eb3c1d42f1a2a8615b721748738db5aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

The RICH detectors of LHCb; Description and Operation Antonis Papanestis On behalf of the LHCb RICH collaboration 1
Outline § The LHCb experiment § The LHCb RICH detectors Ø Ø Description Construction and installation Operation Alignment and Calibration § Conclusions 2
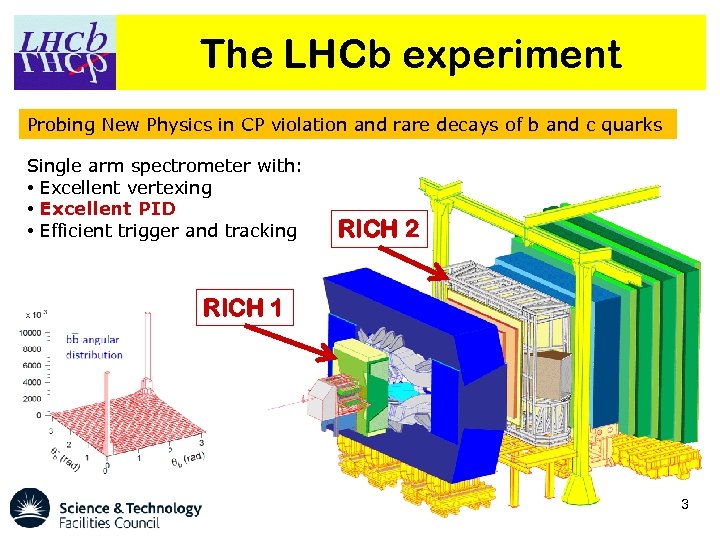
The LHCb experiment Probing New Physics in CP violation and rare decays of b and c quarks Single arm spectrometer with: • Excellent vertexing • Excellent PID • Efficient trigger and tracking RICH 2 RICH 1 3
LHCb event 23 sep 2010 19: 49: 24 Run 79646 Event 143858637 4
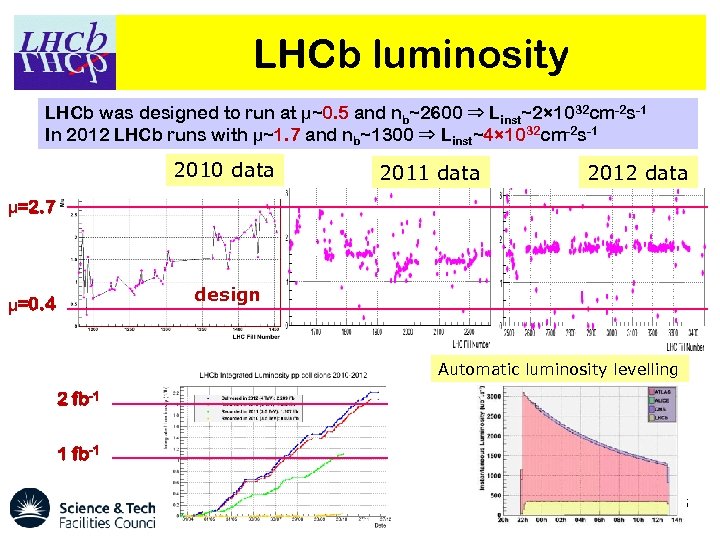
LHCb luminosity LHCb was designed to run at μ~0. 5 and nb~2600 ⇒ Linst~2× 1032 cm-2 s-1 In 2012 LHCb runs with μ~1. 7 and nb~1300 ⇒ Linst~4× 1032 cm-2 s-1 2010 data 2011 data 2012 data μ=2. 7 design μ=0. 4 Automatic luminosity levelling 2 fb-1 1 fb-1 5
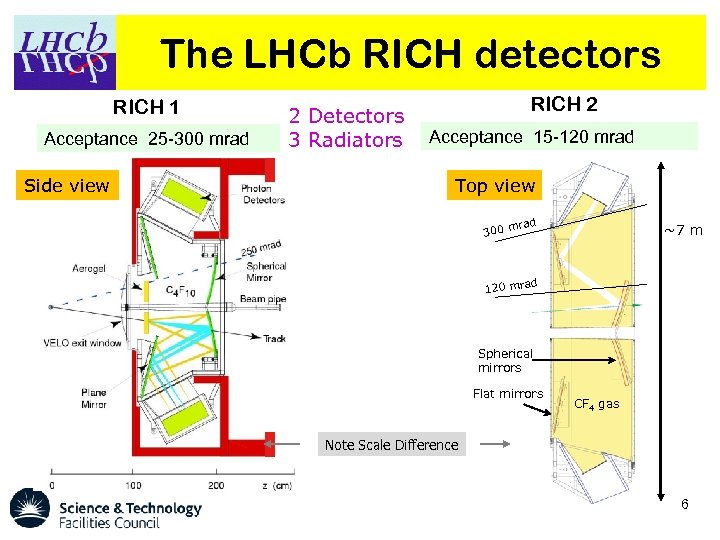
The LHCb RICH detectors RICH 1 Acceptance 25 -300 mrad Side view 2 Detectors 3 Radiators RICH 2 Acceptance 15 -120 mrad Top view 300 mrad ~7 m d 120 mra Spherical mirrors Flat mirrors CF 4 gas Note Scale Difference 6
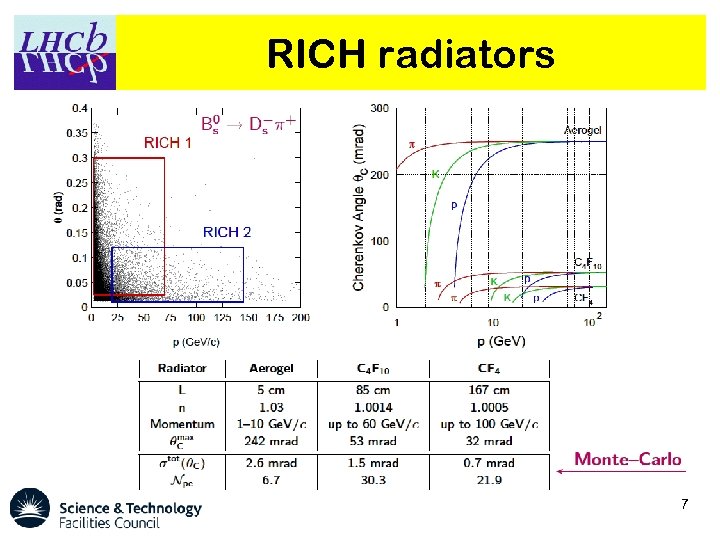
RICH radiators 7
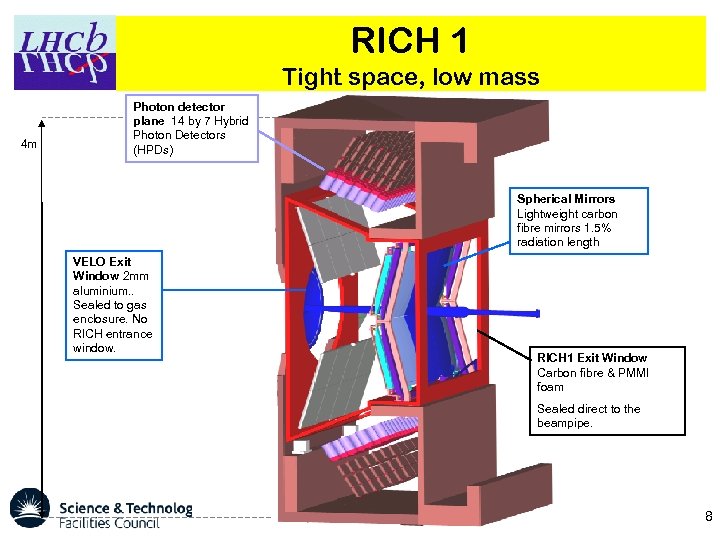
RICH 1 Tight space, low mass 4 m Photon detector plane 14 by 7 Hybrid Photon Detectors (HPDs) Spherical Mirrors Lightweight carbon fibre mirrors 1. 5% radiation length VELO Exit Window 2 mm aluminium. . Sealed to gas enclosure. No RICH entrance window. RICH 1 Exit Window Carbon fibre & PMMI foam Sealed direct to the beampipe. 8

Carbon fibre mirrors and Aerogel is inside a gas tight box flushed with CO 2 to avoid performance degradation from exposure to C 4 F 10 9
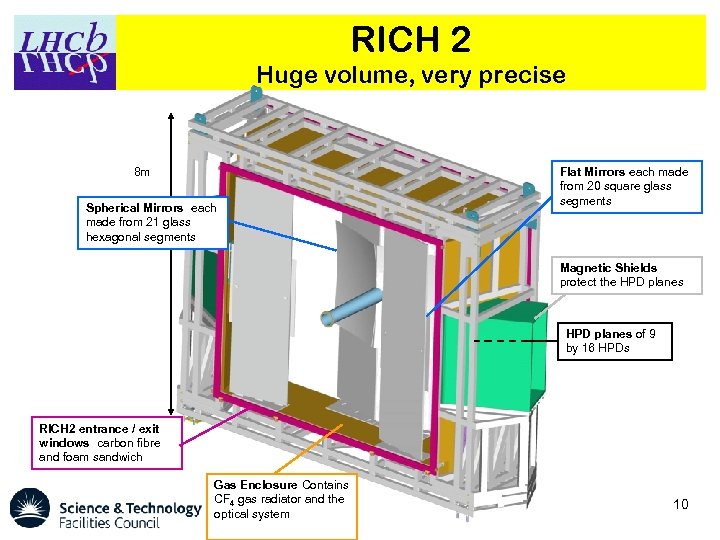
RICH 2 Huge volume, very precise 8 m Spherical Mirrors each made from 21 glass hexagonal segments Flat Mirrors each made from 20 square glass segments Magnetic Shields protect the HPD planes of 9 by 16 HPDs RICH 2 entrance / exit windows carbon fibre and foam sandwich Gas Enclosure Contains CF 4 gas radiator and the optical system 10

Entry and exit windows 11
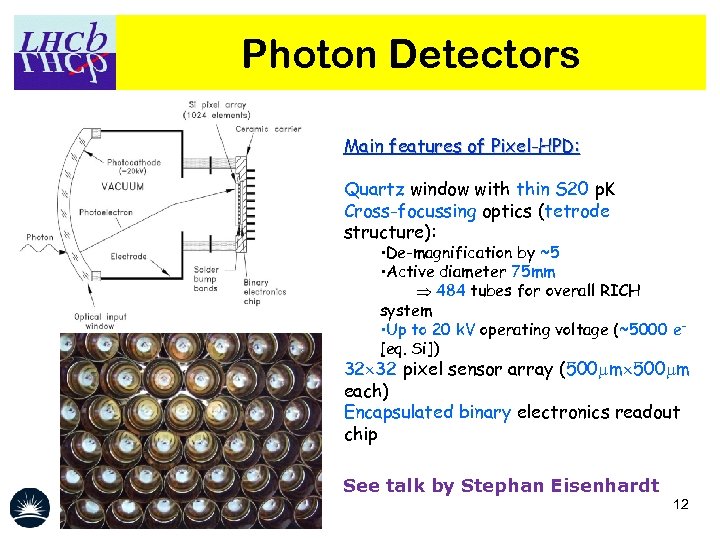
Photon Detectors Main features of Pixel-HPD: Quartz window with thin S 20 p. K Cross-focussing optics (tetrode structure): • De-magnification by ~5 • Active diameter 75 mm 484 tubes for overall RICH system • Up to 20 k. V operating voltage (~5000 e– [eq. Si]) Schematic view 32 32 pixel sensor array (500 mm each) Encapsulated binary electronics readout chip See talk by Stephan Eisenhardt 12
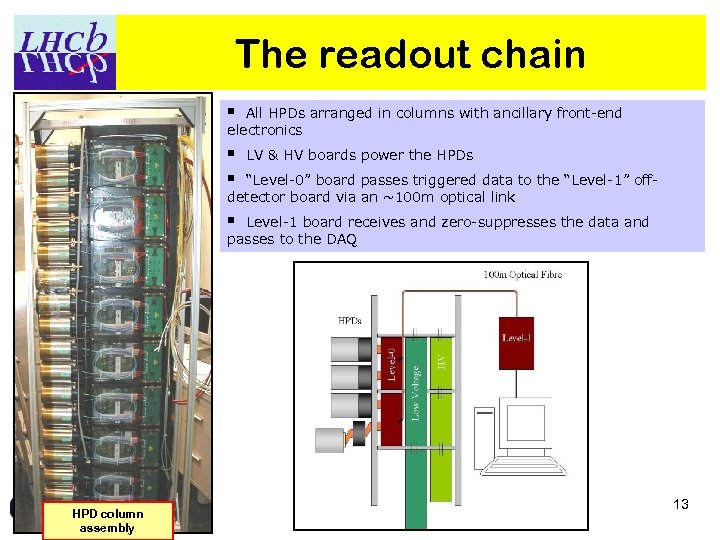
The readout chain § All HPDs arranged in columns with ancillary front-end electronics § § LV & HV boards power the HPDs “Level-0” board passes triggered data to the “Level-1” offdetector board via an ~100 m optical link § Level-1 board receives and zero-suppresses the data and passes to the DAQ HPD column assembly 13
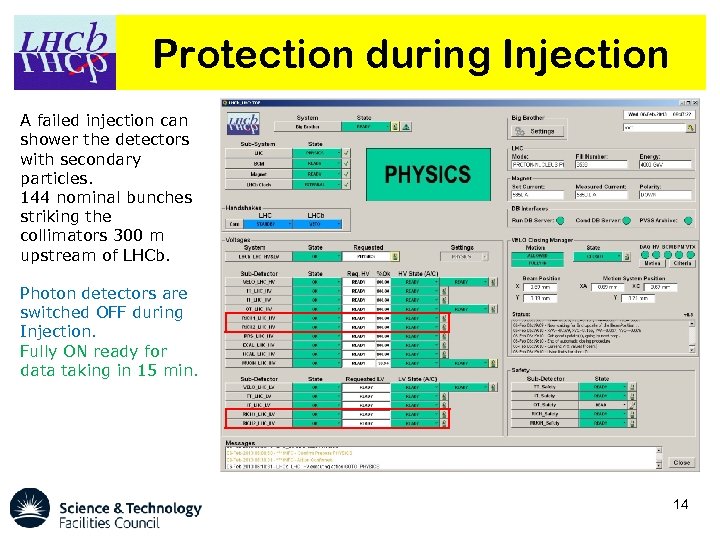
Protection during Injection A failed injection can shower the detectors with secondary particles. 144 nominal bunches striking the collimators 300 m upstream of LHCb. Photon detectors are switched OFF during Injection. Fully ON ready for data taking in 15 min. 14
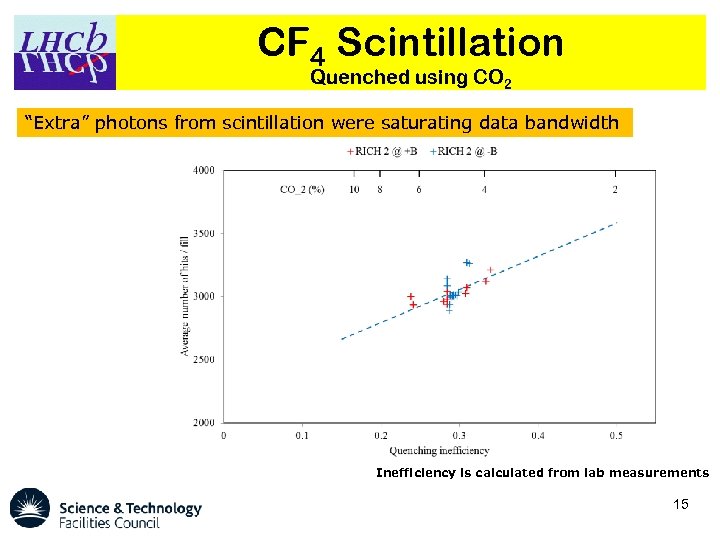
CF 4 Scintillation Quenched using CO 2 “Extra” photons from scintillation were saturating data bandwidth Inefficiency is calculated from lab measurements 15
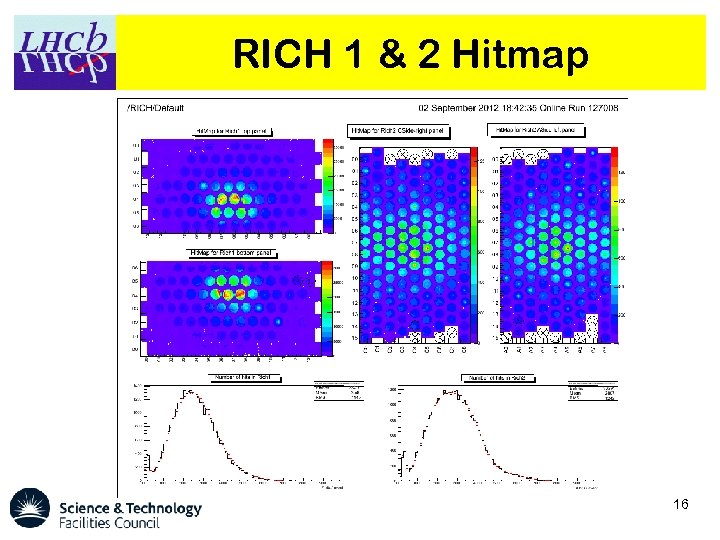
RICH 1 & 2 Hitmap 16
Alignment & Calibration § Alignment: Ø Ø Ø Silicon sensors Magnetic field corrections HPD alignment See talk by Clara Matteuzzi Mirror alignment Detector alignment (in the LHCb coordinate system) § Calibration: Ø Time alignment (should be constant). Ø Refractive index (from Cherenkov angle). 17
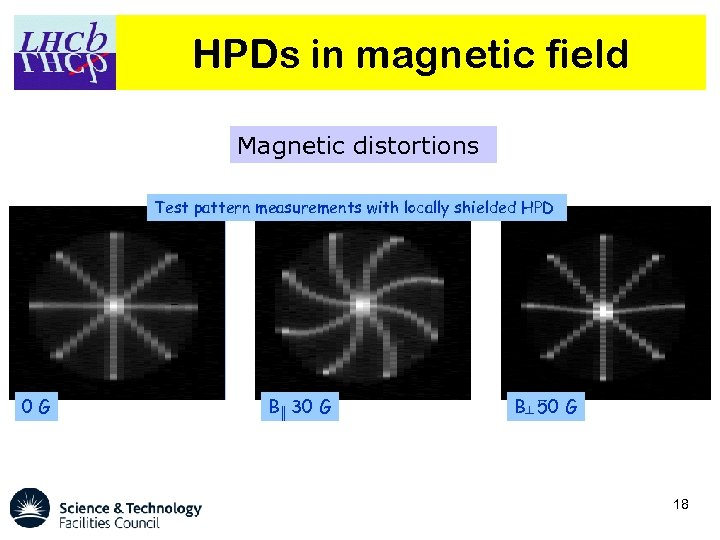
HPDs in magnetic field Magnetic distortions Test pattern measurements with locally shielded HPD 0 G B║ 30 G B┴ 50 G 18
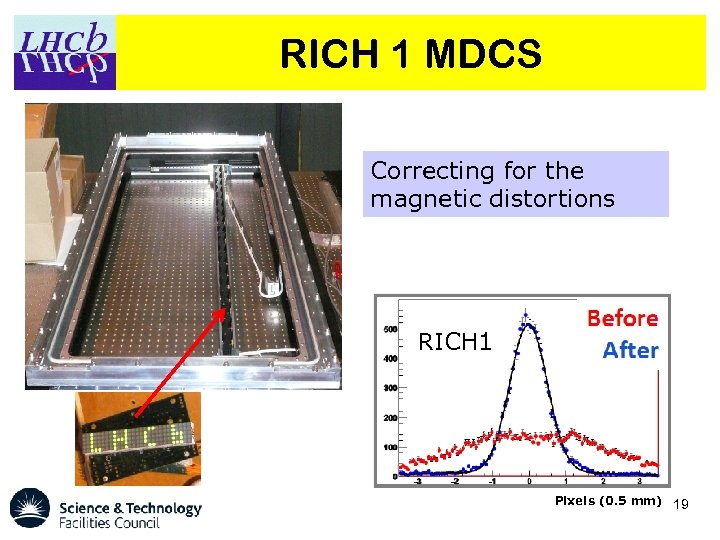
RICH 1 MDCS Correcting for the magnetic distortions RICH 1 Pixels (0. 5 mm) 19
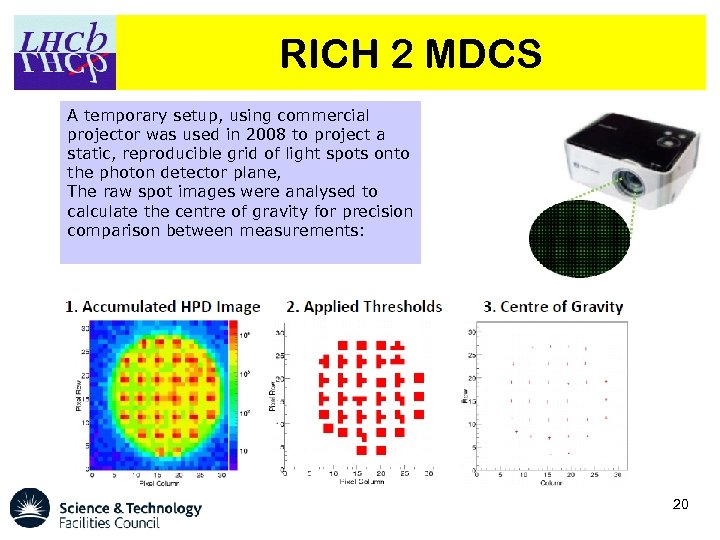
RICH 2 MDCS A temporary setup, using commercial projector was used in 2008 to project a static, reproducible grid of light spots onto the photon detector plane, The raw spot images were analysed to calculate the centre of gravity for precision comparison between measurements: 20
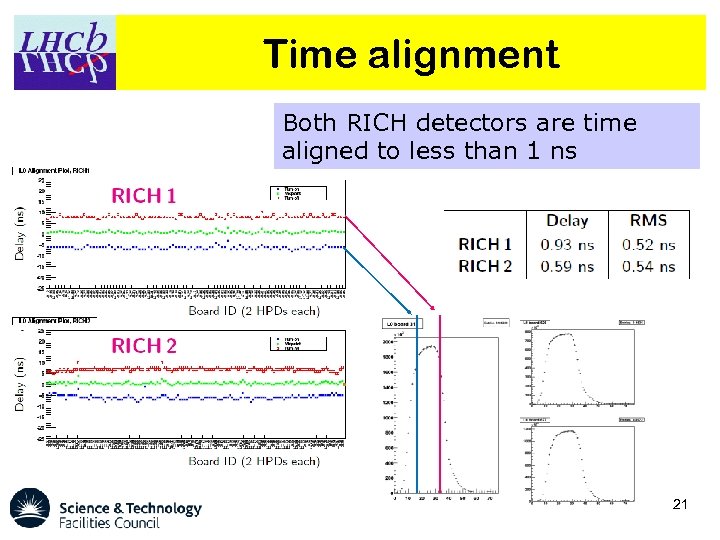
Time alignment Both RICH detectors are time aligned to less than 1 ns 21
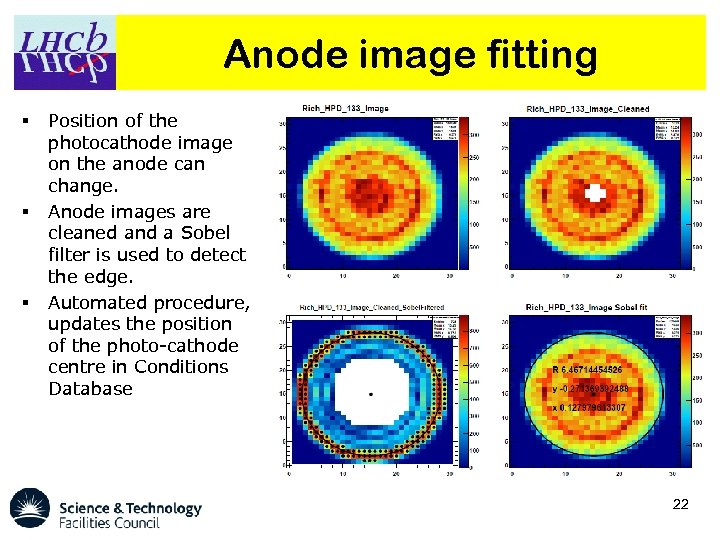
Anode image fitting § § § Position of the photocathode image on the anode can change. Anode images are cleaned and a Sobel filter is used to detect the edge. Automated procedure, updates the position of the photo-cathode centre in Conditions Database 22
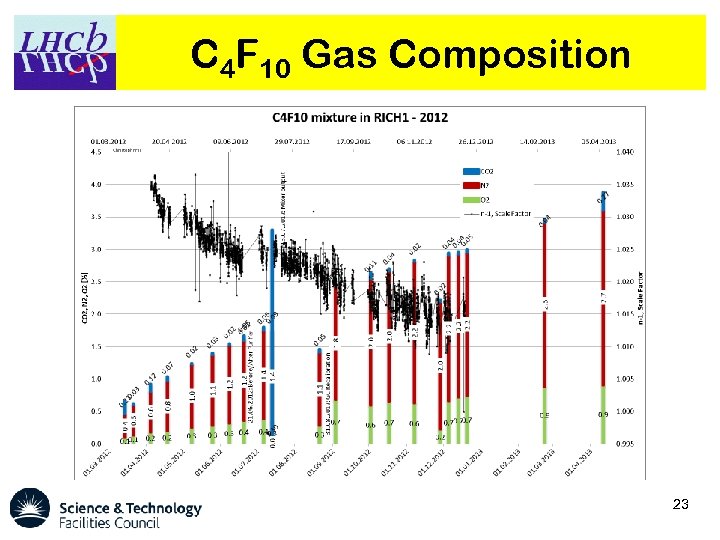
C 4 F 10 Gas Composition 23
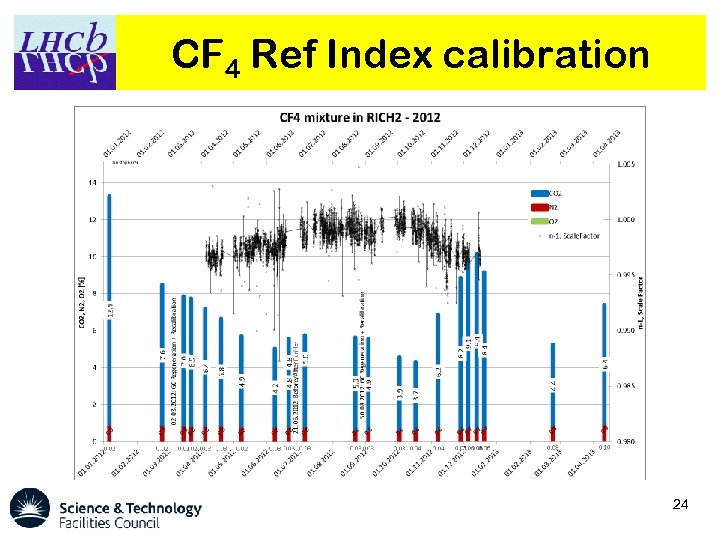
CF 4 Ref Index calibration 24

Conclusions § LHCb recorded 3 fb-1 so far, running at twice the design luminosity, at 90% efficiency, producing a number of world first and world best measurements. § The LHCb RICH detectors are an integral part of LHCb, operating in a challenging high multiplicity environment, working at conditions well above the original specifications. § The outstanding performance of the RICH system is achieved with an excellent and stable optical system and very low noise photon detectors, together with the highly automated alignment and calibration processes. 25
The END 26
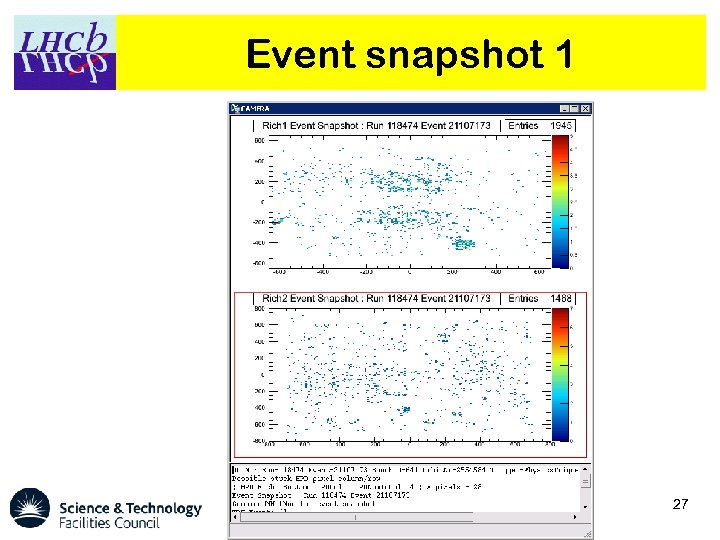
Event snapshot 1 27

Event snapshot 2 28
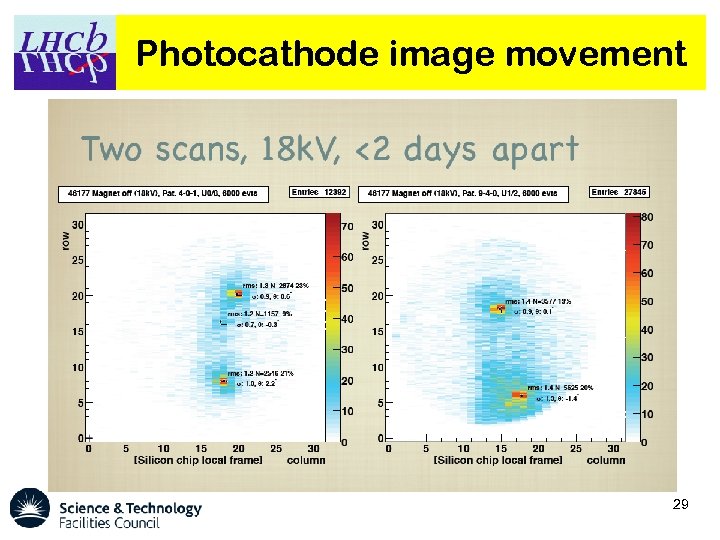
Photocathode image movement 29
30
eb3c1d42f1a2a8615b721748738db5aa.ppt