 • The pumping of the heart sends out blood under pressure to the arteries. • Blood pressure is greatest in the aorta; the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than that of the right ventricle and pumps blood to the entire body. • Blood pressure then decreases as the cross -sectional area of arteries and then arterioles increases.
• The pumping of the heart sends out blood under pressure to the arteries. • Blood pressure is greatest in the aorta; the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than that of the right ventricle and pumps blood to the entire body. • Blood pressure then decreases as the cross -sectional area of arteries and then arterioles increases.
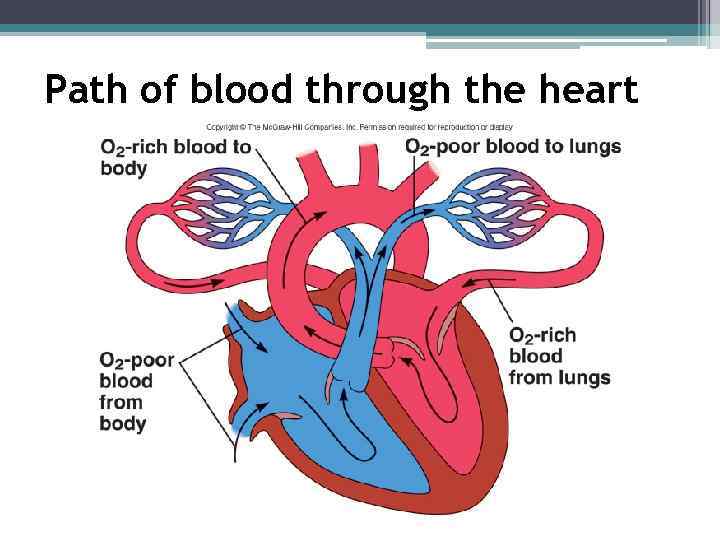 Path of blood through the heart
Path of blood through the heart
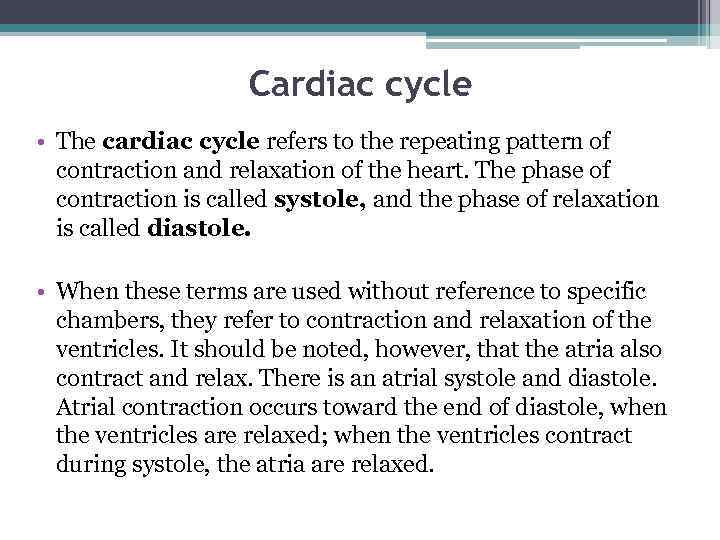 Cardiac cycle • The cardiac cycle refers to the repeating pattern of contraction and relaxation of the heart. The phase of contraction is called systole, and the phase of relaxation is called diastole. • When these terms are used without reference to specific chambers, they refer to contraction and relaxation of the ventricles. It should be noted, however, that the atria also contract and relax. There is an atrial systole and diastole. Atrial contraction occurs toward the end of diastole, when the ventricles are relaxed; when the ventricles contract during systole, the atria are relaxed.
Cardiac cycle • The cardiac cycle refers to the repeating pattern of contraction and relaxation of the heart. The phase of contraction is called systole, and the phase of relaxation is called diastole. • When these terms are used without reference to specific chambers, they refer to contraction and relaxation of the ventricles. It should be noted, however, that the atria also contract and relax. There is an atrial systole and diastole. Atrial contraction occurs toward the end of diastole, when the ventricles are relaxed; when the ventricles contract during systole, the atria are relaxed.
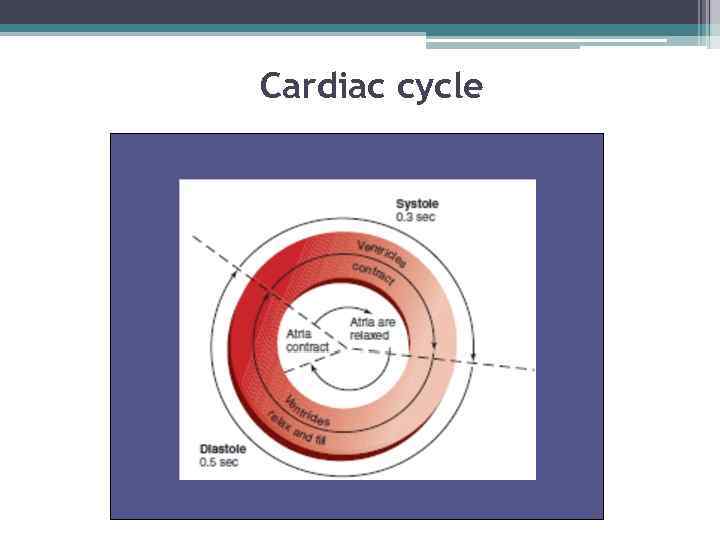 Cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle
 Cardiac Output • Volume of blood pumped per unit time from the ventricle • In mammals this is the volume ejected from either the left or right ventricle, not the combined total • Volume of blood ejected per beat is the stroke volume • Stroke volume determined by dividing cardiac output by heart rate
Cardiac Output • Volume of blood pumped per unit time from the ventricle • In mammals this is the volume ejected from either the left or right ventricle, not the combined total • Volume of blood ejected per beat is the stroke volume • Stroke volume determined by dividing cardiac output by heart rate
 The Heartbeat • Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. • When the heart beats, the two atria contract together, then the two ventricles contract; then the whole heart relaxes. • The heart sounds, lub-dup, are due to the closing of the atrioventricular valves, followed by the closing of the semilunar valves.
The Heartbeat • Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. • When the heart beats, the two atria contract together, then the two ventricles contract; then the whole heart relaxes. • The heart sounds, lub-dup, are due to the closing of the atrioventricular valves, followed by the closing of the semilunar valves.
 Heart rate • • • - Normal range is 60 -100 beats per minute - Tachycardia is greater than 100 bpm - Bradycardia is less than 60 bpm - Sympathetic system INCREASES HR - Parasympathetic system (Vagus) DECREASES HR (CBQ)
Heart rate • • • - Normal range is 60 -100 beats per minute - Tachycardia is greater than 100 bpm - Bradycardia is less than 60 bpm - Sympathetic system INCREASES HR - Parasympathetic system (Vagus) DECREASES HR (CBQ)
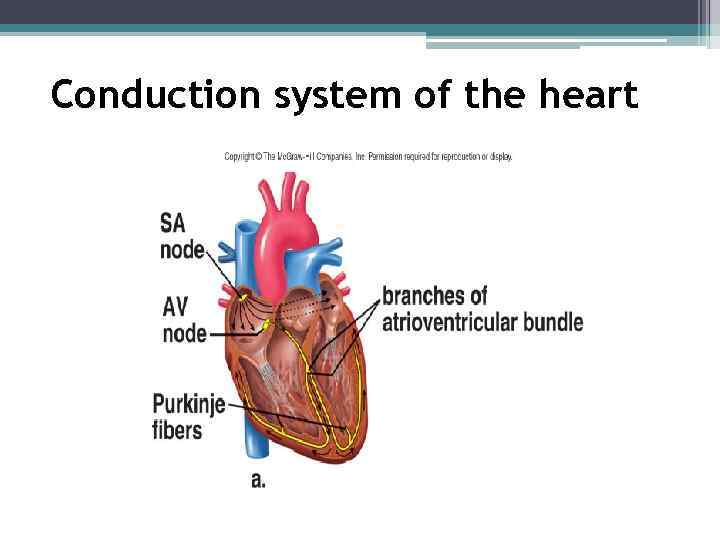 Conduction system of the heart
Conduction system of the heart
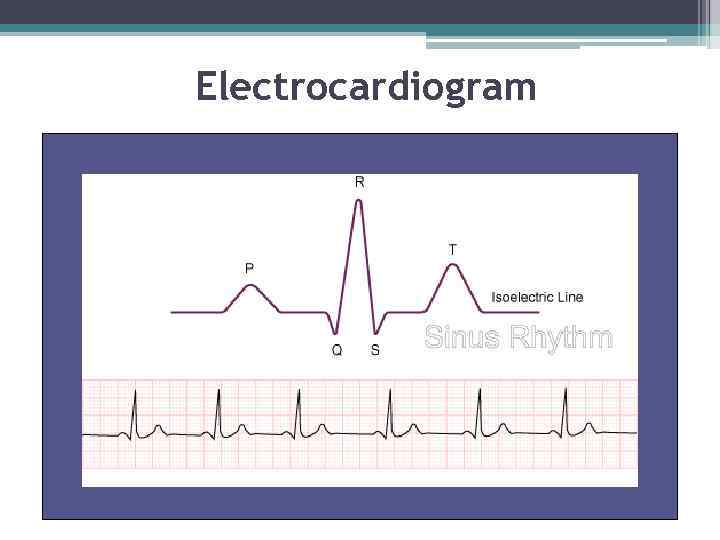
 The Electrocardiogram • An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of the electrical changes that occur in the myocardium during a cardiac cycle. • Atrial depolarization creates the P wave, ventricle depolarization creates the QRS wave, and repolarization of the ventricles produces the T wave.
The Electrocardiogram • An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of the electrical changes that occur in the myocardium during a cardiac cycle. • Atrial depolarization creates the P wave, ventricle depolarization creates the QRS wave, and repolarization of the ventricles produces the T wave.
 Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram