df1bd51332bfa97ef5569c55f735b20c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66
 The Role of GIS for a Utility Regulatory Commission Indiana Utilities Regulatory Commission October 6, 2004 ESRI
The Role of GIS for a Utility Regulatory Commission Indiana Utilities Regulatory Commission October 6, 2004 ESRI
 GIS helps Utilities 85% Manage Integrate Share Query Analyze Visualize Map & Record Key Decisional Support Information
GIS helps Utilities 85% Manage Integrate Share Query Analyze Visualize Map & Record Key Decisional Support Information
 ESRI View of GIS “maps produced by ESRI's software really just the door prize. In other words, the maps, as compelling and necessary as they may be, are simply a means to deliver the information and insights contained in the spatially oriented data and revealed through GIS analysis. ” - Jack Dangermond
ESRI View of GIS “maps produced by ESRI's software really just the door prize. In other words, the maps, as compelling and necessary as they may be, are simply a means to deliver the information and insights contained in the spatially oriented data and revealed through GIS analysis. ” - Jack Dangermond
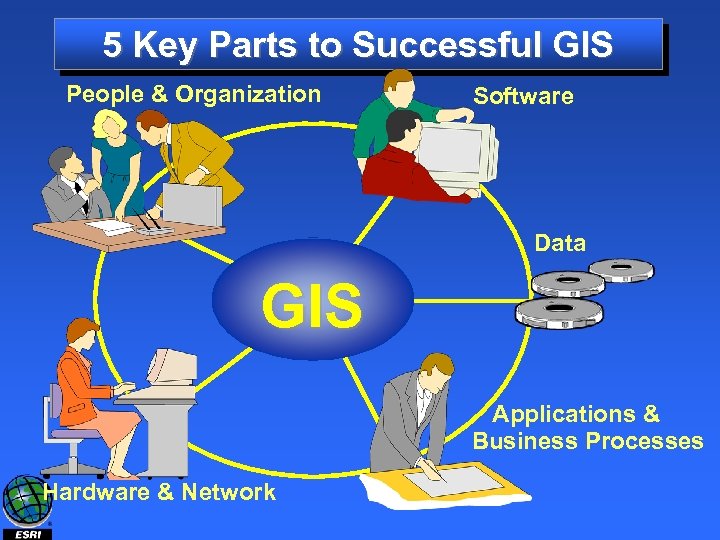 5 Key Parts to Successful GIS People & Organization Software Data GIS Applications & Business Processes Hardware & Network
5 Key Parts to Successful GIS People & Organization Software Data GIS Applications & Business Processes Hardware & Network
 Data How does GIS Work?
Data How does GIS Work?
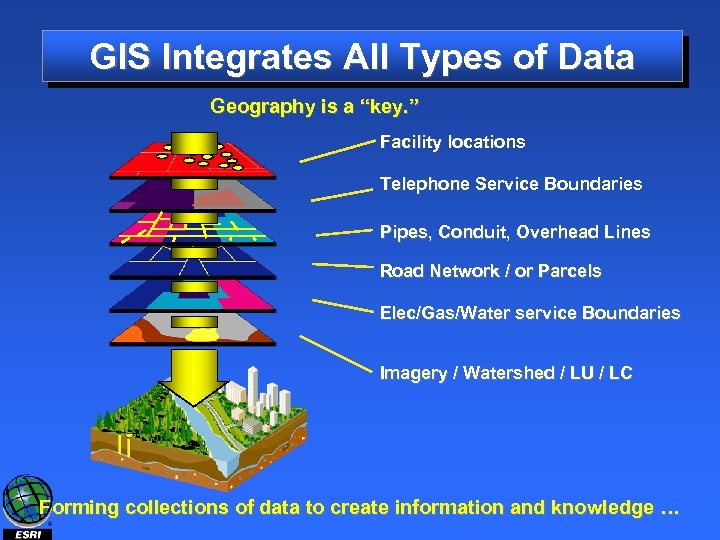 GIS Integrates All Types of Data Geography is a “key. ” Facility locations Telephone Service Boundaries Pipes, Conduit, Overhead Lines Road Network / or Parcels Elec/Gas/Water service Boundaries Imagery / Watershed / LU / LC Forming collections of data to create information and knowledge …
GIS Integrates All Types of Data Geography is a “key. ” Facility locations Telephone Service Boundaries Pipes, Conduit, Overhead Lines Road Network / or Parcels Elec/Gas/Water service Boundaries Imagery / Watershed / LU / LC Forming collections of data to create information and knowledge …
 Small Scale View
Small Scale View
 Mid-scale View
Mid-scale View
 Large-scale View
Large-scale View
 Data – State of Indiana • • • USGS quads Road networks Imagery Land Ownership Others
Data – State of Indiana • • • USGS quads Road networks Imagery Land Ownership Others
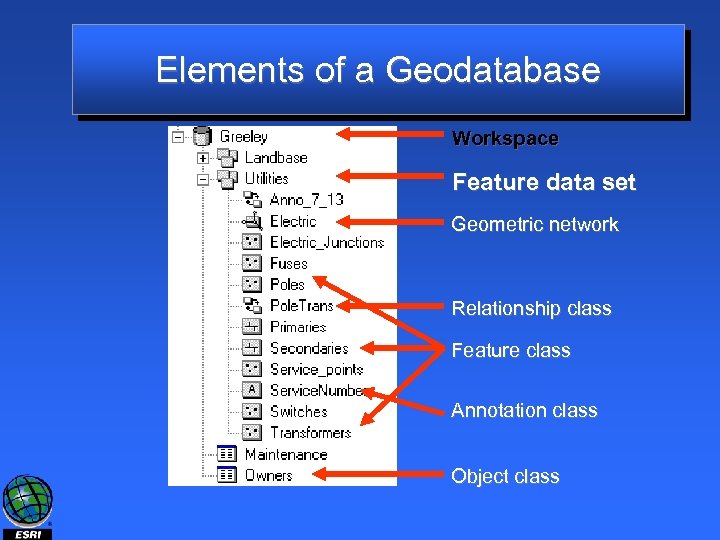 Elements of a Geodatabase Workspace Feature data set Geometric network Relationship class Feature class Annotation class Object class
Elements of a Geodatabase Workspace Feature data set Geometric network Relationship class Feature class Annotation class Object class
 ESRI Solutions for Typical Applications and/or Business Processes within Electric and Gas Utilities Applications & Business Processes How does GIS Work?
ESRI Solutions for Typical Applications and/or Business Processes within Electric and Gas Utilities Applications & Business Processes How does GIS Work?
 GIS plays a major role in Utilities…. Executive---Operations---Land---Regulation---Marketing---Field • Design Support – Plan – As Built – Staking Sheet • • • Asset Management Comprehensive Information Sharing Support Structural Load Modeling Support’s Circuit Load Modeling Support for Outage Management Trouble Call / Customer Response Customer Service Regulatory Requirements Inspections Risk Mitigation Data Integration
GIS plays a major role in Utilities…. Executive---Operations---Land---Regulation---Marketing---Field • Design Support – Plan – As Built – Staking Sheet • • • Asset Management Comprehensive Information Sharing Support Structural Load Modeling Support’s Circuit Load Modeling Support for Outage Management Trouble Call / Customer Response Customer Service Regulatory Requirements Inspections Risk Mitigation Data Integration
 Application Examples
Application Examples
 Pipeline Facility Management / GIS Data Viewer
Pipeline Facility Management / GIS Data Viewer
 Pipeline Alignment Sheet Manager
Pipeline Alignment Sheet Manager
 Infrastructure Assets Gas Pipe – Distribution How does GIS Work?
Infrastructure Assets Gas Pipe – Distribution How does GIS Work?
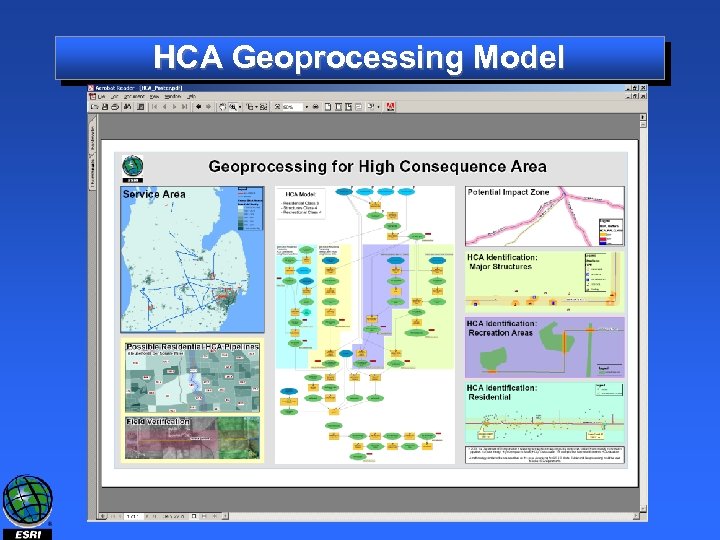 HCA Geoprocessing Model
HCA Geoprocessing Model
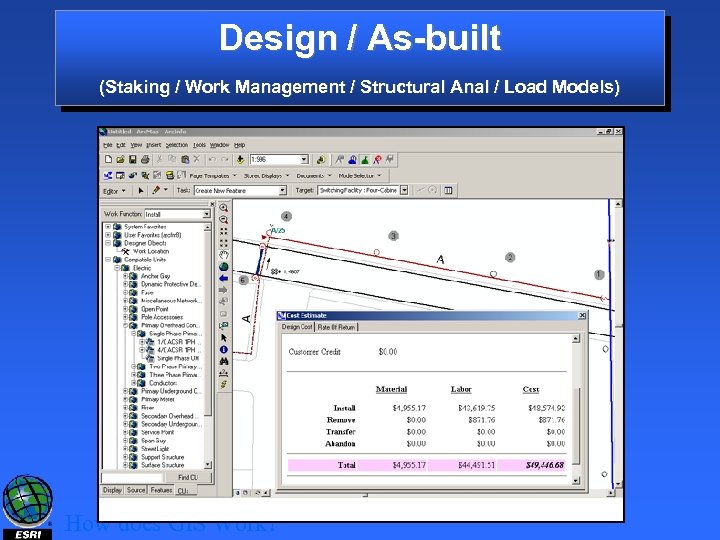 Design / As-built (Staking / Work Management / Structural Anal / Load Models) How does GIS Work?
Design / As-built (Staking / Work Management / Structural Anal / Load Models) How does GIS Work?
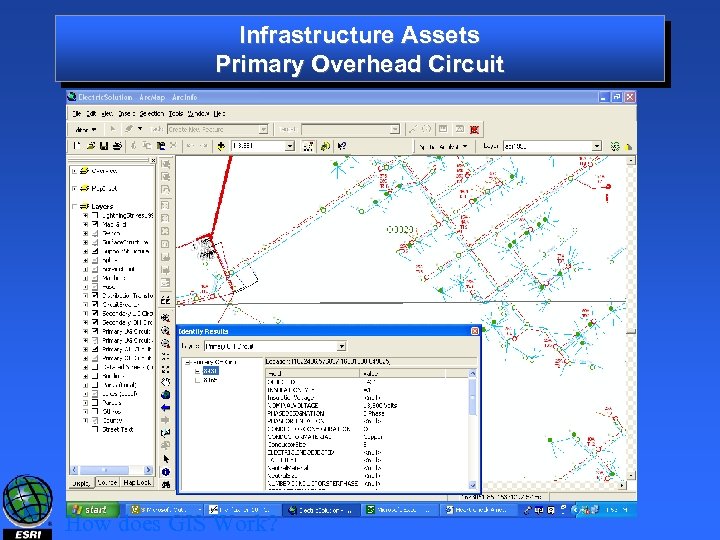 Infrastructure Assets Primary Overhead Circuit How does GIS Work?
Infrastructure Assets Primary Overhead Circuit How does GIS Work?
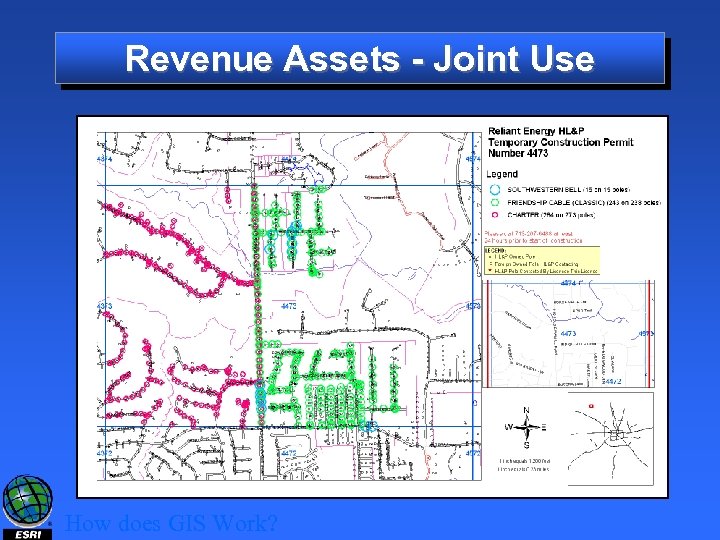 Revenue Assets - Joint Use How does GIS Work?
Revenue Assets - Joint Use How does GIS Work?
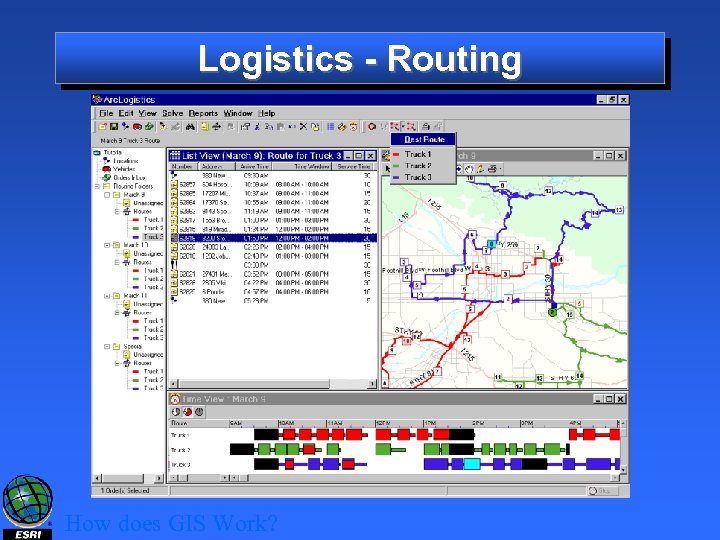 Logistics - Routing How does GIS Work?
Logistics - Routing How does GIS Work?
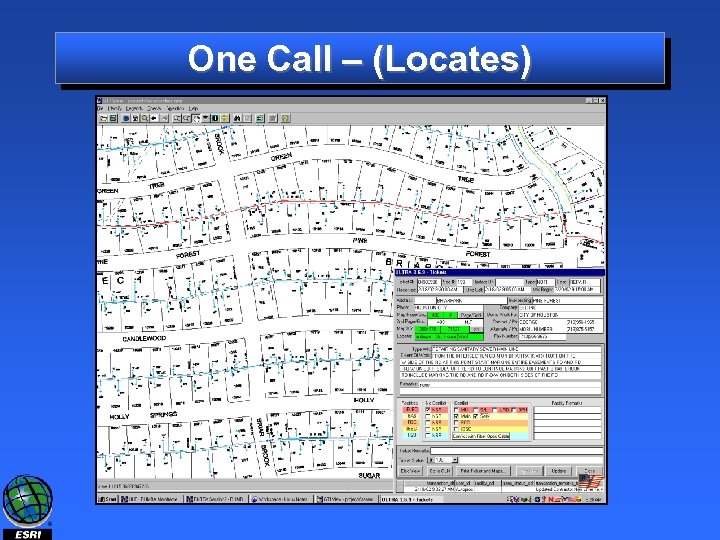 One Call – (Locates)
One Call – (Locates)
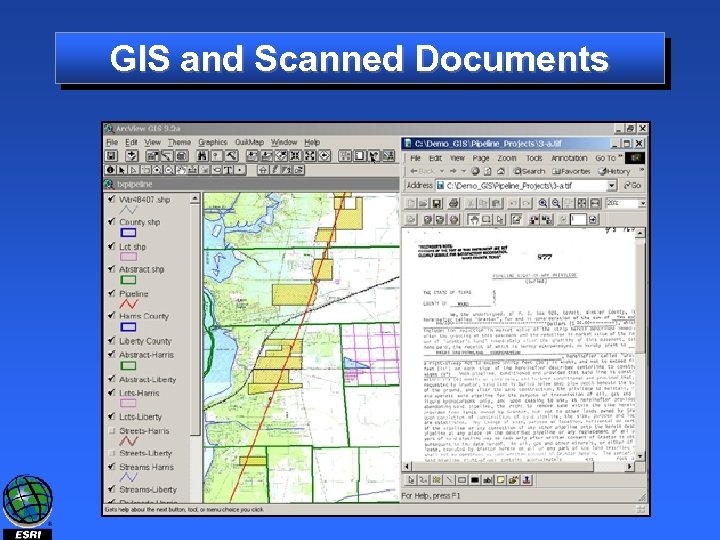 GIS and Scanned Documents
GIS and Scanned Documents
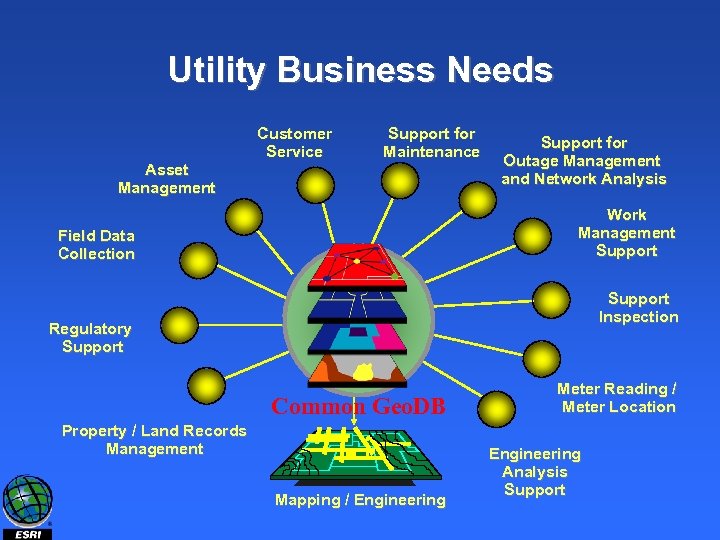 Utility Business Needs Asset Management Customer Service Support for Maintenance Work Management Support Field Data Collection Regulatory Support for Outage Management and Network Analysis Common Database Common Geo. DB Property / Land Records Management Mapping / Engineering Support Inspection Meter Reading / Meter Location Engineering Analysis Support
Utility Business Needs Asset Management Customer Service Support for Maintenance Work Management Support Field Data Collection Regulatory Support for Outage Management and Network Analysis Common Database Common Geo. DB Property / Land Records Management Mapping / Engineering Support Inspection Meter Reading / Meter Location Engineering Analysis Support
 ESRI Software How does GIS Work?
ESRI Software How does GIS Work?
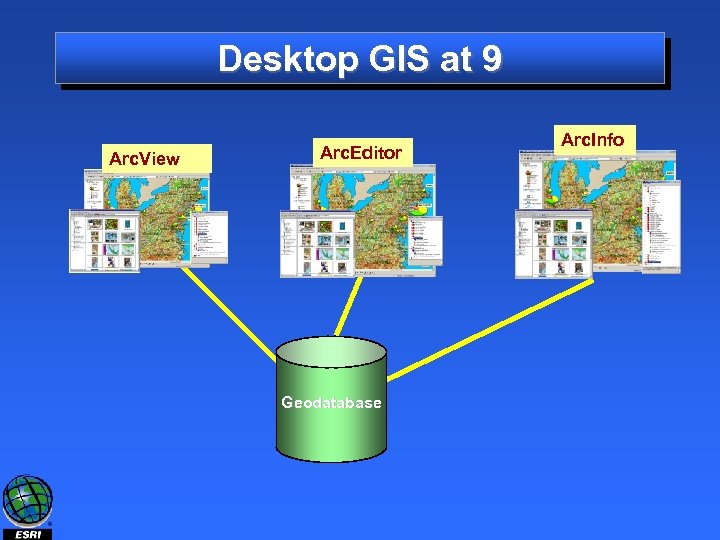 Desktop GIS at 9 Arc. View Arc. Editor Geodatabase Arc. Info
Desktop GIS at 9 Arc. View Arc. Editor Geodatabase Arc. Info
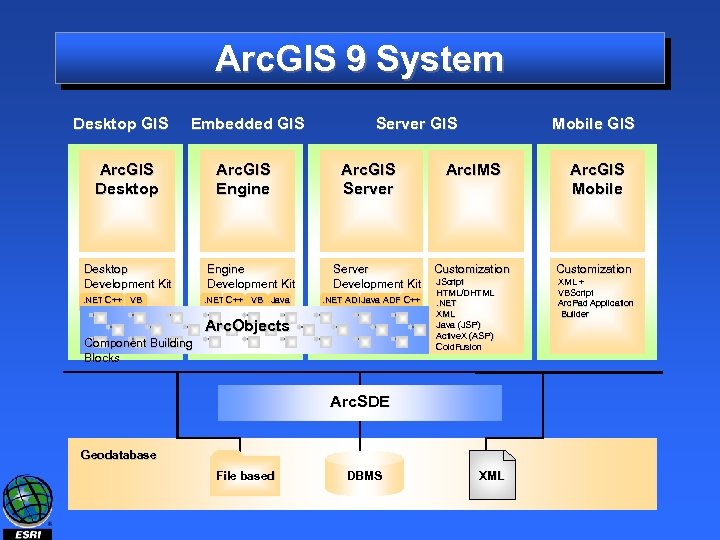 Arc. GIS 9 System Desktop GIS Embedded GIS Arc. GIS Desktop Development Kit. NET C++ VB Arc. GIS Engine Development Kit. NET C++ VB Java Server GIS Arc. GIS Server Development Kit. NET ADFJava ADF C++ Arc. Objects Component Building Blocks Mobile GIS Arc. IMS Customization JScript HTML/DHTML. NET XML Java (JSP) Active. X (ASP) Cold. Fusion XML + VBScript Arc. Pad Application Builder Arc. SDE Geodatabase File based DBMS Arc. GIS Mobile XML
Arc. GIS 9 System Desktop GIS Embedded GIS Arc. GIS Desktop Development Kit. NET C++ VB Arc. GIS Engine Development Kit. NET C++ VB Java Server GIS Arc. GIS Server Development Kit. NET ADFJava ADF C++ Arc. Objects Component Building Blocks Mobile GIS Arc. IMS Customization JScript HTML/DHTML. NET XML Java (JSP) Active. X (ASP) Cold. Fusion XML + VBScript Arc. Pad Application Builder Arc. SDE Geodatabase File based DBMS Arc. GIS Mobile XML
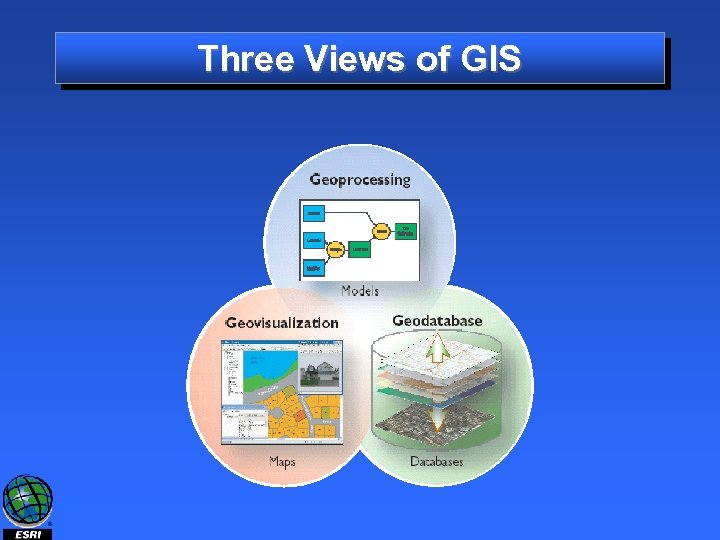 Three Views of GIS
Three Views of GIS
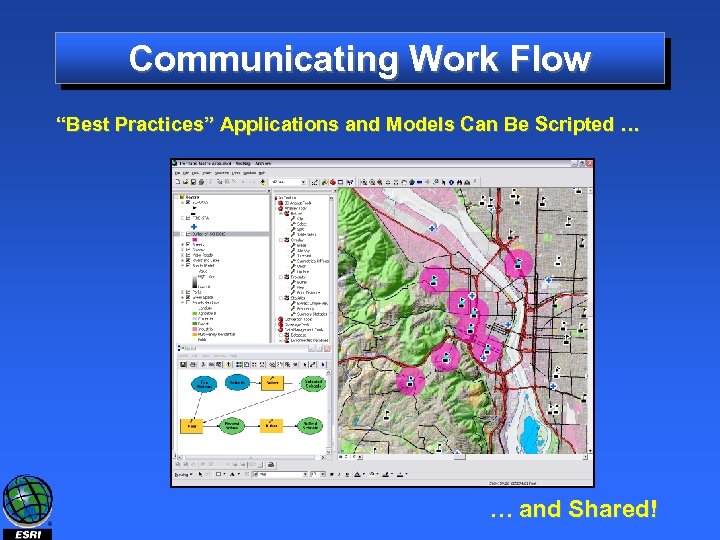 Communicating Work Flow “Best Practices” Applications and Models Can Be Scripted … … and Shared!
Communicating Work Flow “Best Practices” Applications and Models Can Be Scripted … … and Shared!
 Hardware and Network Hardware & Network How does GIS Work?
Hardware and Network Hardware & Network How does GIS Work?
 Fundamental Technology Strategies • • • Built on IT Standards Open and Interoperable Multiparticipant Federated Systems Cross Platform Support Integrating Business Logic
Fundamental Technology Strategies • • • Built on IT Standards Open and Interoperable Multiparticipant Federated Systems Cross Platform Support Integrating Business Logic
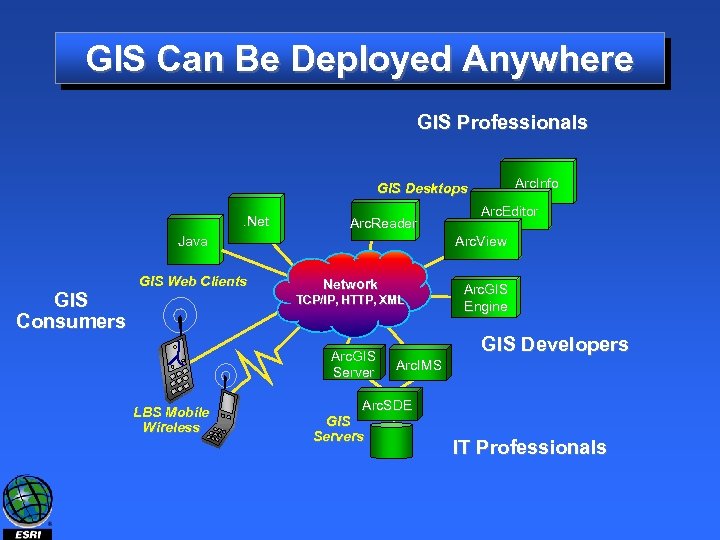 GIS Can Be Deployed Anywhere GIS Professionals Arc. Info GIS Desktops. Net Arc. Reader Arc. View Java GIS Consumers GIS Web Clients Network TCP/IP, HTTP, XML Arc. GIS Server LBS Mobile Wireless Arc. Editor Arc. GIS Engine GIS Developers Arc. IMS Arc. SDE GIS Servers IT Professionals
GIS Can Be Deployed Anywhere GIS Professionals Arc. Info GIS Desktops. Net Arc. Reader Arc. View Java GIS Consumers GIS Web Clients Network TCP/IP, HTTP, XML Arc. GIS Server LBS Mobile Wireless Arc. Editor Arc. GIS Engine GIS Developers Arc. IMS Arc. SDE GIS Servers IT Professionals
 People and Organization People & Organization How does GIS Work?
People and Organization People & Organization How does GIS Work?
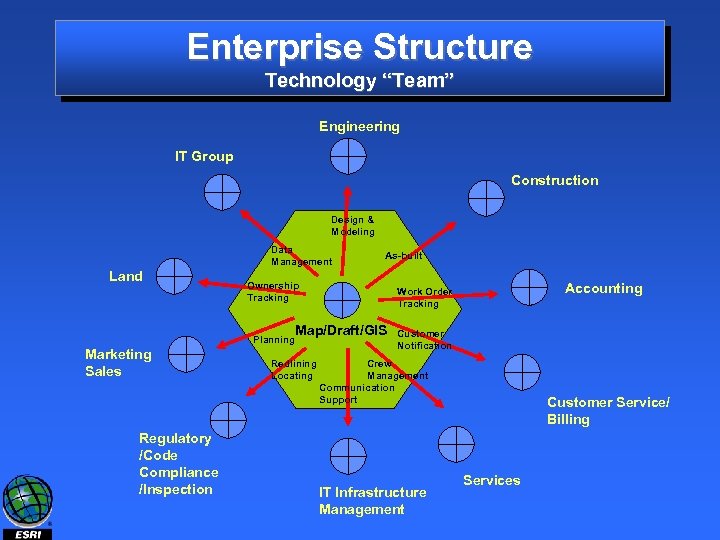 Enterprise Structure Technology “Team” Engineering IT Group Construction Design & Modeling Data Management Land As-built Ownership Tracking Map/Draft/GIS Planning Marketing Sales Regulatory /Code Compliance /Inspection Redlining Locating Accounting Work Order Tracking Customer Notification Crew Management Communication Support IT Infrastructure Management Customer Service/ Billing Services
Enterprise Structure Technology “Team” Engineering IT Group Construction Design & Modeling Data Management Land As-built Ownership Tracking Map/Draft/GIS Planning Marketing Sales Regulatory /Code Compliance /Inspection Redlining Locating Accounting Work Order Tracking Customer Notification Crew Management Communication Support IT Infrastructure Management Customer Service/ Billing Services
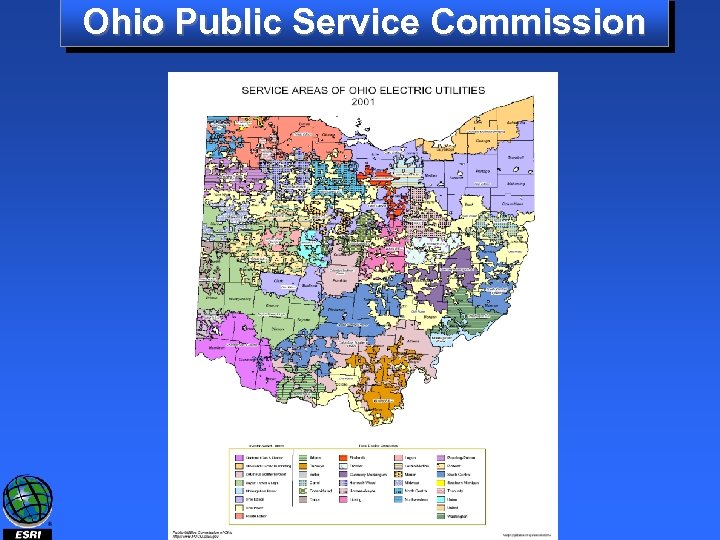 Ohio Public Service Commission
Ohio Public Service Commission
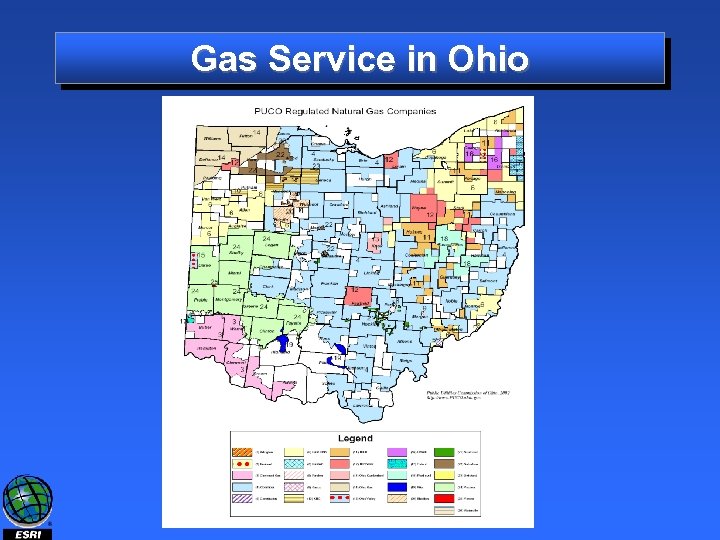 Gas Service in Ohio
Gas Service in Ohio


 Summary • • • Discussions Questions Wrap-up / action items
Summary • • • Discussions Questions Wrap-up / action items
 Section 2 • Arc. IMS • Arc. GIS Server
Section 2 • Arc. IMS • Arc. GIS Server
 Server GIS • Arc. SDE – an advanced spatial data server for managing GIS in RDBMS • Arc. IMS – a scalable Internet map server for GIS publishing • Arc. GIS Server – a GIS application server for the enterprise
Server GIS • Arc. SDE – an advanced spatial data server for managing GIS in RDBMS • Arc. IMS – a scalable Internet map server for GIS publishing • Arc. GIS Server – a GIS application server for the enterprise
 Arc. IMS • Arc. IMS: Mature, stable server-side technology for geopublishing on the internet/intranet. • High volume relatively simple cartography. • Access to advanced cartography through Arc. Map Server or Arc. GIS Desktop • Highly scaleable, cross platform. • Standards based architecture and communications • Open for developers – Arc. XML • Java Dev Framework provided by MO Java • Connectors for Active. X, CF, and Java Dev
Arc. IMS • Arc. IMS: Mature, stable server-side technology for geopublishing on the internet/intranet. • High volume relatively simple cartography. • Access to advanced cartography through Arc. Map Server or Arc. GIS Desktop • Highly scaleable, cross platform. • Standards based architecture and communications • Open for developers – Arc. XML • Java Dev Framework provided by MO Java • Connectors for Active. X, CF, and Java Dev
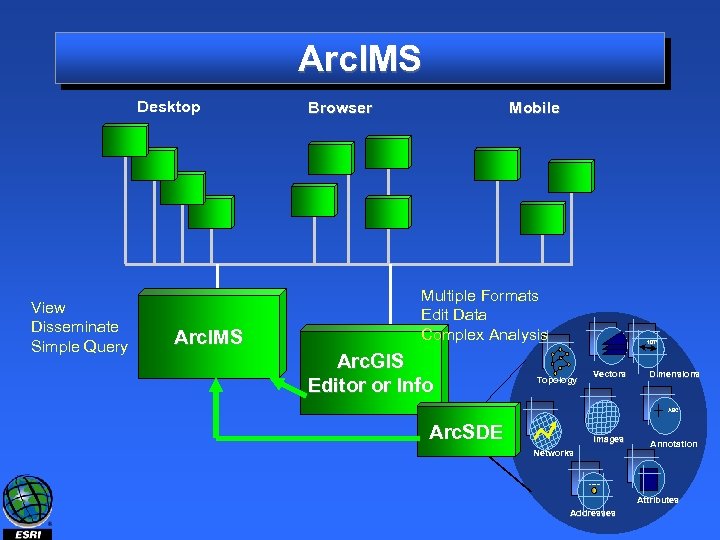 Arc. IMS Desktop View Disseminate Simple Query Arc. IMS Browser Mobile Multiple Formats Edit Data Complex Analysis Arc. GIS Editor or Info 107’ Topology Vectors Dimensions ABC Arc. SDE Images Networks Annotation 27 Main St. Attributes Addresses
Arc. IMS Desktop View Disseminate Simple Query Arc. IMS Browser Mobile Multiple Formats Edit Data Complex Analysis Arc. GIS Editor or Info 107’ Topology Vectors Dimensions ABC Arc. SDE Images Networks Annotation 27 Main St. Attributes Addresses
 Arc. GIS Server 9. 0 is … • Intended for organizations who want to integrate fullfunction GIS with enterprise information systems • A developer-oriented product • Focuses on web application developer – Use rich Arc. Objects functionality to build web applications and web services • Out of the box templates and web services for simple mapping and geocoding • Built from the same core Arc. Objects that make up Arc. GIS Desktop and Arc. GIS Engine
Arc. GIS Server 9. 0 is … • Intended for organizations who want to integrate fullfunction GIS with enterprise information systems • A developer-oriented product • Focuses on web application developer – Use rich Arc. Objects functionality to build web applications and web services • Out of the box templates and web services for simple mapping and geocoding • Built from the same core Arc. Objects that make up Arc. GIS Desktop and Arc. GIS Engine
 Arc. GIS Server 9. 0 is… A platform for building: • Spatially enabled enterprise applications • Enterprise GIS applications (focused) – Web Applications – Web Services – Applications built using industry standards –. Net, J 2 EE • Centralized implementations serving advanced GIS functionality to multiple users • Strong developer APIs - Java, . Net, SOAP/XML
Arc. GIS Server 9. 0 is… A platform for building: • Spatially enabled enterprise applications • Enterprise GIS applications (focused) – Web Applications – Web Services – Applications built using industry standards –. Net, J 2 EE • Centralized implementations serving advanced GIS functionality to multiple users • Strong developer APIs - Java, . Net, SOAP/XML
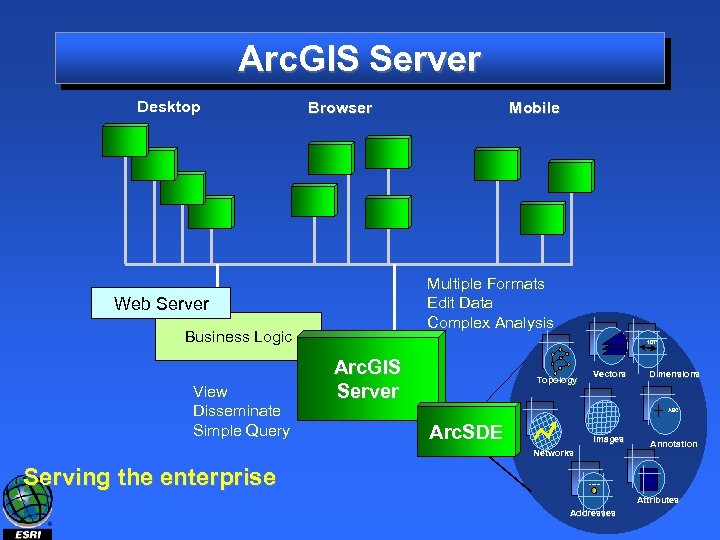 Arc. GIS Server Desktop Browser Multiple Formats Edit Data Complex Analysis Web Server Business Logic View Disseminate Simple Query Mobile 107’ Arc. GIS Server Topology Vectors ABC Arc. SDE Images Networks Serving the enterprise Dimensions Annotation 27 Main St. Attributes Addresses
Arc. GIS Server Desktop Browser Multiple Formats Edit Data Complex Analysis Web Server Business Logic View Disseminate Simple Query Mobile 107’ Arc. GIS Server Topology Vectors ABC Arc. SDE Images Networks Serving the enterprise Dimensions Annotation 27 Main St. Attributes Addresses
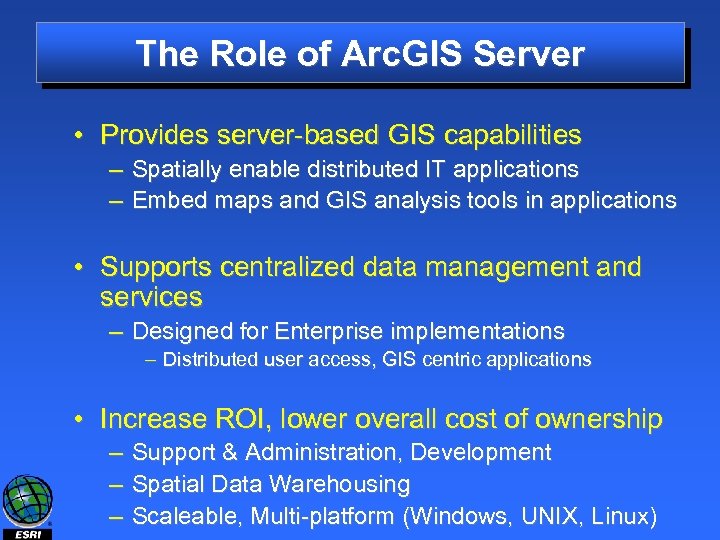 The Role of Arc. GIS Server • Provides server-based GIS capabilities – Spatially enable distributed IT applications – Embed maps and GIS analysis tools in applications • Supports centralized data management and services – Designed for Enterprise implementations – Distributed user access, GIS centric applications • Increase ROI, lower overall cost of ownership – – – Support & Administration, Development Spatial Data Warehousing Scaleable, Multi-platform (Windows, UNIX, Linux)
The Role of Arc. GIS Server • Provides server-based GIS capabilities – Spatially enable distributed IT applications – Embed maps and GIS analysis tools in applications • Supports centralized data management and services – Designed for Enterprise implementations – Distributed user access, GIS centric applications • Increase ROI, lower overall cost of ownership – – – Support & Administration, Development Spatial Data Warehousing Scaleable, Multi-platform (Windows, UNIX, Linux)
 Summary of Arc. GIS Server Benefits • Arc. GIS server shares many of the same benefits of Arc. IMS Arc. Map Server: – Share Arc. GIS map documents across a LAN or the Internet – Maintain high cartographic quality – Serve map layouts – Server maps using all Arc. GIS supported data types • In addition, Arc. GIS Server supports full customization of individual applications via Arc. Objects. Examples include: – Dynamic layers – Dynamic symbology – Remote Editing
Summary of Arc. GIS Server Benefits • Arc. GIS server shares many of the same benefits of Arc. IMS Arc. Map Server: – Share Arc. GIS map documents across a LAN or the Internet – Maintain high cartographic quality – Serve map layouts – Server maps using all Arc. GIS supported data types • In addition, Arc. GIS Server supports full customization of individual applications via Arc. Objects. Examples include: – Dynamic layers – Dynamic symbology – Remote Editing
 Extra Slides
Extra Slides
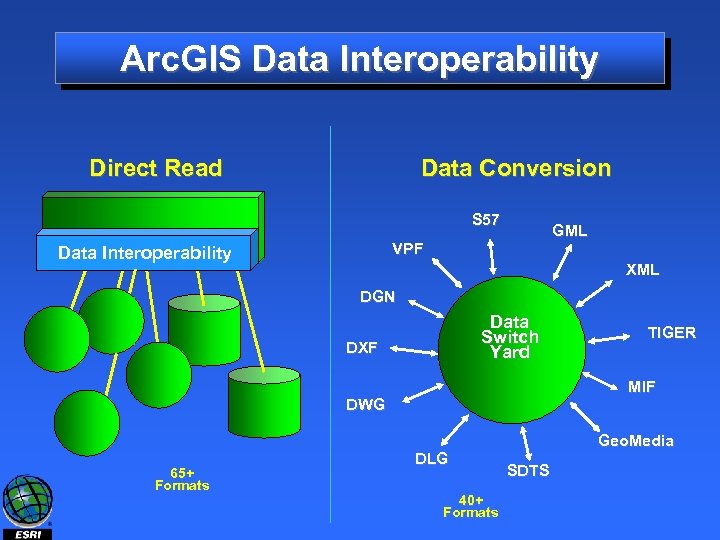 Arc. GIS Data Interoperability Direct Read Data Conversion S 57 GML VPF Data Interoperability XML DGN Data Switch Yard DXF MIF DWG 65+ Formats TIGER DLG 40+ Formats Geo. Media SDTS
Arc. GIS Data Interoperability Direct Read Data Conversion S 57 GML VPF Data Interoperability XML DGN Data Switch Yard DXF MIF DWG 65+ Formats TIGER DLG 40+ Formats Geo. Media SDTS
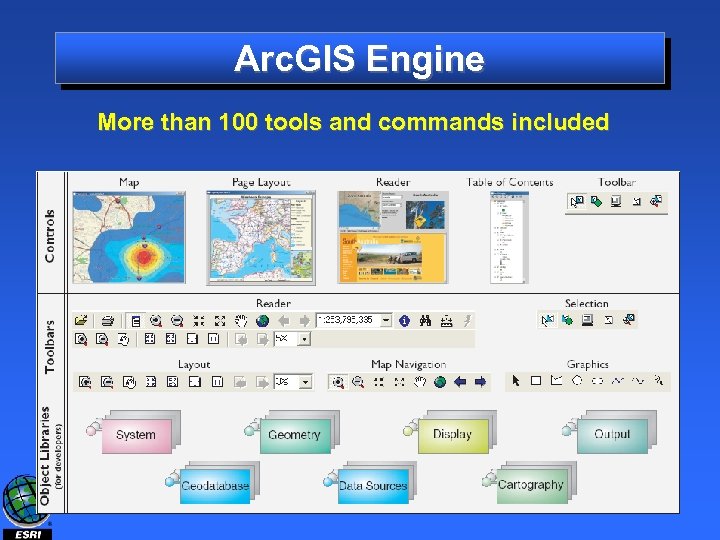 Arc. GIS Engine More than 100 tools and commands included
Arc. GIS Engine More than 100 tools and commands included
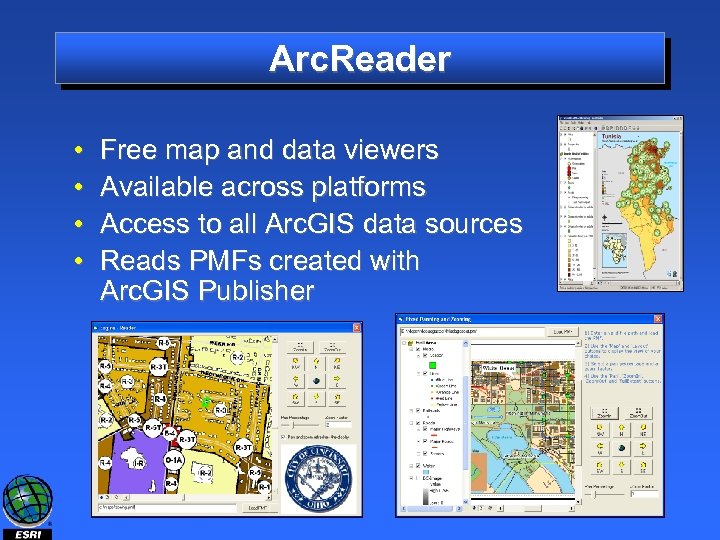 Arc. Reader • • Free map and data viewers Available across platforms Access to all Arc. GIS data sources Reads PMFs created with Arc. GIS Publisher
Arc. Reader • • Free map and data viewers Available across platforms Access to all Arc. GIS data sources Reads PMFs created with Arc. GIS Publisher
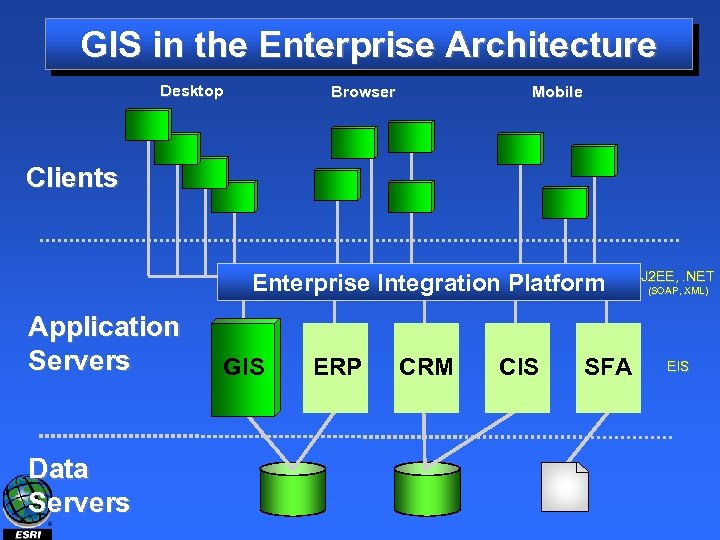 GIS in the Enterprise Architecture Desktop Browser Mobile Clients Enterprise Integration Platform Application Servers Data Servers GIS ERP CRM CIS SFA J 2 EE, . NET (SOAP, XML) EIS
GIS in the Enterprise Architecture Desktop Browser Mobile Clients Enterprise Integration Platform Application Servers Data Servers GIS ERP CRM CIS SFA J 2 EE, . NET (SOAP, XML) EIS
 Arc. GIS Server 9. 0 has… • A Web Application Developer Framework that makes it easy to build GIS Web Applications – Easy to Use – Web Controls, Web Application Templates • A GIS Server that hosts server objects for use by web applications running within standard. Net and J 2 EE application servers – Supports building scalable solutions – Supports easily working with GIS resources
Arc. GIS Server 9. 0 has… • A Web Application Developer Framework that makes it easy to build GIS Web Applications – Easy to Use – Web Controls, Web Application Templates • A GIS Server that hosts server objects for use by web applications running within standard. Net and J 2 EE application servers – Supports building scalable solutions – Supports easily working with GIS resources
 Arc. GIS Server Extensions • Spatial – provides a powerful set of functions that allow you to create, query and analyze cell based raster data • 3 D – provides a powerful set of functions that allow your applications to create and analyze surfaces • Street. Map – provides street-level mapping and address matching. All data comes compressed on CDROM
Arc. GIS Server Extensions • Spatial – provides a powerful set of functions that allow you to create, query and analyze cell based raster data • 3 D – provides a powerful set of functions that allow your applications to create and analyze surfaces • Street. Map – provides street-level mapping and address matching. All data comes compressed on CDROM
 Arc. GIS Server • Arc. GIS Server: Server-side technology for geoprocessing on the internet/intranet. • Developer focused • Access to all of Arc. Objects on the Server • Standards based architecture and communications • Cross platform. Scaleable? • Web developer access through SOAP/XML • . NET and Java Dev Frameworks
Arc. GIS Server • Arc. GIS Server: Server-side technology for geoprocessing on the internet/intranet. • Developer focused • Access to all of Arc. Objects on the Server • Standards based architecture and communications • Cross platform. Scaleable? • Web developer access through SOAP/XML • . NET and Java Dev Frameworks
 Arc. GIS Server Use cases • To build Web applications and services that provide advanced mapping, geocoding, tracing, linear referencing, spatial and 3 D analysis, editing, access to geodatabase topology, geometric networks, subtypes, etc… – Focused web applications – Insurance Risk Assessment, Building Permit Applications, Forestry Management, Utility Network Analysis – Centralized services – Gazetteer, image & base map services – Integration of GIS and Enterprise Applications – Customer Relation Management Systems, Emergency Response, Public Access, etc.
Arc. GIS Server Use cases • To build Web applications and services that provide advanced mapping, geocoding, tracing, linear referencing, spatial and 3 D analysis, editing, access to geodatabase topology, geometric networks, subtypes, etc… – Focused web applications – Insurance Risk Assessment, Building Permit Applications, Forestry Management, Utility Network Analysis – Centralized services – Gazetteer, image & base map services – Integration of GIS and Enterprise Applications – Customer Relation Management Systems, Emergency Response, Public Access, etc.
 Arc. GIS Data Interoperability • Integrates Safe Software Technology with the Arc. GIS Desktop • Adds many new data sources to Arc. GIS • Authors complex data translators – 100+ data manipulation tools – Framework for writing sophisticated translators • Joint product from Safe Software and ESRI
Arc. GIS Data Interoperability • Integrates Safe Software Technology with the Arc. GIS Desktop • Adds many new data sources to Arc. GIS • Authors complex data translators – 100+ data manipulation tools – Framework for writing sophisticated translators • Joint product from Safe Software and ESRI
 Key Features of Arc. GIS Server • • Framework for Enterprise GIS Standard Application Deployment Integrates Into IT Infrastructure Standard Programming Languages Application server for GIS functionality
Key Features of Arc. GIS Server • • Framework for Enterprise GIS Standard Application Deployment Integrates Into IT Infrastructure Standard Programming Languages Application server for GIS functionality
 Capabilities of Arc. GIS Server • A new way to centrally manage feature rich applications. • Extend GIS use and consumption through browsers and Web services. • Leverage all existing investments in GIS. • Integrate with other core business systems through IT standards.
Capabilities of Arc. GIS Server • A new way to centrally manage feature rich applications. • Extend GIS use and consumption through browsers and Web services. • Leverage all existing investments in GIS. • Integrate with other core business systems through IT standards.
 Arc. GIS Server Demonstration Summary • Central Enterprise GIS – Remote Editing of Central GIS Database in a Web Application – Focused Spatial Analysis • Integrated GIS and IT – GIS Components in an Enterprise Computing Architecture • Centrally Hosted Web Applications • Non-Web Applications
Arc. GIS Server Demonstration Summary • Central Enterprise GIS – Remote Editing of Central GIS Database in a Web Application – Focused Spatial Analysis • Integrated GIS and IT – GIS Components in an Enterprise Computing Architecture • Centrally Hosted Web Applications • Non-Web Applications
 Users / Partners • Numerous Investor Owned Utilities – – – – • • • NIPSCO (Ni. Source) - 1. 1 Mil Meters (3) Westar – 700 K Meters One. OK – 2 Mil Meters Laclede Gas – 600 K Meters Arkansas Oklahoma Gas – 40 K Meters Centerpoint Energy – Millions of Meters – Gas&Elec Alliant Energy Dominion Southern Companies 100’s of Rural Electric Coops 100’s of Municipal Operations
Users / Partners • Numerous Investor Owned Utilities – – – – • • • NIPSCO (Ni. Source) - 1. 1 Mil Meters (3) Westar – 700 K Meters One. OK – 2 Mil Meters Laclede Gas – 600 K Meters Arkansas Oklahoma Gas – 40 K Meters Centerpoint Energy – Millions of Meters – Gas&Elec Alliant Energy Dominion Southern Companies 100’s of Rural Electric Coops 100’s of Municipal Operations
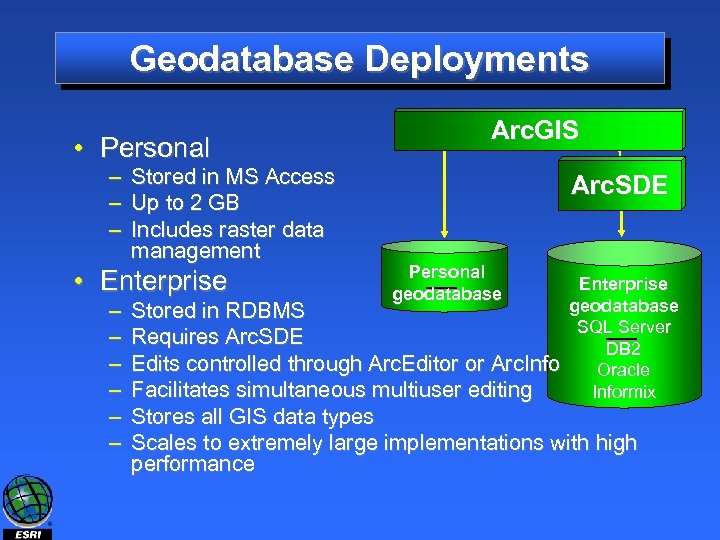 Geodatabase Deployments • Personal – Stored in MS Access – Up to 2 GB – Includes raster data management • Enterprise – – – Arc. GIS Arc. SDE Personal geodatabase Enterprise geodatabase SQL Server DB 2 Oracle Informix Stored in RDBMS Requires Arc. SDE Edits controlled through Arc. Editor or Arc. Info Facilitates simultaneous multiuser editing Stores all GIS data types Scales to extremely large implementations with high performance
Geodatabase Deployments • Personal – Stored in MS Access – Up to 2 GB – Includes raster data management • Enterprise – – – Arc. GIS Arc. SDE Personal geodatabase Enterprise geodatabase SQL Server DB 2 Oracle Informix Stored in RDBMS Requires Arc. SDE Edits controlled through Arc. Editor or Arc. Info Facilitates simultaneous multiuser editing Stores all GIS data types Scales to extremely large implementations with high performance
 Electric and Gas Data Models How does GIS Work?
Electric and Gas Data Models How does GIS Work?
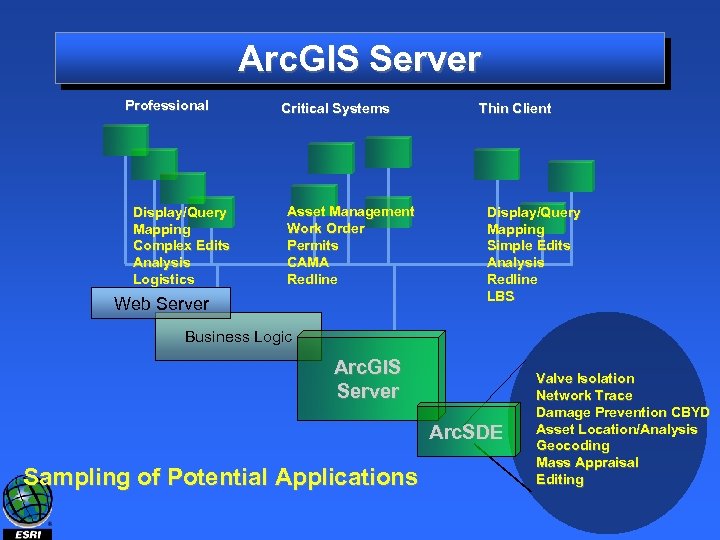 Arc. GIS Server Professional Display/Query Mapping Complex Edits Analysis Logistics Critical Systems Asset Management Work Order Permits CAMA Redline Web Server Thin Client Display/Query Mapping Simple Edits Analysis Redline LBS Business Logic Arc. GIS Server Arc. SDE Sampling of Potential Applications Valve Isolation Network Trace Damage Prevention CBYD Asset Location/Analysis Geocoding Mass Appraisal Editing
Arc. GIS Server Professional Display/Query Mapping Complex Edits Analysis Logistics Critical Systems Asset Management Work Order Permits CAMA Redline Web Server Thin Client Display/Query Mapping Simple Edits Analysis Redline LBS Business Logic Arc. GIS Server Arc. SDE Sampling of Potential Applications Valve Isolation Network Trace Damage Prevention CBYD Asset Location/Analysis Geocoding Mass Appraisal Editing


