f6d5ae8d98ec2c45c34f123b11b42fbb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 The Purchasing Function: An Overview Chapter 1
The Purchasing Function: An Overview Chapter 1
 Objectives • Describe commerce • Outline the purchasing function • Analyze the optimal goals of selection and procurement • Describe the desired attributes and knowledge required of a buyer
Objectives • Describe commerce • Outline the purchasing function • Analyze the optimal goals of selection and procurement • Describe the desired attributes and knowledge required of a buyer
 Objectives (cont’d. ) • Describe a storeroom policies and procedures manual • Differentiate among the various types of sellers and how to best work with them
Objectives (cont’d. ) • Describe a storeroom policies and procedures manual • Differentiate among the various types of sellers and how to best work with them
 Objectives (cont’d. ) • Distinguish among the various purchasing options and contracts available to buyers • Identify the benefits of a healthy buyer– seller relationship
Objectives (cont’d. ) • Distinguish among the various purchasing options and contracts available to buyers • Identify the benefits of a healthy buyer– seller relationship
 Historical Perspectives in Trade • Early humans were hunter-gatherers – Agriculture (seed planting) began later • Trade (commerce) is the voluntary exchange of goods or services – First form of trade was bartering – When currency was invented, selling and buying became separate transactions
Historical Perspectives in Trade • Early humans were hunter-gatherers – Agriculture (seed planting) began later • Trade (commerce) is the voluntary exchange of goods or services – First form of trade was bartering – When currency was invented, selling and buying became separate transactions
 The Goals of Selection and Procurement • Selection – Choosing from available alternatives – A spec and a detailed description of what is needed guides selection • Procurement – Systematic exchange of payment for goods or services between buyer and seller
The Goals of Selection and Procurement • Selection – Choosing from available alternatives – A spec and a detailed description of what is needed guides selection • Procurement – Systematic exchange of payment for goods or services between buyer and seller
 An Optimal Goal • Optimal purchasing – Matches the specific characteristics of the product with the specific needs of the business
An Optimal Goal • Optimal purchasing – Matches the specific characteristics of the product with the specific needs of the business
 An Optimal Goal (cont’d. ) • Considerations that are evaluated – Product attributes – Supplier attributes – Delivery requirements – Sanitation – Dependability
An Optimal Goal (cont’d. ) • Considerations that are evaluated – Product attributes – Supplier attributes – Delivery requirements – Sanitation – Dependability
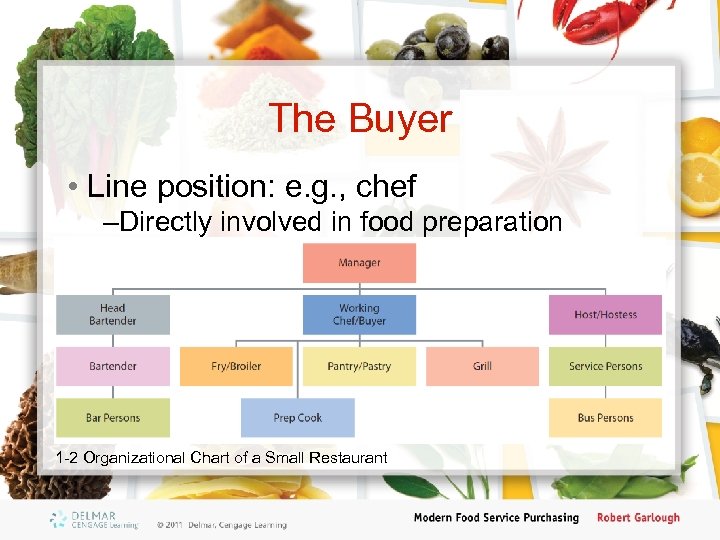 The Buyer • Line position: e. g. , chef –Directly involved in food preparation 1 -2 Organizational Chart of a Small Restaurant
The Buyer • Line position: e. g. , chef –Directly involved in food preparation 1 -2 Organizational Chart of a Small Restaurant
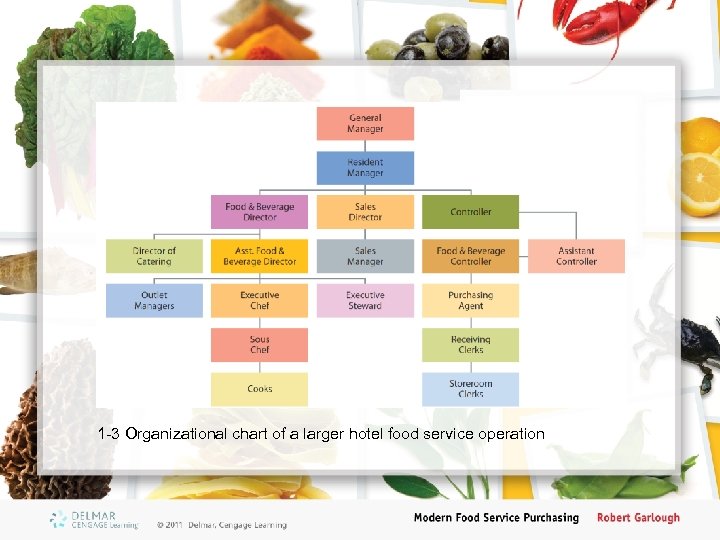 1 -3 Organizational chart of a larger hotel food service operation
1 -3 Organizational chart of a larger hotel food service operation
 Required Attributes and Knowledge • Ethical standards – Honest and fair treatment of all • Conceptual skills – Understands relationships between functions and how actions affect society • Communication skills – Listen to and articulate needs
Required Attributes and Knowledge • Ethical standards – Honest and fair treatment of all • Conceptual skills – Understands relationships between functions and how actions affect society • Communication skills – Listen to and articulate needs
 Required Attributes and Knowledge (cont’d. ) • • • Mathematical skills Computer skills Market awareness Understand laws of commerce Product knowledge – Obtained by exposure to various forms of food products
Required Attributes and Knowledge (cont’d. ) • • • Mathematical skills Computer skills Market awareness Understand laws of commerce Product knowledge – Obtained by exposure to various forms of food products
 Storeroom Policies and Procedures • Develop a policies and procedures manual – Addresses who does what and when in purchasing – Includes supplier selection criteria – Guidelines on sales calls and accepting gifts from suppliers
Storeroom Policies and Procedures • Develop a policies and procedures manual – Addresses who does what and when in purchasing – Includes supplier selection criteria – Guidelines on sales calls and accepting gifts from suppliers
 The Seller • Buyer must establish mutually satisfying relationships with sellers (purveyors) • When sellers are successful: – They can broaden their product line – There are more to choose from, ensuring competitive pricing
The Seller • Buyer must establish mutually satisfying relationships with sellers (purveyors) • When sellers are successful: – They can broaden their product line – There are more to choose from, ensuring competitive pricing
 Selecting Sellers • Respect is important • Research food service resources – Internet commerce – Local suppliers – National distributors • Broadline distributors have wide product range
Selecting Sellers • Respect is important • Research food service resources – Internet commerce – Local suppliers – National distributors • Broadline distributors have wide product range
 Selecting Sellers (cont’d. ) • Set up an introductory meeting – Prepare a list of questions to ask – Keep the meeting to one hour • Inspect the purveyor’s facilities – Look for sanitary conditions and practices
Selecting Sellers (cont’d. ) • Set up an introductory meeting – Prepare a list of questions to ask – Keep the meeting to one hour • Inspect the purveyor’s facilities – Look for sanitary conditions and practices
 Establishing Purchasing Options and Contracts • Inquire about purchasing options – Formal or informal arrangements • Depends on size and structure of seller’s organization or buyer’s business – Cooperative buying • Group formed to buy directly from source in large quantities
Establishing Purchasing Options and Contracts • Inquire about purchasing options – Formal or informal arrangements • Depends on size and structure of seller’s organization or buyer’s business – Cooperative buying • Group formed to buy directly from source in large quantities
 Purchasing Service and Maintenance Contracts • Food service operators enter into contracts with outside service vendors – Some examples: • Pest control, waste removal and recycling, cleaning, facility and equipment maintenance, laundry and linen supply, bookkeeping, legal, insurance, utilities, advertising, flowers and plants, and vending machines
Purchasing Service and Maintenance Contracts • Food service operators enter into contracts with outside service vendors – Some examples: • Pest control, waste removal and recycling, cleaning, facility and equipment maintenance, laundry and linen supply, bookkeeping, legal, insurance, utilities, advertising, flowers and plants, and vending machines
 Informal Buying Practices • Practiced by smaller operations where chef or owner does the buying • Advantages of informal buying – Takes little time away from daily operations – Varying quantity needs can be addressed – Urgent needs may be addressed quickly – Take advantage of price fluctuations
Informal Buying Practices • Practiced by smaller operations where chef or owner does the buying • Advantages of informal buying – Takes little time away from daily operations – Varying quantity needs can be addressed – Urgent needs may be addressed quickly – Take advantage of price fluctuations
 Formal Buying Practices • Bid buying – Buyer requests price quotation from sellers • Cost plus fixed fee buying – Agreement with distributor fixed markup above their costs
Formal Buying Practices • Bid buying – Buyer requests price quotation from sellers • Cost plus fixed fee buying – Agreement with distributor fixed markup above their costs
 Formal Buying Practices (cont’d. ) • Volume buying and warehousing – Goods are held by supplier and delivered as needed • Prime vendor contracts – Similar to cost plus fixed fee but multiple vendors are used
Formal Buying Practices (cont’d. ) • Volume buying and warehousing – Goods are held by supplier and delivered as needed • Prime vendor contracts – Similar to cost plus fixed fee but multiple vendors are used
 Formal Buying Practices (cont’d. ) • Long term contracts – Based on fixed prices; delivered as needed • Hedging (forward buying) – Buying quantities before they are needed to avoid price increases – If price falls, buyer loses
Formal Buying Practices (cont’d. ) • Long term contracts – Based on fixed prices; delivered as needed • Hedging (forward buying) – Buying quantities before they are needed to avoid price increases – If price falls, buyer loses
 The Buying Process • Buying occurs after menu planning is completed • Buying consists of three major steps – Identifying the need – Planning for the purchase – Making the purchase
The Buying Process • Buying occurs after menu planning is completed • Buying consists of three major steps – Identifying the need – Planning for the purchase – Making the purchase
 Identifying the Need • Determine stock levels – Consider shelf life – Minimum quantity known as safety stock • Consider normal usage rates • Determine whether additional quantities are needed for special events
Identifying the Need • Determine stock levels – Consider shelf life – Minimum quantity known as safety stock • Consider normal usage rates • Determine whether additional quantities are needed for special events
 Planning for the Purchase • Determine rate at which operation uses the items • Compare quantities needed with stock on hand • Prepare an order sheet • Consider urgency of needing products
Planning for the Purchase • Determine rate at which operation uses the items • Compare quantities needed with stock on hand • Prepare an order sheet • Consider urgency of needing products
 Making the Purchase • List of selected and approved suppliers • Identify local retailers that carry product • Create an order record – Column for each vendor on the form • Completed order forms saved in a secure location • Use purchase order or blanket P. O.
Making the Purchase • List of selected and approved suppliers • Identify local retailers that carry product • Create an order record – Column for each vendor on the form • Completed order forms saved in a secure location • Use purchase order or blanket P. O.
 Making the Purchase (cont’d. ) • Standing orders – Volume commitment for daily delivery • Daily orders – Delivered within 24 hours • Drop shipments – Seller arranges for wholesaler or manufacturer to deliver to buyer directly
Making the Purchase (cont’d. ) • Standing orders – Volume commitment for daily delivery • Daily orders – Delivered within 24 hours • Drop shipments – Seller arranges for wholesaler or manufacturer to deliver to buyer directly
 Buyer-Seller Relations: A Win-Win Approach • Relationships between buyers and sellers should be mutually beneficial – When both parties consider relationship advantageous, future business together is sought after and encouraged
Buyer-Seller Relations: A Win-Win Approach • Relationships between buyers and sellers should be mutually beneficial – When both parties consider relationship advantageous, future business together is sought after and encouraged
 Conducting Sales Meetings • Regularly scheduled and planned in advance • Negotiate purchases – Create partnerships – Understand the needs of both parties – Know yourself
Conducting Sales Meetings • Regularly scheduled and planned in advance • Negotiate purchases – Create partnerships – Understand the needs of both parties – Know yourself
 Supplier Performance Evaluation • Evaluate both the product and the process • Develop a cross-functional team to identify priorities that should be evaluated – Define most important factors to evaluate – Determine a rating scale
Supplier Performance Evaluation • Evaluate both the product and the process • Develop a cross-functional team to identify priorities that should be evaluated – Define most important factors to evaluate – Determine a rating scale
 Ethical and Professional Standards and Practices • Management should articulate ethical standards of the organization • Management may not benefit personally from the company’s financial gains • Do not allow conflict of interest • Avoid tips, supplier gifts, or bonuses
Ethical and Professional Standards and Practices • Management should articulate ethical standards of the organization • Management may not benefit personally from the company’s financial gains • Do not allow conflict of interest • Avoid tips, supplier gifts, or bonuses
 Summary • Buyers and sellers should strive for a mutually beneficial relationship • Many different types of purchasing exist • Developing a policies and procedures manual is important • Evaluating suppliers and maintaining ethical standards key for success
Summary • Buyers and sellers should strive for a mutually beneficial relationship • Many different types of purchasing exist • Developing a policies and procedures manual is important • Evaluating suppliers and maintaining ethical standards key for success


