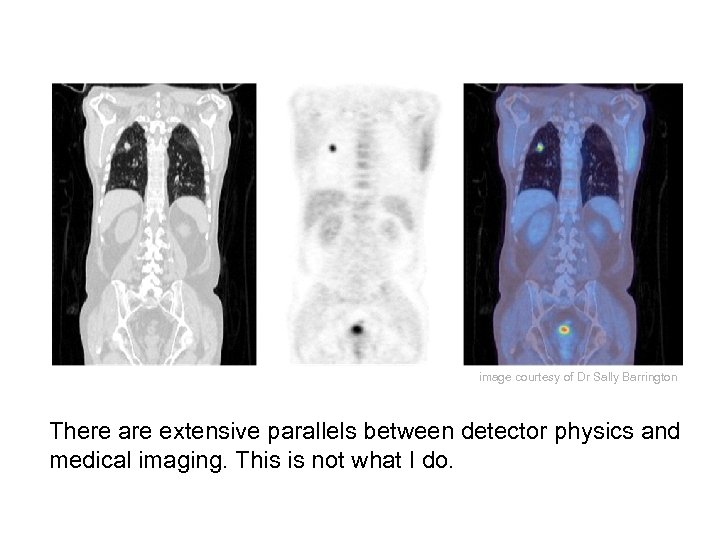 image courtesy of Dr Sally Barrington There are extensive parallels between detector physics and medical imaging. This is not what I do.
image courtesy of Dr Sally Barrington There are extensive parallels between detector physics and medical imaging. This is not what I do.
 Clinical Operational Research Unit (CORU) Dr Martin Utley Director UCL Department of Mathematics University College London Gower Street London WC 1 E 6 BT Tel: Fax: E-Mail: Web: +44 (0)20 7679 4508 +44 (0)20 7813 2814 m. utley@ucl. ac. uk www. ucl. ac. uk/operational-research
Clinical Operational Research Unit (CORU) Dr Martin Utley Director UCL Department of Mathematics University College London Gower Street London WC 1 E 6 BT Tel: Fax: E-Mail: Web: +44 (0)20 7679 4508 +44 (0)20 7813 2814 m. utley@ucl. ac. uk www. ucl. ac. uk/operational-research
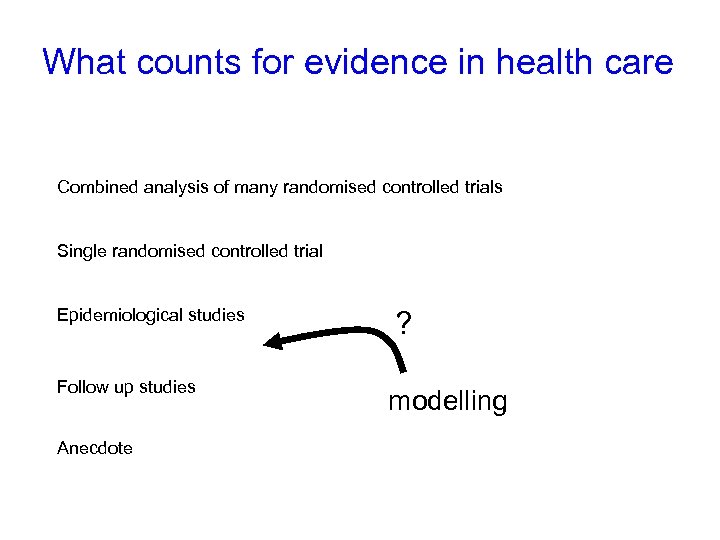 What counts for evidence in health care Combined analysis of many randomised controlled trials Single randomised controlled trial Epidemiological studies Follow up studies Anecdote ? modelling
What counts for evidence in health care Combined analysis of many randomised controlled trials Single randomised controlled trial Epidemiological studies Follow up studies Anecdote ? modelling
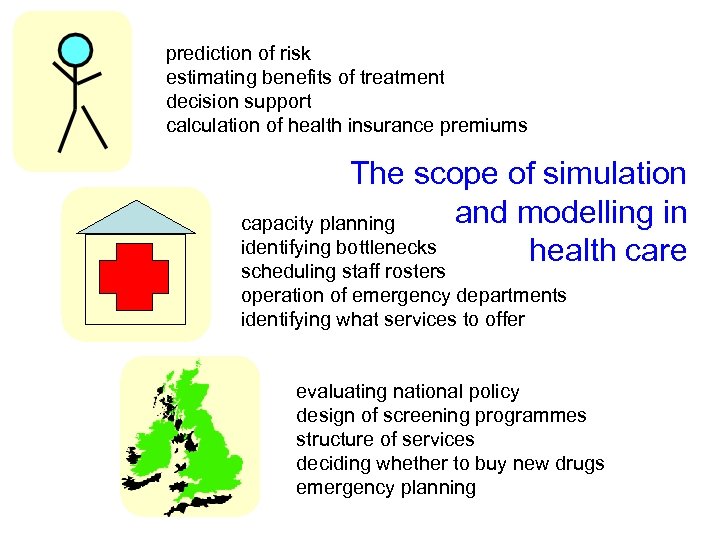 prediction of risk estimating benefits of treatment decision support calculation of health insurance premiums The scope of simulation and modelling in capacity planning identifying bottlenecks health care scheduling staff rosters operation of emergency departments identifying what services to offer evaluating national policy design of screening programmes structure of services deciding whether to buy new drugs emergency planning
prediction of risk estimating benefits of treatment decision support calculation of health insurance premiums The scope of simulation and modelling in capacity planning identifying bottlenecks health care scheduling staff rosters operation of emergency departments identifying what services to offer evaluating national policy design of screening programmes structure of services deciding whether to buy new drugs emergency planning
 UK National Health Service • Free for all at point of access • Funded via general taxation • Under political control • Third largest organisation in the world
UK National Health Service • Free for all at point of access • Funded via general taxation • Under political control • Third largest organisation in the world
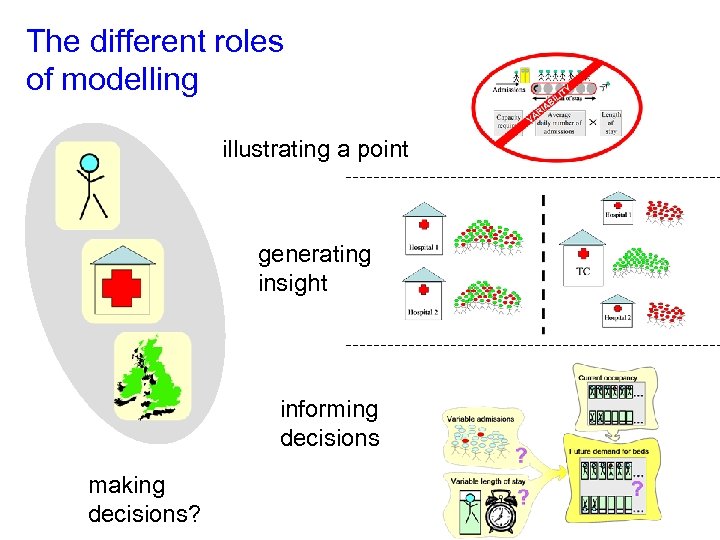 The different roles of modelling illustrating a point generating insight informing decisions making decisions?
The different roles of modelling illustrating a point generating insight informing decisions making decisions?
 Booked admissions policy • Before 2001, short notice cancellations of elective operations were frequent. • Government put in place policy whereby patients were given a firm commitment to date of surgery. • Little thought was given to implications.
Booked admissions policy • Before 2001, short notice cancellations of elective operations were frequent. • Government put in place policy whereby patients were given a firm commitment to date of surgery. • Little thought was given to implications.
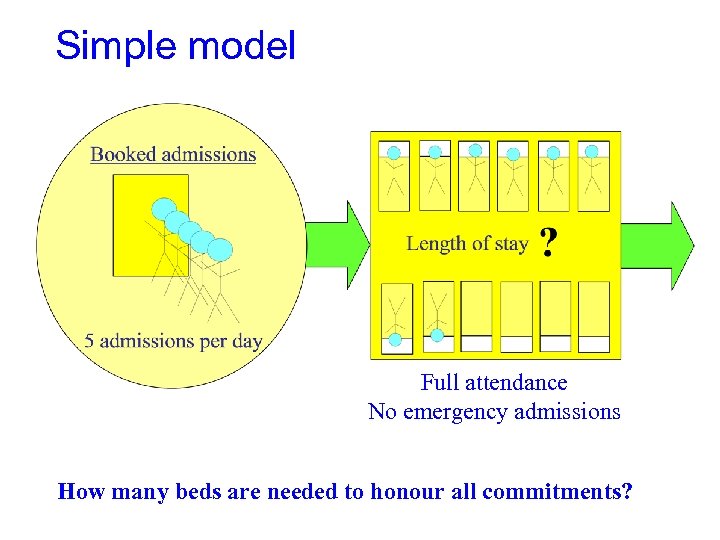 Simple model Full attendance No emergency admissions How many beds are needed to honour all commitments?
Simple model Full attendance No emergency admissions How many beds are needed to honour all commitments?
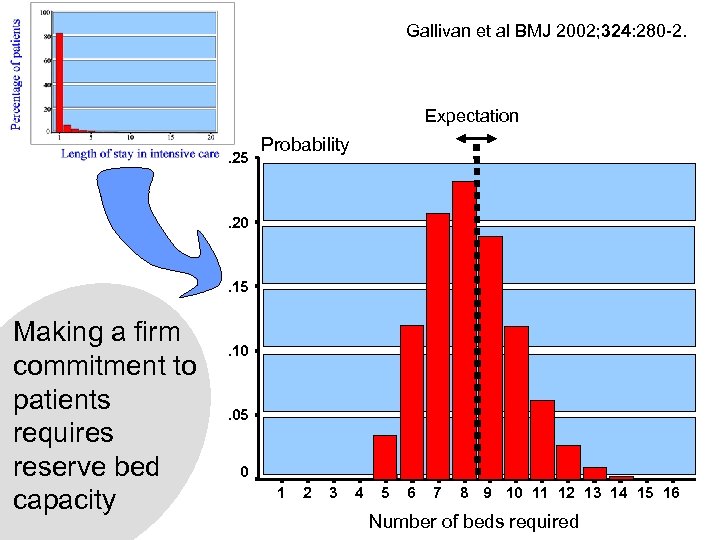 Gallivan et al BMJ 2002; 324: 280 -2. Expectation. 25 Probability . 20 . 15 Making a firm commitment to patients requires reserve bed capacity . 10 . 05 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Number of beds required
Gallivan et al BMJ 2002; 324: 280 -2. Expectation. 25 Probability . 20 . 15 Making a firm commitment to patients requires reserve bed capacity . 10 . 05 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Number of beds required
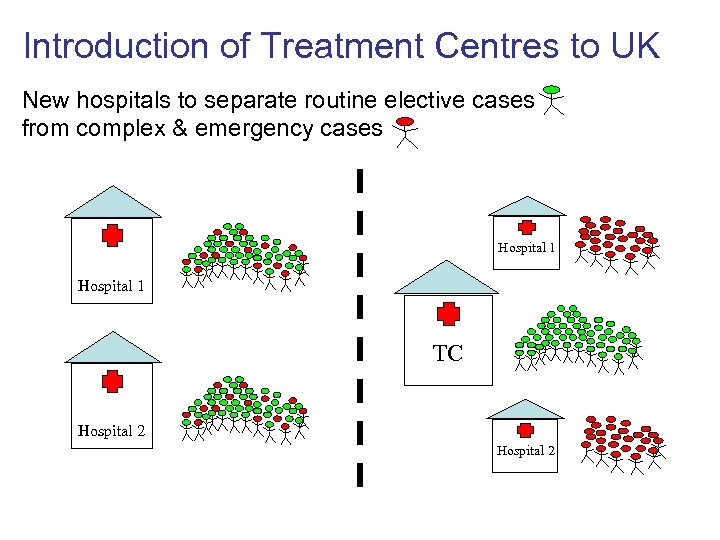 Introduction of Treatment Centres to UK New hospitals to separate routine elective cases from complex & emergency cases Hospital 1 TC Hospital 2
Introduction of Treatment Centres to UK New hospitals to separate routine elective cases from complex & emergency cases Hospital 1 TC Hospital 2
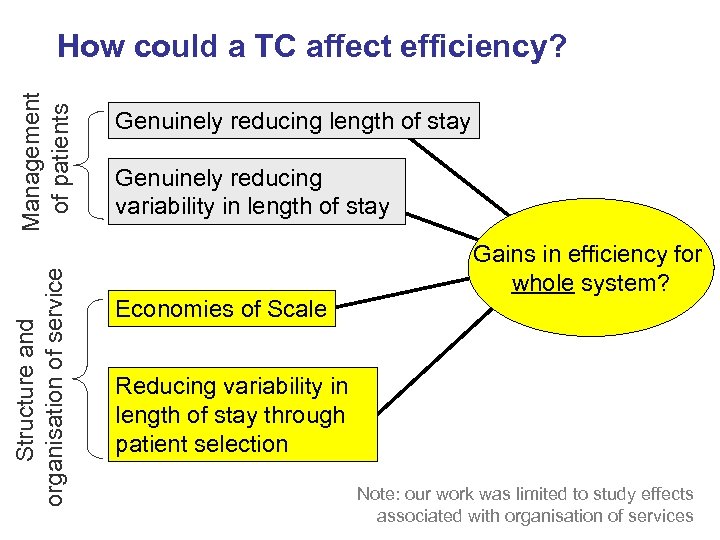 Structure and organisation of service Management of patients How could a TC affect efficiency? Genuinely reducing length of stay Genuinely reducing variability in length of stay Economies of Scale Gains in efficiency for whole system? Reducing variability in length of stay through patient selection Note: our work was limited to study effects associated with organisation of services
Structure and organisation of service Management of patients How could a TC affect efficiency? Genuinely reducing length of stay Genuinely reducing variability in length of stay Economies of Scale Gains in efficiency for whole system? Reducing variability in length of stay through patient selection Note: our work was limited to study effects associated with organisation of services
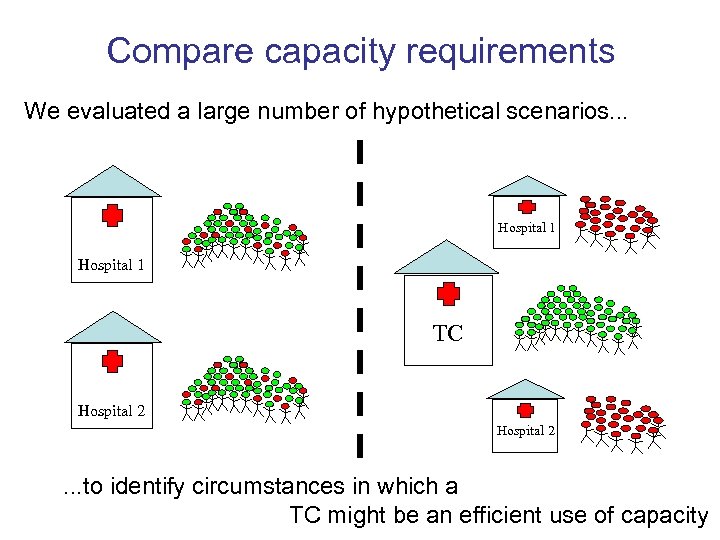 Compare capacity requirements We evaluated a large number of hypothetical scenarios. . . Hospital 1 TC Hospital 2 . . . to identify circumstances in which a TC might be an efficient use of capacity
Compare capacity requirements We evaluated a large number of hypothetical scenarios. . . Hospital 1 TC Hospital 2 . . . to identify circumstances in which a TC might be an efficient use of capacity
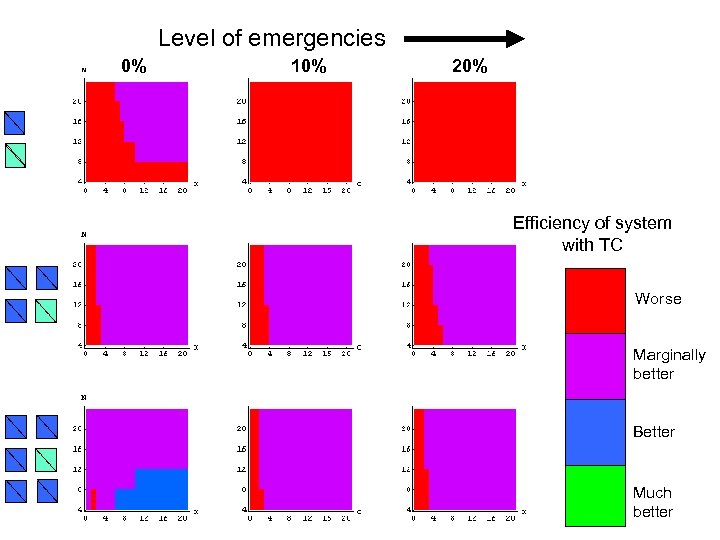 Level of emergencies 0% 10% 20% Efficiency of system with TC Worse Marginally better Better Much better
Level of emergencies 0% 10% 20% Efficiency of system with TC Worse Marginally better Better Much better
 Findings • In many circumstances, there is no theoretical benefit associated with treatment centres*. • Theoretical benefits exist if there is successful identification of shorter-stay patients and a number of participating non-TC hospitals. Benefits rely on cooperation between providers. Meanwhile, other policies foster competition. *in terms of the efficient use of capacity – there a whole host of other considerations Utley et al, Health Care Management Science, Sept 2008
Findings • In many circumstances, there is no theoretical benefit associated with treatment centres*. • Theoretical benefits exist if there is successful identification of shorter-stay patients and a number of participating non-TC hospitals. Benefits rely on cooperation between providers. Meanwhile, other policies foster competition. *in terms of the efficient use of capacity – there a whole host of other considerations Utley et al, Health Care Management Science, Sept 2008
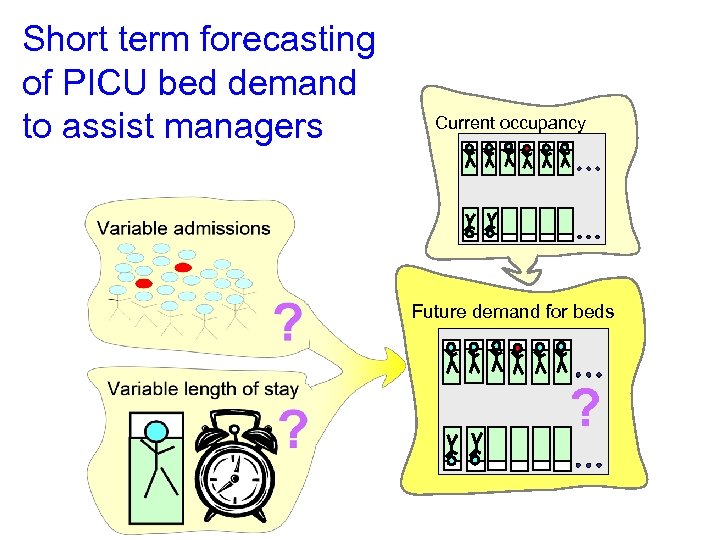 Short term forecasting of PICU bed demand to assist managers Current occupancy ? Future demand for beds Variable demand for beds ?
Short term forecasting of PICU bed demand to assist managers Current occupancy ? Future demand for beds Variable demand for beds ?
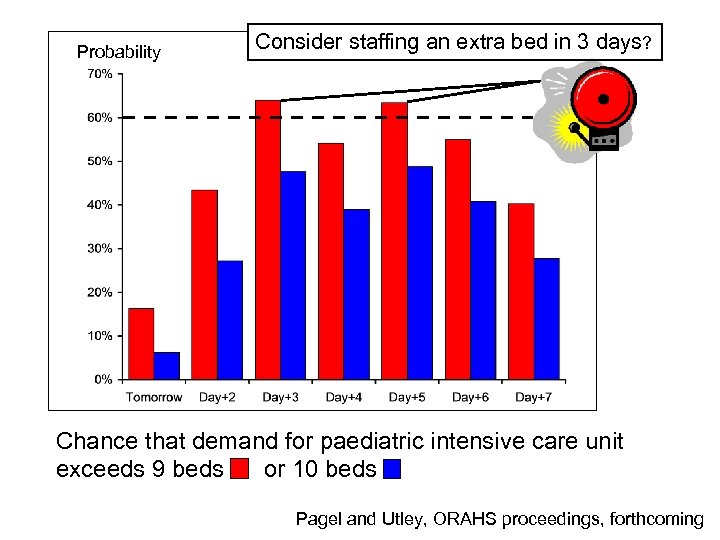 Probability Consider staffing an extra bed in 3 days? Chance that demand for paediatric intensive care unit exceeds 9 beds or 10 beds Pagel and Utley, ORAHS proceedings, forthcoming
Probability Consider staffing an extra bed in 3 days? Chance that demand for paediatric intensive care unit exceeds 9 beds or 10 beds Pagel and Utley, ORAHS proceedings, forthcoming
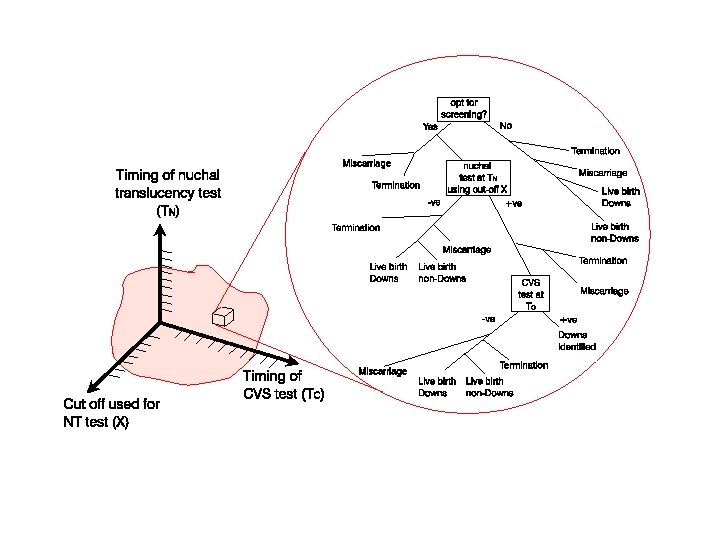
 Front page of British Medical Journal last week Mathematical modelling study £ 500 M decision concerning national vaccination programme Decision based on cost-per-QALY Jit et al, BMJ, Aug 9 2008
Front page of British Medical Journal last week Mathematical modelling study £ 500 M decision concerning national vaccination programme Decision based on cost-per-QALY Jit et al, BMJ, Aug 9 2008
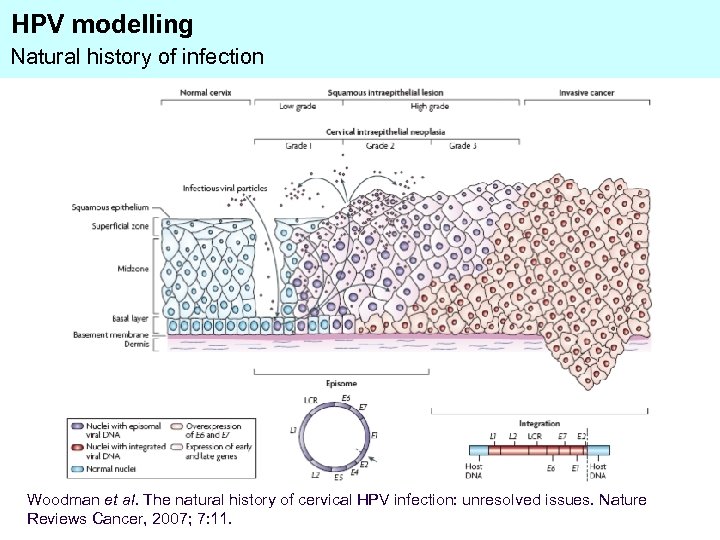 HPV modelling Natural history of infection Woodman et al. The natural history of cervical HPV infection: unresolved issues. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2007; 7: 11.
HPV modelling Natural history of infection Woodman et al. The natural history of cervical HPV infection: unresolved issues. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2007; 7: 11.
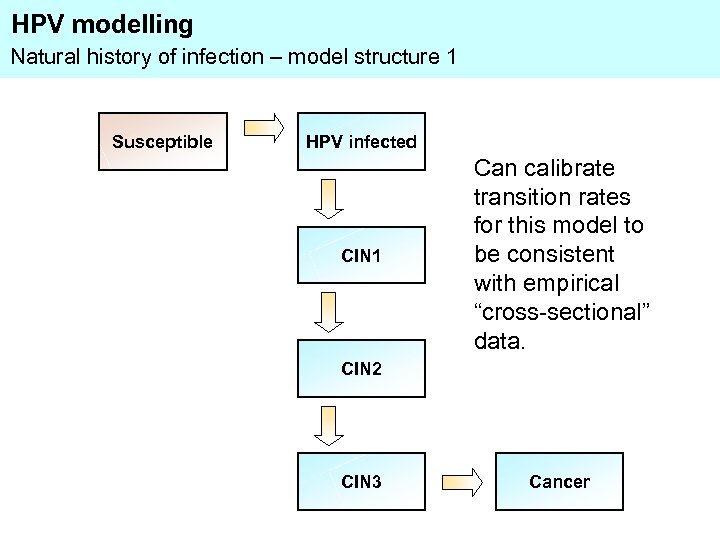 HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 1 Susceptible HPV infected CIN 1 Can calibrate transition rates for this model to be consistent with empirical “cross-sectional” data. CIN 2 CIN 3 Cancer
HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 1 Susceptible HPV infected CIN 1 Can calibrate transition rates for this model to be consistent with empirical “cross-sectional” data. CIN 2 CIN 3 Cancer
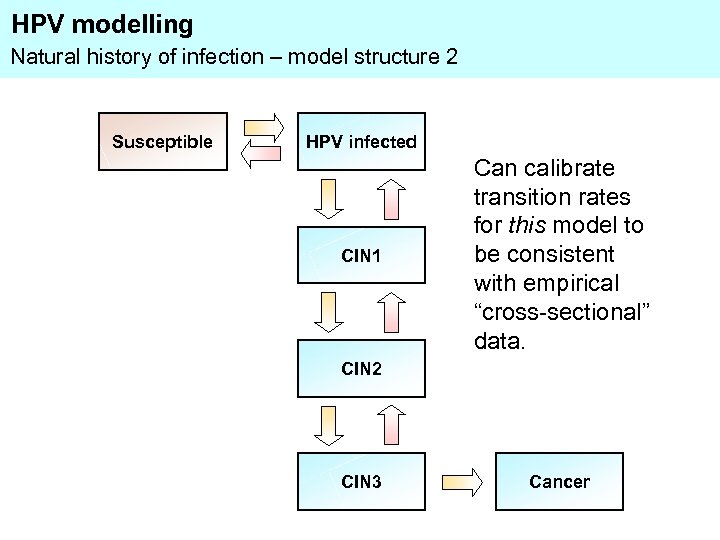 HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 2 Susceptible HPV infected CIN 1 Can calibrate transition rates for this model to be consistent with empirical “cross-sectional” data. CIN 2 CIN 3 Cancer
HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 2 Susceptible HPV infected CIN 1 Can calibrate transition rates for this model to be consistent with empirical “cross-sectional” data. CIN 2 CIN 3 Cancer
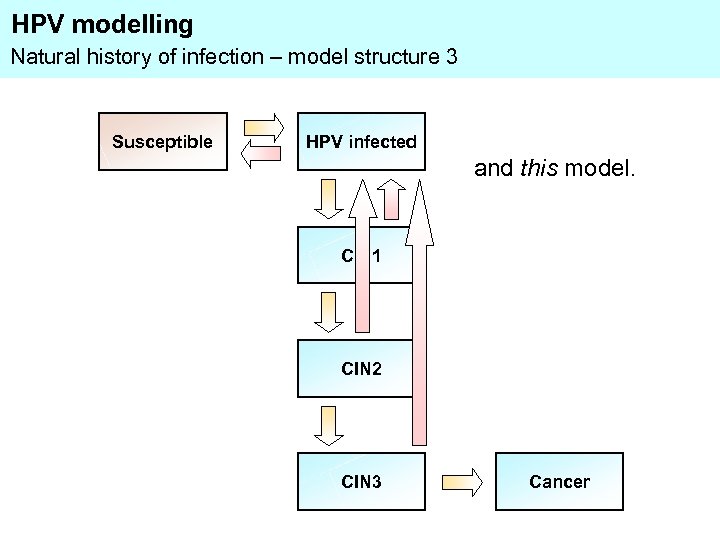 HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 3 Susceptible HPV infected and this model. CIN 1 CIN 2 CIN 3 Cancer
HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 3 Susceptible HPV infected and this model. CIN 1 CIN 2 CIN 3 Cancer
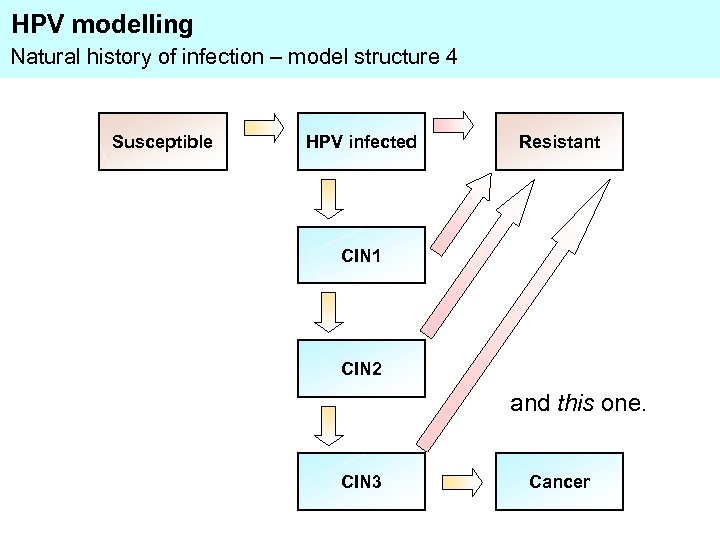 HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 4 Susceptible HPV infected Resistant CIN 1 CIN 2 and this one. CIN 3 Cancer
HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 4 Susceptible HPV infected Resistant CIN 1 CIN 2 and this one. CIN 3 Cancer
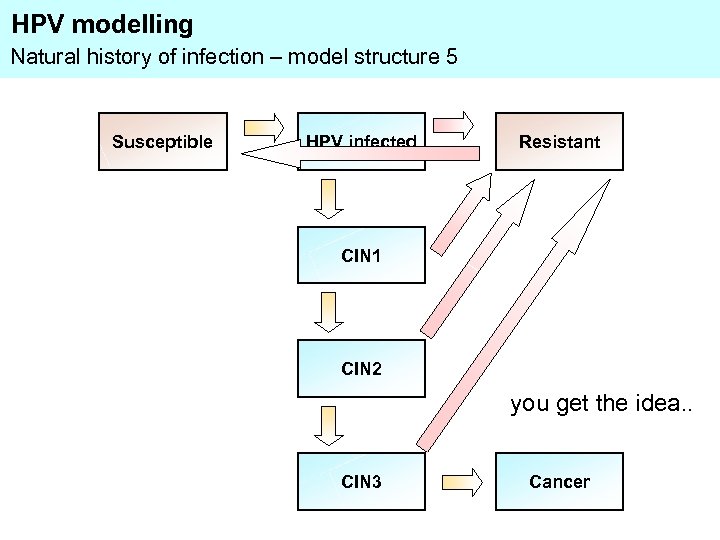 HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 5 Susceptible HPV infected Resistant CIN 1 CIN 2 you get the idea. . CIN 3 Cancer
HPV modelling Natural history of infection – model structure 5 Susceptible HPV infected Resistant CIN 1 CIN 2 you get the idea. . CIN 3 Cancer
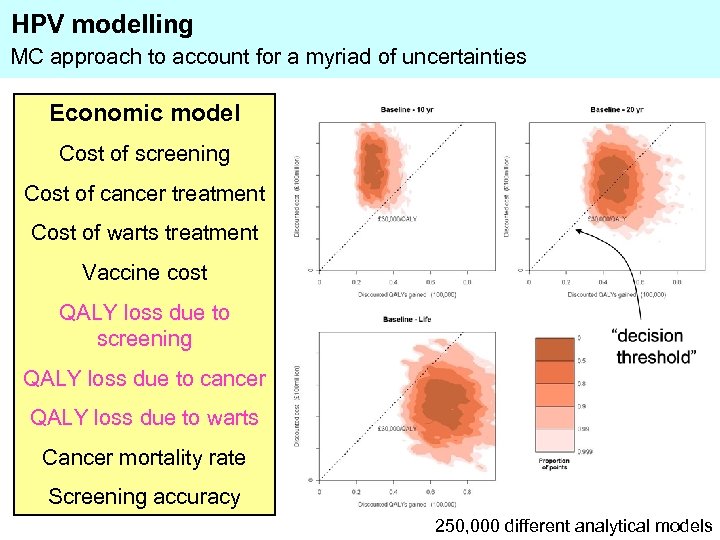 HPV modelling MC approach to account for a myriad of uncertainties Economic model Cost of screening Cost of cancer treatment Cost of warts treatment Vaccine cost QALY loss due to screening QALY loss due to cancer QALY loss due to warts Cancer mortality rate Screening accuracy 250, 000 different analytical models
HPV modelling MC approach to account for a myriad of uncertainties Economic model Cost of screening Cost of cancer treatment Cost of warts treatment Vaccine cost QALY loss due to screening QALY loss due to cancer QALY loss due to warts Cancer mortality rate Screening accuracy 250, 000 different analytical models
 Different tools used in health care modelling Discrete event simulation Monte Carlo simulation System dynamics Queueing theory Game theory Decision analysis Stochastic analysis Optimisation techniques Mathematical programming Hybrid methods
Different tools used in health care modelling Discrete event simulation Monte Carlo simulation System dynamics Queueing theory Game theory Decision analysis Stochastic analysis Optimisation techniques Mathematical programming Hybrid methods
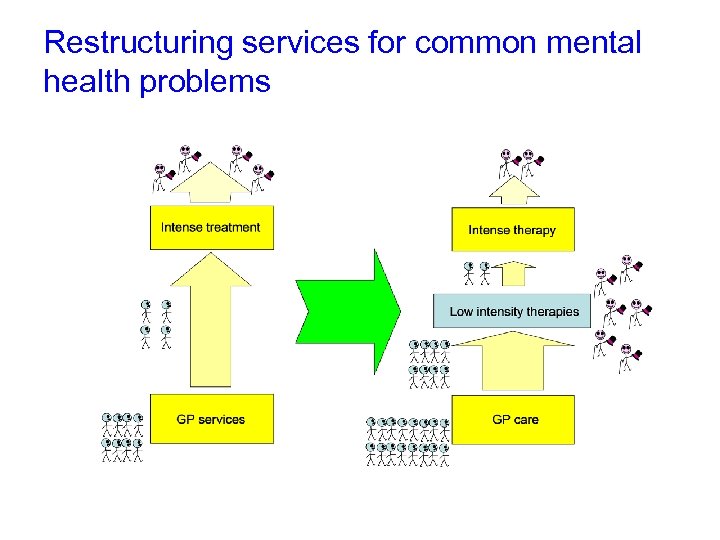 Restructuring services for common mental health problems
Restructuring services for common mental health problems
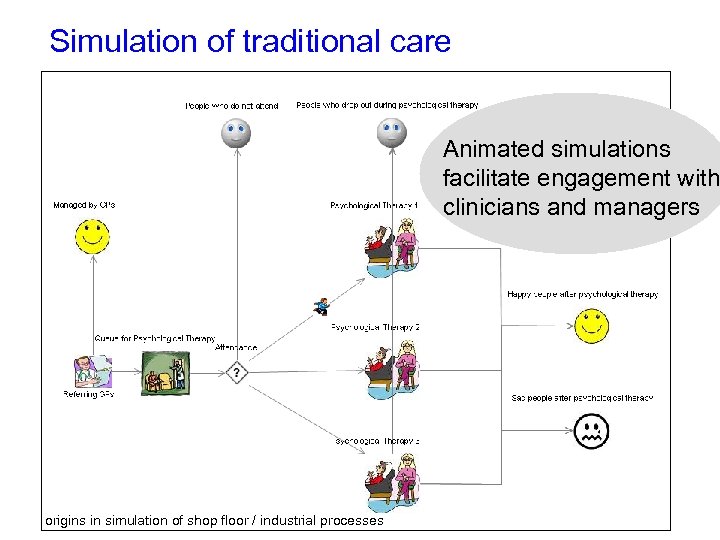 Simulation of traditional care Animated simulations facilitate engagement with clinicians and managers Snapshot of 1 year origins in simulation of shop floor / industrial processes
Simulation of traditional care Animated simulations facilitate engagement with clinicians and managers Snapshot of 1 year origins in simulation of shop floor / industrial processes
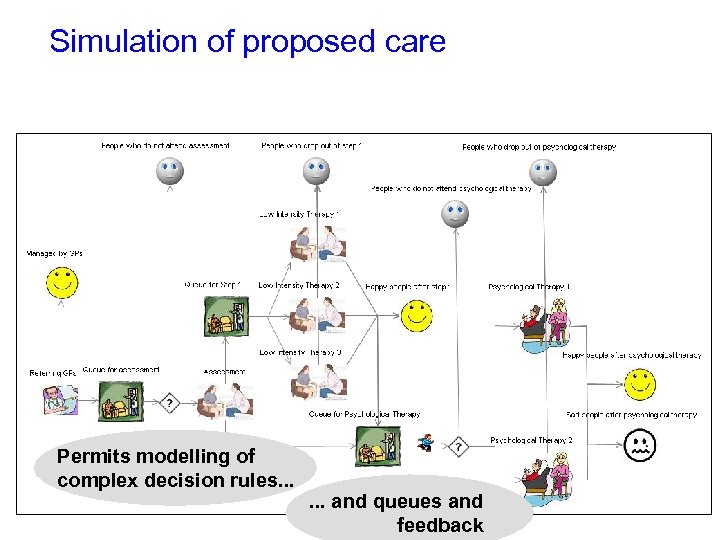 Simulation of proposed care Permits modelling of complex decision rules. . . and queues and feedback
Simulation of proposed care Permits modelling of complex decision rules. . . and queues and feedback
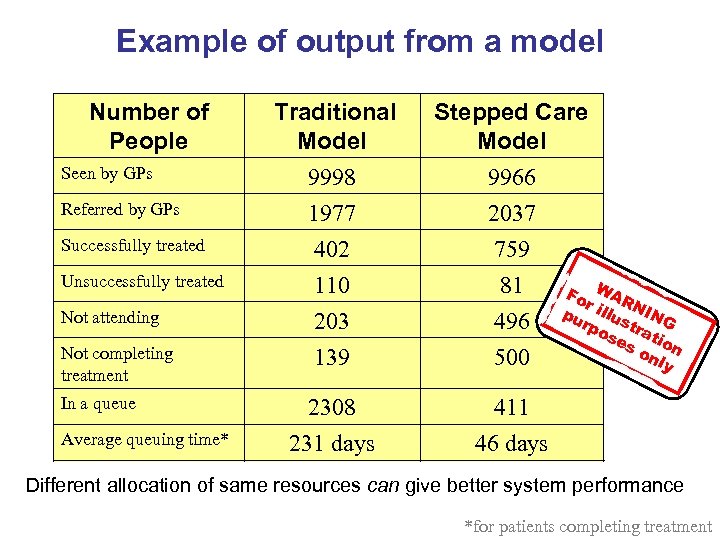 Example of output from a model Number of People Seen by GPs Referred by GPs Successfully treated Unsuccessfully treated Not attending Not completing treatment In a queue Average queuing time* Traditional Model 9998 1977 Stepped Care Model 9966 2037 402 110 203 139 759 81 496 500 2308 231 days 411 46 days Fo WAR r pu illus NING rp os trat es ion on ly Different allocation of same resources can give better system performance *for patients completing treatment
Example of output from a model Number of People Seen by GPs Referred by GPs Successfully treated Unsuccessfully treated Not attending Not completing treatment In a queue Average queuing time* Traditional Model 9998 1977 Stepped Care Model 9966 2037 402 110 203 139 759 81 496 500 2308 231 days 411 46 days Fo WAR r pu illus NING rp os trat es ion on ly Different allocation of same resources can give better system performance *for patients completing treatment
 Pitfalls to simulation in health care Model development almost too easy insufficient thought given to purpose of model detail added solely because it can be added modellers can start to believe their models. If you think 19 free parameters is untidy, you should see some of the models developed in healthcare
Pitfalls to simulation in health care Model development almost too easy insufficient thought given to purpose of model detail added solely because it can be added modellers can start to believe their models. If you think 19 free parameters is untidy, you should see some of the models developed in healthcare
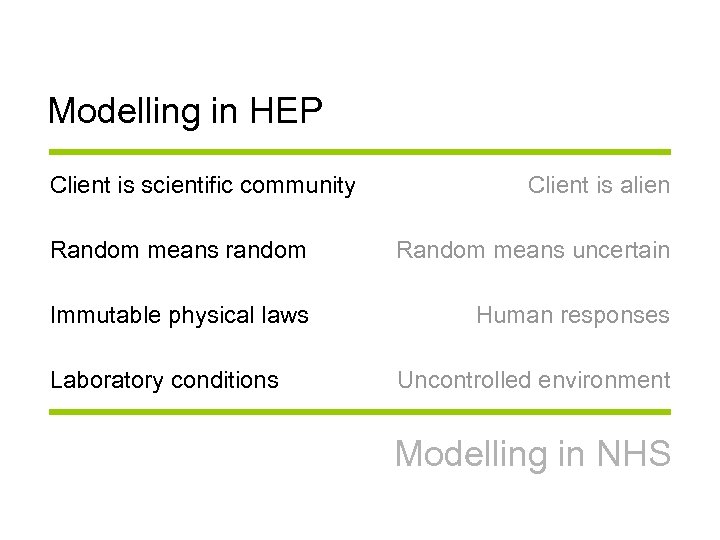 Modelling in HEP Client is scientific community Client is alien Random means random Random means uncertain Immutable physical laws Human responses Laboratory conditions Uncontrolled environment Modelling in NHS
Modelling in HEP Client is scientific community Client is alien Random means random Random means uncertain Immutable physical laws Human responses Laboratory conditions Uncontrolled environment Modelling in NHS
 Clients Decisions are made by politicians, health care managers and clinicians. . . reason vies with political dogma, professional rivalries & financial incentives*. * oh, and management consultants
Clients Decisions are made by politicians, health care managers and clinicians. . . reason vies with political dogma, professional rivalries & financial incentives*. * oh, and management consultants
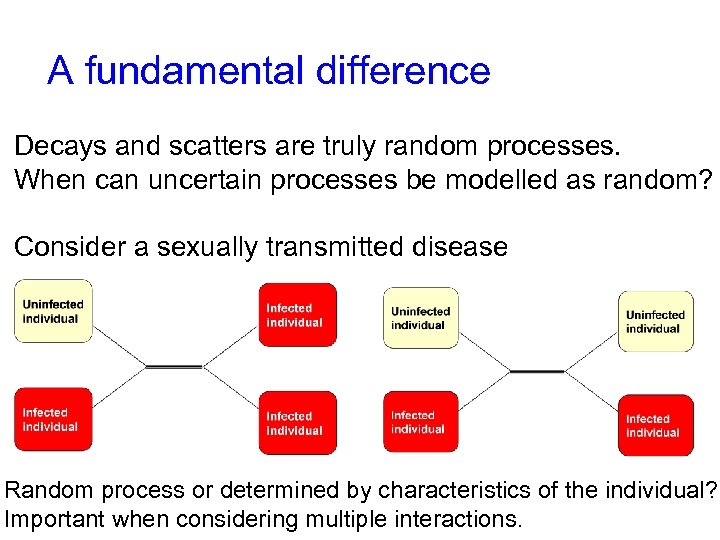 A fundamental difference Decays and scatters are truly random processes. When can uncertain processes be modelled as random? Consider a sexually transmitted disease Random process or determined by characteristics of the individual? Important when considering multiple interactions.
A fundamental difference Decays and scatters are truly random processes. When can uncertain processes be modelled as random? Consider a sexually transmitted disease Random process or determined by characteristics of the individual? Important when considering multiple interactions.
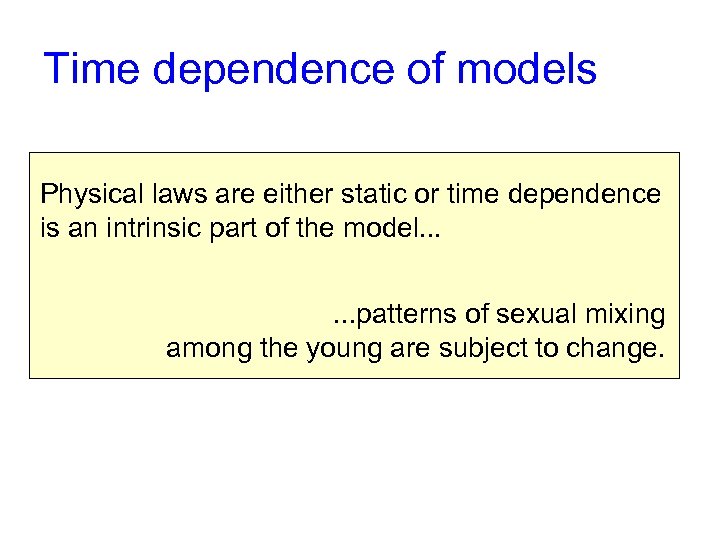 Time dependence of models Physical laws are either static or time dependence is an intrinsic part of the model. . . patterns of sexual mixing among the young are subject to change.
Time dependence of models Physical laws are either static or time dependence is an intrinsic part of the model. . . patterns of sexual mixing among the young are subject to change.
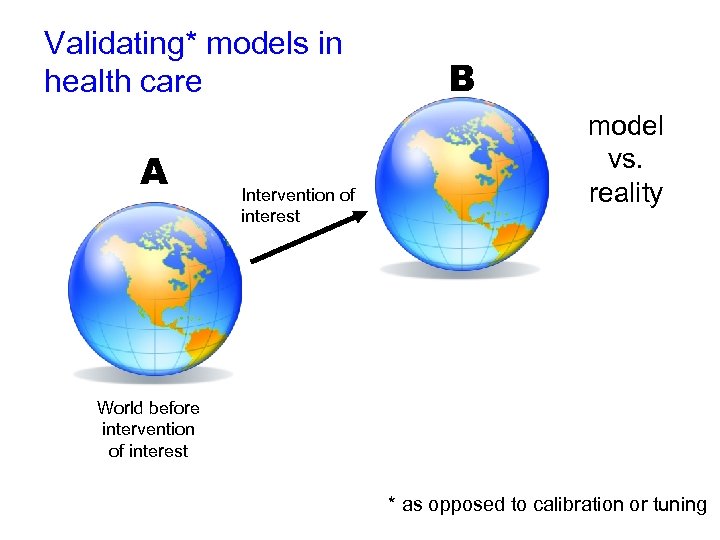 Validating* models in health care A Intervention of interest B model vs. reality World before intervention of interest * as opposed to calibration or tuning
Validating* models in health care A Intervention of interest B model vs. reality World before intervention of interest * as opposed to calibration or tuning
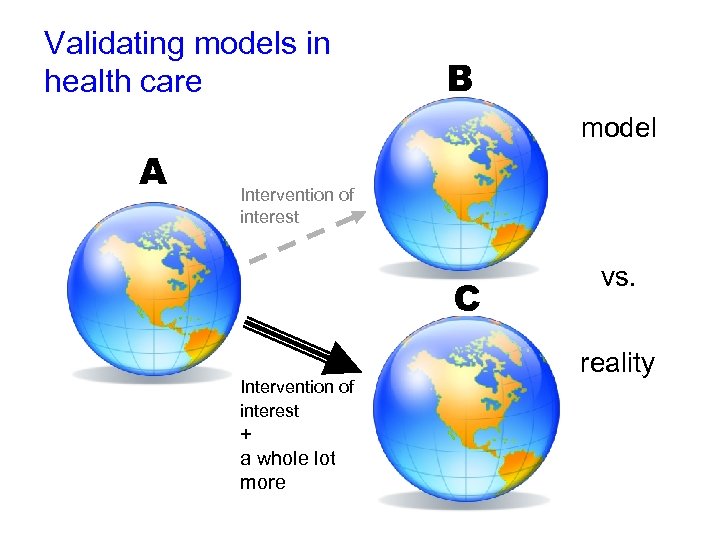 Validating models in health care B model A Intervention of interest C Intervention of interest + a whole lot more vs. reality
Validating models in health care B model A Intervention of interest C Intervention of interest + a whole lot more vs. reality
 George Box said. . . “All models are wrong. . . some are useful”
George Box said. . . “All models are wrong. . . some are useful”
 A modeller’s checklist All models are wrong. . . some are useful What counts as useful? ?
A modeller’s checklist All models are wrong. . . some are useful What counts as useful? ?
 One response but decisions will get made, with or without our input.
One response but decisions will get made, with or without our input.
 Are you a bright, financially secure, analytical thinker with exemplary people skills and the belief that you can improve the NHS? I hate you.
Are you a bright, financially secure, analytical thinker with exemplary people skills and the belief that you can improve the NHS? I hate you.
 END
END
 Uninfected individual Infected individual
Uninfected individual Infected individual
 The role of simulation and modelling in health care Martin Utley Director, Clinical Operational Research Unit University College London
The role of simulation and modelling in health care Martin Utley Director, Clinical Operational Research Unit University College London
 prediction of risk estimating benefits of treatment
prediction of risk estimating benefits of treatment
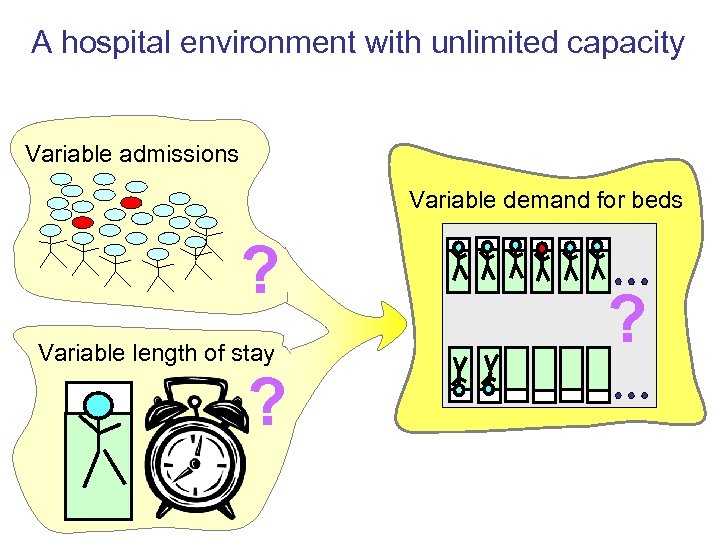 A hospital environment with unlimited capacity Variable admissions Variable demand for beds ? Variable length of stay ? ?
A hospital environment with unlimited capacity Variable admissions Variable demand for beds ? Variable length of stay ? ?
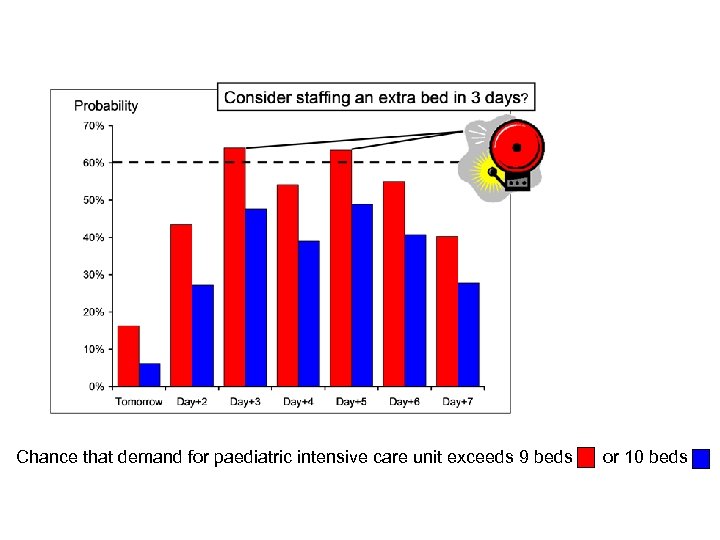 Chance that demand for paediatric intensive care unit exceeds 9 beds or 10 beds
Chance that demand for paediatric intensive care unit exceeds 9 beds or 10 beds
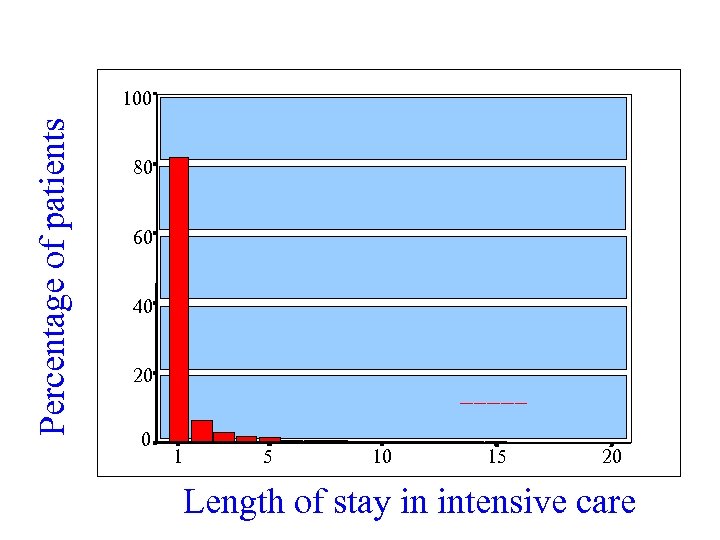 Percentage of patients 100 80 60 40 20 0 1 5 10 15 20 Length of stay in intensive care
Percentage of patients 100 80 60 40 20 0 1 5 10 15 20 Length of stay in intensive care
 TY LI I B A V IA R
TY LI I B A V IA R
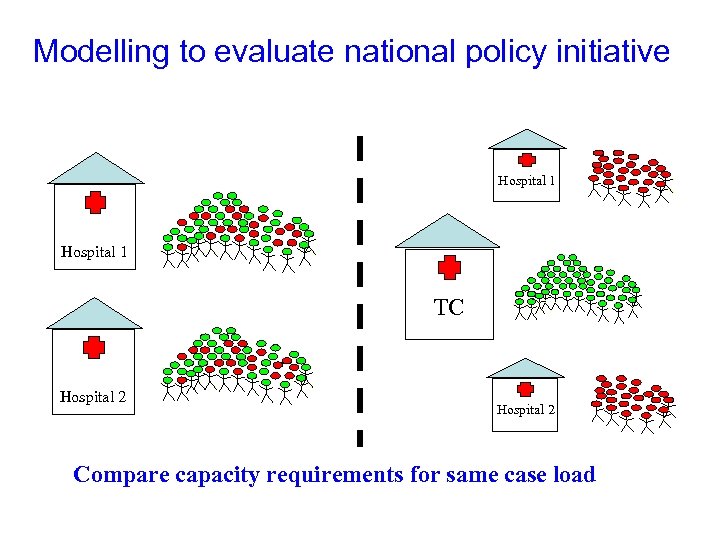 Modelling to evaluate national policy initiative Hospital 1 TC Hospital 2 Compare capacity requirements for same case load
Modelling to evaluate national policy initiative Hospital 1 TC Hospital 2 Compare capacity requirements for same case load
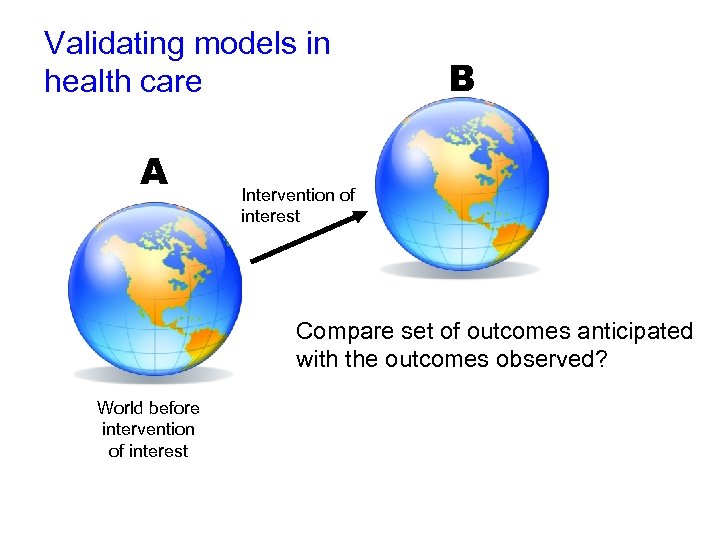 Validating models in health care A B Intervention of interest Compare set of outcomes anticipated with the outcomes observed? World before intervention of interest
Validating models in health care A B Intervention of interest Compare set of outcomes anticipated with the outcomes observed? World before intervention of interest
 The role of simulation and modelling in health care Martin Utley, Clinical Operational Research Unit University College London
The role of simulation and modelling in health care Martin Utley, Clinical Operational Research Unit University College London
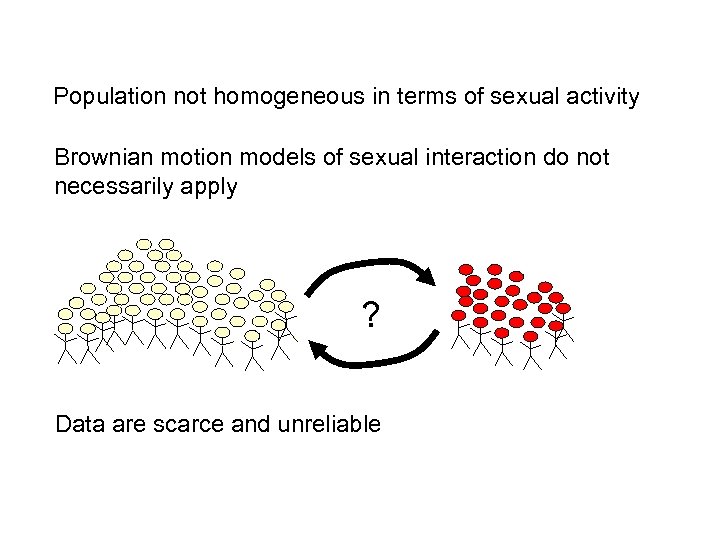 Population not homogeneous in terms of sexual activity Brownian motion models of sexual interaction do not necessarily apply ? Data are scarce and unreliable
Population not homogeneous in terms of sexual activity Brownian motion models of sexual interaction do not necessarily apply ? Data are scarce and unreliable


