4b6a43e7b58ff1dcc8e202631277a3bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 The Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction
The Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction
 Today’s overview • History of WMD Chemical, Bio, Nuke • International Treaties • Nuclear Weapons Today • North Korea, Iraq, Pakistan • Iran?
Today’s overview • History of WMD Chemical, Bio, Nuke • International Treaties • Nuclear Weapons Today • North Korea, Iraq, Pakistan • Iran?
 World War I
World War I
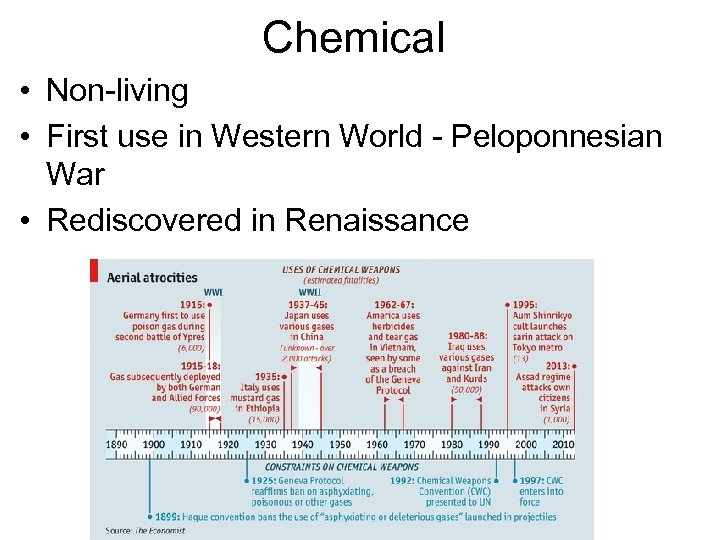 Chemical • Non-living • First use in Western World - Peloponnesian War • Rediscovered in Renaissance
Chemical • Non-living • First use in Western World - Peloponnesian War • Rediscovered in Renaissance
 Chemical - Modern uses • Iraq-Iran War • “Is military research hazardous to veteran’s health? ” (1994) US Senate • Japan - Aum Shinrikyo • Russian forces - Moscow theater hostages
Chemical - Modern uses • Iraq-Iran War • “Is military research hazardous to veteran’s health? ” (1994) US Senate • Japan - Aum Shinrikyo • Russian forces - Moscow theater hostages
 The Chemical Threat
The Chemical Threat
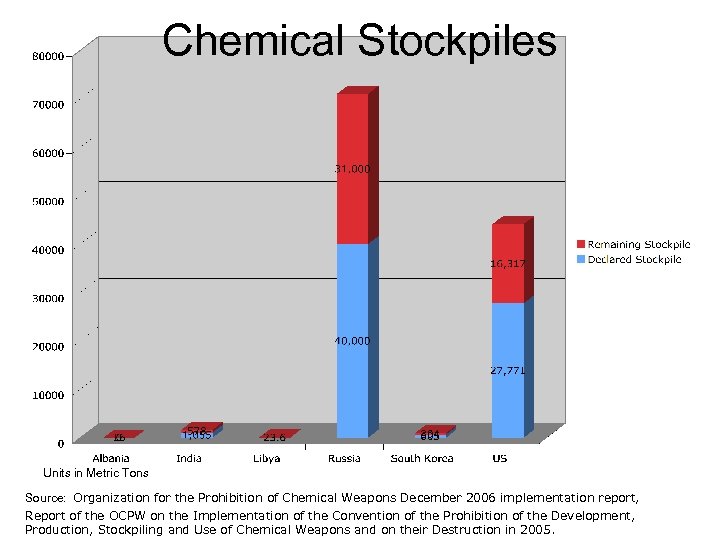 Chemical Stockpiles Units in Metric Tons Source: Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons December 2006 implementation report, Report of the OCPW on the Implementation of the Convention of the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on their Destruction in 2005.
Chemical Stockpiles Units in Metric Tons Source: Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons December 2006 implementation report, Report of the OCPW on the Implementation of the Convention of the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on their Destruction in 2005.
 Biological • Living organisms – Anthrax • • • Cold War focused on retaliation A Poor Nation’s WMD Iraq Nearly impossible to detect Dual-use technologies
Biological • Living organisms – Anthrax • • • Cold War focused on retaliation A Poor Nation’s WMD Iraq Nearly impossible to detect Dual-use technologies
 The Biological Threat • H 5 N 1/Bird Flu • 1918 “Spanish Lady”
The Biological Threat • H 5 N 1/Bird Flu • 1918 “Spanish Lady”
 International Treaties • 1899 Hague Conference – Navy Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan - "the inventiveness of Americans should not be restricted in the development of new weapons. " • 1925 Geneva Protocol – Bans chemical & biological weapons – Nothing on production, storage, or transfer • 1993 Chemical Weapons Convention
International Treaties • 1899 Hague Conference – Navy Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan - "the inventiveness of Americans should not be restricted in the development of new weapons. " • 1925 Geneva Protocol – Bans chemical & biological weapons – Nothing on production, storage, or transfer • 1993 Chemical Weapons Convention
 Chemical Weapons Convention Bans: * Developing, producing, acquiring, stockpiling, or retaining chemical weapons. * The direct or indirect transfer of chemical weapons. * Chemical weapons use or military preparation for use. * Assisting, encouraging, or inducing other states to engage in CWC-prohibited activity. * The use of riot control agents “as a method of warfare. ” –Didn’t ratify/sign: Bahamas, Congo, Dominican Republic, Guinea-Bissau, Israel, Myanmar, Angola, North Korea, Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, Somalia, Syria
Chemical Weapons Convention Bans: * Developing, producing, acquiring, stockpiling, or retaining chemical weapons. * The direct or indirect transfer of chemical weapons. * Chemical weapons use or military preparation for use. * Assisting, encouraging, or inducing other states to engage in CWC-prohibited activity. * The use of riot control agents “as a method of warfare. ” –Didn’t ratify/sign: Bahamas, Congo, Dominican Republic, Guinea-Bissau, Israel, Myanmar, Angola, North Korea, Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, Somalia, Syria
 Biological Weapons Treaties • 1972 Biological Weapons Convention – 158 states – Bans creation & storage, but not usage – Also applies to private parties • Reviews in early 1990 s, US says “not in national interest” before 9/11. – 2003: National mechanisms for security – 2004: Enhancing international response to disease/outbreaks – 2004: strengthens detection & capabilities – 2005: codes of conduct for scientists
Biological Weapons Treaties • 1972 Biological Weapons Convention – 158 states – Bans creation & storage, but not usage – Also applies to private parties • Reviews in early 1990 s, US says “not in national interest” before 9/11. – 2003: National mechanisms for security – 2004: Enhancing international response to disease/outbreaks – 2004: strengthens detection & capabilities – 2005: codes of conduct for scientists
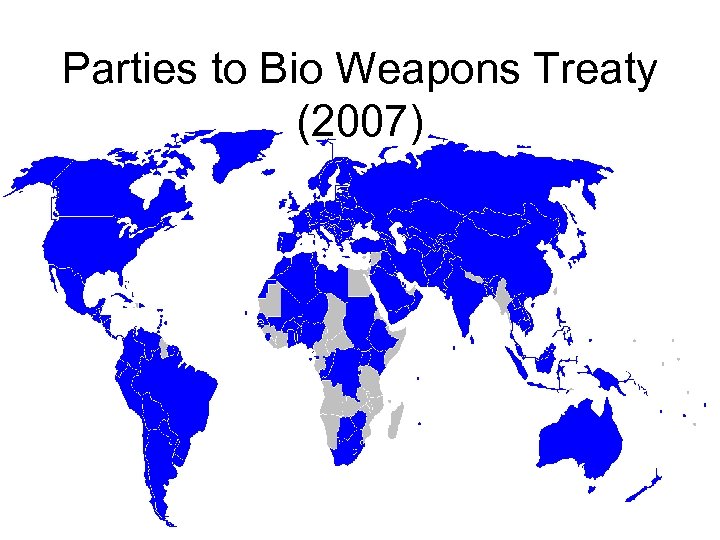 Parties to Bio Weapons Treaty (2007)
Parties to Bio Weapons Treaty (2007)
 The Manhattan Project • University of Chicago • Oakridge TN (K -25, Y-12, S-50) for U-235 • Hanford WA for Plutonium • Los Alamos NM for Bomb Assembly & Test
The Manhattan Project • University of Chicago • Oakridge TN (K -25, Y-12, S-50) for U-235 • Hanford WA for Plutonium • Los Alamos NM for Bomb Assembly & Test
 The Manhattan Project Separating U 235 & U 238 • Gaseous Diffusion • Electromagnetic Separation • Thermal Diffusion • Centrifuge Separation YF 12 Calutron Operation - Oakridge
The Manhattan Project Separating U 235 & U 238 • Gaseous Diffusion • Electromagnetic Separation • Thermal Diffusion • Centrifuge Separation YF 12 Calutron Operation - Oakridge
 Nuclear Weapons • First known nuclear test was done in New Mexico on July 16 th 1945 • How many tests to date? • US bombs Hiroshima & Nagasaki • USSR tests weapon in 1949 • Hydrogen bomb • Only countries to test weapons: US, Russia, UK, France, India, China, Pakistan, and North Korea (possibly South Africa/Israel).
Nuclear Weapons • First known nuclear test was done in New Mexico on July 16 th 1945 • How many tests to date? • US bombs Hiroshima & Nagasaki • USSR tests weapon in 1949 • Hydrogen bomb • Only countries to test weapons: US, Russia, UK, France, India, China, Pakistan, and North Korea (possibly South Africa/Israel).
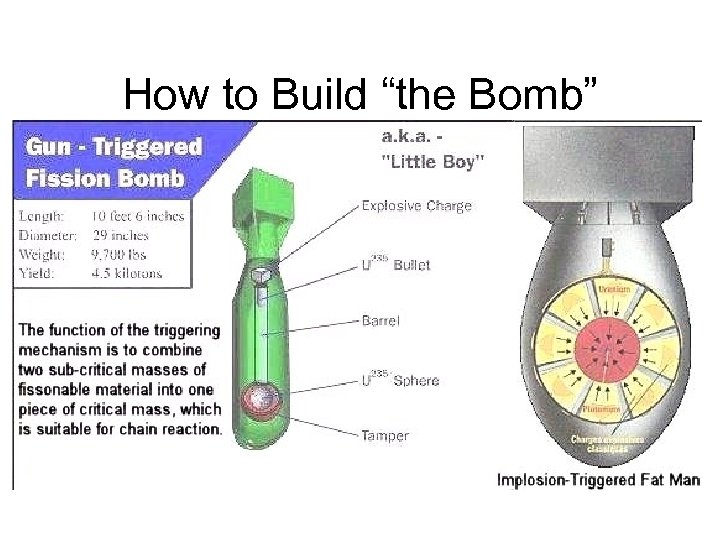 How to Build “the Bomb”
How to Build “the Bomb”
 “Little Boy” Hiroshima
“Little Boy” Hiroshima
 Fat Man - Nagasaki
Fat Man - Nagasaki
 NPT • 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty – Prohibits all above ground testing • 1968 Non-Proliferation Treaty – Except: India, Israel, Pakistan, North Korea – Non-proflieration, Disarmament, Peaceful Use – IAEA
NPT • 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty – Prohibits all above ground testing • 1968 Non-Proliferation Treaty – Except: India, Israel, Pakistan, North Korea – Non-proflieration, Disarmament, Peaceful Use – IAEA
 The Nuclear Non. Proliferation Treaty 1968 • • Ratified by 188 states Atoms for Peace 1. IAEA – dual mission of prevention & promotion 2. The Fissile Bank - Failure 3. Goal of disarmament - Failure • The “Big Five” (haves) v. “have-nots”
The Nuclear Non. Proliferation Treaty 1968 • • Ratified by 188 states Atoms for Peace 1. IAEA – dual mission of prevention & promotion 2. The Fissile Bank - Failure 3. Goal of disarmament - Failure • The “Big Five” (haves) v. “have-nots”
 Giving up nukes • South America - Treaty of Tlatelolco (‘ 67) – Weapons-Free Zone – Gave up programs: Argentina & Brazil – Nobel Prizes to creators of treaty • South Africa – Relinquishes weapons after apartheid
Giving up nukes • South America - Treaty of Tlatelolco (‘ 67) – Weapons-Free Zone – Gave up programs: Argentina & Brazil – Nobel Prizes to creators of treaty • South Africa – Relinquishes weapons after apartheid
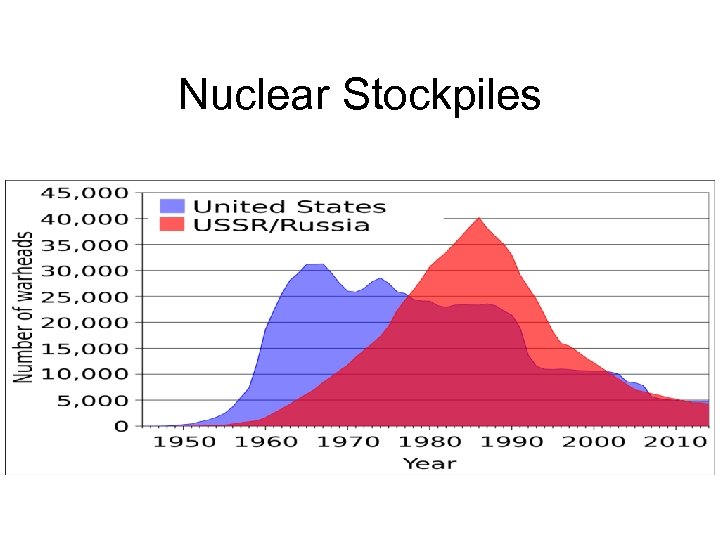 Nuclear Stockpiles
Nuclear Stockpiles
 Loose Nukes • • Cold War “Near Misses” Deterrence and Balance of Power The Former Soviet Union: Nunn/Luger A “Dirty Bomb” Military Utility of Nuclear Weapons Regime Security AQ Khan and the Black Market
Loose Nukes • • Cold War “Near Misses” Deterrence and Balance of Power The Former Soviet Union: Nunn/Luger A “Dirty Bomb” Military Utility of Nuclear Weapons Regime Security AQ Khan and the Black Market
 Chemical & Biological Weapons • • • Easier to make Easier to deploy Harder to detect Harder to fix blame Can be used in an asymmetrical context • Therefore, harder to deter
Chemical & Biological Weapons • • • Easier to make Easier to deploy Harder to detect Harder to fix blame Can be used in an asymmetrical context • Therefore, harder to deter
 WMD - Case Studies North Korea, Iraq, Pakistan & Iran
WMD - Case Studies North Korea, Iraq, Pakistan & Iran
 Nuclear State of the World: N. Korea • • KFR Withdrew from NNPT in 1985 Clinton Agreement The North Korean “Detonation” on Oct. 9 th 2006 • Bush Agreement
Nuclear State of the World: N. Korea • • KFR Withdrew from NNPT in 1985 Clinton Agreement The North Korean “Detonation” on Oct. 9 th 2006 • Bush Agreement
 New Regime 2011 Kim Jong Un
New Regime 2011 Kim Jong Un
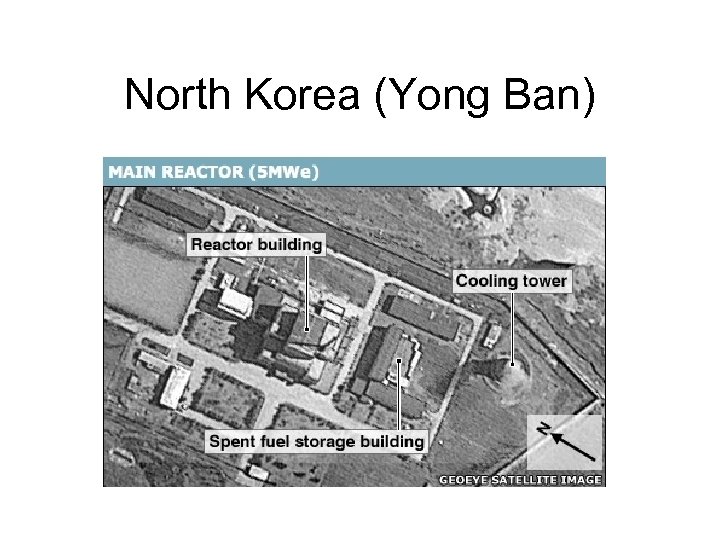 North Korea (Yong Ban)
North Korea (Yong Ban)
 N. Korea - Potential Disaster • -Formidable Threat: 1. 2 million soldiers, 100, 000 elite forces, one of the world’s largest chemical and biological weapons arsenals. One million South Koreans live within Artillery range. • -Deployment of weapons of mass destruction: Believed to have 30 -60 nuclear warheads, the likelihood of their use increases with greater regime instability. Hwasong-14 can hit the US with potentially a Hydrogen warhead
N. Korea - Potential Disaster • -Formidable Threat: 1. 2 million soldiers, 100, 000 elite forces, one of the world’s largest chemical and biological weapons arsenals. One million South Koreans live within Artillery range. • -Deployment of weapons of mass destruction: Believed to have 30 -60 nuclear warheads, the likelihood of their use increases with greater regime instability. Hwasong-14 can hit the US with potentially a Hydrogen warhead
 Potential Disaster (con’t) • -Regime Collapse: “collapse of the chain of command of the KFR could be more dangerous than the preservation of it, particularly when one considers control over WMD. ” -Colonel Maxwell, • -Refugee Crisis: South Koreans and Chinese fear an influx of refugees more than NK missiles. “Mother of all relief operations”: The US could be presented with the greatest stabilization effort since WWII, and have to coordinate operations with the Chinese PLA.
Potential Disaster (con’t) • -Regime Collapse: “collapse of the chain of command of the KFR could be more dangerous than the preservation of it, particularly when one considers control over WMD. ” -Colonel Maxwell, • -Refugee Crisis: South Koreans and Chinese fear an influx of refugees more than NK missiles. “Mother of all relief operations”: The US could be presented with the greatest stabilization effort since WWII, and have to coordinate operations with the Chinese PLA.
 Kim Jong Un’s Objectives • 1: Preserve the Regime – Maintain US enemy to justify hardships of the people • 2: Gain acceptance to the international community and get sanctions lifted • 3: Split the alliance between South Korea and the U. S. Support in SK for US intervention has dwindled, & many may rally to nationalist calls for the US not to interfere.
Kim Jong Un’s Objectives • 1: Preserve the Regime – Maintain US enemy to justify hardships of the people • 2: Gain acceptance to the international community and get sanctions lifted • 3: Split the alliance between South Korea and the U. S. Support in SK for US intervention has dwindled, & many may rally to nationalist calls for the US not to interfere.
 Kim Jong Un’s Objectives • 4: Manipulate the South Korean left (by Force or by guile) – Olympic diplomacy – by inflicting sufficient damage to press them to seek a negotiated settlement. – provoke American attacks to cause them to place blame on the US for the violence. • 5: Nuclear Blackmail or Deterrence? -(Everyone thought Kim Il Sung was too weak to invade in 1950) -Force US withdrawal from the Peninsula (or at least stop exercises.
Kim Jong Un’s Objectives • 4: Manipulate the South Korean left (by Force or by guile) – Olympic diplomacy – by inflicting sufficient damage to press them to seek a negotiated settlement. – provoke American attacks to cause them to place blame on the US for the violence. • 5: Nuclear Blackmail or Deterrence? -(Everyone thought Kim Il Sung was too weak to invade in 1950) -Force US withdrawal from the Peninsula (or at least stop exercises.
 Cyber War – “The Interview” • • Took out 70% of Sony Pictures computer system Ransomware attacks on UK hospitals Bangladesh Central Bank US Attacks on North Korea (Missile Sabotage)
Cyber War – “The Interview” • • Took out 70% of Sony Pictures computer system Ransomware attacks on UK hospitals Bangladesh Central Bank US Attacks on North Korea (Missile Sabotage)
 What Can the US/Global Community Do? • China’s role • Increase/Decrease Sanctions – 1990 Famine Killed 1/10 of population • Freeze Exercises • Accept North Korea as a nuclear power – Like Pakistan or India • Attack North Korea 10 K US dependents near Seoul • Trump rhetoric – “Little rocket Man” • Containment
What Can the US/Global Community Do? • China’s role • Increase/Decrease Sanctions – 1990 Famine Killed 1/10 of population • Freeze Exercises • Accept North Korea as a nuclear power – Like Pakistan or India • Attack North Korea 10 K US dependents near Seoul • Trump rhetoric – “Little rocket Man” • Containment
 Reunification • Regional BOP – Centers on China – Threat to Japan? • Cost to South Korea • Kim Jong Un?
Reunification • Regional BOP – Centers on China – Threat to Japan? • Cost to South Korea • Kim Jong Un?
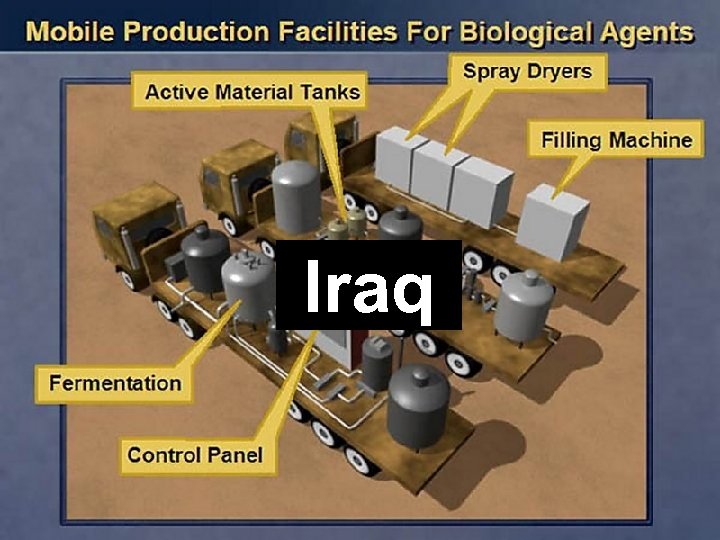 Iraq
Iraq
 Iraq • Uses poison gas in Iran-Iraq War, also against Kurds • Iraq in the 90’s. 1991: Gulf War ends, UN weapons inspectors begin work in the Iraq. 1992 -94: Iraq largely disarmed of WMD’s, while retaining some research and development capabilities 1995 -96: Saddam’s remaining WMD programs wind down. Period of weakened internal security and political turmoil. High-level officials defect. 1998: Saddam kicks out weapons inspectors, arousing international suspicion.
Iraq • Uses poison gas in Iran-Iraq War, also against Kurds • Iraq in the 90’s. 1991: Gulf War ends, UN weapons inspectors begin work in the Iraq. 1992 -94: Iraq largely disarmed of WMD’s, while retaining some research and development capabilities 1995 -96: Saddam’s remaining WMD programs wind down. Period of weakened internal security and political turmoil. High-level officials defect. 1998: Saddam kicks out weapons inspectors, arousing international suspicion.
 What we thought (Pollock • Iraq continues WMD programs in defiance of sanctions. • Iraq will have a nuke w/i a decade or 1 year if it can acquire fissile materiel from abroad. • Iraq has invested heavily in missile tech • Iraq has renewed production of chemical agents and it researching weaponization of bio agents
What we thought (Pollock • Iraq continues WMD programs in defiance of sanctions. • Iraq will have a nuke w/i a decade or 1 year if it can acquire fissile materiel from abroad. • Iraq has invested heavily in missile tech • Iraq has renewed production of chemical agents and it researching weaponization of bio agents
 What we now know to be true! • Iraq had preserved some nuclear technology, but had not restarted its nuclear program. • No chemical weapons or bio weapons were produced, but some research was carried out and 1 bio lab was maintained clandestinely. • Saddam was most aggressive in pursuit of ballistic missile technology.
What we now know to be true! • Iraq had preserved some nuclear technology, but had not restarted its nuclear program. • No chemical weapons or bio weapons were produced, but some research was carried out and 1 bio lab was maintained clandestinely. • Saddam was most aggressive in pursuit of ballistic missile technology.
 • Overselling the case • Correcting intelligence problems
• Overselling the case • Correcting intelligence problems
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 AQ Khan “provided the country—single handedly, it was widely believed—with an arsenal of nuclear weapons (Langewiesche, 2005). ”
AQ Khan “provided the country—single handedly, it was widely believed—with an arsenal of nuclear weapons (Langewiesche, 2005). ”
 AQ Khan • Background • Spread technology to: – Iran, Libya, and North Korea – Transfer to non-state actors? • Pakistani & US Reaction
AQ Khan • Background • Spread technology to: – Iran, Libya, and North Korea – Transfer to non-state actors? • Pakistani & US Reaction
 IRAN
IRAN
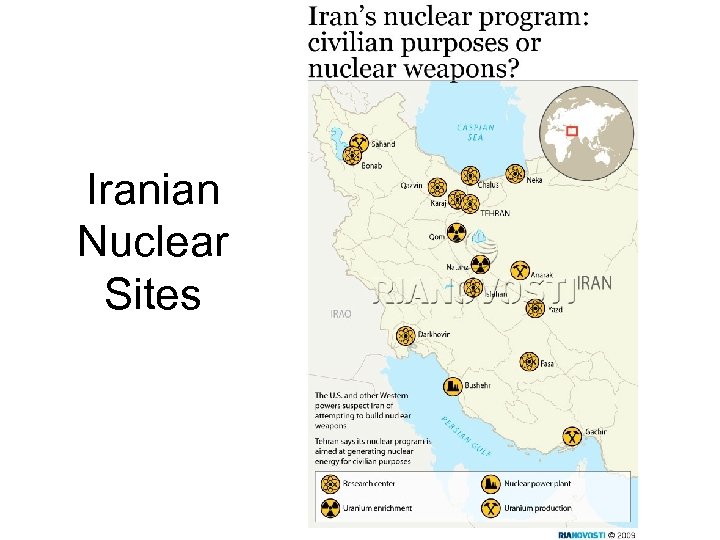 Iranian Nuclear Sites
Iranian Nuclear Sites
 What will US/Israel do?
What will US/Israel do?
 Obama’s Nuclear Policy • World w/o Nukes, but role remains deterrence • Renounce 1 st Use • Will not use nuclear weapons to retaliate against a non-nuclear state (including Chem/Bio) • Remove all weapons from alert status • Control all fissile materiel
Obama’s Nuclear Policy • World w/o Nukes, but role remains deterrence • Renounce 1 st Use • Will not use nuclear weapons to retaliate against a non-nuclear state (including Chem/Bio) • Remove all weapons from alert status • Control all fissile materiel
 Trump’s Nuclear Policy ?
Trump’s Nuclear Policy ?


