438c75c1da112f91a6292200345f6f4c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 The rise & spread of islam 622 c. e. to 1450 c. e. Calligraphy says, “Salam. ”
The rise & spread of islam 622 c. e. to 1450 c. e. Calligraphy says, “Salam. ”
 Mohammed • Merchant from Mecca • Last prophet • Fled to Medina in 622 starting the Islamic calendar (hijra) Mohammed is traditionally pictured without a face in order to avoid the issue of people worshiping him and not God.
Mohammed • Merchant from Mecca • Last prophet • Fled to Medina in 622 starting the Islamic calendar (hijra) Mohammed is traditionally pictured without a face in order to avoid the issue of people worshiping him and not God.
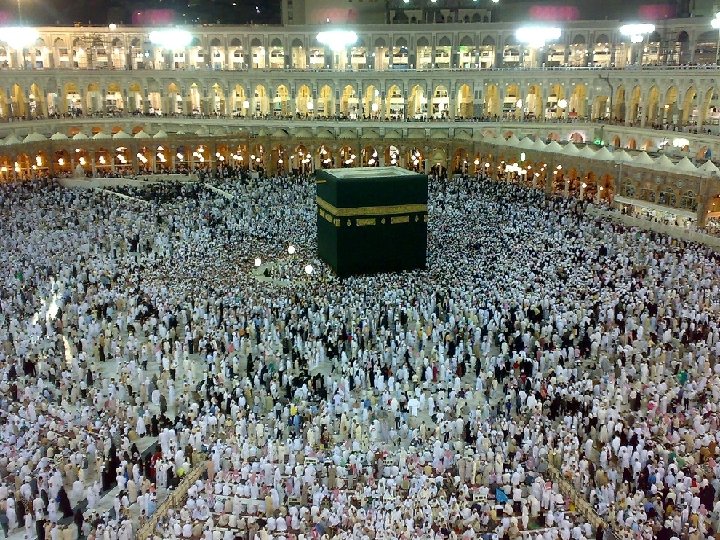
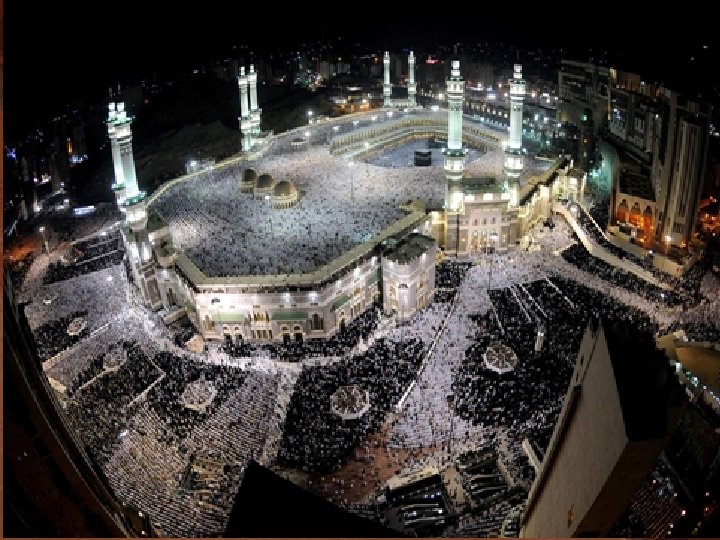
 Basics of Islam • 5 Pillars of Faith – Do you know them? • • Monotheistic Koran (Qu ŕan) Kabba Mosques - minarets Egypt Kabba in Mecca
Basics of Islam • 5 Pillars of Faith – Do you know them? • • Monotheistic Koran (Qu ŕan) Kabba Mosques - minarets Egypt Kabba in Mecca


 Concepts in Islam • Hadith – the deeds and speeches of Mohammed • Imam – religious leader chosen by age or status • Mullah – local religious leader
Concepts in Islam • Hadith – the deeds and speeches of Mohammed • Imam – religious leader chosen by age or status • Mullah – local religious leader
 • Islam unifies the Empire • Islam is a religion and a way of life – Islamic Law • Islam splits between Sunni and Shiite – Religious leaders can be anyone – Religious leaders must be descendants of Mohammed Religion
• Islam unifies the Empire • Islam is a religion and a way of life – Islamic Law • Islam splits between Sunni and Shiite – Religious leaders can be anyone – Religious leaders must be descendants of Mohammed Religion
 Sunni and Shiite
Sunni and Shiite
 Men and Women in Islam Men Women • Make all major decisions • Women lose rights as Islam spread east • Can have four wives (travelling merchants) • Often secluded in the home • Divorce is easy • Fewer education opportunities • Often have restrictive dress code • Divorce nearly impossible • Spiritually not secularly equal. – Seclusion – Veiling (purdah)
Men and Women in Islam Men Women • Make all major decisions • Women lose rights as Islam spread east • Can have four wives (travelling merchants) • Often secluded in the home • Divorce is easy • Fewer education opportunities • Often have restrictive dress code • Divorce nearly impossible • Spiritually not secularly equal. – Seclusion – Veiling (purdah)
 Jihad in Islam • The Word “Jihad” means to struggle or strive • Levels of Jihad – Struggle to improve yourself – Struggle against evil in society – Struggle on the battlefield • Valid reasons for Jihad on the battlefield – Self Defense • To remove human tyranny, oppression, and persecution
Jihad in Islam • The Word “Jihad” means to struggle or strive • Levels of Jihad – Struggle to improve yourself – Struggle against evil in society – Struggle on the battlefield • Valid reasons for Jihad on the battlefield – Self Defense • To remove human tyranny, oppression, and persecution
 Spread of Islam video Setting • By 750 C. E. the Islamic Empire stretched from India to Spain • Controlled transportation routes • By 1450, the empire was smaller but still influential Cordoba, Spain Move to spread Delhi, India
Spread of Islam video Setting • By 750 C. E. the Islamic Empire stretched from India to Spain • Controlled transportation routes • By 1450, the empire was smaller but still influential Cordoba, Spain Move to spread Delhi, India
 Politics • Caliphs - religious and political leaders • Sultans - political leaders • Strong armies • Extensive bureaucracies • Crusades weaken caliphates and empire fragments • Saladin leads Mamluks (slave army made up of Asia Minor people) against crusaders • Mamluks then seize power in Egypt after the death of Saladin.
Politics • Caliphs - religious and political leaders • Sultans - political leaders • Strong armies • Extensive bureaucracies • Crusades weaken caliphates and empire fragments • Saladin leads Mamluks (slave army made up of Asia Minor people) against crusaders • Mamluks then seize power in Egypt after the death of Saladin.
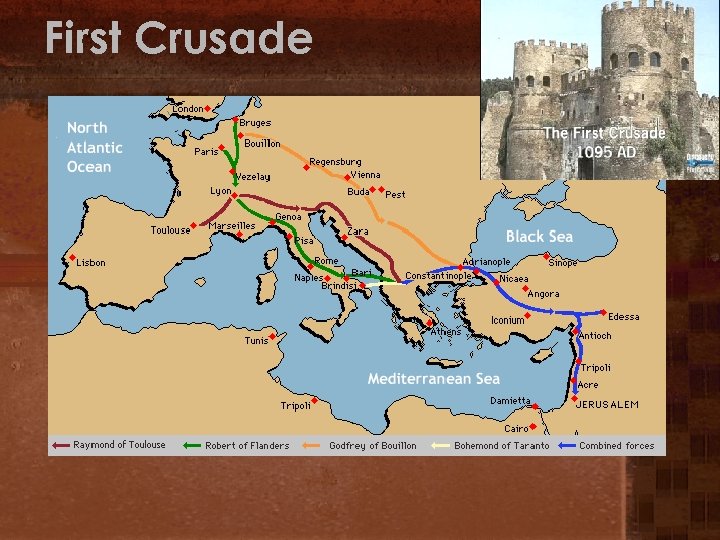 First Crusade
First Crusade
 Saladin and Crusaders
Saladin and Crusaders
 Innovations • Medicine – Prescription drugs – surgery • Mathematics – Algebra • Literature – Poetry – calligraphy • Art • Architecture – arabesque • Libraries
Innovations • Medicine – Prescription drugs – surgery • Mathematics – Algebra • Literature – Poetry – calligraphy • Art • Architecture – arabesque • Libraries
 Algebra
Algebra
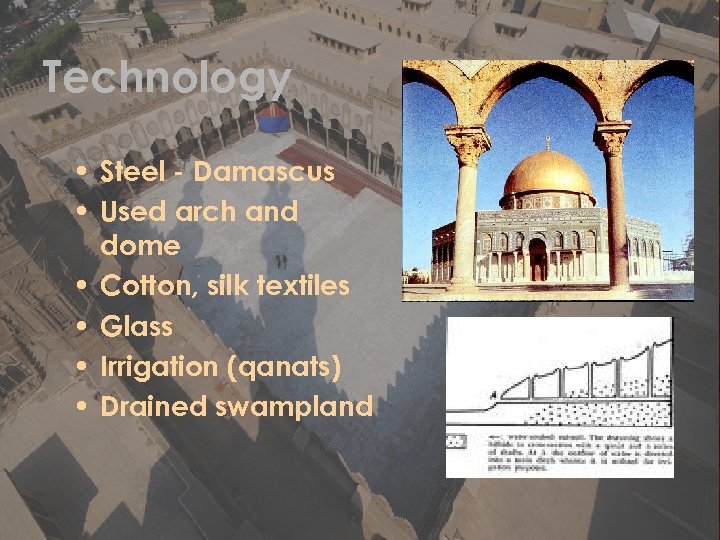 Technology • Steel - Damascus • Used arch and dome • Cotton, silk textiles • Glass • Irrigation (qanats) • Drained swampland
Technology • Steel - Damascus • Used arch and dome • Cotton, silk textiles • Glass • Irrigation (qanats) • Drained swampland
 Economy • Agriculture was important in areas with good climates • Merchants VERY important • Trade Networks – Silk Road – Indian Ocean Routes – Saharan camel routes • Systems to transfer money – Banking and branch banking – Checks – Credit – Currency Exchange • Economic controls – Worker and craft guilds (quality regulation)
Economy • Agriculture was important in areas with good climates • Merchants VERY important • Trade Networks – Silk Road – Indian Ocean Routes – Saharan camel routes • Systems to transfer money – Banking and branch banking – Checks – Credit – Currency Exchange • Economic controls – Worker and craft guilds (quality regulation)
 Who am I?
Who am I?
 Society • Social Mobility – Based on education and achievements • Tax on non-Muslims – “People of the Book” not persecuted • Slavery – Only non-Muslims could be enslaved – Slaves could buy freedom – Children of slaves who converted were freed • Merchants were honored (Mohammed
Society • Social Mobility – Based on education and achievements • Tax on non-Muslims – “People of the Book” not persecuted • Slavery – Only non-Muslims could be enslaved – Slaves could buy freedom – Children of slaves who converted were freed • Merchants were honored (Mohammed
 Why did Islam Spread? • Motivation for Bedouins – Gave them an excuse to raid their enemies – United them and broke clan/family ties – Accepted polygamy
Why did Islam Spread? • Motivation for Bedouins – Gave them an excuse to raid their enemies – United them and broke clan/family ties – Accepted polygamy
 Why Did Islam Spread? • Military Success – Bravery was a culture trait of the Bedouins of Arabia – Organization and mobility (horse) – Superior military tactics – Persian and Byzantine Empires were weak – Conquered soldiers were converted and incorporated into Muslim army – A place in Paradise if
Why Did Islam Spread? • Military Success – Bravery was a culture trait of the Bedouins of Arabia – Organization and mobility (horse) – Superior military tactics – Persian and Byzantine Empires were weak – Conquered soldiers were converted and incorporated into Muslim army – A place in Paradise if
 Why Did Islam Spread? • Trade Networks – Islamic lands linked Africa, Asia and Europe • Merchants traveled the “Silk Roads” and Indian Ocean sea routes – Cultural centers like Cairo, Mecca, Alexandria and Baghdad provided centers of learning to which thousands traveled each year – Sufis were merchant missionaries. They spread Islam peacefully, were mystics.
Why Did Islam Spread? • Trade Networks – Islamic lands linked Africa, Asia and Europe • Merchants traveled the “Silk Roads” and Indian Ocean sea routes – Cultural centers like Cairo, Mecca, Alexandria and Baghdad provided centers of learning to which thousands traveled each year – Sufis were merchant missionaries. They spread Islam peacefully, were mystics.
 Why Did Islam Spread? • Treatment of Conquered Peoples – Toleration • Often led to acceptance • Muslims welcomed in areas where people had been persecuted – Conquered Christians and Jews often converted because of similarities
Why Did Islam Spread? • Treatment of Conquered Peoples – Toleration • Often led to acceptance • Muslims welcomed in areas where people had been persecuted – Conquered Christians and Jews often converted because of similarities
 Islamic Empires: Umayyad • Capital - Damascus • A small Arab/Muslim aristocracy ruled over a people who were not Arab and largely not “Muslim” - Mawali. (They converted but were not recognized) • “People of the Book” were generally tolerated. • Expansion across North Africa to Iberian Peninsula as well as into Central Asia. • Declined: – – “more political than pious” (luxury and soft living) Revolts by dissenting Muslims Non-Arab resentment Army revolt led under the black banner of the Abbasid Party defeated the Umayyad and slaughtered most of the family at a reconciliation
Islamic Empires: Umayyad • Capital - Damascus • A small Arab/Muslim aristocracy ruled over a people who were not Arab and largely not “Muslim” - Mawali. (They converted but were not recognized) • “People of the Book” were generally tolerated. • Expansion across North Africa to Iberian Peninsula as well as into Central Asia. • Declined: – – “more political than pious” (luxury and soft living) Revolts by dissenting Muslims Non-Arab resentment Army revolt led under the black banner of the Abbasid Party defeated the Umayyad and slaughtered most of the family at a reconciliation
 Umayyad Architecture
Umayyad Architecture
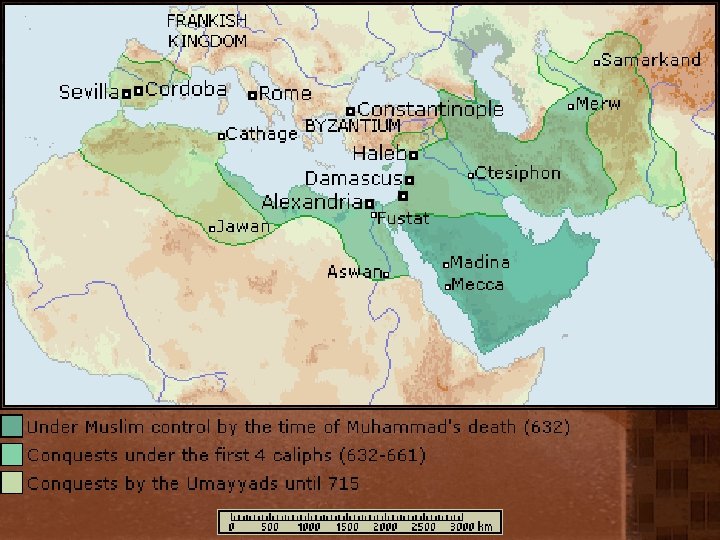
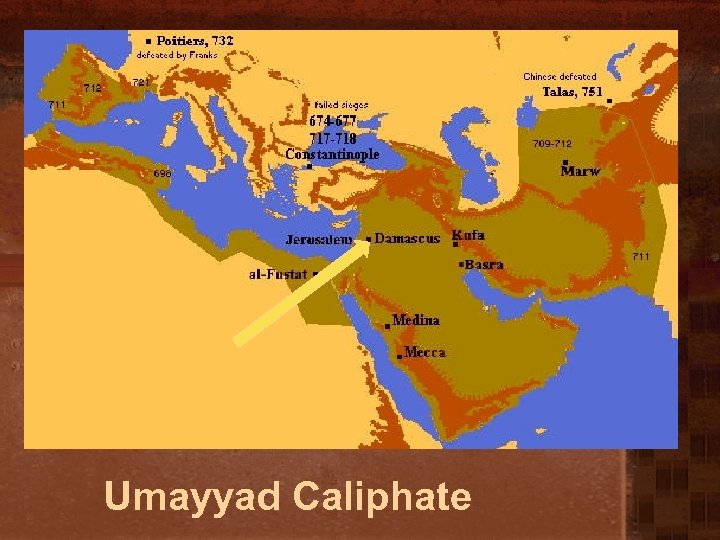 Umayyad Caliphate
Umayyad Caliphate
 Islamic Empires: Abbasid • Ends Arab domination, Mawali conversion in mass from Berbers and Moors to Turks. • Capital at Baghdad – Persians dominate the expanding bureaucracy – Harun al Rashid ruled from 786 -809 • Wealth and splendor equal to Byzantium • Exchanged gifts and ambassadors with Charlemagne • Lavish court, palace was 1/3 of the city of Baghdad
Islamic Empires: Abbasid • Ends Arab domination, Mawali conversion in mass from Berbers and Moors to Turks. • Capital at Baghdad – Persians dominate the expanding bureaucracy – Harun al Rashid ruled from 786 -809 • Wealth and splendor equal to Byzantium • Exchanged gifts and ambassadors with Charlemagne • Lavish court, palace was 1/3 of the city of Baghdad
 • Muslim Empires: Wealth and Prosperity – Revival of trade routes Abbasid across Sahara, – – – Mediterranean Sea and Silk Road Merchants were Christians, Muslims and Jews Bazaars held spices, minerals, dyes, gems, olives, wine, wheat, silk, porcelain, horses, etc Joint Stock companies Banking with credit and checks Workshops made glass, jewelry, tapestries, Damascus Steel, Cordoba
• Muslim Empires: Wealth and Prosperity – Revival of trade routes Abbasid across Sahara, – – – Mediterranean Sea and Silk Road Merchants were Christians, Muslims and Jews Bazaars held spices, minerals, dyes, gems, olives, wine, wheat, silk, porcelain, horses, etc Joint Stock companies Banking with credit and checks Workshops made glass, jewelry, tapestries, Damascus Steel, Cordoba
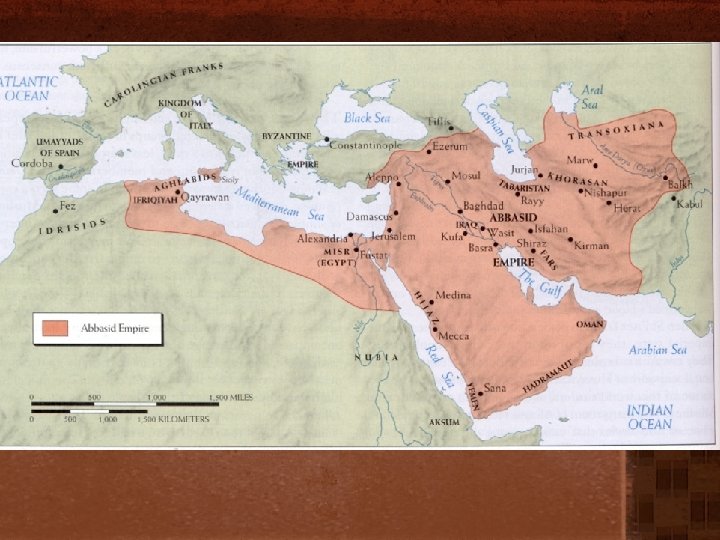
 Collapse of the Abbasid • Causes: – Social Stratification • Arabs played and increasingly smaller role in the society as Turks and other non-Arabs migrated in – Sectarian Divisions • Different Islamic groups vied for power – Regional Separation • Empire was too large for weakened military to control
Collapse of the Abbasid • Causes: – Social Stratification • Arabs played and increasingly smaller role in the society as Turks and other non-Arabs migrated in – Sectarian Divisions • Different Islamic groups vied for power – Regional Separation • Empire was too large for weakened military to control
 Division in the Muslim World after collapse of Abbasid • Umayyads still in Spain (750 -1100) • Fatimids in Egypt (900+) • Mamluks in Egypt (1250 -1517) • Seljuk Turks in Isfahan (Persia) (1050+) • Mongols in Baghdad (1258+) • Ottoman Turks in Asia Minor (1300 -1919) • Safavids in Isfahan (1499+)
Division in the Muslim World after collapse of Abbasid • Umayyads still in Spain (750 -1100) • Fatimids in Egypt (900+) • Mamluks in Egypt (1250 -1517) • Seljuk Turks in Isfahan (Persia) (1050+) • Mongols in Baghdad (1258+) • Ottoman Turks in Asia Minor (1300 -1919) • Safavids in Isfahan (1499+)
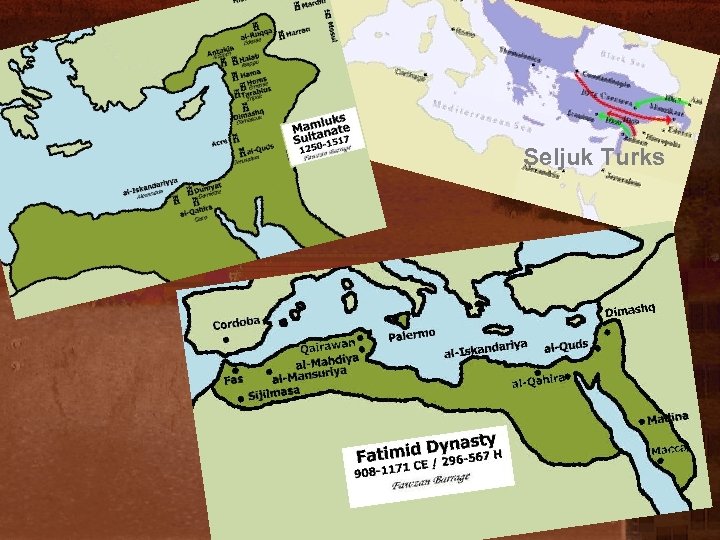 Seljuk Turks
Seljuk Turks
 And now…Kenya
And now…Kenya
 China
China
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Iran
Iran
 Desecrated WW I graves in France
Desecrated WW I graves in France
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Indonesia
Indonesia


