RESPIRATORY ppt SP 09-1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 The Respiratory System Rachel S. Natividad, RN, MSN, NP N 212 Medical Surgical Nursing 1
The Respiratory System Rachel S. Natividad, RN, MSN, NP N 212 Medical Surgical Nursing 1
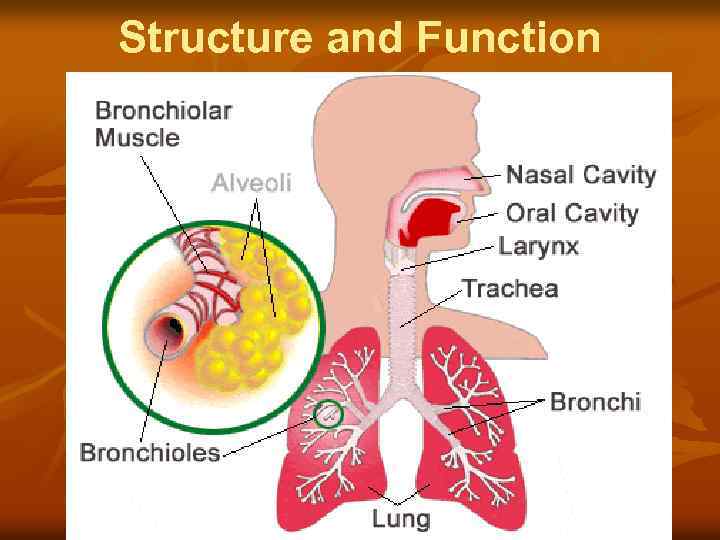 Structure and Function
Structure and Function
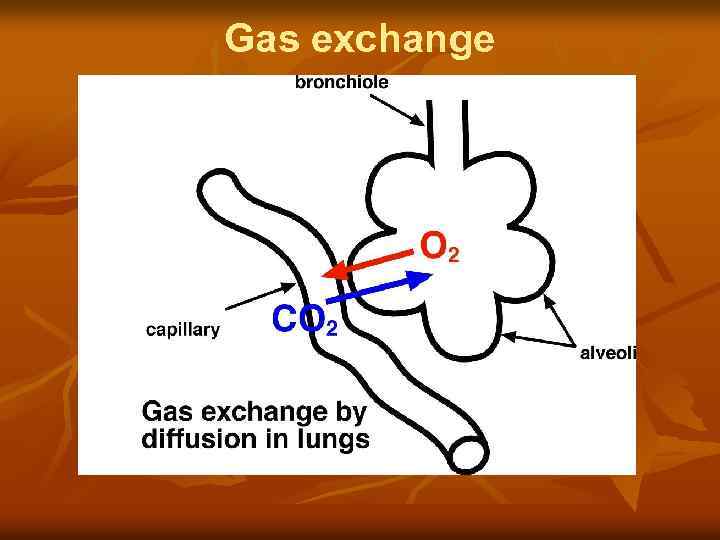 Gas exchange
Gas exchange
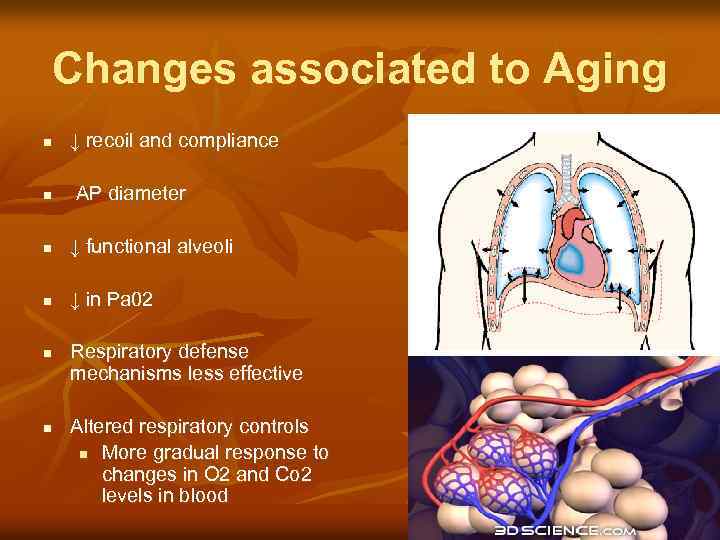 Changes associated to Aging n ↓ recoil and compliance n AP diameter n ↓ functional alveoli n ↓ in Pa 02 n n Respiratory defense mechanisms less effective Altered respiratory controls n More gradual response to changes in O 2 and Co 2 levels in blood
Changes associated to Aging n ↓ recoil and compliance n AP diameter n ↓ functional alveoli n ↓ in Pa 02 n n Respiratory defense mechanisms less effective Altered respiratory controls n More gradual response to changes in O 2 and Co 2 levels in blood
 Diagnostics n n n Pulse Oximetry Chest X-Ray Computed Tomography (CT scan) n Bronchoscopy n Thoracentesis n n Pulmonary Function Tests Sputum Specimen and Cultures
Diagnostics n n n Pulse Oximetry Chest X-Ray Computed Tomography (CT scan) n Bronchoscopy n Thoracentesis n n Pulmonary Function Tests Sputum Specimen and Cultures
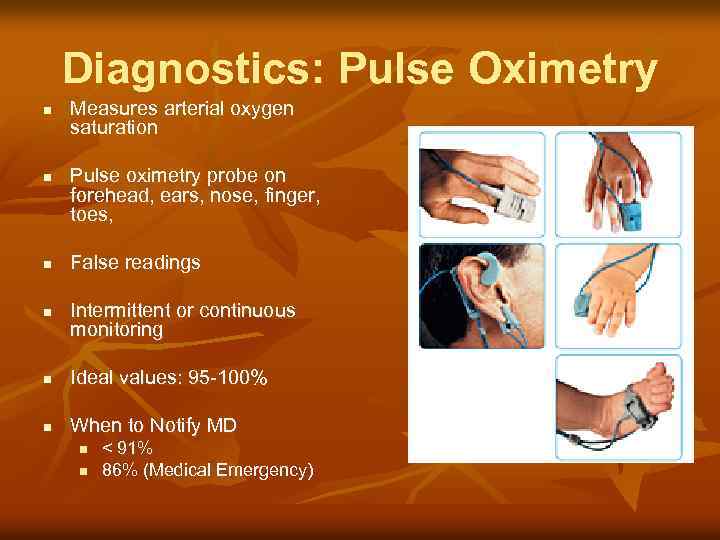 Diagnostics: Pulse Oximetry n n Measures arterial oxygen saturation Pulse oximetry probe on forehead, ears, nose, finger, toes, False readings Intermittent or continuous monitoring n Ideal values: 95 -100% n When to Notify MD n n < 91% 86% (Medical Emergency)
Diagnostics: Pulse Oximetry n n Measures arterial oxygen saturation Pulse oximetry probe on forehead, ears, nose, finger, toes, False readings Intermittent or continuous monitoring n Ideal values: 95 -100% n When to Notify MD n n < 91% 86% (Medical Emergency)
 Diagnostics: Chest X-Ray n n Screen, diagnose, evaluate treatment Instructions: No metals/jewelry
Diagnostics: Chest X-Ray n n Screen, diagnose, evaluate treatment Instructions: No metals/jewelry
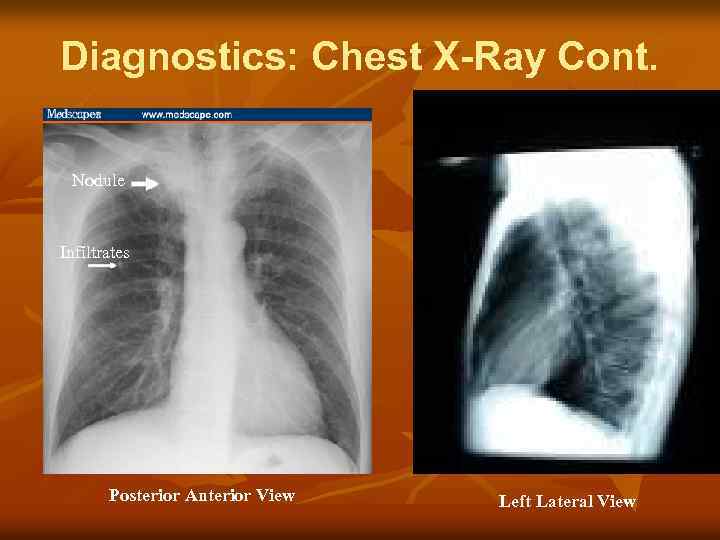 Diagnostics: Chest X-Ray Cont. Nodule Infiltrates Posterior Anterior View Left Lateral View
Diagnostics: Chest X-Ray Cont. Nodule Infiltrates Posterior Anterior View Left Lateral View
 Diagnostics: Sputum Specimen To diagnose; evaluate treatment n Specimen: ID organisms or abnormal cells n Culture & Sensitivity (C&S) n Cytology n Gram stains n n (e. g. Acid Fast Bacilli)
Diagnostics: Sputum Specimen To diagnose; evaluate treatment n Specimen: ID organisms or abnormal cells n Culture & Sensitivity (C&S) n Cytology n Gram stains n n (e. g. Acid Fast Bacilli)
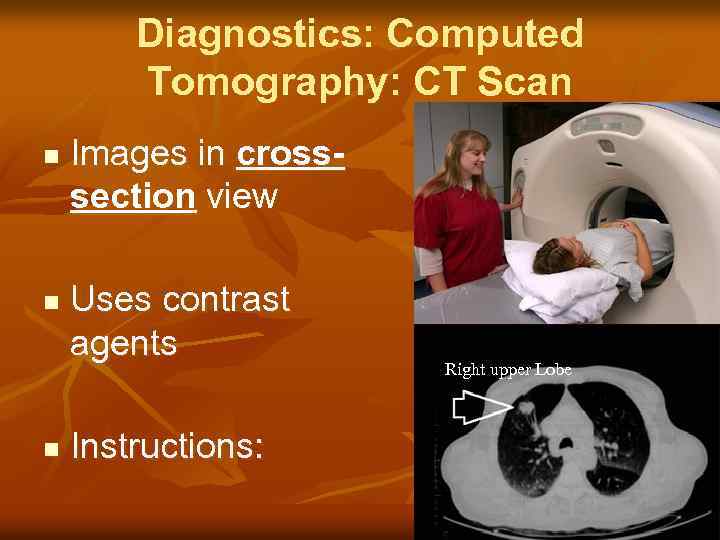 Diagnostics: Computed Tomography: CT Scan n Images in crosssection view Uses contrast agents Instructions: Right upper Lobe
Diagnostics: Computed Tomography: CT Scan n Images in crosssection view Uses contrast agents Instructions: Right upper Lobe
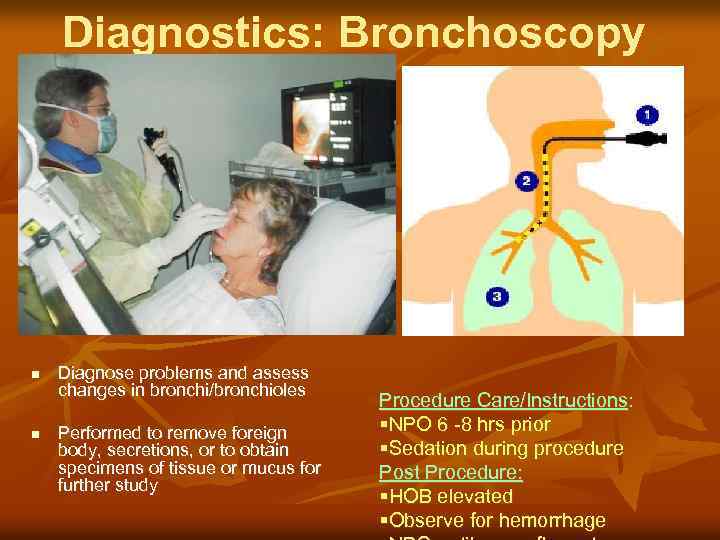 Diagnostics: Bronchoscopy n n Diagnose problems and assess changes in bronchi/bronchioles Performed to remove foreign body, secretions, or to obtain specimens of tissue or mucus for further study Procedure Care/Instructions: §NPO 6 -8 hrs prior §Sedation during procedure Post Procedure: §HOB elevated §Observe for hemorrhage
Diagnostics: Bronchoscopy n n Diagnose problems and assess changes in bronchi/bronchioles Performed to remove foreign body, secretions, or to obtain specimens of tissue or mucus for further study Procedure Care/Instructions: §NPO 6 -8 hrs prior §Sedation during procedure Post Procedure: §HOB elevated §Observe for hemorrhage
 Diagnostics: Pulmonary Function Test (PFTs) n n Evaluate lung function Observe for increased dyspnea or bronchospasm Instructions: No bronchodilators 6 hours prior
Diagnostics: Pulmonary Function Test (PFTs) n n Evaluate lung function Observe for increased dyspnea or bronchospasm Instructions: No bronchodilators 6 hours prior
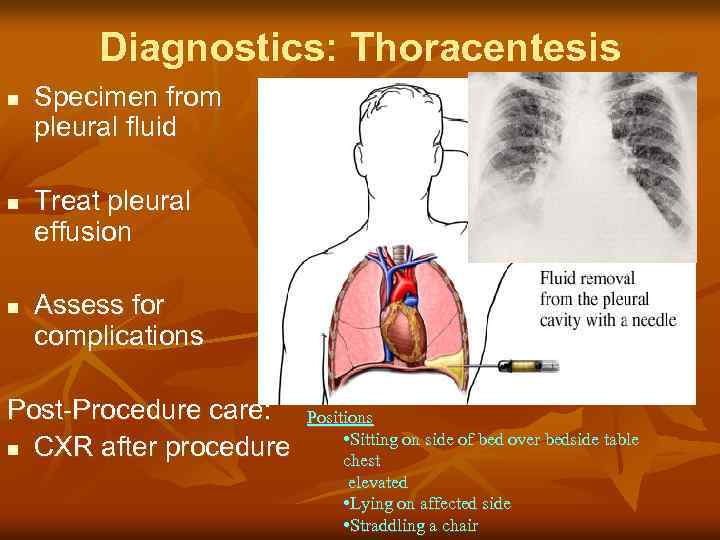 Diagnostics: Thoracentesis n n n Specimen from pleural fluid Treat pleural effusion Assess for complications Post-Procedure care: n CXR after procedure Positions • Sitting on side of bed over bedside table chest elevated • Lying on affected side • Straddling a chair
Diagnostics: Thoracentesis n n n Specimen from pleural fluid Treat pleural effusion Assess for complications Post-Procedure care: n CXR after procedure Positions • Sitting on side of bed over bedside table chest elevated • Lying on affected side • Straddling a chair
 Assessment: Cues to Respiratory Problems Dyspnea Cough Sputum
Assessment: Cues to Respiratory Problems Dyspnea Cough Sputum
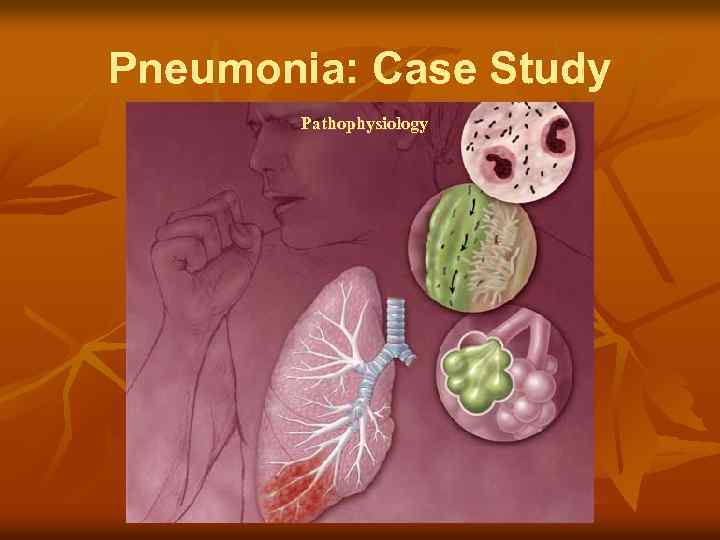 Pneumonia: Case Study Pathophysiology
Pneumonia: Case Study Pathophysiology
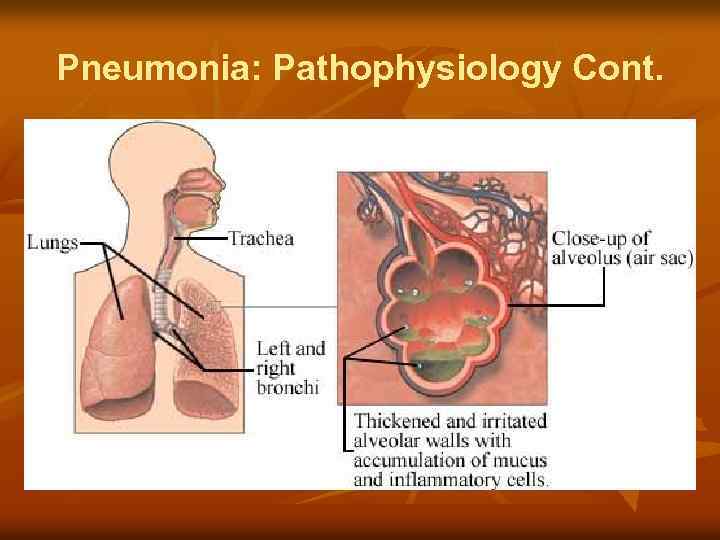 Pneumonia: Pathophysiology Cont.
Pneumonia: Pathophysiology Cont.
 Pneumonia: Etiology n Cause n n n bacteria (75%) viruses fungi Mycoplasma Parasites chemicals
Pneumonia: Etiology n Cause n n n bacteria (75%) viruses fungi Mycoplasma Parasites chemicals
 Pneumonia: Classifications n Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) n n Onset in community or during 1 st 2 days of hospitalization (Strep. pneumoniae most common) Hospital-acquired Pneumonia(HAP/nosocomial) n Occurring 48 hrs or longer after hospitalization n Aspiration pneumonia n Pneumonia caused by opportunistic organisms n Pneumocystis Carinii
Pneumonia: Classifications n Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) n n Onset in community or during 1 st 2 days of hospitalization (Strep. pneumoniae most common) Hospital-acquired Pneumonia(HAP/nosocomial) n Occurring 48 hrs or longer after hospitalization n Aspiration pneumonia n Pneumonia caused by opportunistic organisms n Pneumocystis Carinii
 Pneumonia: Risk Factors n n CAP Older adult Chronic/coexisting condition Recent history or exposure to viral or influenza infections History of tobacco or alcohol use n n n n HAP Older adult Chronic lung disease ALOC Aspiration ET, Trach, NG / GT Immunocompromised Mechanical ventilation
Pneumonia: Risk Factors n n CAP Older adult Chronic/coexisting condition Recent history or exposure to viral or influenza infections History of tobacco or alcohol use n n n n HAP Older adult Chronic lung disease ALOC Aspiration ET, Trach, NG / GT Immunocompromised Mechanical ventilation
 Pneumonia: Clinical Manifestations n n n Fevers, chills, anorexia Pleuritic chest pain SOB Crackles/wheezes Cough, sputum production Tachypnea
Pneumonia: Clinical Manifestations n n n Fevers, chills, anorexia Pleuritic chest pain SOB Crackles/wheezes Cough, sputum production Tachypnea
 Pneumonia: Clinical Manifestations-Cont. Mycoplasma (Atypical) n feeling tired or weak, headaches, sore throat, or diarrhea. n n Eventually, most develop a dry cough. They can, also, develop fever, chills, earaches, chest pain “walking pneumonia”
Pneumonia: Clinical Manifestations-Cont. Mycoplasma (Atypical) n feeling tired or weak, headaches, sore throat, or diarrhea. n n Eventually, most develop a dry cough. They can, also, develop fever, chills, earaches, chest pain “walking pneumonia”
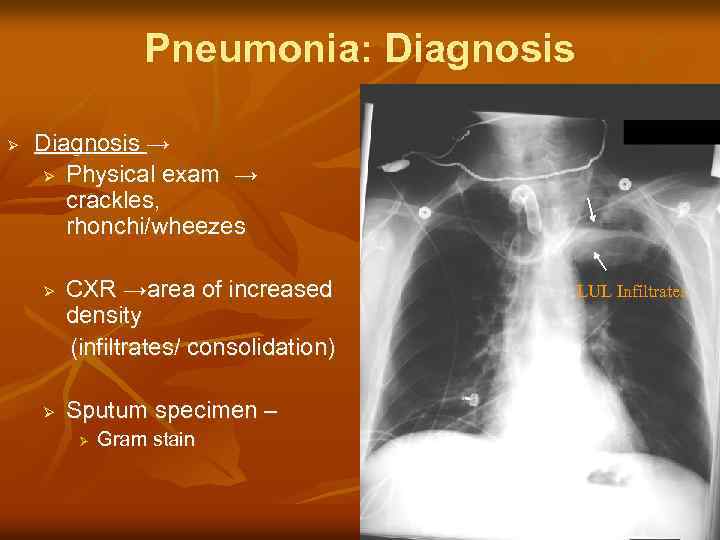 Pneumonia: Diagnosis Ø Diagnosis → Ø Physical exam → crackles, rhonchi/wheezes CXR →area of increased density (infiltrates/ consolidation) Ø Ø Sputum specimen – Ø Gram stain LUL Infiltrates
Pneumonia: Diagnosis Ø Diagnosis → Ø Physical exam → crackles, rhonchi/wheezes CXR →area of increased density (infiltrates/ consolidation) Ø Ø Sputum specimen – Ø Gram stain LUL Infiltrates
 Pneumonia : Interventions/Tx Ø Treatment Ø Antibiotics → choose based on age, suspected cause & immune status Ø Ø Supportive care → IV fluids, supplemental oxygen therapy, respiratory monitoring, cough enhancement *may take 6 -8 weeks for CXR to normalize
Pneumonia : Interventions/Tx Ø Treatment Ø Antibiotics → choose based on age, suspected cause & immune status Ø Ø Supportive care → IV fluids, supplemental oxygen therapy, respiratory monitoring, cough enhancement *may take 6 -8 weeks for CXR to normalize
 Nursing Diagnoses… n n Impaired gas exchange R/T Pneumonia Pain R/T infection in lung Pneumonia
Nursing Diagnoses… n n Impaired gas exchange R/T Pneumonia Pain R/T infection in lung Pneumonia
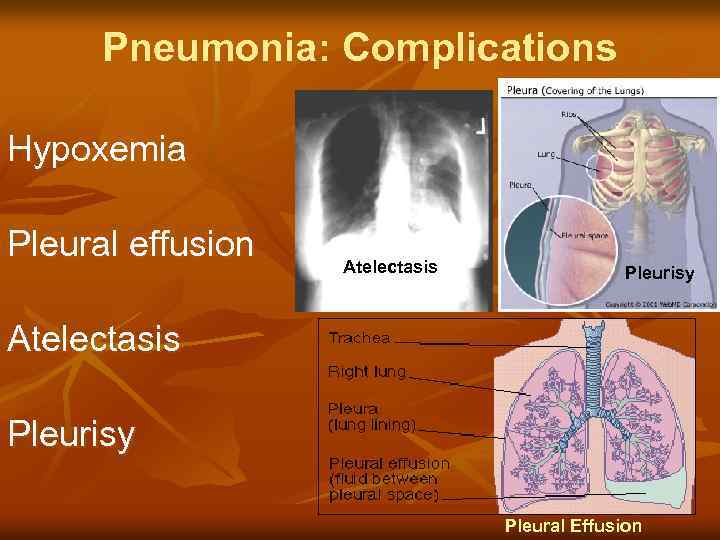 Pneumonia: Complications Hypoxemia Pleural effusion Atelectasis Pleurisy Pleural Effusion
Pneumonia: Complications Hypoxemia Pleural effusion Atelectasis Pleurisy Pleural Effusion
 Toxic sprinkles anyone?
Toxic sprinkles anyone?
 Any Questions?
Any Questions?


