abffacea0e40c3fdee1d1c4c1456b465.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
 The Role of Competitiveness Partnerships in achieving Millennium Development Goals JANAMITRA DEVAN VICE PRESIDENT, FINANCE & PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT WORLD BANK GROUP DONOR FORUM PARIS, MAY 18 -19, 2010
The Role of Competitiveness Partnerships in achieving Millennium Development Goals JANAMITRA DEVAN VICE PRESIDENT, FINANCE & PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT WORLD BANK GROUP DONOR FORUM PARIS, MAY 18 -19, 2010
 The private sector is critical to achievement of MDGs MDG 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger 2. Achieve universal primary education 3. Promote gender equality and empower women 4. Reduce child mortality 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases 7. Ensure environmental sustainability 8. Develop a global partnership for development Private Sector • Creates employment • Expands the tax base • Participation in health and education • Public-private collaboration in developing standards
The private sector is critical to achievement of MDGs MDG 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger 2. Achieve universal primary education 3. Promote gender equality and empower women 4. Reduce child mortality 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases 7. Ensure environmental sustainability 8. Develop a global partnership for development Private Sector • Creates employment • Expands the tax base • Participation in health and education • Public-private collaboration in developing standards
 The reform momentum in private sector has been strong… Almost 500 serious reform initiatives in FY 2009 alone… Mexico Simplification of municipal formalities (SARE) across states India Elimination of “license raj” in India Colombia Private administration of building permits Rwanda Simplification of business start-up procedures Macedonia Simplified property registration
The reform momentum in private sector has been strong… Almost 500 serious reform initiatives in FY 2009 alone… Mexico Simplification of municipal formalities (SARE) across states India Elimination of “license raj” in India Colombia Private administration of building permits Rwanda Simplification of business start-up procedures Macedonia Simplified property registration
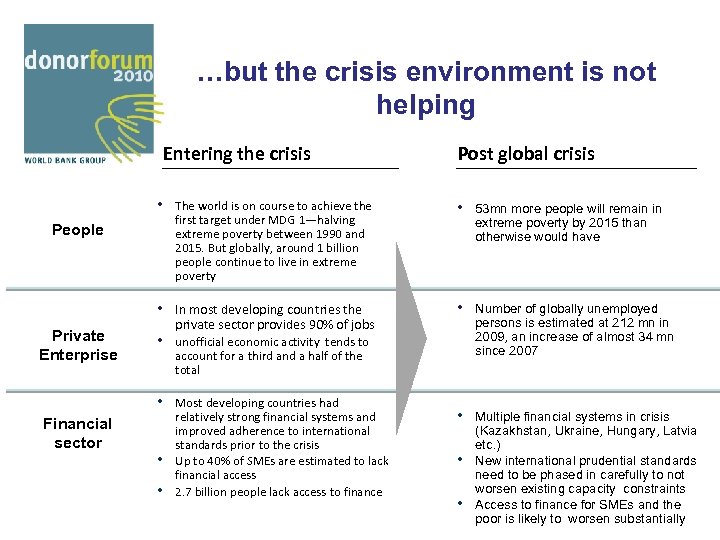 …but the crisis environment is not helping Entering the crisis • The world is on course to achieve the People first target under MDG 1—halving extreme poverty between 1990 and 2015. But globally, around 1 billion people continue to live in extreme poverty • In most developing countries the Private Enterprise private sector provides 90% of jobs • unofficial economic activity tends to account for a third and a half of the total • Most developing countries had Financial sector relatively strong financial systems and improved adherence to international standards prior to the crisis • Up to 40% of SMEs are estimated to lack financial access • 2. 7 billion people lack access to finance Post global crisis • 53 mn more people will remain in extreme poverty by 2015 than otherwise would have • Number of globally unemployed persons is estimated at 212 mn in 2009, an increase of almost 34 mn since 2007 • Multiple financial systems in crisis (Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Hungary, Latvia etc. ) • New international prudential standards need to be phased in carefully to not worsen existing capacity constraints • Access to finance for SMEs and the poor is likely to worsen substantially
…but the crisis environment is not helping Entering the crisis • The world is on course to achieve the People first target under MDG 1—halving extreme poverty between 1990 and 2015. But globally, around 1 billion people continue to live in extreme poverty • In most developing countries the Private Enterprise private sector provides 90% of jobs • unofficial economic activity tends to account for a third and a half of the total • Most developing countries had Financial sector relatively strong financial systems and improved adherence to international standards prior to the crisis • Up to 40% of SMEs are estimated to lack financial access • 2. 7 billion people lack access to finance Post global crisis • 53 mn more people will remain in extreme poverty by 2015 than otherwise would have • Number of globally unemployed persons is estimated at 212 mn in 2009, an increase of almost 34 mn since 2007 • Multiple financial systems in crisis (Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Hungary, Latvia etc. ) • New international prudential standards need to be phased in carefully to not worsen existing capacity constraints • Access to finance for SMEs and the poor is likely to worsen substantially
 Broad policy reform is insufficient; intervention at sectoral level is critical Examples abound… • Broad policy reforms important but insufficient Peruvian asparagus • Small firms can expand to create jobs only in growth markets or if they have pull Malaysian IMP 2 • Anchor tenants critical Singapore avionics What’s needed are Competitiveness Partnerships….
Broad policy reform is insufficient; intervention at sectoral level is critical Examples abound… • Broad policy reforms important but insufficient Peruvian asparagus • Small firms can expand to create jobs only in growth markets or if they have pull Malaysian IMP 2 • Anchor tenants critical Singapore avionics What’s needed are Competitiveness Partnerships….
 What are Competitiveness Partnerships (CP)? CPs… …are joint efforts between public and private sectors …are built on public-private dialogue at industry/sector level …help identify market opportunities and constraints …create inclusive growth by building up supplier and service sectors in an industrial/sectoral ecology Why are CPs needed? Globally competitive industries/sectors create wealth Private sector needs to be engaged using language they understand Public sector can play enabling role for sectoral competitiveness The goal of CPs? To create domestic industries that can compete abroad and generate demand at home
What are Competitiveness Partnerships (CP)? CPs… …are joint efforts between public and private sectors …are built on public-private dialogue at industry/sector level …help identify market opportunities and constraints …create inclusive growth by building up supplier and service sectors in an industrial/sectoral ecology Why are CPs needed? Globally competitive industries/sectors create wealth Private sector needs to be engaged using language they understand Public sector can play enabling role for sectoral competitiveness The goal of CPs? To create domestic industries that can compete abroad and generate demand at home
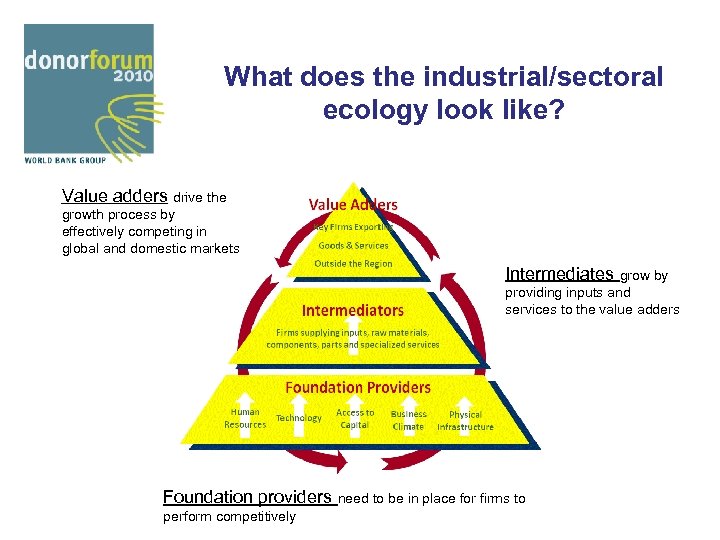 What does the industrial/sectoral ecology look like? Value adders drive the growth process by effectively competing in global and domestic markets Intermediates grow by providing inputs and services to the value adders Foundation providers need to be in place for firms to perform competitively
What does the industrial/sectoral ecology look like? Value adders drive the growth process by effectively competing in global and domestic markets Intermediates grow by providing inputs and services to the value adders Foundation providers need to be in place for firms to perform competitively
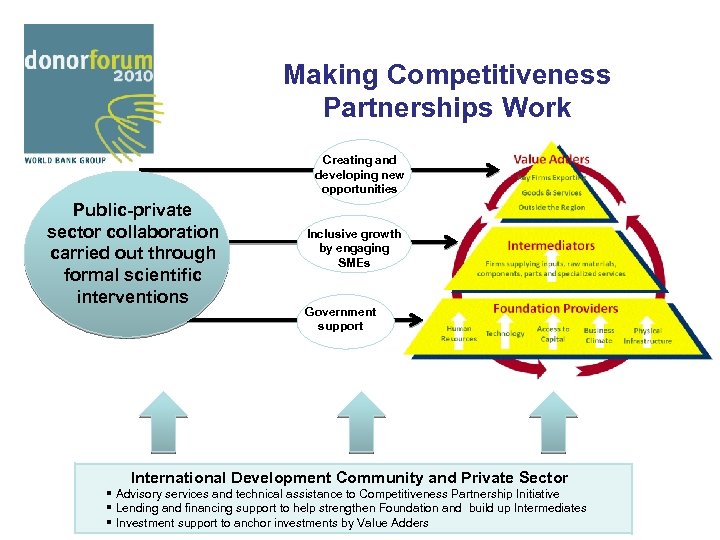 Making Competitiveness Partnerships Work Creating and developing new opportunities Public-private sector collaboration carried out through formal scientific interventions Inclusive growth by engaging SMEs Government support International Development Community and Private Sector § Advisory services and technical assistance to Competitiveness Partnership Initiative § Lending and financing support to help strengthen Foundation and build up Intermediates § Investment support to anchor investments by Value Adders
Making Competitiveness Partnerships Work Creating and developing new opportunities Public-private sector collaboration carried out through formal scientific interventions Inclusive growth by engaging SMEs Government support International Development Community and Private Sector § Advisory services and technical assistance to Competitiveness Partnership Initiative § Lending and financing support to help strengthen Foundation and build up Intermediates § Investment support to anchor investments by Value Adders
 Partnerships and Collaboration Will Be Key! • Among all of us – multilaterals, bilaterals, civil society and private sector – we have all the tools needed to make industrialization a reality: analytics, advisory services, lending, investments and grants • We need to find ways to work together more and better: Þ A global partnership platform for development partners and private sector to • set the agenda and create visibility • focus on development assistance that emphasizes implementation and problem-solving • set clear, quantitative targets that are ambitious and achievable – Strengthen the service delivery within the World Bank Group • adopt a Global Practice model to deliver services in a more focused and goal-oriented manner • strengthen links to lending and investment operations to maximize synergies and impact
Partnerships and Collaboration Will Be Key! • Among all of us – multilaterals, bilaterals, civil society and private sector – we have all the tools needed to make industrialization a reality: analytics, advisory services, lending, investments and grants • We need to find ways to work together more and better: Þ A global partnership platform for development partners and private sector to • set the agenda and create visibility • focus on development assistance that emphasizes implementation and problem-solving • set clear, quantitative targets that are ambitious and achievable – Strengthen the service delivery within the World Bank Group • adopt a Global Practice model to deliver services in a more focused and goal-oriented manner • strengthen links to lending and investment operations to maximize synergies and impact


