05829c9f4616b2030cae21b227c06f50.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 The rise of the information & service economy, 2 The information and service economy September 12 2007 Bob Glushko and Anno Saxenian
The rise of the information & service economy, 2 The information and service economy September 12 2007 Bob Glushko and Anno Saxenian
 Outline 1. 2. 3. Value chains, not firms Explaining rise of service economy The view from marketing: a new view of exchange as service, not goods
Outline 1. 2. 3. Value chains, not firms Explaining rise of service economy The view from marketing: a new view of exchange as service, not goods
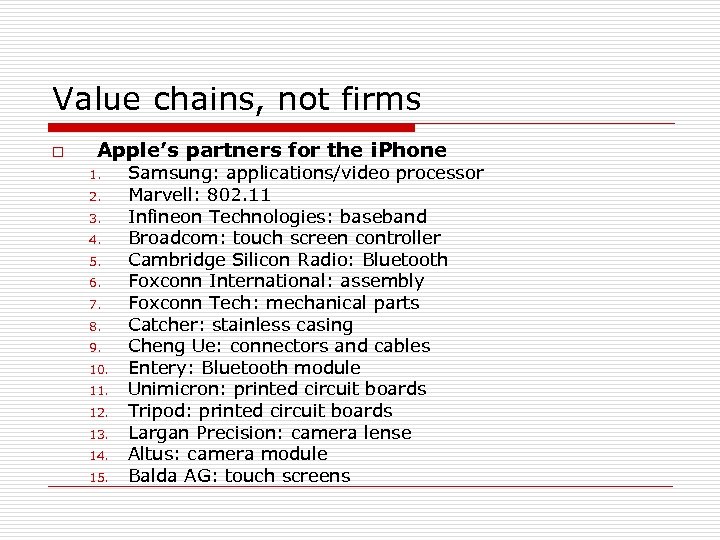 Value chains, not firms o Apple’s partners for the i. Phone 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Samsung: applications/video processor Marvell: 802. 11 Infineon Technologies: baseband Broadcom: touch screen controller Cambridge Silicon Radio: Bluetooth Foxconn International: assembly Foxconn Tech: mechanical parts Catcher: stainless casing Cheng Ue: connectors and cables Entery: Bluetooth module Unimicron: printed circuit boards Tripod: printed circuit boards Largan Precision: camera lense Altus: camera module Balda AG: touch screens
Value chains, not firms o Apple’s partners for the i. Phone 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Samsung: applications/video processor Marvell: 802. 11 Infineon Technologies: baseband Broadcom: touch screen controller Cambridge Silicon Radio: Bluetooth Foxconn International: assembly Foxconn Tech: mechanical parts Catcher: stainless casing Cheng Ue: connectors and cables Entery: Bluetooth module Unimicron: printed circuit boards Tripod: printed circuit boards Largan Precision: camera lense Altus: camera module Balda AG: touch screens
 Decomposing service economy o o Share of value-added, US economy, 2000 n Finance, insurance, real estate (FIRE) & business services: 30% n Community, social & personal: 20% n Wholesale & retail trade, Hotels & restaurants: 15% n Transport, storage & communications: 6% Fastest growing: FIRE & business services
Decomposing service economy o o Share of value-added, US economy, 2000 n Finance, insurance, real estate (FIRE) & business services: 30% n Community, social & personal: 20% n Wholesale & retail trade, Hotels & restaurants: 15% n Transport, storage & communications: 6% Fastest growing: FIRE & business services
 Explaining growth of service sector 1. 2. 3. Differential productivity growth (Baumol) o Lower productivity gains in services (e. g. education, performing arts, social work, etc. ) o Assumes service sector relatively stagnant, manufacturing dynamic Changing patterns of final demand n High income elasticity of demand for luxury services (leisure activities, travel, etc. ) n As incomes rise, consume more services Role of intermediate demand beyond simple two-sector models
Explaining growth of service sector 1. 2. 3. Differential productivity growth (Baumol) o Lower productivity gains in services (e. g. education, performing arts, social work, etc. ) o Assumes service sector relatively stagnant, manufacturing dynamic Changing patterns of final demand n High income elasticity of demand for luxury services (leisure activities, travel, etc. ) n As incomes rise, consume more services Role of intermediate demand beyond simple two-sector models
 Explaining growth of service sector, II o Services as intermediate input providers n Growing outsourcing of services (e. g. customer service, accounting, R&D, etc. ) o o n Over 50% of transportation, communication services are intermediate, 20% final demand Financial and business services produce btwn 4060% of output for final demand Underscores importance of interaction between manufacturing and services o o Growing service content of manufactured goods Increase of high quality business service producers (logistics, R&D, innovation)
Explaining growth of service sector, II o Services as intermediate input providers n Growing outsourcing of services (e. g. customer service, accounting, R&D, etc. ) o o n Over 50% of transportation, communication services are intermediate, 20% final demand Financial and business services produce btwn 4060% of output for final demand Underscores importance of interaction between manufacturing and services o o Growing service content of manufactured goods Increase of high quality business service producers (logistics, R&D, innovation)
 Creative destruction o o o Transformation of global economy is radically undermining conditions for large integrated corporation Vertical fragmentation of production, specialization, and rise of network forms of organization Enhances contribution & productivity of service component of manufacturing
Creative destruction o o o Transformation of global economy is radically undermining conditions for large integrated corporation Vertical fragmentation of production, specialization, and rise of network forms of organization Enhances contribution & productivity of service component of manufacturing
 A new marketing logic o Marketing in the goods economy: financial optimization and the 4 P’s n n o Product Price Placement Promotion Marketing in the service economy n n n An ongoing social and economic process Inherently customer-oriented and relational Goods as distribution/delivery mechanisms for services
A new marketing logic o Marketing in the goods economy: financial optimization and the 4 P’s n n o Product Price Placement Promotion Marketing in the service economy n n n An ongoing social and economic process Inherently customer-oriented and relational Goods as distribution/delivery mechanisms for services
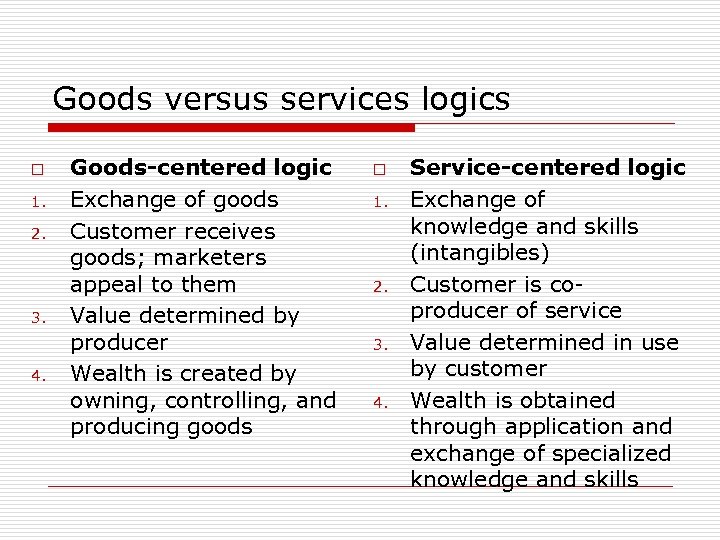 Goods versus services logics o 1. 2. 3. 4. Goods-centered logic Exchange of goods Customer receives goods; marketers appeal to them Value determined by producer Wealth is created by owning, controlling, and producing goods o 1. 2. 3. 4. Service-centered logic Exchange of knowledge and skills (intangibles) Customer is coproducer of service Value determined in use by customer Wealth is obtained through application and exchange of specialized knowledge and skills
Goods versus services logics o 1. 2. 3. 4. Goods-centered logic Exchange of goods Customer receives goods; marketers appeal to them Value determined by producer Wealth is created by owning, controlling, and producing goods o 1. 2. 3. 4. Service-centered logic Exchange of knowledge and skills (intangibles) Customer is coproducer of service Value determined in use by customer Wealth is obtained through application and exchange of specialized knowledge and skills
 Service-dominant model of exchange o o o o Application of specialized knowledge and skills is the fundamental unit of exchange Knowledge is source of competitive advantage Goods are distribution mechanisms for service provision; all economies are service economies Customer is co-producer, co-creator of value Service-centered view is customer-oriented and relational Enterprise can only make value propositions Organizations integrate/combine specialized competences into complex services
Service-dominant model of exchange o o o o Application of specialized knowledge and skills is the fundamental unit of exchange Knowledge is source of competitive advantage Goods are distribution mechanisms for service provision; all economies are service economies Customer is co-producer, co-creator of value Service-centered view is customer-oriented and relational Enterprise can only make value propositions Organizations integrate/combine specialized competences into complex services
 Service-dominant logic (Vargo & Lusch) o o Service, rather than goods, is the focus of economic and social exchange: service is exchanged for service Service: the application of competences for the benefit of another entity Indirect exchange masks fundamental basis of exchange (micro-specialization, intermediaries, etc. ) All economies are service economies; all businesses are service businesses
Service-dominant logic (Vargo & Lusch) o o Service, rather than goods, is the focus of economic and social exchange: service is exchanged for service Service: the application of competences for the benefit of another entity Indirect exchange masks fundamental basis of exchange (micro-specialization, intermediaries, etc. ) All economies are service economies; all businesses are service businesses
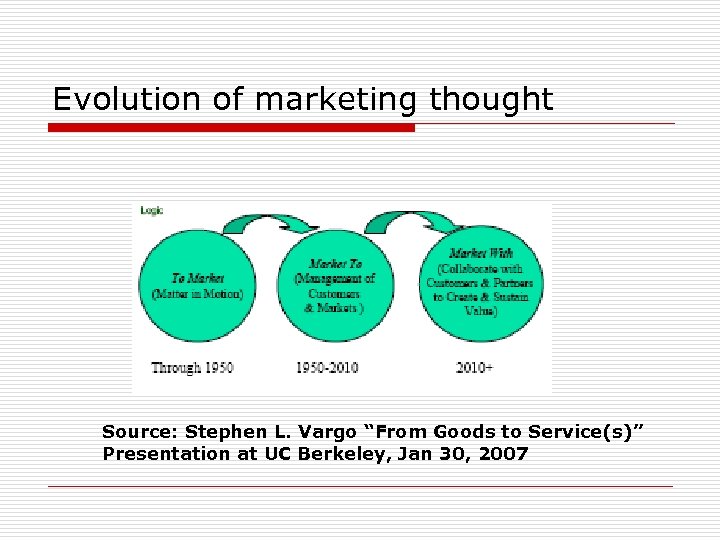 Evolution of marketing thought Source: Stephen L. Vargo “From Goods to Service(s)” Presentation at UC Berkeley, Jan 30, 2007
Evolution of marketing thought Source: Stephen L. Vargo “From Goods to Service(s)” Presentation at UC Berkeley, Jan 30, 2007
 Back to the i. Phone o o Is Apple a service firm? What does Apple do? How does it add value? How does Apple market its products? How does Apple innovate?
Back to the i. Phone o o Is Apple a service firm? What does Apple do? How does it add value? How does Apple market its products? How does Apple innovate?


