c488a832a0745ac824bf8d9b83705ac5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 The Progressive Era Section 1 The Origins of Progressivism GET YOUR CLICKERS!!
The Progressive Era Section 1 The Origins of Progressivism GET YOUR CLICKERS!!
 Four Goals of Progressivism • Progressives aimed to return control of the government to the people, restore economic opportunities and correct injustices in American life • To do this, they had 4 goals
Four Goals of Progressivism • Progressives aimed to return control of the government to the people, restore economic opportunities and correct injustices in American life • To do this, they had 4 goals
 Four Goals of Progressivism • Protecting Social Welfare – Social Gospel, settlement houses inspire other reform groups – Florence Kelley, political activist, advocate for women, children – helps pass law prohibiting child labor, limiting women’s hours with Illinois Factory Act
Four Goals of Progressivism • Protecting Social Welfare – Social Gospel, settlement houses inspire other reform groups – Florence Kelley, political activist, advocate for women, children – helps pass law prohibiting child labor, limiting women’s hours with Illinois Factory Act
 Four Goals of Progressivism • Promoting Moral Improvement – Some feel poor should uplift selves by improving own behavior – Prohibition—banning of alcoholic drinks – Woman’s Christian Temperance Union spearheads prohibition crusade – Carry Nation destroyed kegs of whiskey
Four Goals of Progressivism • Promoting Moral Improvement – Some feel poor should uplift selves by improving own behavior – Prohibition—banning of alcoholic drinks – Woman’s Christian Temperance Union spearheads prohibition crusade – Carry Nation destroyed kegs of whiskey
 Four Goals of Progressivism • Creating Economic Reform – 1893 panic prompts doubts about capitalism; many become socialists – Muckrakers —journalists who expose corruption in politics, business – Ida Tarbell exposed the Standard Oil Co’s cutthroat strategies to eliminate competition
Four Goals of Progressivism • Creating Economic Reform – 1893 panic prompts doubts about capitalism; many become socialists – Muckrakers —journalists who expose corruption in politics, business – Ida Tarbell exposed the Standard Oil Co’s cutthroat strategies to eliminate competition
 Four Goals of Progressivism • Fostering Efficiency – Many use experts, science to make society, workplace more efficient – Louis D. Brandeis uses social scientists’ data in trial – Brandeis Briefs – Scientific management —time and motion studies applied to workplace – Assembly lines speed up production, make people work like machines • cause high worker turnover
Four Goals of Progressivism • Fostering Efficiency – Many use experts, science to make society, workplace more efficient – Louis D. Brandeis uses social scientists’ data in trial – Brandeis Briefs – Scientific management —time and motion studies applied to workplace – Assembly lines speed up production, make people work like machines • cause high worker turnover
 Four Goals of Progressivism • Fostering Efficiency – Frederick W. Taylor used a stopwatch to time motions of employees to shorten wasted time – Henry Ford increased efficiency by paying his employees more - $5 per day
Four Goals of Progressivism • Fostering Efficiency – Frederick W. Taylor used a stopwatch to time motions of employees to shorten wasted time – Henry Ford increased efficiency by paying his employees more - $5 per day
 Who exposed the unethical activities of Standard Oil? • • • A B C D E – John Rockefeller – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
Who exposed the unethical activities of Standard Oil? • • • A B C D E – John Rockefeller – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
 Who became an efficiency expert, timing worker’s movements? • • • A B C D E – John Rockefeller – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
Who became an efficiency expert, timing worker’s movements? • • • A B C D E – John Rockefeller – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
 Who was a prohibitionist who destroyed liquor bottles and beer? • • • A B C D E – John Rockefeller – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
Who was a prohibitionist who destroyed liquor bottles and beer? • • • A B C D E – John Rockefeller – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
 Who used scientific data in his legal cases against industries? • • • A B C D E – Henry Ford – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
Who used scientific data in his legal cases against industries? • • • A B C D E – Henry Ford – Frederick Taylor – Louis Brandeis - Ida Tarbell – Cary Nation
 Reforming Local Governments • Natural disasters played an important role in reforming local governments • Hurricanes and floods tested local authority and put trained people in city positions • Progressive mayors implemented change on the local level
Reforming Local Governments • Natural disasters played an important role in reforming local governments • Hurricanes and floods tested local authority and put trained people in city positions • Progressive mayors implemented change on the local level
 Reforming child labor laws • “Fighting Bob” La. Follette, WI, served 3 terms as governor – Caused the demise of political machines – Took political control away from businesses • James Hogg, TX, took on railroad rates in his state • (He named his daughters Ima and Ura)
Reforming child labor laws • “Fighting Bob” La. Follette, WI, served 3 terms as governor – Caused the demise of political machines – Took political control away from businesses • James Hogg, TX, took on railroad rates in his state • (He named his daughters Ima and Ura)
 Reforming work hours • Muller v. Oregon, 1908 – Louis Brandeis looked at scientific data and argued (and won) that women should limit women to a 10 hr day • Bunting v. Oregon, 1917 – ordered a 10 hr workday for men • Progressives also received compensation for workers killed or injured on the job
Reforming work hours • Muller v. Oregon, 1908 – Louis Brandeis looked at scientific data and argued (and won) that women should limit women to a 10 hr day • Bunting v. Oregon, 1917 – ordered a 10 hr workday for men • Progressives also received compensation for workers killed or injured on the job
 Reforming elections • Initiative – method where voters could compel legislature to consider a bill • Referendum – method that allowed citizens to vote on proposed laws • Recall – enabled voters to remove politician from office
Reforming elections • Initiative – method where voters could compel legislature to consider a bill • Referendum – method that allowed citizens to vote on proposed laws • Recall – enabled voters to remove politician from office
 Reforming elections • Direct election of senators – up to this time, the people elected House of Representatives members • The House members then chose the senators for each state • The 17 th Amendment allows for direct election of senators
Reforming elections • Direct election of senators – up to this time, the people elected House of Representatives members • The House members then chose the senators for each state • The 17 th Amendment allows for direct election of senators

 The Progressive Era Section 2 Women in Public Life
The Progressive Era Section 2 Women in Public Life
 Women in the workforce • Women on the farm saw their lives change little in 100 years • They continued to do all the housework and childrearing, and often, farm labor as well
Women in the workforce • Women on the farm saw their lives change little in 100 years • They continued to do all the housework and childrearing, and often, farm labor as well
 Women in the workforce • Women in the cities took jobs as pay increased • Most were secretarial, teaching, nursing or telephone operators • They paid about half as much as men and could not join a union
Women in the workforce • Women in the cities took jobs as pay increased • Most were secretarial, teaching, nursing or telephone operators • They paid about half as much as men and could not join a union
 Women in the workforce • Women without skills took jobs as domestics – maids, cooks, laundry workers • Most of this work was done by immigrants and black women
Women in the workforce • Women without skills took jobs as domestics – maids, cooks, laundry workers • Most of this work was done by immigrants and black women
 Women reformers • Many of the women who sought more rights for women were college educated • Vassar, Smith and Wellesley were the first to accept women
Women reformers • Many of the women who sought more rights for women were college educated • Vassar, Smith and Wellesley were the first to accept women
 Women reformers • African American women founded the NACW (National Assoc. for Colored Women) and promoted education • Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton joined with Lucy Stone and Julia Ward Howe for women’s suffrage
Women reformers • African American women founded the NACW (National Assoc. for Colored Women) and promoted education • Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton joined with Lucy Stone and Julia Ward Howe for women’s suffrage
 Women reformers • Many men and the liquor industry opposed women’s suffrage
Women reformers • Many men and the liquor industry opposed women’s suffrage
 The Progressive Era Section 3 Teddy Roosevelt’s Square Deal
The Progressive Era Section 3 Teddy Roosevelt’s Square Deal
 Teddy Roosevelt • Roosevelt became president after Pres. Mc. Kinley was assassinated. • The Republican Party chose him to be VP to keep him out of any policy-making office
Teddy Roosevelt • Roosevelt became president after Pres. Mc. Kinley was assassinated. • The Republican Party chose him to be VP to keep him out of any policy-making office
 Teddy Roosevelt • Roosevelt was born into a wealthy NY family, attended Harvard and was the former governor of New York • He was the hero of the Spanish American War after leading his “Rough Riders” up San Juan Hill in Cuba
Teddy Roosevelt • Roosevelt was born into a wealthy NY family, attended Harvard and was the former governor of New York • He was the hero of the Spanish American War after leading his “Rough Riders” up San Juan Hill in Cuba
 Teddy Roosevelt • TR used the presidency to influence – his ‘bully pulpit’ • After settling a coal strike through arbitration, he stated that we wanted a “square deal” for all Americans • One of the first targets of his reform was the trusts
Teddy Roosevelt • TR used the presidency to influence – his ‘bully pulpit’ • After settling a coal strike through arbitration, he stated that we wanted a “square deal” for all Americans • One of the first targets of his reform was the trusts
 Teddy Roosevelt • Using the weak Sherman Antitrust Act, TR took on the railroads with a suit against the Northern Securities Company • The USSC dissolved the trust • TR filed 44 more suits
Teddy Roosevelt • Using the weak Sherman Antitrust Act, TR took on the railroads with a suit against the Northern Securities Company • The USSC dissolved the trust • TR filed 44 more suits
 Teddy Roosevelt • He saw the passage of the Meat Inspection Act after The Jungle was published, exposing the filthy practices of the beef monopolies
Teddy Roosevelt • He saw the passage of the Meat Inspection Act after The Jungle was published, exposing the filthy practices of the beef monopolies
 Teddy Roosevelt • Medicine and food had no restrictions on ingredients or restrictions on claims of what they could cure • The Pure Food and Drug Act demanded truth in labeling
Teddy Roosevelt • Medicine and food had no restrictions on ingredients or restrictions on claims of what they could cure • The Pure Food and Drug Act demanded truth in labeling
 Teddy Roosevelt • TR set aside land for the future
Teddy Roosevelt • TR set aside land for the future
 Teddy Roosevelt • In 1905, TR appointed Gifford Pinchot as head of the US Forest Service
Teddy Roosevelt • In 1905, TR appointed Gifford Pinchot as head of the US Forest Service
 Teddy Roosevelt • TR made little headway in recognizing civil rights for African Americans • Appointing some to federal positions, he backed down at almost every opportunity to offer equality to all
Teddy Roosevelt • TR made little headway in recognizing civil rights for African Americans • Appointing some to federal positions, he backed down at almost every opportunity to offer equality to all
 Teddy Roosevelt • W. E. B. Du. Bois met in Niagara to form the Niagara Movement, demanding equality • The group became the NAACP, the National Assoc. for the Advancement of Colored People
Teddy Roosevelt • W. E. B. Du. Bois met in Niagara to form the Niagara Movement, demanding equality • The group became the NAACP, the National Assoc. for the Advancement of Colored People
 Teddy Roosevelt • TR is known for his saying, “speak softly and carry a big stick. ” • He ordered the new navy, the Great White Fleet, on a round the world mission to show our new ‘muscle’ • He was also responsible for the construction of the Panama Canal
Teddy Roosevelt • TR is known for his saying, “speak softly and carry a big stick. ” • He ordered the new navy, the Great White Fleet, on a round the world mission to show our new ‘muscle’ • He was also responsible for the construction of the Panama Canal
 Who were the muckrakers? • Ida Tarbel – “The History of Standard Oil” (railroad corruption) • Lincoln Steffens – “The Same of the Cities” and “Tweed Days in St. Louis” (government corruption) • Upton Sinclair – “The Jungle” (meatpacking industry)
Who were the muckrakers? • Ida Tarbel – “The History of Standard Oil” (railroad corruption) • Lincoln Steffens – “The Same of the Cities” and “Tweed Days in St. Louis” (government corruption) • Upton Sinclair – “The Jungle” (meatpacking industry)
 The Progressive Era Section 4 Progressivism Under Taft
The Progressive Era Section 4 Progressivism Under Taft
 William howard taft • TR promised not to run for reelection in 1904 but campaigned for his VP, Taft, as someone just like himself • Taft proved himself to be very different from TR
William howard taft • TR promised not to run for reelection in 1904 but campaigned for his VP, Taft, as someone just like himself • Taft proved himself to be very different from TR
 William howard taft • Taft ran on the platform of lowering tariffs • Instead, he signed the Payne. Aldrich Tariff and then bragged about it
William howard taft • Taft ran on the platform of lowering tariffs • Instead, he signed the Payne. Aldrich Tariff and then bragged about it
 William howard taft • Next he appointed Richard Ballinger as Sec. of the Interior who disapproved of land conservation • Pinchot accused Ballinger of caving into special interests for profits • Taft sided with Ballinger
William howard taft • Next he appointed Richard Ballinger as Sec. of the Interior who disapproved of land conservation • Pinchot accused Ballinger of caving into special interests for profits • Taft sided with Ballinger
 William howard taft • The Republican Party split over Taft’s actions with Speaker of the House Joe Cannon • Cannon weakens the Progressive agenda, causing some Progressives to ally with the Democrats
William howard taft • The Republican Party split over Taft’s actions with Speaker of the House Joe Cannon • Cannon weakens the Progressive agenda, causing some Progressives to ally with the Democrats
 William howard taft • In the mid-term elections of 1910, Democrats took many Republican seats • The Republicans still renominated Taft in 1912
William howard taft • In the mid-term elections of 1910, Democrats took many Republican seats • The Republicans still renominated Taft in 1912
 William howard taft • TR fought, and lost, for the Republican nomination • He formed his own splinter party, the Bull Moose Party. • By splitting the Republican voting bloc, Democrats smelled victory • They nominate Woodrow Wilson
William howard taft • TR fought, and lost, for the Republican nomination • He formed his own splinter party, the Bull Moose Party. • By splitting the Republican voting bloc, Democrats smelled victory • They nominate Woodrow Wilson
 Election of 1912 • The Republicans ran an ugly campaign filled with name-calling • “fathead” “dangerous egotist” • “brain of a guinea pig” • Wilson let them do his dirty work
Election of 1912 • The Republicans ran an ugly campaign filled with name-calling • “fathead” “dangerous egotist” • “brain of a guinea pig” • Wilson let them do his dirty work
 Woodrow wilson • Wilson does not receive a majority (plurality) but receives enough electoral votes to win
Woodrow wilson • Wilson does not receive a majority (plurality) but receives enough electoral votes to win
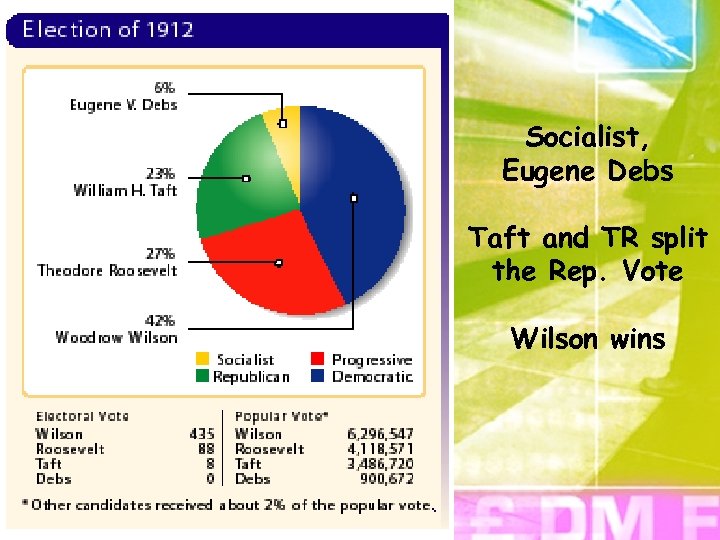 Socialist, Eugene Debs Taft and TR split the Rep. Vote Wilson wins
Socialist, Eugene Debs Taft and TR split the Rep. Vote Wilson wins
 The Progressive Era Section 5 Wilson’s New Freedom
The Progressive Era Section 5 Wilson’s New Freedom
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson too was a progressive president but having different ideas how to give people more power • Wilson was deeply religious, a lawyer and former president of Princeton University • As the governor of NJ, he supported many progressive ideas
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson too was a progressive president but having different ideas how to give people more power • Wilson was deeply religious, a lawyer and former president of Princeton University • As the governor of NJ, he supported many progressive ideas
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • To strengthen the Sherman Antitrust Act, Wilson pushed for the Clayton Antitrust Act which prohibited a merger if it developed into a monopoly • This did not apply to farmers or unions
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • To strengthen the Sherman Antitrust Act, Wilson pushed for the Clayton Antitrust Act which prohibited a merger if it developed into a monopoly • This did not apply to farmers or unions
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson established the Federal Trade Commission to investigate industry for unlawful activity • He reduced tariffs under the Underwood Act, 1913 • To replace the revenue, he earners
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson established the Federal Trade Commission to investigate industry for unlawful activity • He reduced tariffs under the Underwood Act, 1913 • To replace the revenue, he earners
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • The average family made about $1500 year • The minimum income to warrant a tax was $4000 – and people bragged about having to pay it • By 1917 the revenue from income surpassed that of the tariffs
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • The average family made about $1500 year • The minimum income to warrant a tax was $4000 – and people bragged about having to pay it • By 1917 the revenue from income surpassed that of the tariffs
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Federal Reserve System – to regulate America’s banking system and, hopefully, to avoid depressions like the one in 1893, Wilson established the FED • It required bank inspections and regulates the amount of money in our economy
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Federal Reserve System – to regulate America’s banking system and, hopefully, to avoid depressions like the one in 1893, Wilson established the FED • It required bank inspections and regulates the amount of money in our economy
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • The Wilson administration saw the passage of the 19 th Amendment in 1919 giving women the right to vote • Carrie Chapman Catt took Anthony’s place in the fight • Emmeline Pankhurst heckled government officials
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • The Wilson administration saw the passage of the 19 th Amendment in 1919 giving women the right to vote • Carrie Chapman Catt took Anthony’s place in the fight • Emmeline Pankhurst heckled government officials
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson returned to his southern roots with his attitude towards African Americans • He fired all blacks in the White House and enforced segregation in all federal jobs
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson returned to his southern roots with his attitude towards African Americans • He fired all blacks in the White House and enforced segregation in all federal jobs
 Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson ran for re-election in 1916 with the slogan, “He kept us out of the war. ” • America did not want to become involved in Europe’s war and he was re-elected
Woodrow wilson – new freedom • Wilson ran for re-election in 1916 with the slogan, “He kept us out of the war. ” • America did not want to become involved in Europe’s war and he was re-elected
 Other changes in america • Architecture – away from the ornate designs of the gilded age and more streamlined like those designed by Frank Lloyd Wright
Other changes in america • Architecture – away from the ornate designs of the gilded age and more streamlined like those designed by Frank Lloyd Wright


