b143a25768f26abd4d333e60ece55787.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35


The Rising Storm • Losing the bubble? • Sailors say the ship’s navigator has lost a clear sense of where he is and where he is bound

Uneasy Balances • Gag Rule (in Congress) • More states entering union: AK (Slave), MI (Free), TX (slave) • Congressional debates erupt in violence

Mexican Territory and the issue • Polk: Extend Missouri Com. To Pacific O • Douglas: Popular Sovereignty – • Wilmot Proviso: – – Wilmot’s answer to newly purchased territory from Mexico – Threats: secession, cut of commercial relations with North, refusal to pay debts owed to North – Never passed

1848 Election Lewis Cass Dem. - split Pop. Sov. Zachary Taylor Whig -Unknown political views Martin Van Buren Free Soil Party’s beliefs?

Free Soil Party Free Soil! Free Speech! Free Labor! Free Men! § “Barnburners” – discontented northern Democrats. § Anti-slave members of the Liberty and Whig Parties. § Opposition to the extension of slavery in the new territories! WHY?
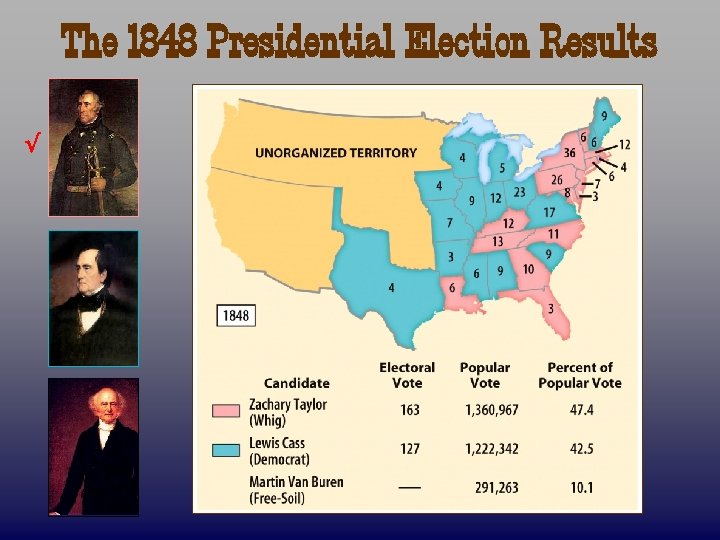
The 1848 Presidential Election Results √

ß Problems of Sectional Balance California statehood. in 1850 ß Southern “fire-eaters” threatening secession. ß Underground RR & fugitive slave issues: § Personal liberty laws § Prigg v. Pennsylvania (1842)
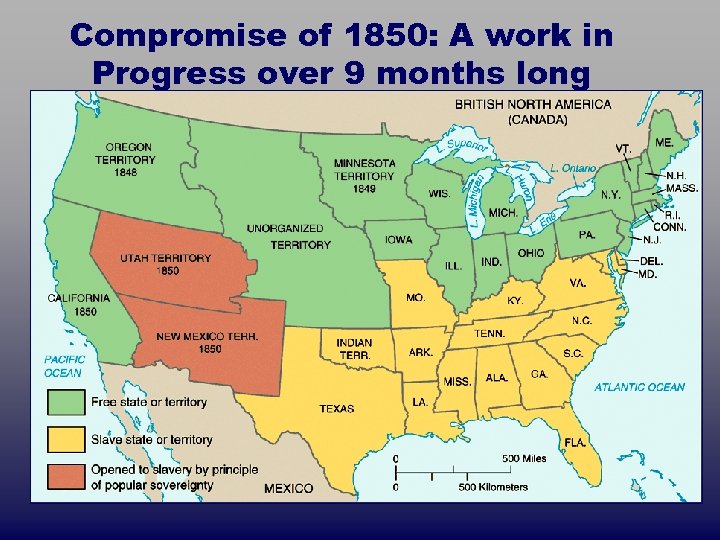
Compromise of 1850: A work in Progress over 9 months long

Elements of the Compromise 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bonus: If Pres. Taylor was against this, how did it ultimately pass?

Fugitive Slave Act • “Personal Liberty Laws” as a means of combatting this Act • How did enforcement of this Act change the nation?

Harriet Beecher Stowe (18111896) Uncle Tom’s Cabin, 1852 § Sold 300, 000 copies in the first year. § 2 million in a decade! § “So this is the lady that started the civil war!” Abraham Lincoln

1852 Presidential Election Franklin Pierce Gen. Winfield Scott Democrat (NH) -Compr. 1850 supporter Whig John Parker Hale -Free Soil
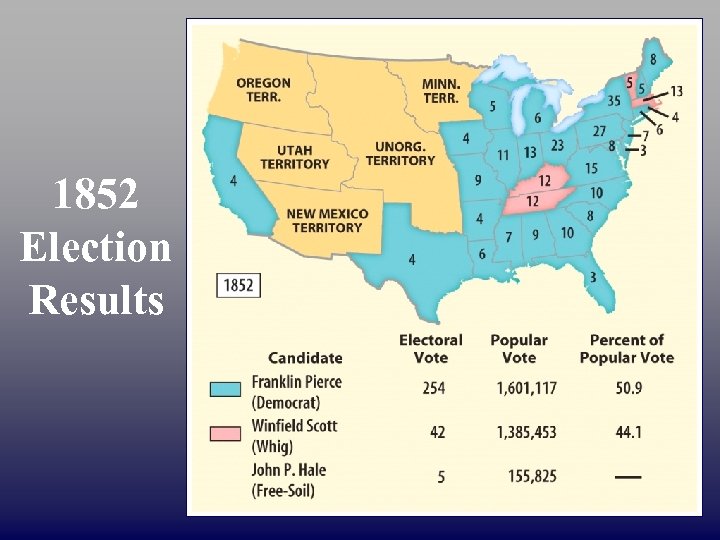
1852 Election Results
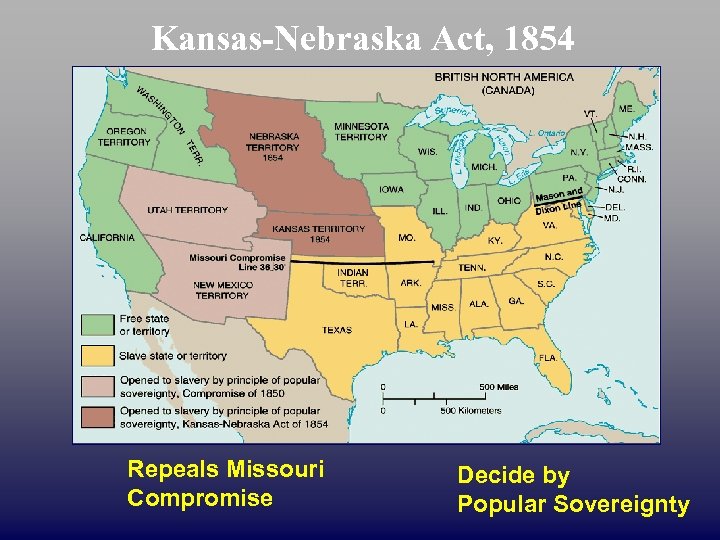
Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854 Repeals Missouri Compromise Decide by Popular Sovereignty
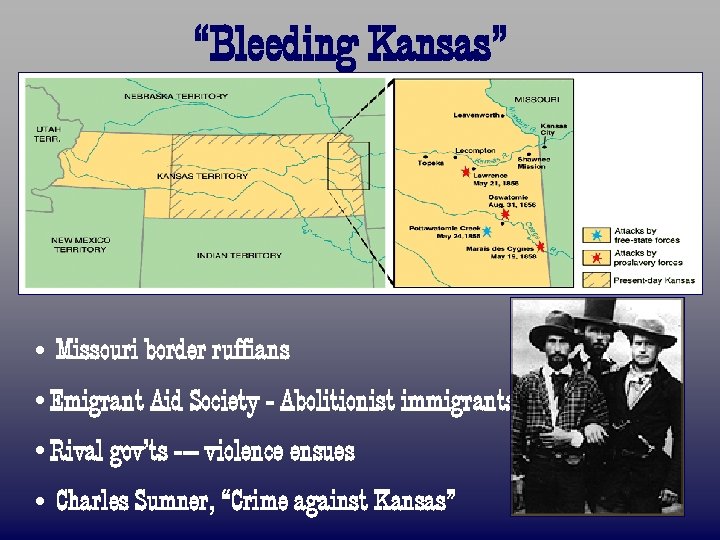
“Bleeding Kansas” • Missouri border ruffians • Emigrant Aid Society - Abolitionist immigrants • Rival gov’ts --- violence ensues • Charles Sumner, “Crime against Kansas”

John Brown: Madman, Hero or Martyr? Mural in the Kansas Capitol building by John Steuart Curry (20 c)

“The Crime Against Kansas” Sen. Charles Sumner (R-MA) Congr. Preston Brooks (D-SC)

Birth of the Republican Party, 1854 K-N Act Bleeding KS ß Opposed to expansion of slavery, not abolition ß Northern Anti-slavery Whigs and Democrats ß Free-Soilers, Know-Nothing’s ß Other miscellaneous opponents of the Kansas-Nebraska Act.

1856 Presidential Election James Buchanan (PA) Democrat John C. Frémont Millard Fillmore Republican Whig
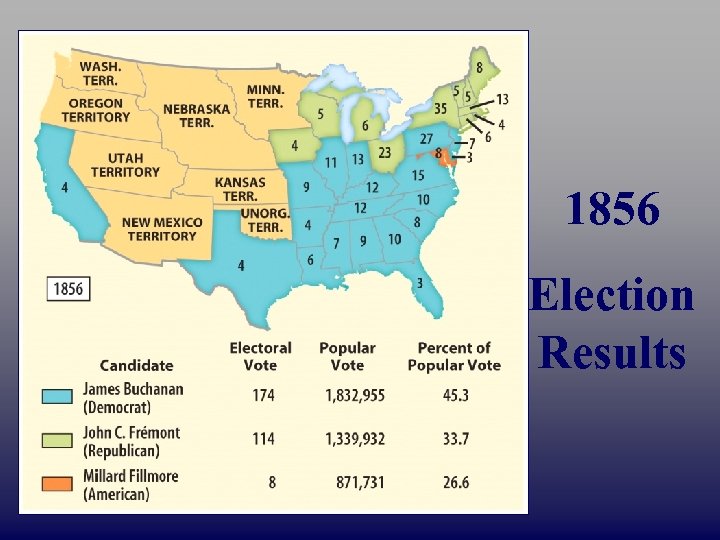
1856 Election Results

Dred Scott v. Sanford, 1857

The Lincoln-Douglas (Illinois Senate) Debates, 1858 A House divided against itself, cannot stand.

Stephen Douglas & the Freeport Doctrine Popular Sovereignty ?

John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry, 1859

√ Abraham Lincoln Republican John Bell Constitutional Union 1860 Presidential Election Stephen A. Douglas Northern Democrat Stephen John C. Breckinridge Southern Democrat

Republican Party Platform in 1860 ß Non-extension of slavery [for the Free-Soilers. ß Protective tariff [for the No. Industrialists]. ß No abridgment of rights for immigrants [a disappointment for the “Know-Nothings”]. ß Government aid to build a Pacific RR [for the Northwest]. ß Internal improvements [for the West] at federal expense. ß Free homesteads for the public domain [for farmers].

1860 Election: 3 “Outs” & 1 ”Run!”

1860 Election: A Nation Coming Apart? !
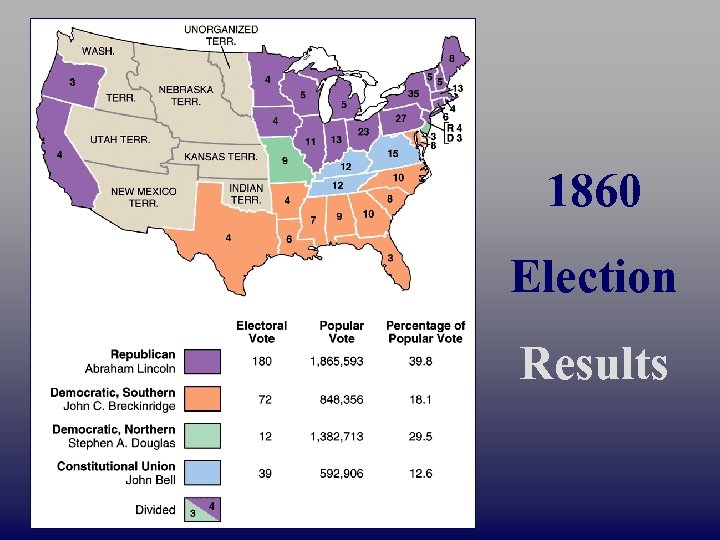
1860 Election Results

Crittenden Compromise: A Last Ditch Appeal to Sanity Senator John J. Crittenden (Know-Nothing. KY)
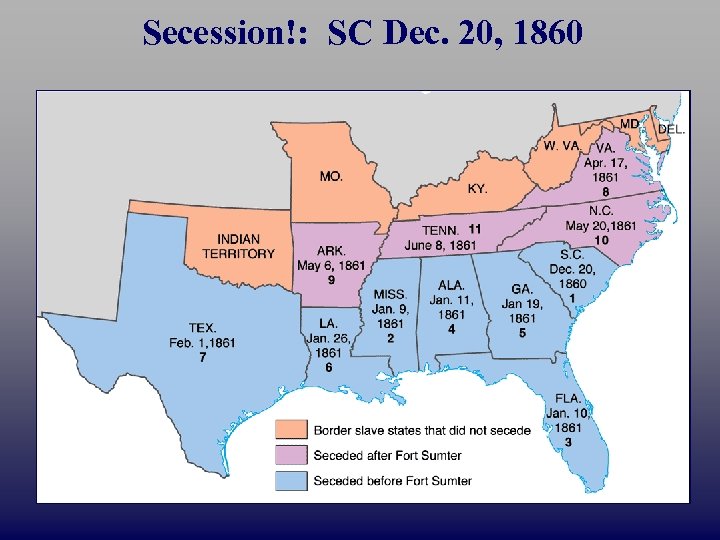
Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860

Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 A strategic Location

Events of that day • Union Major Robert Anderson needed reinforcements • He refused to abandon Fort Sumter • P. G. T. Beauregard and troops opened fire • After 34 hours, Anderson formally surrendered
b143a25768f26abd4d333e60ece55787.ppt