7f4f16b317a7489ffba326dcea133ec6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 The Role of Communication and Information Technology and Informatics in the Patient-Dentist Relationship Michael Kirshner, DDS, MPH Dental Informatics and Dental Research: Making the Connection Bethesda, MD June 12, 2003
The Role of Communication and Information Technology and Informatics in the Patient-Dentist Relationship Michael Kirshner, DDS, MPH Dental Informatics and Dental Research: Making the Connection Bethesda, MD June 12, 2003
 Overview n n n Importance of doctor-patient relationship Problem and solutions Defining & measuring doctor-patient relationship Dental CIT applications Role of dental informatics 2
Overview n n n Importance of doctor-patient relationship Problem and solutions Defining & measuring doctor-patient relationship Dental CIT applications Role of dental informatics 2
 Importance n n Doctor-patient relationship valued throughout history Linked to important health outcomes n n Increased treatment adherence Reduce malpractice claims Fewer tests and second opinions Improved quality of life 3
Importance n n Doctor-patient relationship valued throughout history Linked to important health outcomes n n Increased treatment adherence Reduce malpractice claims Fewer tests and second opinions Improved quality of life 3
 Problem n Quality of relationship on the decline n n n Consumerism Healthcare system constraints Poor communication skills 4
Problem n Quality of relationship on the decline n n n Consumerism Healthcare system constraints Poor communication skills 4
 Solution n n Refocus on patient centeredness Leverage communication and information technology Conduct research to study effects Look to informatics for a model that integrates CIT with human relationship 5
Solution n n Refocus on patient centeredness Leverage communication and information technology Conduct research to study effects Look to informatics for a model that integrates CIT with human relationship 5
 Doctor-patient relationship defined n n n Sustained open trusted conversation Sharing of information and knowledge Exemplified in patient-centered care model 6
Doctor-patient relationship defined n n n Sustained open trusted conversation Sharing of information and knowledge Exemplified in patient-centered care model 6
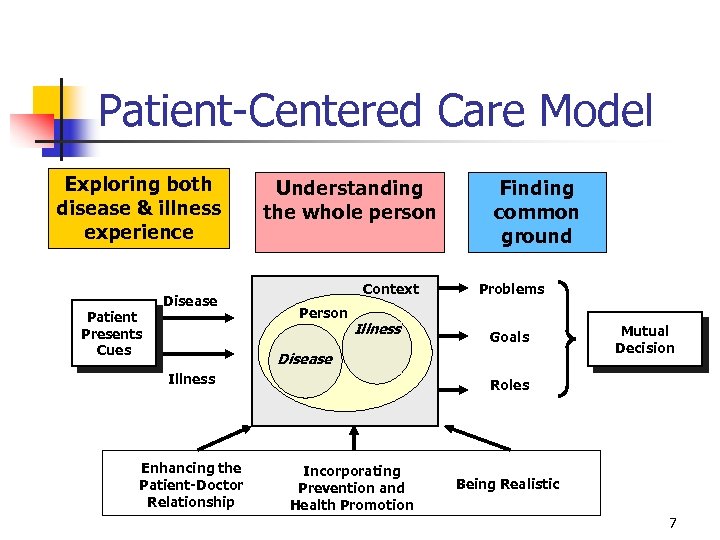 Patient-Centered Care Model Exploring both disease & illness experience Patient Presents Cues Disease Understanding the whole person Context Person Illness Finding common ground Problems Goals Disease Illness Enhancing the Patient-Doctor Relationship Mutual Decision Roles Incorporating Prevention and Health Promotion Being Realistic 7
Patient-Centered Care Model Exploring both disease & illness experience Patient Presents Cues Disease Understanding the whole person Context Person Illness Finding common ground Problems Goals Disease Illness Enhancing the Patient-Doctor Relationship Mutual Decision Roles Incorporating Prevention and Health Promotion Being Realistic 7
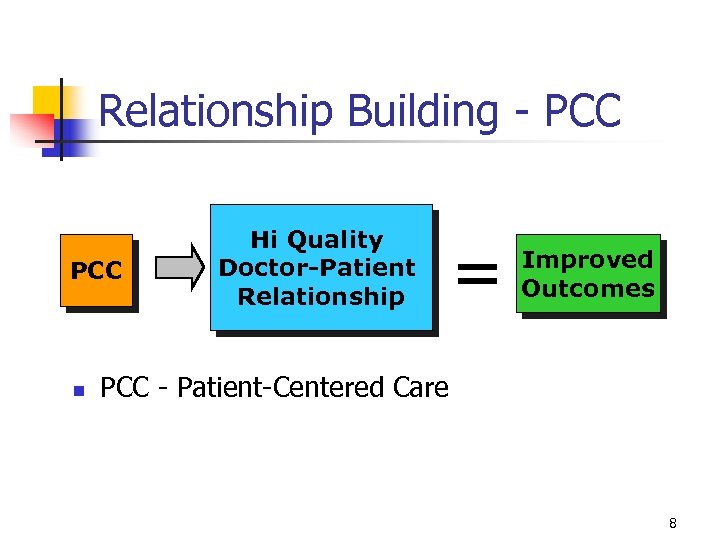 Relationship Building - PCC n Hi Quality Doctor-Patient Relationship = Improved Outcomes PCC - Patient-Centered Care 8
Relationship Building - PCC n Hi Quality Doctor-Patient Relationship = Improved Outcomes PCC - Patient-Centered Care 8
 Measure Quality Relationship n Primary Care Assessment Survey n n n Conceptual model of framework to measure doctor-patient relationship Validated instrument 4 scales measuring personal relationship Source: Safran 1998 9
Measure Quality Relationship n Primary Care Assessment Survey n n n Conceptual model of framework to measure doctor-patient relationship Validated instrument 4 scales measuring personal relationship Source: Safran 1998 9
 Personal Relationship Scales n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and social support Contextual knowledge Trust 10
Personal Relationship Scales n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and social support Contextual knowledge Trust 10
 Personal Relationship Scales n Communication and decision support n Thoroughness of questions about symptoms, attention to what patients say, clarity of explanations, instructions, and advice and help in making decisions. 11
Personal Relationship Scales n Communication and decision support n Thoroughness of questions about symptoms, attention to what patients say, clarity of explanations, instructions, and advice and help in making decisions. 11
 Personal Relationship Scales n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and support n Patience, friendliness, caring, respect, and time spent with the patient. Sharing power and enhancing selfawareness. 12
Personal Relationship Scales n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and support n Patience, friendliness, caring, respect, and time spent with the patient. Sharing power and enhancing selfawareness. 12
 Personal Relationship Scales n n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and support Contextual knowledge of the patient n Knowledge of the patient’s life history, medical history, responsibilities at work, home or school, principal health concerns, values, and beliefs. 13
Personal Relationship Scales n n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and support Contextual knowledge of the patient n Knowledge of the patient’s life history, medical history, responsibilities at work, home or school, principal health concerns, values, and beliefs. 13
 Personal Relationship Scales n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and support Contextual knowledge of the patient Trust n Integrity, honesty, competence, and role as the patient’s agent. Expressing a sense of security and well-being. 14
Personal Relationship Scales n n Communication and decision support Interpersonal caring and support Contextual knowledge of the patient Trust n Integrity, honesty, competence, and role as the patient’s agent. Expressing a sense of security and well-being. 14
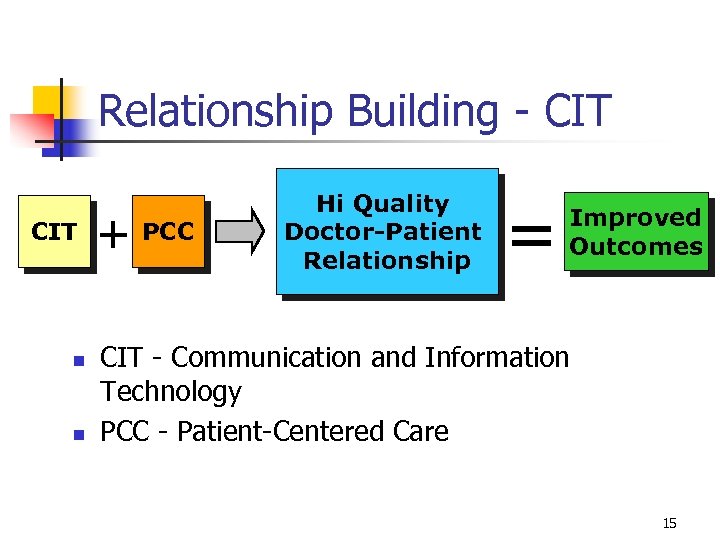 Relationship Building - CIT n n + PCC Hi Quality Doctor-Patient Relationship = Improved Outcomes CIT - Communication and Information Technology PCC - Patient-Centered Care 15
Relationship Building - CIT n n + PCC Hi Quality Doctor-Patient Relationship = Improved Outcomes CIT - Communication and Information Technology PCC - Patient-Centered Care 15
 Communication & Information Technology n n What aspects of CIT affect patientdentist relationship Use existing models n n PCAS for relationship Schleyer’s taxonomy of dental CIT 16
Communication & Information Technology n n What aspects of CIT affect patientdentist relationship Use existing models n n PCAS for relationship Schleyer’s taxonomy of dental CIT 16
 Dental CIT n Schleyer’s Categories n n n Internet Clinical Administrative 17
Dental CIT n Schleyer’s Categories n n n Internet Clinical Administrative 17
 CIT Internet Devices 18
CIT Internet Devices 18
 CIT Clinical & Administrative Devices 19
CIT Clinical & Administrative Devices 19
 Mobile & Wearable Devices 20
Mobile & Wearable Devices 20
 Internet n n Office Web portal Email Personal Health Record Teledentistry 21
Internet n n Office Web portal Email Personal Health Record Teledentistry 21
 Web Portal n Service n n n n Doctor and Staff info Location, hours n Relationship Benefit Practice philosophy n Informed patient Office policies n Match & shared values Patient education n Set expectations Automated scheduling n Sense of control Automated reminders Patient testimonials & images n Build trust 22
Web Portal n Service n n n n Doctor and Staff info Location, hours n Relationship Benefit Practice philosophy n Informed patient Office policies n Match & shared values Patient education n Set expectations Automated scheduling n Sense of control Automated reminders Patient testimonials & images n Build trust 22
 Email n Service n n n Secure Web-based Triaged Linked to EOHR Becomes part of PHR n Relationship Benefit n n n Ease of access Open communication Trust 23
Email n Service n n n Secure Web-based Triaged Linked to EOHR Becomes part of PHR n Relationship Benefit n n n Ease of access Open communication Trust 23
 PHR n Service n n n Treatment history Dental history Meds Family history Radiographs n Relationship Benefit n n n Contextual knowledge Sharing & participation Access & control Level power asymmetry Trust and confidence 24
PHR n Service n n n Treatment history Dental history Meds Family history Radiographs n Relationship Benefit n n n Contextual knowledge Sharing & participation Access & control Level power asymmetry Trust and confidence 24
 Teledentsitry n Service n n n Remote care Consultations X-rays and images Teleconference Real-time, store and forward n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Decision support Contextual knowledge Convenience Continuity of care Trust 25
Teledentsitry n Service n n n Remote care Consultations X-rays and images Teleconference Real-time, store and forward n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Decision support Contextual knowledge Convenience Continuity of care Trust 25
 Clinical EOHR n Digital Imaging n Treatment Planning n 26
Clinical EOHR n Digital Imaging n Treatment Planning n 26
 EOHR n Service n n n n Exam Charting Treatment Planner Clinical and psychosocial n Relationship Benefit data n Communication Preference data n Contextual Knowledge History and trends n Confidence Knowledge-based n Continuity of care n Trust 27
EOHR n Service n n n n Exam Charting Treatment Planner Clinical and psychosocial n Relationship Benefit data n Communication Preference data n Contextual Knowledge History and trends n Confidence Knowledge-based n Continuity of care n Trust 27
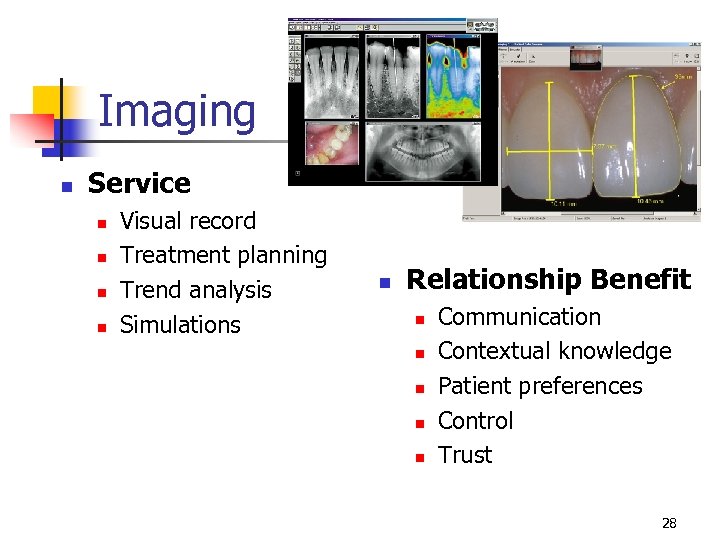 Imaging n Service n n Visual record Treatment planning Trend analysis Simulations n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Contextual knowledge Patient preferences Control Trust 28
Imaging n Service n n Visual record Treatment planning Trend analysis Simulations n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Contextual knowledge Patient preferences Control Trust 28
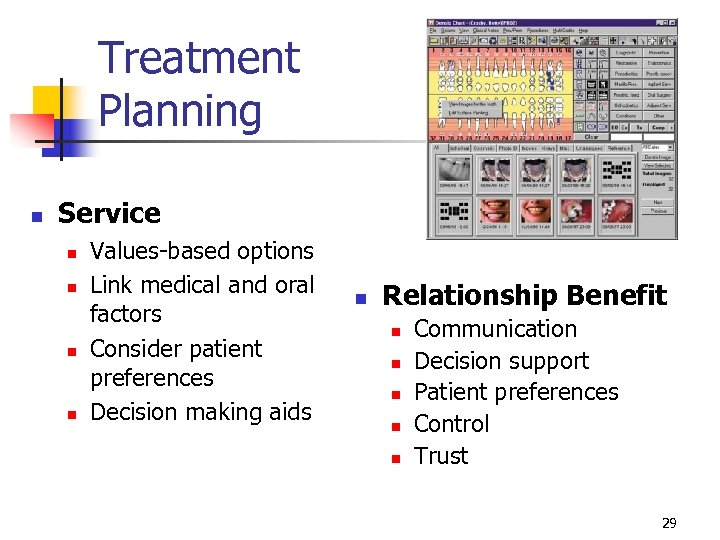 Treatment Planning n Service n n Values-based options Link medical and oral factors Consider patient preferences Decision making aids n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Decision support Patient preferences Control Trust 29
Treatment Planning n Service n n Values-based options Link medical and oral factors Consider patient preferences Decision making aids n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Decision support Patient preferences Control Trust 29
 Administrative: Practice Mgt. n Services n n n n Appointment scheduling Patient registration Tailored messages Demographics Insurance billing Claims submission Recall n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Contextual knowledge Access Confidence Convenience Trust 30
Administrative: Practice Mgt. n Services n n n n Appointment scheduling Patient registration Tailored messages Demographics Insurance billing Claims submission Recall n Relationship Benefit n n n Communication Contextual knowledge Access Confidence Convenience Trust 30
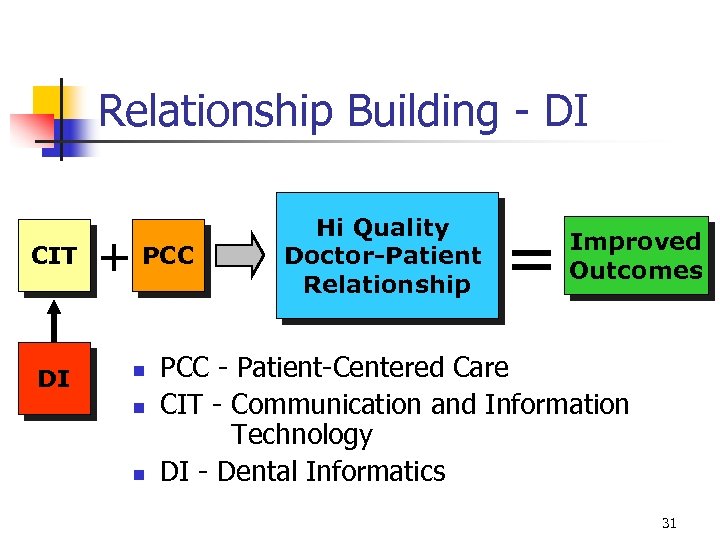 Relationship Building - DI CIT DI + PCC n n n Hi Quality Doctor-Patient Relationship = Improved Outcomes PCC - Patient-Centered Care CIT - Communication and Information Technology DI - Dental Informatics 31
Relationship Building - DI CIT DI + PCC n n n Hi Quality Doctor-Patient Relationship = Improved Outcomes PCC - Patient-Centered Care CIT - Communication and Information Technology DI - Dental Informatics 31
 Role of Informatics Research n Define research questions and methods that will inform the process of making CIT more effective at building quality patient-dentist relationships 32
Role of Informatics Research n Define research questions and methods that will inform the process of making CIT more effective at building quality patient-dentist relationships 32
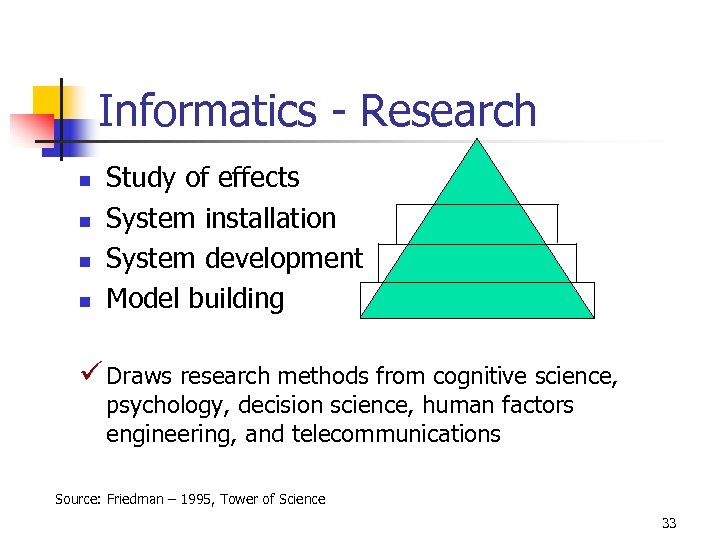 Informatics - Research n n Study of effects System installation System development Model building ü Draws research methods from cognitive science, psychology, decision science, human factors engineering, and telecommunications Source: Friedman – 1995, Tower of Science 33
Informatics - Research n n Study of effects System installation System development Model building ü Draws research methods from cognitive science, psychology, decision science, human factors engineering, and telecommunications Source: Friedman – 1995, Tower of Science 33
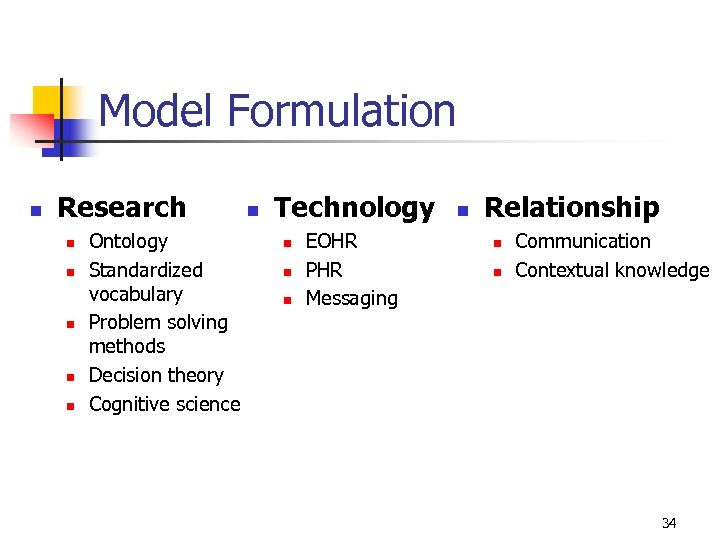 Model Formulation n Research n n n Ontology Standardized vocabulary Problem solving methods Decision theory Cognitive science n Technology n n n EOHR PHR Messaging n Relationship n n Communication Contextual knowledge 34
Model Formulation n Research n n n Ontology Standardized vocabulary Problem solving methods Decision theory Cognitive science n Technology n n n EOHR PHR Messaging n Relationship n n Communication Contextual knowledge 34
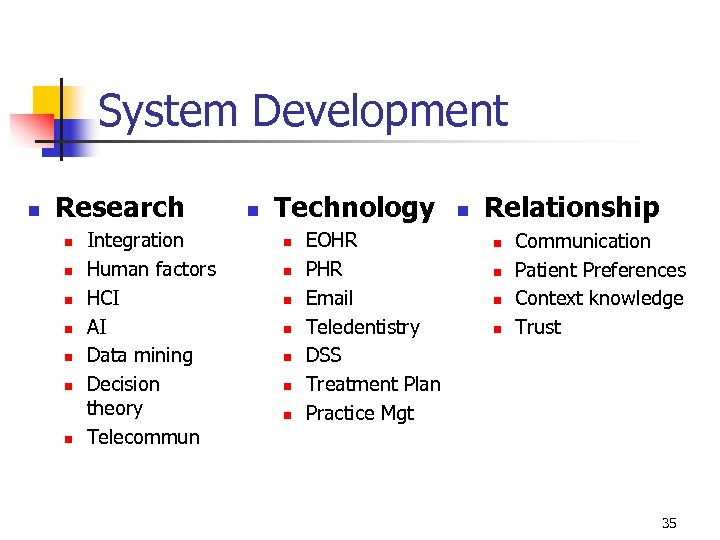 System Development n Research n n n n Integration Human factors HCI AI Data mining Decision theory Telecommun n Technology n n n n EOHR PHR Email Teledentistry DSS Treatment Plan Practice Mgt n Relationship n n Communication Patient Preferences Context knowledge Trust 35
System Development n Research n n n n Integration Human factors HCI AI Data mining Decision theory Telecommun n Technology n n n n EOHR PHR Email Teledentistry DSS Treatment Plan Practice Mgt n Relationship n n Communication Patient Preferences Context knowledge Trust 35
 System Installation n Research n n Integration UI Organizational theory Cognitive psychology n Technology n n n n n Website Email Scheduling EOHR POHR Email Teledentistry DSS Practice Mgt n Relationship n n Communication Patient Preferences Context knowledge Trust 36
System Installation n Research n n Integration UI Organizational theory Cognitive psychology n Technology n n n n n Website Email Scheduling EOHR POHR Email Teledentistry DSS Practice Mgt n Relationship n n Communication Patient Preferences Context knowledge Trust 36
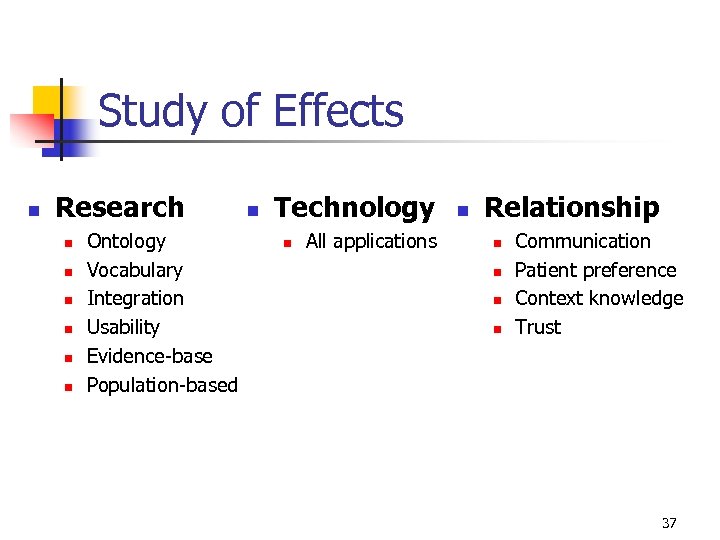 Study of Effects n Research n n n Ontology Vocabulary Integration Usability Evidence-base Population-based n Technology n All applications n Relationship n n Communication Patient preference Context knowledge Trust 37
Study of Effects n Research n n n Ontology Vocabulary Integration Usability Evidence-base Population-based n Technology n All applications n Relationship n n Communication Patient preference Context knowledge Trust 37
 Next Steps n n Conduct Informatics research on dental CIT vis-a-vis the doctor-patient relationship Build relationship with CIT developers and vendors to influence software design based on research findings Educate and engage clinicians in relationship skills More? ? 38
Next Steps n n Conduct Informatics research on dental CIT vis-a-vis the doctor-patient relationship Build relationship with CIT developers and vendors to influence software design based on research findings Educate and engage clinicians in relationship skills More? ? 38


