44bbf8c886b29f13033c38daa4fce994.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
The Project : Enabling Data Intensive Science at Universities http: //ultralight. org Collaboration Caltech (lead inst. ) BNL Michigan MIT Florida International FNAL San Diego SLAC Vanderbilt R. Cavanaugh University of Florida (Richard. Cavanaugh@cern. ch) T 3 Meeting Princeton 1

Ultra. Light: A New Class of Integrated Information Systems • Delivering the next generation of network-aware realtime Grids – The network as an integrated, managed resource – Hybrid packet-switched + dynamic optical paths • Leveraging Trans-US, Transatlantic & Transpacific network partnerships; – With ESnet, USNet, KEK, Kreonet, GLORIAD, CHEPREO, WHREN/LILA, Awave, FLR, Pacific Wave, Translight, Netherlight – Extensions to Korea, Brazil, Japan and Taiwan • MONALISA/VINCI: End-to-end monitoring, tracking, dynamic BW provisioning and workflow optimization 2
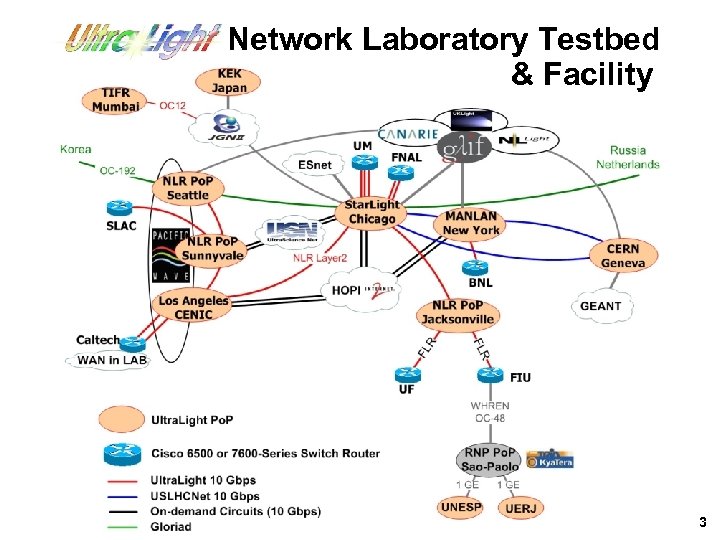
Ultra. Light Network Laboratory Testbed & Facility 3
![http: //supercomputing. caltech. edu/ 100 Gbps mark 0 Cumulative [TB] Example: • Supercomputing 2005 http: //supercomputing. caltech. edu/ 100 Gbps mark 0 Cumulative [TB] Example: • Supercomputing 2005](https://present5.com/presentation/44bbf8c886b29f13033c38daa4fce994/image-4.jpg)
http: //supercomputing. caltech. edu/ 100 Gbps mark 0 Cumulative [TB] Example: • Supercomputing 2005 • 151 Gbps peak rate • 100+ Gbps sustained throughput for hours • 475 Terabytes of physics data transported in less than 24 hours • Sustained rate of 100+ Gb/s translates to > 1 Petabyte per day Testbed? Rate [Gbs] What is Achievable on the 15 30 45 60 t [min] 18 24 t [hours] 476 TB Aggregate in 24 hours 0 6 12 End-2 -end monitoring using Mon. ALISA 4
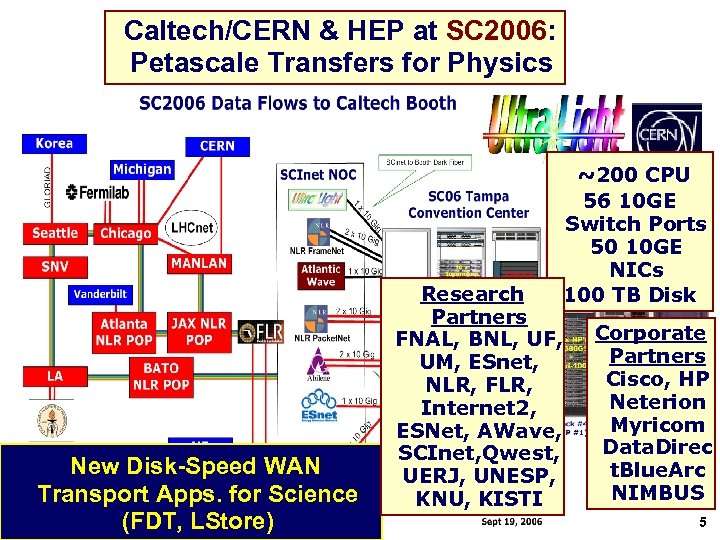
Caltech/CERN & HEP at SC 2006: Petascale Transfers for Physics ~200 CPU 56 10 GE Switch Ports 50 10 GE NICs 100 TB Disk New Disk-Speed WAN Transport Apps. for Science (FDT, LStore) Research Partners FNAL, BNL, UF, UM, ESnet, NLR, FLR, Internet 2, ESNet, AWave, SCInet, Qwest, UERJ, UNESP, KNU, KISTI Corporate Partners Cisco, HP Neterion Myricom Data. Direc t. Blue. Arc NIMBUS 5
FDT – Fast Data Transport A New Application for Efficient Data Transfers http: //monalisa. cern. ch/FDT/ • Reading and writing at disk speed over wide area networks (standard TCP) for the first time • Portable and easy to use: runs on all major platforms. • Based on an asynchronous, flexible multithreaded system, using the Java NIO libraries, that: – Streams a dataset (list of files) continuously, from a managed pool of buffers in kernel space, through an open TCP socket – Smooth flow of data from each disk – No protocol start phase between files • Uses independent threads to read and write on each physical device • Transfers data in parallel on multiple TCP streams, when necessary • Uses appropriate-sized buffers for disk I/O and for the network • Restores the files from buffers asynchronously • Resumes a file transfer session without loss, when needed • GSI Authentication built in FDT being deployed within the Alice experiment 6
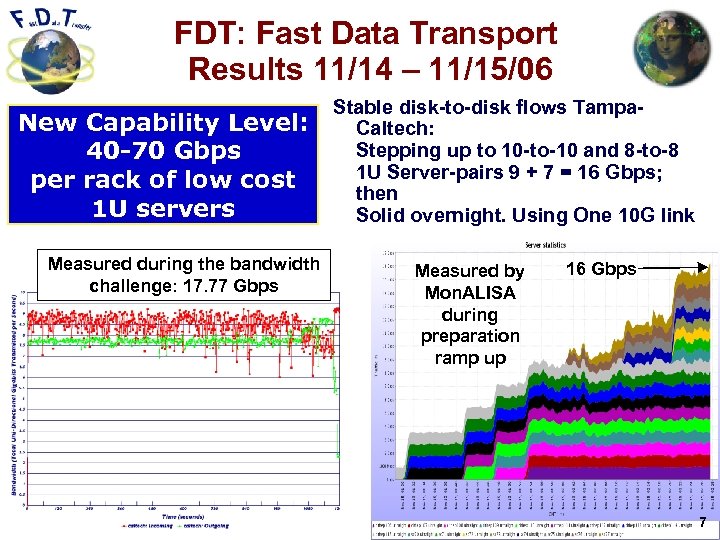
FDT: Fast Data Transport Results 11/14 – 11/15/06 New Capability Level: 40 -70 Gbps per rack of low cost 1 U servers Measured during the bandwidth challenge: 17. 77 Gbps Stable disk-to-disk flows Tampa. Caltech: Stepping up to 10 -to-10 and 8 -to-8 1 U Server-pairs 9 + 7 = 16 Gbps; then Solid overnight. Using One 10 G link Measured by Mon. ALISA during preparation ramp up 16 Gbps 7
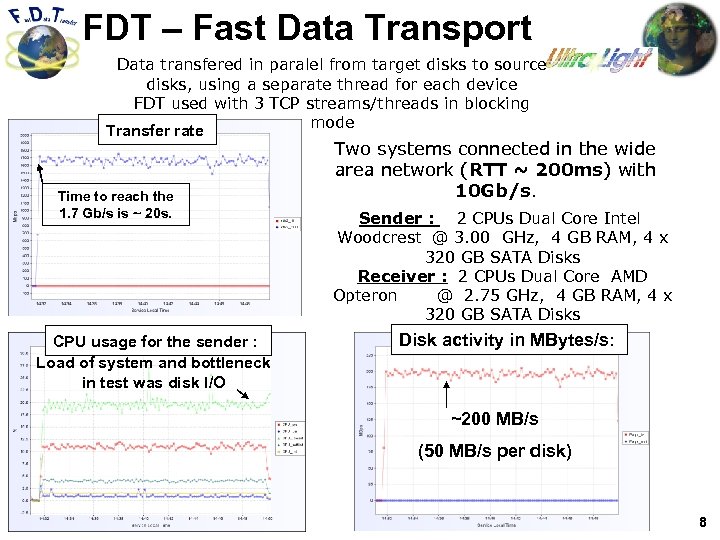
FDT – Fast Data Transport Data transfered in paralel from target disks to source disks, using a separate thread for each device FDT used with 3 TCP streams/threads in blocking mode Transfer rate Time to reach the 1. 7 Gb/s is ~ 20 s. CPU usage for the sender : Load of system and bottleneck in test was disk I/O Two systems connected in the wide area network (RTT ~ 200 ms) with 10 Gb/s. Sender : 2 CPUs Dual Core Intel Woodcrest @ 3. 00 GHz, 4 GB RAM, 4 x 320 GB SATA Disks Receiver : 2 CPUs Dual Core AMD Opteron @ 2. 75 GHz, 4 GB RAM, 4 x 320 GB SATA Disks Disk activity in MBytes/s: ~200 MB/s (50 MB/s per disk) 8
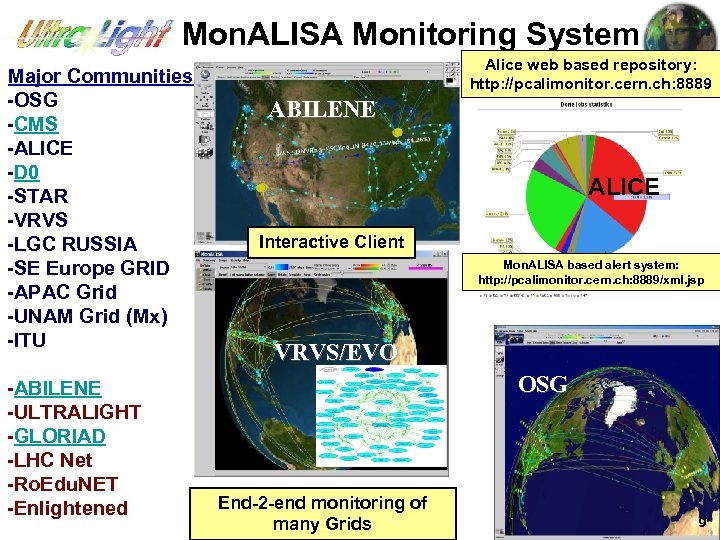
Mon. ALISA Monitoring System Major Communities -OSG -CMS -ALICE -D 0 -STAR -VRVS -LGC RUSSIA -SE Europe GRID -APAC Grid -UNAM Grid (Mx) -ITU -ABILENE -ULTRALIGHT -GLORIAD -LHC Net -Ro. Edu. NET -Enlightened Alice web based repository: http: //pcalimonitor. cern. ch: 8889 ABILENE - - VRVS ALICE Interactive Client Mon. ALISA based alert system: http: //pcalimonitor. cern. ch: 8889/xml. jsp VRVS/EVO OSG End-2 -end monitoring of many Grids 9
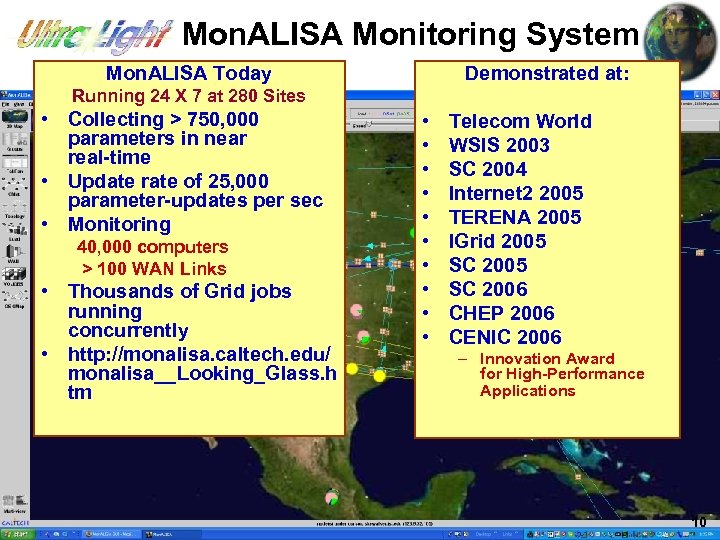
Mon. ALISA Monitoring System Mon. ALISA Today Demonstrated at: Running 24 X 7 at 280 Sites • Collecting > 750, 000 parameters in near real-time • Update rate of 25, 000 parameter-updates per sec • Monitoring 40, 000 computers > 100 WAN Links • Thousands of Grid jobs running concurrently • http: //monalisa. caltech. edu/ monalisa__Looking_Glass. h tm • • • Telecom World WSIS 2003 SC 2004 Internet 2 2005 TERENA 2005 IGrid 2005 SC 2006 CHEP 2006 OSG CENIC 2006 – Innovation Award for High-Performance Applications 10

L-Store: File System Interface to Global Storage Cloud http: //www. lstore. org/ • Provides a file system interface to (globally) distributed storage devices (“depots”) • Parallelism for high performance and reliability • Uses IBP (from UTenn) for data transfer & storage service Æ Generic, high performance, wide-area-capable storage virtualization service; transport plug-in support Æ Write: break file into blocks, upload blocks simultaneously to multiple depots (reverse for reads) • Multiple metadata servers increase performance & fault tolerance • L-Store supports beyond-RAID 6 -equivalent encoding of stored files for reliability and fault tolerance • Supports scalable streaming of Physics Analysis Data in/out of L-Store over the WAN 11
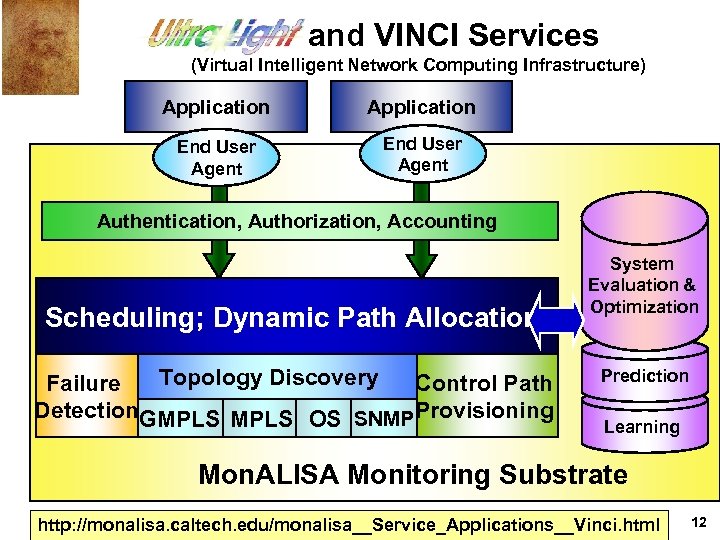
and VINCI Services (Virtual Intelligent Network Computing Infrastructure) Application End User Agent Authentication, Authorization, Accounting Scheduling; Dynamic Path Allocation Topology Discovery Failure Control Path Detection. GMPLS OS SNMPProvisioning System Evaluation & Optimization Prediction Learning Mon. ALISA Monitoring Substrate http: //monalisa. caltech. edu/monalisa__Service_Applications__Vinci. html 12
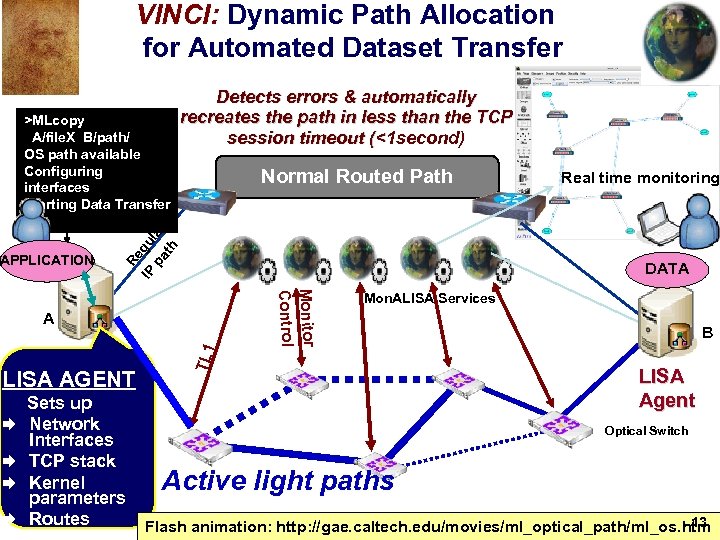
VINCI: Dynamic Path Allocation for Automated Dataset Transfer APPLICATION Normal Routed Path Re IP gu pa lar th >MLcopy A/file. X B/path/ OS path available Configuring interfaces Starting Data Transfer Detects errors & automatically recreates the path in less than the TCP session timeout (<1 second) DATA Æ Æ Sets up Network Interfaces TCP stack Kernel parameters Routes TL 1 Monitor Control A LISA AGENT Real time monitoring Mon. ALISA Services B LISA Agent Optical Switch Active light paths 13 Flash animation: http: //gae. caltech. edu/movies/ml_optical_path/ml_os. htm
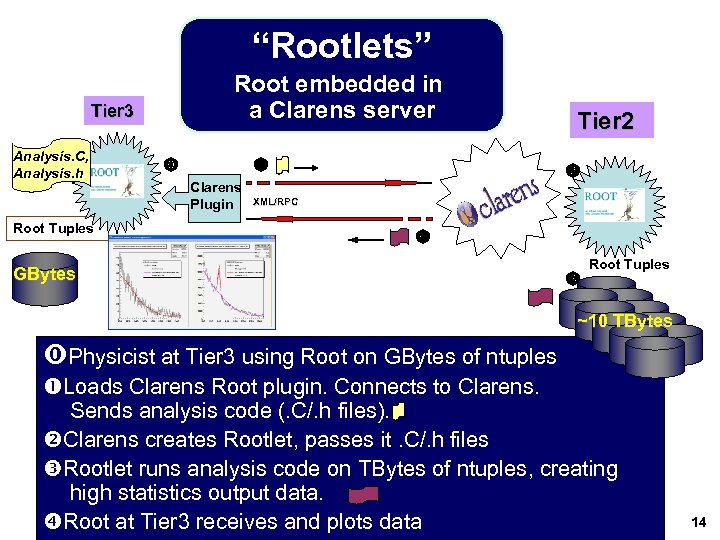
“Rootlets” Root embedded in a Clarens server Tier 3 Analysis. C, Analysis. h Root Tuples Clarens Plugin Tier 2 XML/RPC GBytes Root Tuples ~10 TBytes Physicist at Tier 3 using Root on GBytes of ntuples Loads Clarens Root plugin. Connects to Clarens. Sends analysis code (. C/. h files). Clarens creates Rootlet, passes it. C/. h files Rootlet runs analysis code on TBytes of ntuples, creating high statistics output data. Root at Tier 3 receives and plots data 14
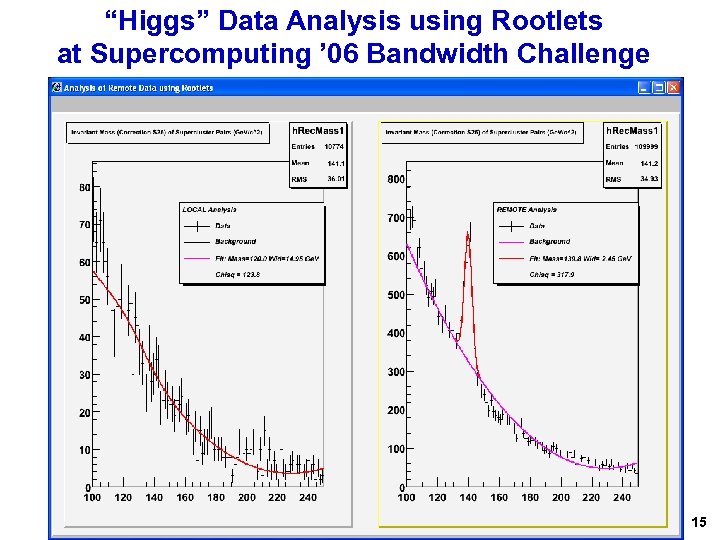
“Higgs” Data Analysis using Rootlets at Supercomputing ’ 06 Bandwidth Challenge 15
Summary: Ultra. Light Network R&D Global Planning Services • Ultra. Light is a global Laboratory, uniquely positioned – Spans Tier-0, some Tier-1 s, several Tier-2 s, and Tier-3 s • Ultra. Light (optical networks in general) moving towards a managed “control plane” – Light-paths will be allocated/scheduled to data-flow requests via policy based priorities, queues, and advanced reservations – Clear need to match “Network Resource Management” with “Storage Resource Management” • Available Ultra. Light Infrastructure / Services / Applications for Tier 3 s – – – • High performance network infrastructure (http: //ultralight. org/) Fast Data Transport Tool – FDT (http: //monalisa. cern. ch/FDT/) Mon. ALISA + VINCI (http: //monalisa. caltech. edu/) LStore (http: //www. lstore. org/) Rootlets Ultra. Light working to develop (generic) systems solutions by – Researching and developing Global Planning Services – Using an end-to-end approach • devices, parameters, end-host services, WAN, high-level services, applications fabric level Services application level 16
44bbf8c886b29f13033c38daa4fce994.ppt