7c2a41e77328269e315dba3919da5cc2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 The Revolutionary War
The Revolutionary War
 • • Continental Army General George Washington Goal: protect by retreat and counterattack when they had the advantage • Strengths - manpower? - fighting on own soil - guerilla warfare - resourceful leaders - fighting for home and family
• • Continental Army General George Washington Goal: protect by retreat and counterattack when they had the advantage • Strengths - manpower? - fighting on own soil - guerilla warfare - resourceful leaders - fighting for home and family
 Continental Army • Challenges - raising and organizing army - supplies and equipment - $$$$$$$$$$ - needed foreign support - dealing with state govt. - real center of authority
Continental Army • Challenges - raising and organizing army - supplies and equipment - $$$$$$$$$$ - needed foreign support - dealing with state govt. - real center of authority
 British Army • The Regulars • Led by Gen. William Howe • Strategy: confront and defeat Continental Army and isolate radical Patriots of New England • Advantages - superior military - financial - most powerful navy
British Army • The Regulars • Led by Gen. William Howe • Strategy: confront and defeat Continental Army and isolate radical Patriots of New England • Advantages - superior military - financial - most powerful navy
 George Washington • Held army and country together • Lacked military genius • Gained respect of most of patriots • Faced mutiny from troops • Faced removal from Congress
George Washington • Held army and country together • Lacked military genius • Gained respect of most of patriots • Faced mutiny from troops • Faced removal from Congress
 Battle of Bunker Hill
Battle of Bunker Hill
 Bunker Hill • • • Breed’s Hill June 17, 1775 Place: Charlestown Peninsula on north side of Boston Harbor Combatants: British troops of the Boston garrison against troops of the Continental Army Generals: Major General Howe against General Artemas Ward and General Israel Putnam Size of the armies: 2, 400 British troops against 1, 500 Americans.
Bunker Hill • • • Breed’s Hill June 17, 1775 Place: Charlestown Peninsula on north side of Boston Harbor Combatants: British troops of the Boston garrison against troops of the Continental Army Generals: Major General Howe against General Artemas Ward and General Israel Putnam Size of the armies: 2, 400 British troops against 1, 500 Americans.
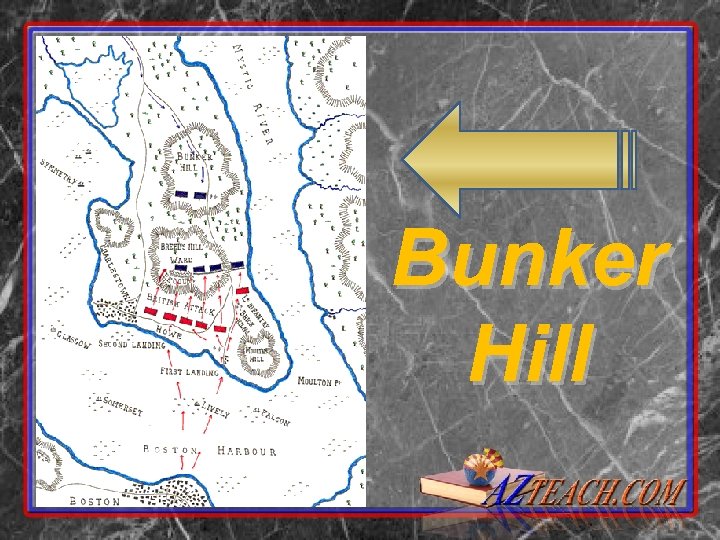 Bunker Hill
Bunker Hill
 Don’t shoot until you see the whites of their eyes!
Don’t shoot until you see the whites of their eyes!

 The death of the American General Warren at the climax of the Battle of Bunker Hill by John Trumbull
The death of the American General Warren at the climax of the Battle of Bunker Hill by John Trumbull
 Battle Results • Americans retreated - 450 killed or wounded • British victory? - 1, 150 killed or wounded (1/2) • First major battle of the Revolutionary War
Battle Results • Americans retreated - 450 killed or wounded • British victory? - 1, 150 killed or wounded (1/2) • First major battle of the Revolutionary War
 First Phase • Patriots surrounded Boston- British left in March 1776 • British didn’t gain huge loyalist support in South • Patriots lost Canada - siege of Canada failed - Montgomery and Benedict Arnold Death of General Wolf at the Battle of Quebec
First Phase • Patriots surrounded Boston- British left in March 1776 • British didn’t gain huge loyalist support in South • Patriots lost Canada - siege of Canada failed - Montgomery and Benedict Arnold Death of General Wolf at the Battle of Quebec
 The Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence
 The Committee Thomas Jefferson John Adams Benjamin Franklin Robert Livingston Roger Sherman
The Committee Thomas Jefferson John Adams Benjamin Franklin Robert Livingston Roger Sherman
 Drafting the Declaration • Three Stages 1. Written by Jefferson 2. Changes made by Franklin and Adams 3. Changes made by Congress
Drafting the Declaration • Three Stages 1. Written by Jefferson 2. Changes made by Franklin and Adams 3. Changes made by Congress
 The Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence
 Second Phase 1776 -1778 • Conventional war - British in position to win but fouled it up • British drove Americans from NY into Pennsylvania • Dec. 26, 1776 Washington defeated Hessians at Trenton
Second Phase 1776 -1778 • Conventional war - British in position to win but fouled it up • British drove Americans from NY into Pennsylvania • Dec. 26, 1776 Washington defeated Hessians at Trenton
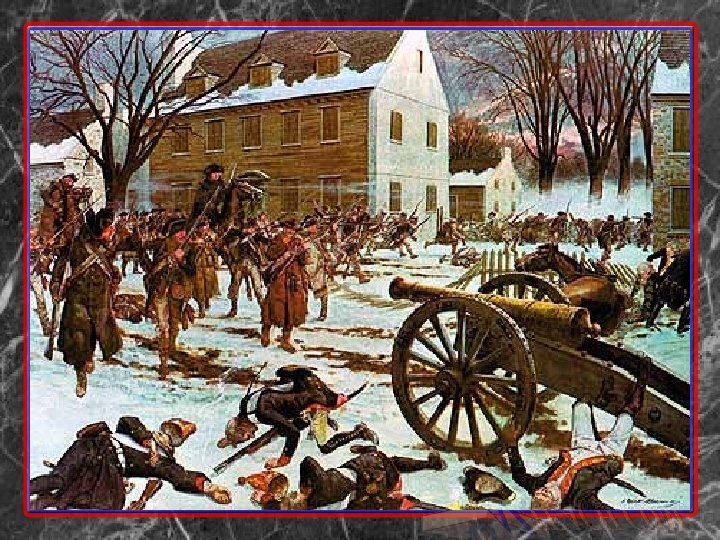


 Great Britain's Mistakes • Planned to cut US in 2 • Burgoyne pursued and Howe changed plan • Howe took Philadelphia • Burgoyne suffered several defeats
Great Britain's Mistakes • Planned to cut US in 2 • Burgoyne pursued and Howe changed plan • Howe took Philadelphia • Burgoyne suffered several defeats
 The Battle of Saratoga October 7, 1777 Turning Point of the War
The Battle of Saratoga October 7, 1777 Turning Point of the War
 British General John Burgoyne surrendered to American General Horatio Gates at Saratoga, New York France decided to help the Americans
British General John Burgoyne surrendered to American General Horatio Gates at Saratoga, New York France decided to help the Americans
 Winter 1777 -1778 Valley Forge, Pennsylvania
Winter 1777 -1778 Valley Forge, Pennsylvania
 Location was close enough to apply pressure, but far enough away to avoid a sneak attack 2, 000 huts built, miles of trenches dug Fortifications built
Location was close enough to apply pressure, but far enough away to avoid a sneak attack 2, 000 huts built, miles of trenches dug Fortifications built
 2, 000 soldiers die 2/3 from disease: influenza, smallpox typhus, typhoid, and dysentery
2, 000 soldiers die 2/3 from disease: influenza, smallpox typhus, typhoid, and dysentery
 Baron Friedrich von Steuben trained the troops
Baron Friedrich von Steuben trained the troops
 Final Phase • Characterized by guerilla warfare • British looked for loyalist aid - found more Patriots than thought - Lost loyalist sympathy due to slavery • Stalemate in the North • Battles in West won by Patriot, George Rogers Clark • British won some in South, but hounded by guerillas
Final Phase • Characterized by guerilla warfare • British looked for loyalist aid - found more Patriots than thought - Lost loyalist sympathy due to slavery • Stalemate in the North • Battles in West won by Patriot, George Rogers Clark • British won some in South, but hounded by guerillas
 Yorktown
Yorktown
 • Washington & French v. Cornwallis • Washington joined with Lafayette in march by land • French circled by sea • October 17, 1781 Cornwallis surrounded – surrendered • Final battle of the Revolutionary War • Treaty of Paris signed September 3, 1783
• Washington & French v. Cornwallis • Washington joined with Lafayette in march by land • French circled by sea • October 17, 1781 Cornwallis surrounded – surrendered • Final battle of the Revolutionary War • Treaty of Paris signed September 3, 1783
 Treaty of Paris 1783 • Unconditional recognition of independence! • Land gained - S. boundary of Canada to N. boundary of Florida - Atlantic to Mississippi River
Treaty of Paris 1783 • Unconditional recognition of independence! • Land gained - S. boundary of Canada to N. boundary of Florida - Atlantic to Mississippi River


