 The Queuing Models Covered Here All Assume 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Arrivals follow the Poisson distribution FIFO service Single phase Unlimited queue length Steady state conditions We will look at 5 of the most commonly used queuing systems. EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
The Queuing Models Covered Here All Assume 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Arrivals follow the Poisson distribution FIFO service Single phase Unlimited queue length Steady state conditions We will look at 5 of the most commonly used queuing systems. EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
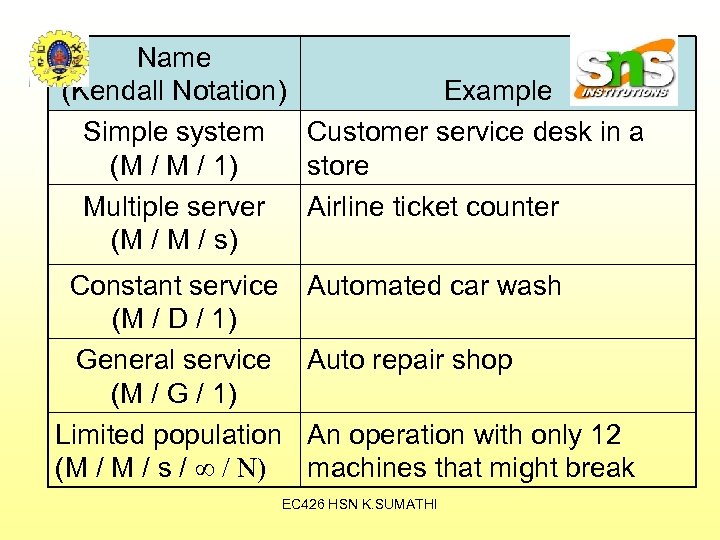 Name Models Covered (Kendall Notation) Example Simple system Customer service desk in a (M / 1) store Multiple server Airline ticket counter (M / s) Constant service (M / D / 1) General service (M / G / 1) Limited population (M / s / ∞ / N) Automated car wash Auto repair shop An operation with only 12 machines that might break EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Name Models Covered (Kendall Notation) Example Simple system Customer service desk in a (M / 1) store Multiple server Airline ticket counter (M / s) Constant service (M / D / 1) General service (M / G / 1) Limited population (M / s / ∞ / N) Automated car wash Auto repair shop An operation with only 12 machines that might break EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
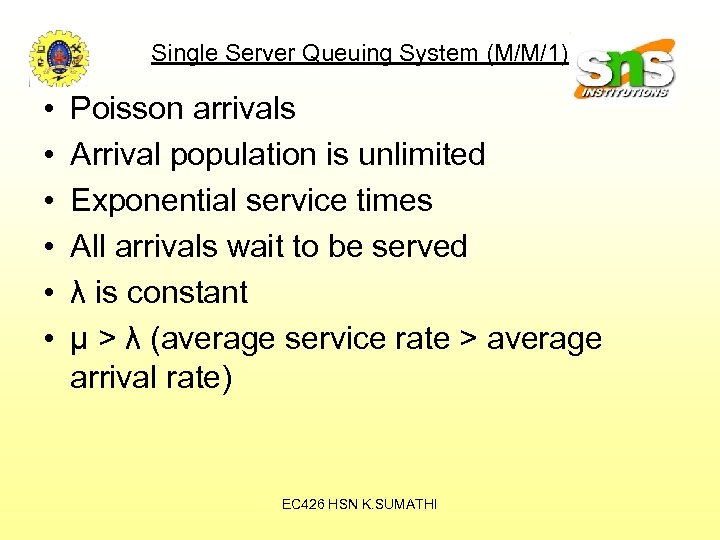 Single Server Queuing System (M/M/1) • • • Poisson arrivals Arrival population is unlimited Exponential service times All arrivals wait to be served λ is constant μ > λ (average service rate > average arrival rate) EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Single Server Queuing System (M/M/1) • • • Poisson arrivals Arrival population is unlimited Exponential service times All arrivals wait to be served λ is constant μ > λ (average service rate > average arrival rate) EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
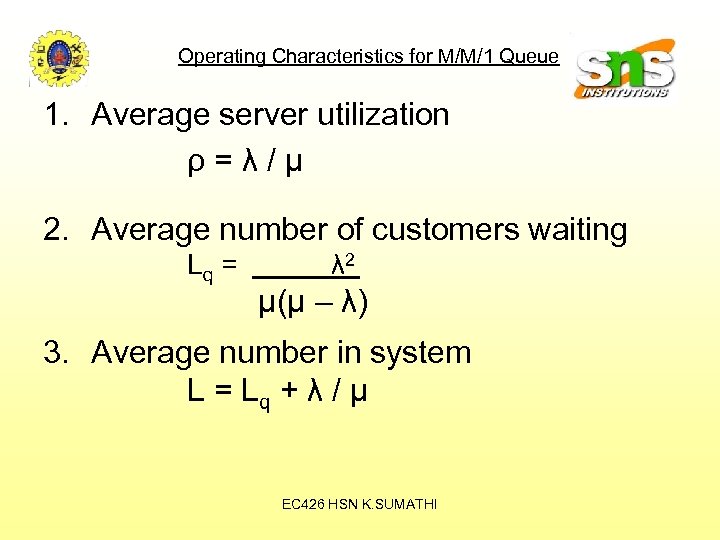 Operating Characteristics for M/M/1 Queue 1. Average server utilization ρ=λ/μ 2. Average number of customers waiting Lq = λ 2 μ(μ – λ) 3. Average number in system L = Lq + λ / μ EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Operating Characteristics for M/M/1 Queue 1. Average server utilization ρ=λ/μ 2. Average number of customers waiting Lq = λ 2 μ(μ – λ) 3. Average number in system L = Lq + λ / μ EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
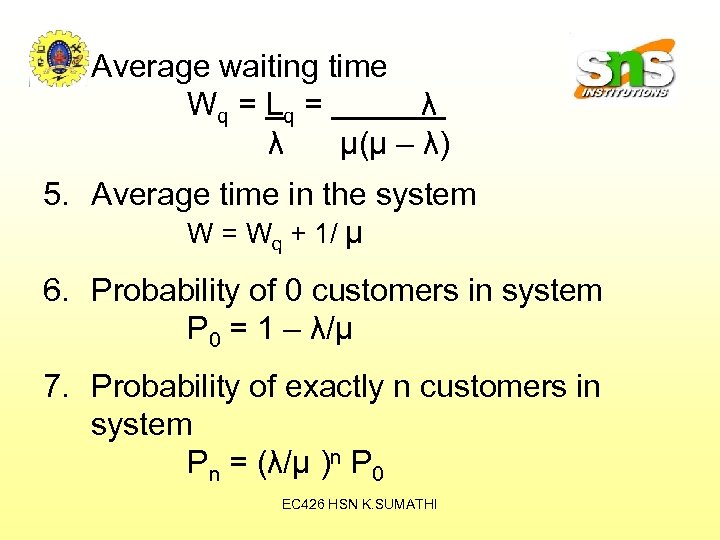 4. Average waiting time W q = Lq = λ λ μ(μ – λ) 5. Average time in the system W = Wq + 1/ μ 6. Probability of 0 customers in system P 0 = 1 – λ/μ 7. Probability of exactly n customers in system Pn = (λ/μ )n P 0 EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
4. Average waiting time W q = Lq = λ λ μ(μ – λ) 5. Average time in the system W = Wq + 1/ μ 6. Probability of 0 customers in system P 0 = 1 – λ/μ 7. Probability of exactly n customers in system Pn = (λ/μ )n P 0 EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
 Arnold’s Muffler Shop Example • Customers arrive on average 2 per hour (λ = 2 per hour) • Average service time is 20 minutes (μ = 3 per hour) Install Excel. Modules Go to file 9 -2. xls EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Arnold’s Muffler Shop Example • Customers arrive on average 2 per hour (λ = 2 per hour) • Average service time is 20 minutes (μ = 3 per hour) Install Excel. Modules Go to file 9 -2. xls EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
 Total Cost of Queuing System Total Cost = Cw x L + Cs x s Cw = cost of customer waiting time period L = average number customers in system Cs = cost of servers per time period s = number of servers EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Total Cost of Queuing System Total Cost = Cw x L + Cs x s Cw = cost of customer waiting time period L = average number customers in system Cs = cost of servers per time period s = number of servers EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
 Multiple Server System (M / s) • • Poisson arrivals Exponential service times s servers Total service rate must exceed arrival rate ( sμ > λ) • Many of the operating characteristic formulas are more complicated EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Multiple Server System (M / s) • • Poisson arrivals Exponential service times s servers Total service rate must exceed arrival rate ( sμ > λ) • Many of the operating characteristic formulas are more complicated EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
 Single Server System With Constant Service Time (M/D/1) • Poisson arrivals • Constant service times (not random) • Has shorter queues than M/M/1 system - Lq and Wq are one-half as large EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI
Single Server System With Constant Service Time (M/D/1) • Poisson arrivals • Constant service times (not random) • Has shorter queues than M/M/1 system - Lq and Wq are one-half as large EC 426 HSN K. SUMATHI