8216f9c0cde39f142fdc71c47ee80335.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

The Quantitative Imaging Network QIN Introductory Remarks Robert J. Nordstrom Larry Clarke Pushpa Tandon Yantian Zhang Huiming Zhang Lori Henderson March 27 – 28, 2014 Lalitha Shankar Keyvan Farahani George Redmond James Deye Jacek Capala John Freymann Justin Kirby

Welcome to the QIN 2014

QIN Program Status • 17 teams are active – 2 additional teams are just starting • Medical College of Wisconsin, Schmainda • UCLA, Mc. Nitt-Gray – 2 teams have passed SPL review – 2 teams will enter under Canadian funding – 27 applications waiting for review in two rounds • New program announcement: PAR-14 -116

The new program announcement

Goals for PAR-14 -116 • Enhance the value of quantitative imaging in clinical trials to predict or measure response to therapy. – Develop, optimize & validate quantitative imaging methods and software tools – Address the challenge of integrating existing or new methods and tools into multi-site clinical trials.
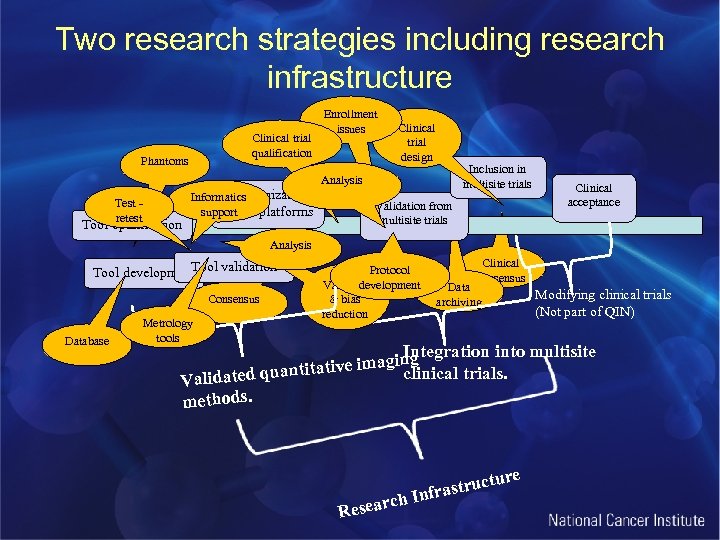
Two research strategies including research infrastructure Clinical trial qualification Phantoms Enrollment issues Clinical trial design Inclusion in multisite trials Analysis Test retest Tool optimization Harmonization Informatics support across platforms Validation from multisite trials Clinical acceptance Analysis Tool validation Tool development Consensus Database Metrology tools Protocol development Variance & bias reduction Clinical consensus Data archiving Modifying clinical trials (Not part of QIN) Integration into multisite e imaging antitativ clinical trials. Validated qu methods. rch Resea ure struct Infra

PAR-14 -116 QIN U 01 Details • Renewal applications are permitted – – – Single Site or multi-site trials (data collections) Domestic and foreign applications encouraged Industry participation encouraged Budget remains capped at $500 k direct costs (5 years) Itemized budget for WG’s, data and tool sharing • Research Strategy: Different Emphasis – Need not to be strong in all areas • QI methods • Selection of clinical trials • Imaging Modalities • Research Infrastructure
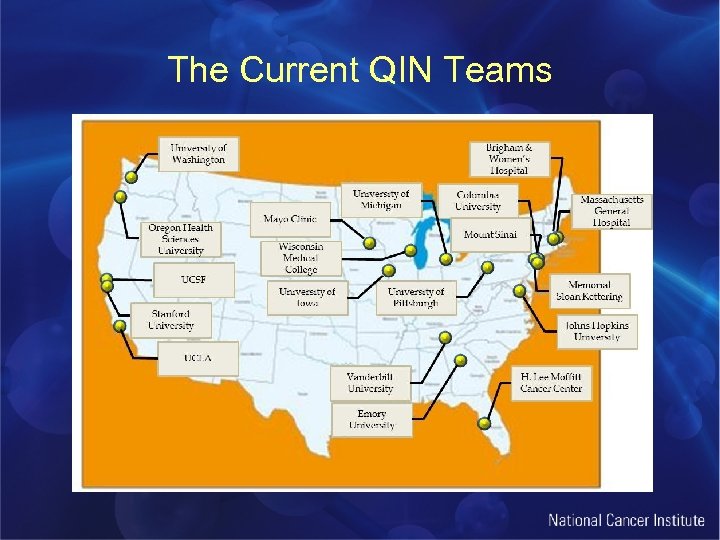
The Current QIN Teams
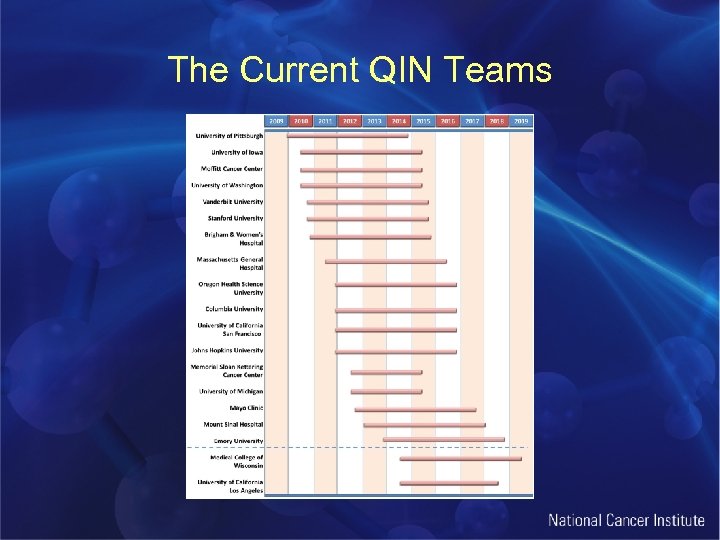
The Current QIN Teams

The Overview Perspective of QIN • Program staff must look at this effort from a number of different perspectives: – What can QIN do for its customers? – How is QIN organized to deliver this? – What will the clinical research community gain? – How can program staff help?

Coordinating Committee All QIN Elements Executive Committee What will QIN do for its customers? (oncologists, pharma) • Provide technically robust and clinically validated quantitative solutions for anatomical and functional imaging to predict and/or measure response of cancer to therapy. • Offer reliable, easy to use adaptable, scalable, and upgradable quantitative imaging tools to promote adaptive therapy. • Interact with industry to establish pathways leading to commercialization of quantitative imaging tools. How can program staff supportneeded? What will shareholders see as a result? What QIN processes are QIN activities? (Cancer Centers, clinical trial groups) • Establish methods for open communication strategies and balanced activities among the QIN program through application justifications to the SPL. Continue to bring new teams into. Working Groups, the Executive Committee, and external groups. Add associate members to the QIN. • Relevant, clinically validated quantitative imaging tools offered Continue to hold meaningful QIN Program Director meetings on a timely basis. to community in a timely and Coordinating Committee, • the oncology criteria on Working Group, cost-effective manner. Develop meaningful. Active participationto measure the effectiveness of the Working Groups on a evaluation and Executive Committee conference calls, keeping the missions regular basis and be prepared to make changes in organization and/or direction. of • Standardized imaging methods and terminology that will provide each group tools and avoid mission creep. • Encourage dissemination of in focus todata through peer-reviewed QIN publications, TCIA, and accurate quantitative measures of therapy response and reliable outcome through clinical trial cooperative groups. prediction. • • Identify and catalyze. Guide group teaming to leverage(data sharing, algorithm validation, etc. ) areas of technical collaboration collective intellectual capital and reduce the formation of silos where they might occur. among QIN members to accelerate achievement of program goals. • Facilitate outreach to industry and regulatory bodies as well as professional societies. • Strive for open science solutions to members. • Organize and conduct meaningful meetings of the QINencourage sharing of data and algorithms. • Encourage leveraging of limited resources to achieve program goals. • • Program Staff
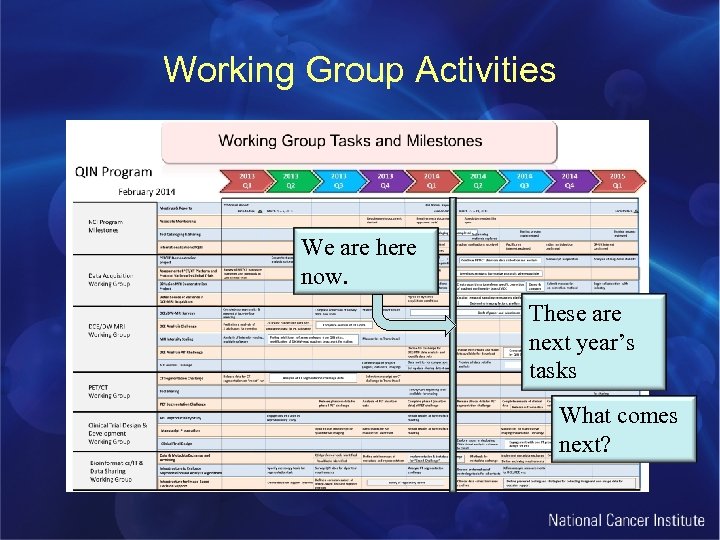
Working Group Activities We are here now. These are next year’s tasks What comes next?

Coordinating Committee • Chairs & co-chairs of the working groups. • Must elect a chair for this group. • Meet by teleconference every-other month. – 2 nd Wednesday of month, 2 PM EDT – Next meeting, May 14, 2014 • Have next 2 -year working group chart finalized.

Individual Team Goals Find areas of cooperation. Plan events such as challenges. Check progress.

Next Year’s Report • Focus on working groups – Challenge results – Tool cataloging & sharing • Contributions from each technical team • Printed for distribution • Posted on an appropriate web site

Expected Outcomes from the Meeting • Revised Working Group plans for the coming year (2014). • Draft of Working Group plans for 2015. • Leadership initiation in all groups. • Associate membership launched. • International relationships created. • Channels for QIN outreach developed.

NCI Program/SPL Review of Applications • • Clinical relevance of proposed trial/drug Rationale: Single site or multi-site clinical trial Clinical rational: Scientific Innovation Network wide : • Consensus publications • Leadership ( EC, CC, WG’s) • Participation ( EC, CC, WG’s) • Delivery of a specific QI methodology across one or ideally across several clinical sites

QIN Outreach • Scientific Societies – RSNA, ISMRM, SNM, AAPM, MICIA, SPIE – Grand Challenges for QI methods/analysis • Industry – Network wide participation • International – – Canada, UK, India, China, EU. . ) Sharing of research resources Development of an international consensus Shared targeted collaboration with industry

QIN Hub & Spoke Models Program Contact: Yantian Zhang (CIP) • PAR 13 169: Academic Industry Partnerships – QIN currently has 6 AIP linked to QIN – Clinical and pre clinical or co clinical imaging – http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-13 -169. html • Informatics Technology for Cancer Research – ( R 01, U 24) – QIN currently has one U 24 (SLICER) – http: //itcr. nci. nih. gov/ • NIH BIG DATA Initiatives ( next slides) –

BD 2 K New Funding Opportunities PA-14 -154: Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science (R 43/R 44) http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PA-14154. html PA-14 -155): Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science (R 01) http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PA-14 -155. html PA-14 -156: Extended Development, Hardening and Dissemination of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics and Big Data Science (R 01) http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PA-14 -156. html PA-14 -157: Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science (R 41/R 42) http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PA-14157. html

BD 2 K New Funding Opportunities RFA-HL-14 -031: Development of an NIH BD 2 K Data Discovery Index Coordination Consortium(U 24) http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/rfa-files/RFA-HL-14 -031. html RFA-HG-14 -020: Development of Software and Analysis Methods for Biomedical Big Data in Targeted Areas of High Need (U 01) http: //grants. nih. gov/grants/guide/rfa-files/RFA-HG-14 -020. html

Other Exploratory Opportunities • Imaging Phenotype-Genomics Correlations – Workshop (June 2013), White Paper (2014) – QIN can serve the role as a technical resource • Preclinical and Co Clinical Drug Trials – – Collaboration with Mouse Models MMHCC Interest in development of QIN standards NCI CBIIT contract ( Informatics support) NCI CBIIT Workshop ( 2013), and planned ( 2014) • NCI Outreach: WMIC South Korea (2014): – Promote standards for mouse models and QI methods – Preclinical and Co-Clinical Trials

8216f9c0cde39f142fdc71c47ee80335.ppt