1357bfc6679fd72427cd1fa5dccc78fe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA PRESENTATION ON: ‘’COMBATING CORRUPTION AND STRENGTHENING ACCOUNTABILITY FOR THE PROMOTION OF GOOD GOVERNANCE’’ AT A PATRIOTISM DEVELOPMENT TRAINING. HELD AT NKUMBA UNIVERSITY 3/15/2018 By The Directorate of Education and Prevention of Corruption, Inspectorate of Government. Mwebesa Peter 1

Introduction Corruption is a scourge that pervades all sectors of society. It is a widespread phenomenon which undermines good governance, eroding the rule of law, hampering economic growth, distorting business transactions and social and human values. It is subversive and becoming pervasive in Uganda. Corruption is increasingly being seen as a threat to human existence to the extent that some commentators have called for it to be recognized as a ‘crime against humanity. ’ 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 2

Meaning and Definition of Corruption Derived from the Latin verb “Corruptus” which means “to break”, literally meaning “broken Object” Corrupt behavior is dishonest or wicked behavior Behavior which departs or deviates from the established, known and generally accepted ethics, morals, traditions, laws and civic values and virtues of society. It is a departure from what is pure or correct. A corrupt person is therefore one whose morals, conduct, character, values and ethics have broken and collapsed. In a broader sense: Behavior of persons; whether politicians, civil servants, business managers, or private individuals in which they improperly and unlawfully enrich themselves, or those close to them, by misuse of the power , responsibility, or resources entrusted to them. Corruption also implies lack of integrity and ethical uprightness. Integrity; The permanent adherence to a strict moral or ethical code, consistency, between one’s actions and one’s principles. Integrity encompasses transparency and defence of the common good as opposed to serving ‘personal interest’. Ethical behavior; Observing positive values and accepted norms. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 3

Definition of Corruption: The World Bank and Transparency International have defined corruption as ‘‘the misuse of entrusted power for private or personal gain. ’’ By this definition, corruption entails misusing one’s office for a private gain or unofficial end. This version of the definition is the one adopted by the African Union Convention on Prevention and Combating of Corruption and Related Offences, Article 4 thereof. The Inspectorate of Government Act, 2002 defines corruption as ‘‘The abuse of public office for private gain and includes but is not limited to embezzlement, bribery, nepotism, influence peddling, theft of public funds or assets, fraud, forgery, causing financial or property loss and false accounting in public affairs. ’’ 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 4

Definition of Corruption: The 2009 Anti-Corruption Act broadens the definition of corruption. It spells out acts that constitute the offence of corruption and these include; solicitation or acceptance, offering or granting of a bribe; diversion by a public official; fraudulent acquisition of property; corruption between principal and agent; any act or omission in discharge of duties for one’s illicit benefit and neglect of duty. The Act creates new corruption offences in line with UN and AU Conventions. Such offences include; diversion of public funds, influence peddling, conflict of interest, sectarianism, illicit enrichment etc… The Act consolidates anti-corruption penal laws which were hitherto scattered into POCA and the penal code. Such include; loss of public property, abuse of office, embezzlement, causing financial loss, fraudulent false accounting, etc. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 5

Some Quotes on Corruption: “I have often noticed that a bribe has that effect…. . it changes a relation. The man who offers a bribe gives away a little of his own importance; the bribe once accepted, he becomes the inferior, like a man who has paid for a prostitute”. Graham Greene, 1904 – 1991, British Novelist. “The most dangerous object one can meet is not a lion, python, or leopard; it is an educated man (person) but with no character”. Martin Luther Junior “Corruption is like a ball of snow, once it is set rolling it must increase”. (Charles Caleb Colton English writer, 1780 -1832) “The accomplice to the crime of corruption is frequently our own indifference” Bess Myerson 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 6

Changing trends of corruption Over the past few years, the nature and trends in corruption have continued to change greatly as the culprits adopt even tougher measures to conceal their actions. “Technical corruption”. This is corruption that is participated in by professionals who use their technical knowledge. “Syndicate corruption”. This is where public officials within say a government department such as procurement, administration, accounts and technical departments work together and may not be detected easily as there is a lot of cover up. It is also promoted by the ‘’Corruption-Nepotism Nexus’’ Intended crisis: This occurs when public officials wait until the very last possible time to take decisions especially those involving procurement, thereby stampeding the process with all the attendant results. (Management by crisis) Greed factor: Greed has overtaken need as the sustaining factor of corruption (3 rd NIS) 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 7

Changing trends of corruption “Administrative and financial injustices”. Where different people do similar duties with pay discrepancies in public institutions. The defense of “you are paid because of who you are not what you do” assertion. Glorification of corruption: Corruption has been glorified as an acceptable way of life. Corrupt people who are wealthy are respected and easily get into positions of leadership. Those who lead modest lives or are poor are regarded as failures in society. Emergence of briefcase companies/NGOs that exist for a week or month: Fictitious bank accounts are opened, used and abandoned or closed. From petty, to grand, to institutional, to systemic, corruption is becoming kleptocratic. Corruption has permeated through all the spheres and levels of society: Age-refer to the ‘’Shifting of the Middle Age Crisis’’ Profession Gender Tribe/Community Educated or otherwise Citizen/aliens Employed or otherwise Religious and otherwise Transnational 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 8

Good Governance Good governance World Bank “Good Governance is exercising authority in ways that respect the integrity, rights, and needs of everyone within the state” Simple terms “Good governance is about making sure power, authority and decision making are not concentrated in the hands of a single individual or a group” Question to ponder on-: Why are strikes becoming more rampant in our schools? 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 9
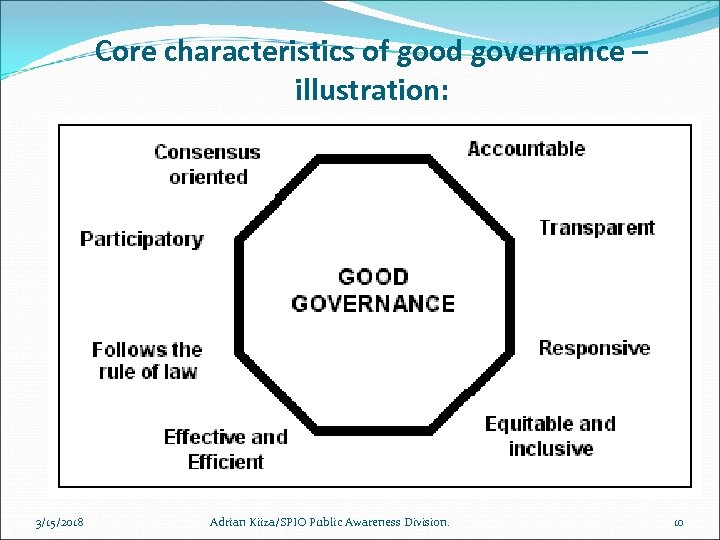
Core characteristics of good governance – illustration: 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 10

Evaluation of Good Governance for Uganda According to International reports like the recently released Mo Ibrahim Index 2012 which aims to be Africa’s leading assessment of governance that informs and empowers citizens and governments to measure progress, Uganda was ranked the third best performer in the Eastern Region. The report revealed that Uganda scored 55. 1% on governance quality in 2012 and was ranked 19 th out of 52 countries. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 11
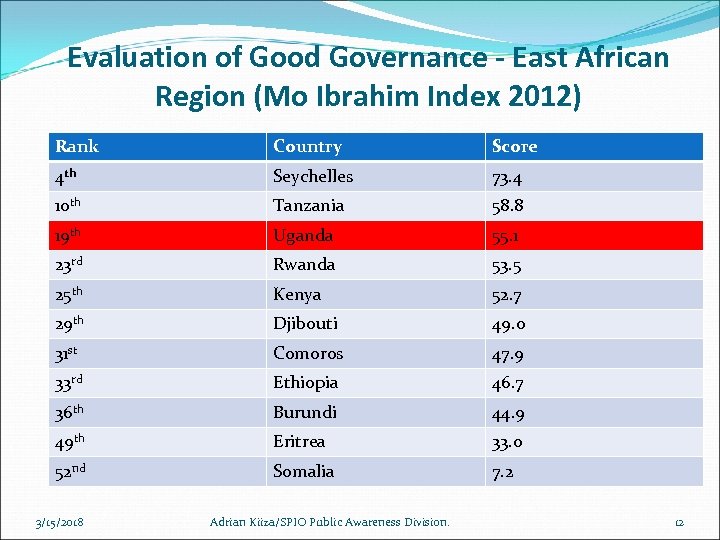
Evaluation of Good Governance - East African Region (Mo Ibrahim Index 2012) Rank Country Score 4 th Seychelles 73. 4 10 th Tanzania 58. 8 19 th Uganda 55. 1 23 rd Rwanda 53. 5 25 th Kenya 52. 7 29 th Djibouti 49. 0 31 st Comoros 47. 9 33 rd Ethiopia 46. 7 36 th Burundi 44. 9 49 th Eritrea 33. 0 52 nd Somalia 7. 2 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 12

Governance issues in Uganda NATIONAL VALUES The concept of good governance was shaped by the 1995 Constitution of Uganda in the National objectives and directive principles of state policy. The values according to the constitution include accountability, democracy, state security, nationalism etc These values are fundamental in the attainment of good governance and are mainly based on: Objective iii Objective v Objective ix Objective xxvi Objective xxix 3/15/2018 Democratic principles National Unity and stability Fundamental and other human rights and freedoms The right to development Role of the people in development Accountability Duties of a citizen Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 13

Accountability The Constitution of the Republic of Uganda, National objective XXVI on Accountability states that; All public offices shall be held in trust for the people All persons placed in positions of leadership and responsibility shall, in their work, be answerable to the people All lawful measures shall be taken to expose, combat and eradicate corruption and abuse or misuse of power by those holding political and other public offices. Article 17 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uganda provides for Duties of a citizen (1) (d) to protect and preserve public property. (i) to combat corruption and misuse or wastage of public property 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 14

Definition of accountability A typical definition is that accountability concerns the processes by which “those who exercise power whether as governments, as elected representatives or as appointed officials, must be able to show that they have exercised their powers and discharged their duties properly”. Accountability has also been defined as “responsibility of government and its agents towards the public to achieve previously set objectives and to account for them in public” It is also regarded as a commitment required from public officials individually and collectively to accept public responsibility for their own action and inaction. Accountability is therefore an ethical virtue, since ethics concern principles and rules that govern the moral value of people’s behavior. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 15

Political Oversight and Public Accountability Elected leaders of government and the opposition place a great deal of emphasis upon, and give much attention to assuring that governmental agencies and their personal staff are highly sensitive to issues of public accountability. Legislative bodies contribute to the accountability of the government by the oversight work that is carried out through their committee activity i. e. (PAC) and other committees. Accountability procedures therefore require all officials and those who seek to influence them to follow established rules defining acceptable processes and outcomes, and to demonstrate that they have followed those procedures. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 16

Anti- Corruption and Accountability Initiatives Implemented in Uganda A ) The Legal Framework The Anti-Corruption Act 2009, The Inspectorate of Government Act 2002, The Public Finance and Accountability Act 2003 (PFAA), The Leadership Code Act 2002 (LCA) The Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Act 2003. The Whistleblowers Protection Act 2010 B) The Institutional Framework The Inspectorate of Government: Established under Article 223 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uganda, is the lead anti-corruption body in Uganda, with the mandate to eliminate and foster the elimination of corruption, abuse of authority and of public office - Article 225. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 17

Anti- Corruption Initiatives Implemented in Uganda Office of the Auditor General: Provided for under the Constitution and the Audit Act, 2008; this institution is responsible for auditing of the accounts of Central Government, Local Governments, Administrative Units, Public Organisations and bodies in which the Government has any interest. Directorate of Public Prosecutions (DPP): The office of the DPP is established under Article 120 of the Constitution of Uganda, and is in charge of all criminal prosecutions in Uganda. In execution of his mandate, the DPP supervises investigations carried out by the CIID of the Uganda Police. Criminal Intelligence & Investigations Department of the Uganda Police (CIID): The Directorate’s mandate is to ensure effective investigations, detection and prevention of crime in the country 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 18

Anti- Corruption Initiatives Implemented in Uganda Public Accounts Committees of Parliament: The Public Accounts Committee and the Local Government Public Accounts Committee are standing committees of Parliament, as provided for under Part XXIV of the Rules of Procedure of the Parliament of Uganda; which scrutinise the reports of the Auditor General and make appropriate recommendations for consideration of the Plenary (Parliament). The Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Authority (PPDA): PPDA is the regulatory body for public procurement and disposal activities in Uganda established through the Public Procurement and Disposal of Public Assets Act No. 1 of 2003. Its overall objective is to promote transparency and efficiency in public procurement and disposal through the elimination of all forms of corruption that have greatly hindered development in the country. The establishment of the Anti-Corruption Court as a Division of the High Court to exclusively handle corruption cases. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 19

Anti- Corruption Initiatives Implemented in Uganda The Directorate of Ethics and Integrity in the Office of the President: The Directorate is responsible for initiating national anti-corruption legislation, policies and other initiatives. The directorate was established to raise the issue of corruption to a cabinet level, to coordinate government efforts in its fight against corruption through the Inter Agency Forum, and to establish an integrity system that promotes good governance. It is mandated to implement the government's zero tolerance to corruption policy. Ministry of Finance, Planning and Economic Development: Under the Public Finance and Accountability Act, 2003; the Secretary to the Treasury is designated as the chief implementing officer for the Act, which provides for the regulation of financial management in Government; and prescribes responsibilities of those entrusted with financial management in Government. C) Political, Economic and Administrative Reforms in the last two decades: These have included; political pluralism, electoral reforms, 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 20 liberalization, decentralization etc. .

Probable measures to enhance good governance Re-invent patriotism Strengthening all government institutions charged with managing and implementing government programs to endeavor they perform and ensure that there is timely and quality service delivery For civil servants and other public officers, there is a need to introduce the concept of performance contracts based on the principle of result oriented management. There is need to intensify sensitization of the public servants on the relevant laws, policies and government strategic development programs so as to efficiently perform their roles. Need to uphold the principle of separation of powers and recognize the different roles played by different stakeholders Those institutions charged with managing and implementing government programs should endeavor to perform and ensure that there is timely and quality service delivery. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 21

Probable measures to enhance good governance Development of integrity clubs among the youth and Integrity Committees in public offices. Investigate and prosecute Raising public awareness Institutional Development/Systems building Research including surveys Partnership with state and non state actors Declaration of assets/verification Reward and recognition measures Rebuild ethics and integrity values Adherence to standard procurement and disposal standards Personal commitment to abhor corruption There is need to build a national value system to appreciate what is public good and promotion of social justice. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 22

Conclusion On the whole, governance issues have increasingly been brought to the fore in Uganda since the NRM Government came to power. The eagerness to ensure good governance has been so overwhelming to the extent that a number of policies, procedures, guidelines and institutions have been put in place with respect to the governance process. With all these measures in place, if concerted effort and political will are guaranteed, Uganda will continue to build on the successes already achieved and overcome the challenges hindering good governance today. 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 23

End Thank you for listening to me FOR GOD AND MY COUNTRY 3/15/2018 Adrian Kiiza/SPIO Public Awareness Division. 24
1357bfc6679fd72427cd1fa5dccc78fe.ppt