8f4e4f5dbb3e59af2f429b6b0d30e900.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 The Roaring 20’s An era of prosperity, power, and conflict
The Roaring 20’s An era of prosperity, power, and conflict
 Roaring 20 s reflection Why do you think the 1920 s is called the roaring 20 s? n During the notes make a T chart (2 column chart) n – 1 column for the positives of the decade – 1 column for the negatives of the decade
Roaring 20 s reflection Why do you think the 1920 s is called the roaring 20 s? n During the notes make a T chart (2 column chart) n – 1 column for the positives of the decade – 1 column for the negatives of the decade
 WWI is over- now what? n Women and minorities filled jobs but pushed out when soldiers returned home – They will fight for equality WWI was brutal, soldiers want to enjoy life and forget the horrors of the war n The U. S. had money after WWI which allowed for investment and economic growth n Roaring 20 s n
WWI is over- now what? n Women and minorities filled jobs but pushed out when soldiers returned home – They will fight for equality WWI was brutal, soldiers want to enjoy life and forget the horrors of the war n The U. S. had money after WWI which allowed for investment and economic growth n Roaring 20 s n
 Roaring 20 s n n 1920's collectively known as the "Roaring 20's", or the "Jazz Age" in sum, a period of great change in American Society modern America is born at this time
Roaring 20 s n n 1920's collectively known as the "Roaring 20's", or the "Jazz Age" in sum, a period of great change in American Society modern America is born at this time
 Age of Prosperity n Economic expansion Mass Production Assembly Line Age of the Automobile n Ailing Agriculture… n n n
Age of Prosperity n Economic expansion Mass Production Assembly Line Age of the Automobile n Ailing Agriculture… n n n
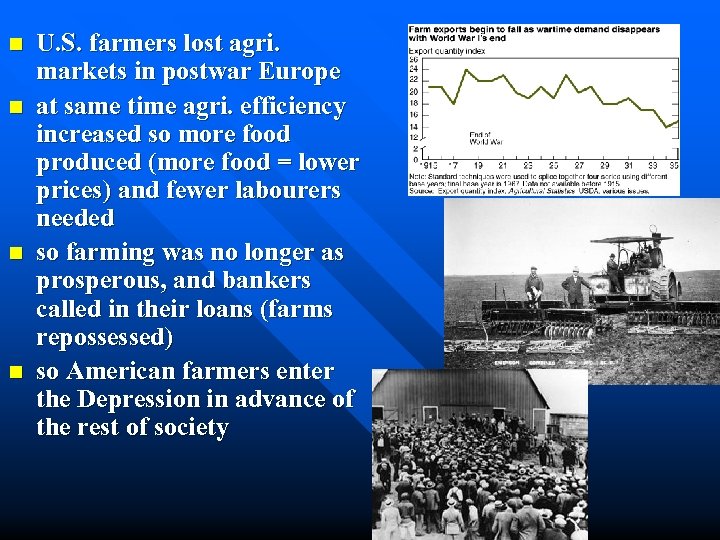 n n U. S. farmers lost agri. markets in postwar Europe at same time agri. efficiency increased so more food produced (more food = lower prices) and fewer labourers needed so farming was no longer as prosperous, and bankers called in their loans (farms repossessed) so American farmers enter the Depression in advance of the rest of society
n n U. S. farmers lost agri. markets in postwar Europe at same time agri. efficiency increased so more food produced (more food = lower prices) and fewer labourers needed so farming was no longer as prosperous, and bankers called in their loans (farms repossessed) so American farmers enter the Depression in advance of the rest of society
 Black Americans in this period continued to live in poverty n sharecropping kept them in mild form of slavery n 1915 – bugs wiped out the cotton crop n white landowners went bankrupt & forced blacks off their land n
Black Americans in this period continued to live in poverty n sharecropping kept them in mild form of slavery n 1915 – bugs wiped out the cotton crop n white landowners went bankrupt & forced blacks off their land n
 President Coolidge “The business of America is business. ” n Fordney- Mc. Cumber Tariff n Smoot-Hawley Tariff – Buy American goods n No help for farmers
President Coolidge “The business of America is business. ” n Fordney- Mc. Cumber Tariff n Smoot-Hawley Tariff – Buy American goods n No help for farmers
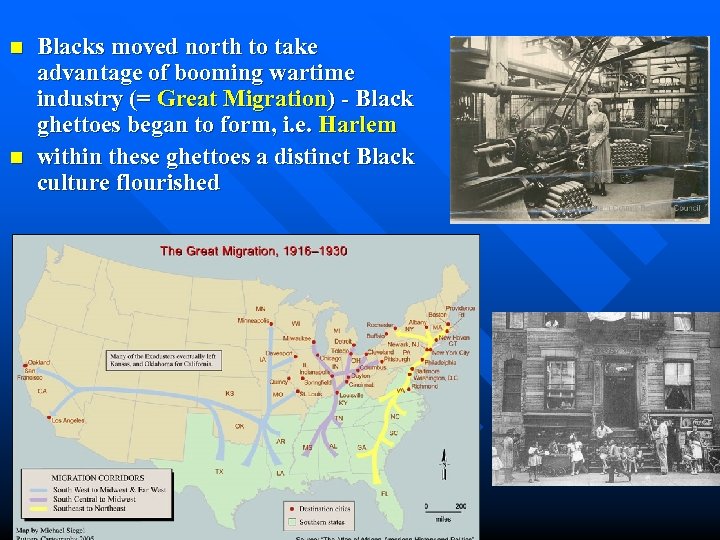 n n Blacks moved north to take advantage of booming wartime industry (= Great Migration) - Black ghettoes began to form, i. e. Harlem within these ghettoes a distinct Black culture flourished
n n Blacks moved north to take advantage of booming wartime industry (= Great Migration) - Black ghettoes began to form, i. e. Harlem within these ghettoes a distinct Black culture flourished
 Culture of the Roaring 20’s Radio Pole Sitting Crazy trends of the 1920 s Modern Times Silent Movies Movie Stars
Culture of the Roaring 20’s Radio Pole Sitting Crazy trends of the 1920 s Modern Times Silent Movies Movie Stars
 Celebrities Babe Ruth &Ty Cobb Charles Lindbergh The Spirit of St. Louis Jack Dempsey
Celebrities Babe Ruth &Ty Cobb Charles Lindbergh The Spirit of St. Louis Jack Dempsey
 The 20’s is The Jazz Age The Flappers make up cigarettes short skirts Writers Musicians F. Scott Fitzgerald Flappers and Dances. Louis Armstrong Ernest Hemingway Duke Ellington
The 20’s is The Jazz Age The Flappers make up cigarettes short skirts Writers Musicians F. Scott Fitzgerald Flappers and Dances. Louis Armstrong Ernest Hemingway Duke Ellington
 Harlem Renaissance n A literary, artistic, and intellectual movement which sparked a new black identity in the U. S.
Harlem Renaissance n A literary, artistic, and intellectual movement which sparked a new black identity in the U. S.
 n n n 1920's also brought about great changes for women. . . 1920 - 19 th Amendment gave them the federal vote More women began to work outside the home and more women went to college and clamoured to join the professions women didn't want to sacrifice wartime gains amounted to a social revolt characterized by the FLAPPER/ "new woman" – (bobbed hair, short dresses, smoked in public. . . )
n n n 1920's also brought about great changes for women. . . 1920 - 19 th Amendment gave them the federal vote More women began to work outside the home and more women went to college and clamoured to join the professions women didn't want to sacrifice wartime gains amounted to a social revolt characterized by the FLAPPER/ "new woman" – (bobbed hair, short dresses, smoked in public. . . )
 Women Before and After n Victorian Woman Jazz Age Woman 15
Women Before and After n Victorian Woman Jazz Age Woman 15
 A Society in Conflict n n Anti-immigrant Racism grows – KKK
A Society in Conflict n n Anti-immigrant Racism grows – KKK
 The Ku Klux Klan Great increase In power Anti-black Anti-immigrant Anti-Semitic Anti-Catholic Anti-women’s suffrage Anti-bootleggers
The Ku Klux Klan Great increase In power Anti-black Anti-immigrant Anti-Semitic Anti-Catholic Anti-women’s suffrage Anti-bootleggers
 Prohibition Volstead Act 18 th Amendment Gangsters Al Capone
Prohibition Volstead Act 18 th Amendment Gangsters Al Capone
 n n n PROHIBITION - on manuf. and sale of alcohol adopted in 1919 - 18 th AMENDMENT in WWI, temperance became a patriotic mvmt. drunkenness caused low productivity & inefficiency, and alcohol needed to treat the wounded a difficult law to enforce. . . organized crime, speakeasies, bootleggers were on the rise Prohibition finally ended in 1933 w/ the 21 st Amendment forced organized crime to pursue other interests…
n n n PROHIBITION - on manuf. and sale of alcohol adopted in 1919 - 18 th AMENDMENT in WWI, temperance became a patriotic mvmt. drunkenness caused low productivity & inefficiency, and alcohol needed to treat the wounded a difficult law to enforce. . . organized crime, speakeasies, bootleggers were on the rise Prohibition finally ended in 1933 w/ the 21 st Amendment forced organized crime to pursue other interests…
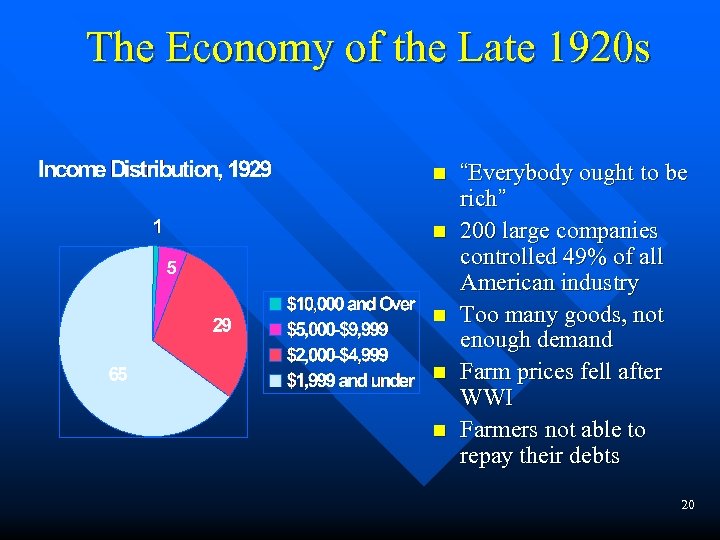 The Economy of the Late 1920 s n n n “Everybody ought to be rich” 200 large companies controlled 49% of all American industry Too many goods, not enough demand Farm prices fell after WWI Farmers not able to repay their debts 20
The Economy of the Late 1920 s n n n “Everybody ought to be rich” 200 large companies controlled 49% of all American industry Too many goods, not enough demand Farm prices fell after WWI Farmers not able to repay their debts 20
 The Stock Market Crash. Oct. 29, 1929 Stocks hit all-time highs in September of 1929 n In October, stocks began to fall n Ex. General Electric stocks bought for $400 sold for $283 n Black Tuesday— 16. 4 million shares sold, compared to average of 4 million n This collapse of the stock market is known as the Great Crash n 21
The Stock Market Crash. Oct. 29, 1929 Stocks hit all-time highs in September of 1929 n In October, stocks began to fall n Ex. General Electric stocks bought for $400 sold for $283 n Black Tuesday— 16. 4 million shares sold, compared to average of 4 million n This collapse of the stock market is known as the Great Crash n 21
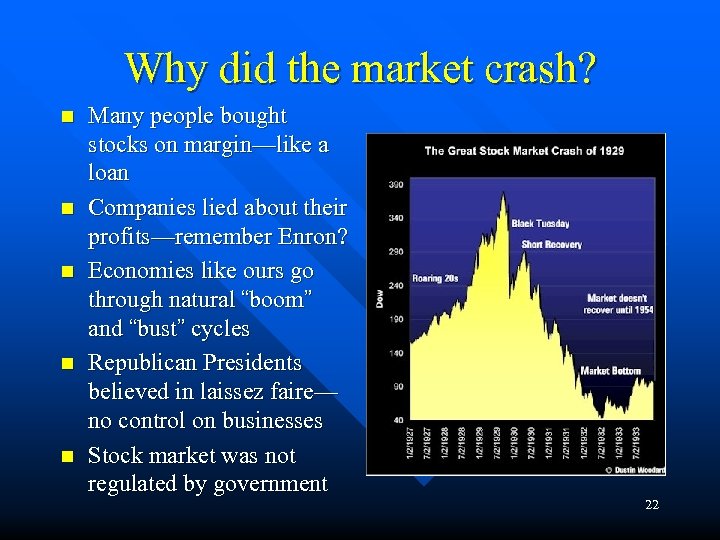 Why did the market crash? n n n Many people bought stocks on margin—like a loan Companies lied about their profits—remember Enron? Economies like ours go through natural “boom” and “bust” cycles Republican Presidents believed in laissez faire— no control on businesses Stock market was not regulated by government 22
Why did the market crash? n n n Many people bought stocks on margin—like a loan Companies lied about their profits—remember Enron? Economies like ours go through natural “boom” and “bust” cycles Republican Presidents believed in laissez faire— no control on businesses Stock market was not regulated by government 22
 The Stock Market Crash From Riches to Ruin n n n Many wealthy families lost everything Some even committed suicide Millions of people who never owned a single stock lost their jobs, farms and homes The crash triggered a much wider, long term crisis known as the Great Depression The Depression lasted from 1929 to 1941 when America entered WWII The Depression had a ripple effect that hurt the economies of other countries 23
The Stock Market Crash From Riches to Ruin n n n Many wealthy families lost everything Some even committed suicide Millions of people who never owned a single stock lost their jobs, farms and homes The crash triggered a much wider, long term crisis known as the Great Depression The Depression lasted from 1929 to 1941 when America entered WWII The Depression had a ripple effect that hurt the economies of other countries 23
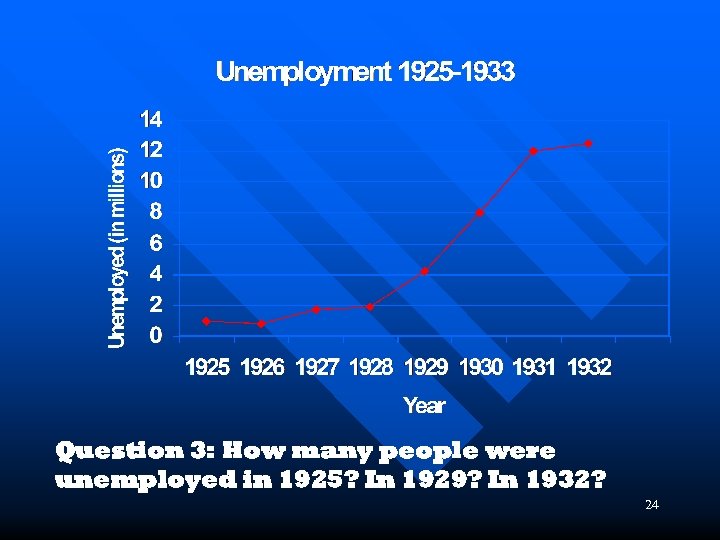 Question 3: How many people were unemployed in 1925? In 1929? In 1932? 24
Question 3: How many people were unemployed in 1925? In 1929? In 1932? 24
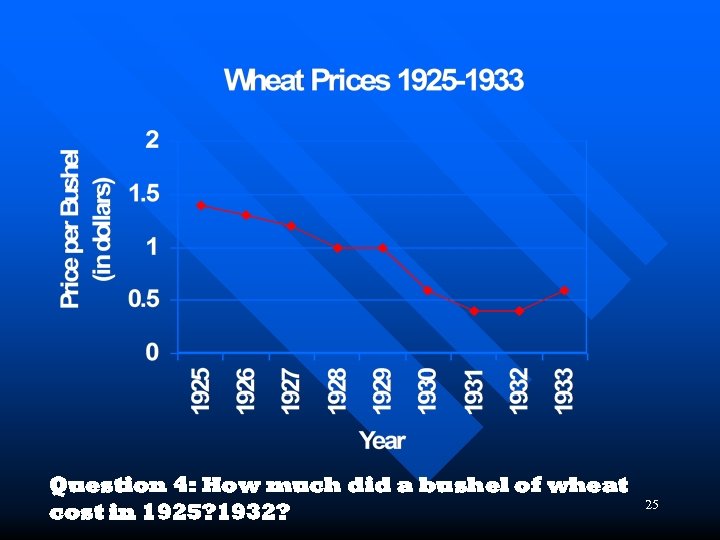 Question 4: How much did a bushel of wheat cost in 1925? 1932? 25
Question 4: How much did a bushel of wheat cost in 1925? 1932? 25
 End of Unit Reflection n The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly – What was good for the U. S. from this unit – What was bad for the U. S. from this unit – What was ugly for the U. S. from this unit
End of Unit Reflection n The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly – What was good for the U. S. from this unit – What was bad for the U. S. from this unit – What was ugly for the U. S. from this unit


