f1fbfcfc1bb3183ffc53e029f2b2a85a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 Origins of Progressivism • As America entered the 20 th century, members of the middle class looked to reform issues at the municipal, state, & national levels. • Problems of the Gilded Age, including: • Economic inequities • Environmental issues • Social welfare • Working conditions • Rights for women and children *Promote efficiency*
Origins of Progressivism • As America entered the 20 th century, members of the middle class looked to reform issues at the municipal, state, & national levels. • Problems of the Gilded Age, including: • Economic inequities • Environmental issues • Social welfare • Working conditions • Rights for women and children *Promote efficiency*
 Social Welfare • Industrialization was largely unregulated. Employers felt little responsibility toward their workers. • Urban centers were centers of crime, poverty, & despair. • As a result, benevolent societies, settlement houses, and churches served the community. (YMCA and Salvation Army) • Local, State, & the Federal government did little to help. Salvation Army Shelter
Social Welfare • Industrialization was largely unregulated. Employers felt little responsibility toward their workers. • Urban centers were centers of crime, poverty, & despair. • As a result, benevolent societies, settlement houses, and churches served the community. (YMCA and Salvation Army) • Local, State, & the Federal government did little to help. Salvation Army Shelter
 Moral Development • Reformers felt that peoples “personal behavior” needed to be changed. • One proposal was to prohibit the drinking of alcohol. • Woman’s Christian Temperance Union lead the fight. (1919) Congress passed the 18 th Amendment
Moral Development • Reformers felt that peoples “personal behavior” needed to be changed. • One proposal was to prohibit the drinking of alcohol. • Woman’s Christian Temperance Union lead the fight. (1919) Congress passed the 18 th Amendment
 Economic Reform • Panic of 1893 prompted Americans to question the capitalist system. • Some workers embraced socialism (government controls the economy). • Eugene Debs organized the American Socialist Party in 1901. Debs encouraged workers to reject American capitalism
Economic Reform • Panic of 1893 prompted Americans to question the capitalist system. • Some workers embraced socialism (government controls the economy). • Eugene Debs organized the American Socialist Party in 1901. Debs encouraged workers to reject American capitalism
 Muckrakers Criticize • Most Progressives did not embrace socialism, but saw the truth in Debs’ criticism. • Investigative journalists, known as “Muckrakers, ” exposed corruption in business. • Ida Tarbell exposed Standard Oil Monopoly. • J. Riis exposed “How the other half lives” (photo’s) • Michael Moore (films today)
Muckrakers Criticize • Most Progressives did not embrace socialism, but saw the truth in Debs’ criticism. • Investigative journalists, known as “Muckrakers, ” exposed corruption in business. • Ida Tarbell exposed Standard Oil Monopoly. • J. Riis exposed “How the other half lives” (photo’s) • Michael Moore (films today)
 Fostering Efficiency • Progressive put their faith in “scientific principles” to make the county better. • Frederick Taylor began using time & motion studies to improve factory efficiency. (produce quick) • Robert La Follette led the way in regulating business. • His Wisconsin Idea wanted: direct primaries, initiatives, referendums, & recall’s
Fostering Efficiency • Progressive put their faith in “scientific principles” to make the county better. • Frederick Taylor began using time & motion studies to improve factory efficiency. (produce quick) • Robert La Follette led the way in regulating business. • His Wisconsin Idea wanted: direct primaries, initiatives, referendums, & recall’s
 Clean Up Government • Reforming all levels of government stemmed from the desire to make government MORE efficient and MORE responsive to citizens. • Prevent corruption and abuse of power (graft) • Some believe it also was meant to limit immigrants’ influence on local governments.
Clean Up Government • Reforming all levels of government stemmed from the desire to make government MORE efficient and MORE responsive to citizens. • Prevent corruption and abuse of power (graft) • Some believe it also was meant to limit immigrants’ influence on local governments.
 Direct Election • Before 1913, state’s legislature chose U. S. Senators. • To force Senators to be more responsive to the public, Progressives pushed for the popular election of senators. • As a result, Congress passed the 17 th Amendment in 1913.
Direct Election • Before 1913, state’s legislature chose U. S. Senators. • To force Senators to be more responsive to the public, Progressives pushed for the popular election of senators. • As a result, Congress passed the 17 th Amendment in 1913.
 Protecting Children • As the number of child workers rose, reformers worked to end child labor. • Children should be educated not being injured at work. • Children’s Bureau (1912) investigates child abuse. • Nearly every state limited or banned child labor by 1918
Protecting Children • As the number of child workers rose, reformers worked to end child labor. • Children should be educated not being injured at work. • Children’s Bureau (1912) investigates child abuse. • Nearly every state limited or banned child labor by 1918
 Legal Decisions • The Supreme & States courts enacted laws to reducing women’s hours of work. • Women were expected to care for family while the husbands worked. • Progressives won compensation cases to aid families of injured workers. Lochner v. NY
Legal Decisions • The Supreme & States courts enacted laws to reducing women’s hours of work. • Women were expected to care for family while the husbands worked. • Progressives won compensation cases to aid families of injured workers. Lochner v. NY
 Domestic Workers • Women without formal education contributed mainly by doing domestic work. • Altogether, 70% of women employed in 1870 were servants. • Other non skilled workers found employment in textile mill, clothing factories, retail stores, & as clerical workers • Long Hours, Low Pay, & Poor Working Conditions
Domestic Workers • Women without formal education contributed mainly by doing domestic work. • Altogether, 70% of women employed in 1870 were servants. • Other non skilled workers found employment in textile mill, clothing factories, retail stores, & as clerical workers • Long Hours, Low Pay, & Poor Working Conditions
 Women Lead Reform • Many of the leading Progressive reformers were middle class women. • They entered the public sphere after graduating college. • E. Stanton & S. Anthony were challenged by Lucy Stone, Julia Howe. • Alice Paul used pickets, marches, & hunger strikes to win suffrage. Colleges like Vassar and Smith allowed women to excel
Women Lead Reform • Many of the leading Progressive reformers were middle class women. • They entered the public sphere after graduating college. • E. Stanton & S. Anthony were challenged by Lucy Stone, Julia Howe. • Alice Paul used pickets, marches, & hunger strikes to win suffrage. Colleges like Vassar and Smith allowed women to excel
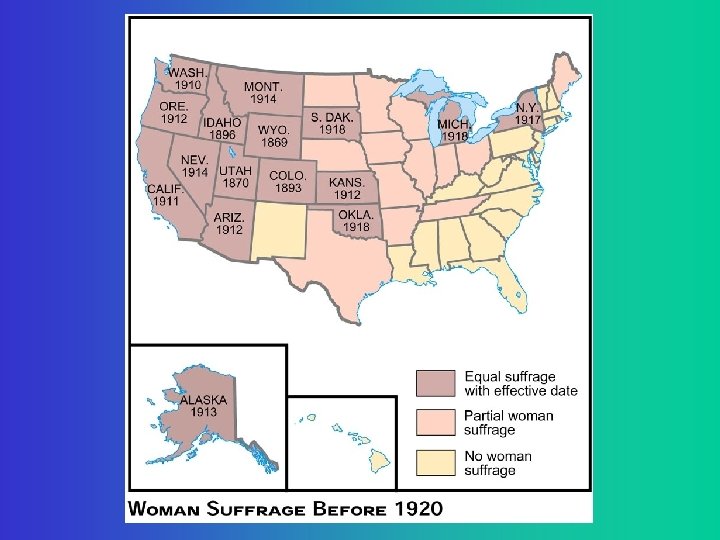
 Strategy for Suffragettes tried three approaches to winning the vote: 1. Convincing state legislatures to adopt the vote. 2. Pursuing court cases to test 14 th Amendment. 3. Pushing for national Constitutional amendment. 19 th Amendment (1920)
Strategy for Suffragettes tried three approaches to winning the vote: 1. Convincing state legislatures to adopt the vote. 2. Pursuing court cases to test 14 th Amendment. 3. Pushing for national Constitutional amendment. 19 th Amendment (1920)
 Roosevelt & Rough Riders • Roosevelt captured national attention by advocating war with Spain in 1898. • His volunteer cavalry brigade, the Rough Riders, won public acclaim for its role in the battle of San Juan Hill in Cuba. • Roosevelt returned a hero and was soon elected governor of NY and later Mc. Kinley’s vice-president.
Roosevelt & Rough Riders • Roosevelt captured national attention by advocating war with Spain in 1898. • His volunteer cavalry brigade, the Rough Riders, won public acclaim for its role in the battle of San Juan Hill in Cuba. • Roosevelt returned a hero and was soon elected governor of NY and later Mc. Kinley’s vice-president.
 Teddy Roosevelt and the Rough Riders
Teddy Roosevelt and the Rough Riders
 Film clip of Theodore Roosevelt and Rough Riders
Film clip of Theodore Roosevelt and Rough Riders
 President Roosevelt Assassinated by an anarchist in Buffalo in September of 1901 • When President Mc. Kinley was assassinated, Theodore Roosevelt became the nation’s 26 th president. (Age 42) • He championed the Progressive Platform & called it the Square Deal. • Became a modern president that could influence the media and shape legislation.
President Roosevelt Assassinated by an anarchist in Buffalo in September of 1901 • When President Mc. Kinley was assassinated, Theodore Roosevelt became the nation’s 26 th president. (Age 42) • He championed the Progressive Platform & called it the Square Deal. • Became a modern president that could influence the media and shape legislation.
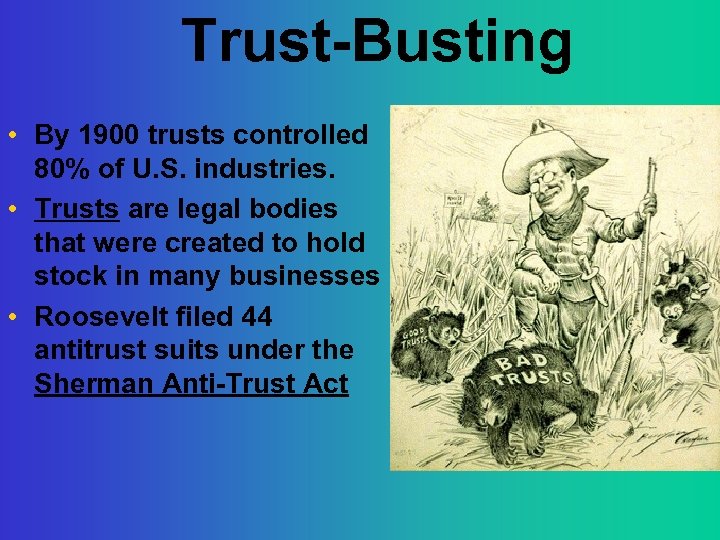 Trust-Busting • By 1900 trusts controlled 80% of U. S. industries. • Trusts are legal bodies that were created to hold stock in many businesses • Roosevelt filed 44 antitrust suits under the Sherman Anti-Trust Act
Trust-Busting • By 1900 trusts controlled 80% of U. S. industries. • Trusts are legal bodies that were created to hold stock in many businesses • Roosevelt filed 44 antitrust suits under the Sherman Anti-Trust Act
 Pennsylvania Coal Strike • In 1902, 140, 000 coal miners in went on strike for increased wages, a 9 -hour work day, and the right to unionize (United Mine Workers). • Mine owners refused to bargain & production stopped. • Roosevelt called for arbitration to settled the dispute. • Thereafter, when a strike threatened public welfare, the federal government was expected to step in and help.
Pennsylvania Coal Strike • In 1902, 140, 000 coal miners in went on strike for increased wages, a 9 -hour work day, and the right to unionize (United Mine Workers). • Mine owners refused to bargain & production stopped. • Roosevelt called for arbitration to settled the dispute. • Thereafter, when a strike threatened public welfare, the federal government was expected to step in and help.
 Food & Drug Regulation • After reading Upton Sinclair novel “the Jungle” Teddy pushed for passage of the Meat Inspection Act of 1906. • Mandated cleaner conditions for meatpacking plants & safer transportation. • He also passed the Pure food & Drug Act in 1906. • Prevented companies from making false claims & list what ingredients were in their products.
Food & Drug Regulation • After reading Upton Sinclair novel “the Jungle” Teddy pushed for passage of the Meat Inspection Act of 1906. • Mandated cleaner conditions for meatpacking plants & safer transportation. • He also passed the Pure food & Drug Act in 1906. • Prevented companies from making false claims & list what ingredients were in their products.
 Regulating the Railroads • 1903 - Congress created the Department of Labor & Commerce. • TR makes a “gentlemen’s agreement” w/ some big companies (open books) • 1906 - Hepburn Act gave the ICC the power to regulate railroad Companies & set rates.
Regulating the Railroads • 1903 - Congress created the Department of Labor & Commerce. • TR makes a “gentlemen’s agreement” w/ some big companies (open books) • 1906 - Hepburn Act gave the ICC the power to regulate railroad Companies & set rates.
 The Environment • Before Roosevelt the federal government paid very little attention to the nation’s natural resources. • Roosevelt made conservation a primary concern of his administration. Film clip of Theodore Roosevelt
The Environment • Before Roosevelt the federal government paid very little attention to the nation’s natural resources. • Roosevelt made conservation a primary concern of his administration. Film clip of Theodore Roosevelt
 Theodore Roosevelt with John Muir (Founder of the Sierra Club)
Theodore Roosevelt with John Muir (Founder of the Sierra Club)
 Accomplishments • 1905 - created the US National Forest Service & appointed Gifford Pinchot as its head. • Roosevelt set aside • 148 million acres of forest reserves • 1. 5 million acres of water-power sites • 50 wildlife sanctuaries • several national parks.
Accomplishments • 1905 - created the US National Forest Service & appointed Gifford Pinchot as its head. • Roosevelt set aside • 148 million acres of forest reserves • 1. 5 million acres of water-power sites • 50 wildlife sanctuaries • several national parks.
 Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming
Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming
 Civil Rights • Roosevelt failed to support Civil Rights for African Americans. • He did support Booker T. Washington b/c his focus was on economics & education. • Mr. Washington founded the Tuskegee Institute to provide a technical education for African Americans.
Civil Rights • Roosevelt failed to support Civil Rights for African Americans. • He did support Booker T. Washington b/c his focus was on economics & education. • Mr. Washington founded the Tuskegee Institute to provide a technical education for African Americans.
 Taft’s Progressivism • William Howard Taft (R) easily defeated Democrat William Jennings Bryan in the 1908 election. • Taft “busted” 90 trusts during his four years in office. • Taft was not popular with the public or the reformers. • He called the Presidency, the “lonesomest” job in the world. ” • By 1910, Democrats had regained control of the House of Representatives. Taft was Roosevelt’s War Secretary
Taft’s Progressivism • William Howard Taft (R) easily defeated Democrat William Jennings Bryan in the 1908 election. • Taft “busted” 90 trusts during his four years in office. • Taft was not popular with the public or the reformers. • He called the Presidency, the “lonesomest” job in the world. ” • By 1910, Democrats had regained control of the House of Representatives. Taft was Roosevelt’s War Secretary
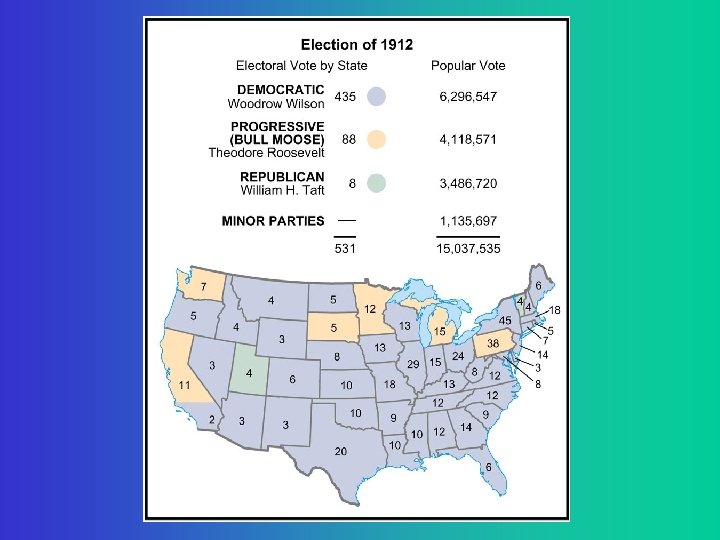
 Election of 1912 • Republicans split in 1912 between Taft &Roosevelt (returned after a safari to Africa). • Convention delegates nominated Taft • Discontented members formed a third party, the Progressive Party (nicknamed the Bull Moose Party), and nominated Roosevelt. • The Democrats put forward a reform-minded New Jersey governor, Woodrow Wilson.
Election of 1912 • Republicans split in 1912 between Taft &Roosevelt (returned after a safari to Africa). • Convention delegates nominated Taft • Discontented members formed a third party, the Progressive Party (nicknamed the Bull Moose Party), and nominated Roosevelt. • The Democrats put forward a reform-minded New Jersey governor, Woodrow Wilson.
 Wilson’s New Freedom • With a strong mandate from the American people, Wilson moved to enact his program, the “New Freedom. ” • He planned his attack on what he called the triple wall of privilege: trusts, tariffs, and high finance.
Wilson’s New Freedom • With a strong mandate from the American people, Wilson moved to enact his program, the “New Freedom. ” • He planned his attack on what he called the triple wall of privilege: trusts, tariffs, and high finance.
 Clayton Anti-Trust Act • In 1914 Congress enacted the Clayton Anti-Trust Act that strengthened the Sherman Act. • It had an anti-trust provision that prevented companies from acquiring stock from another company and supported workers’ unions.
Clayton Anti-Trust Act • In 1914 Congress enacted the Clayton Anti-Trust Act that strengthened the Sherman Act. • It had an anti-trust provision that prevented companies from acquiring stock from another company and supported workers’ unions.
 Federal Trade Commission • The FTC was formed in 1914 to serve as a “watchdog” agency to end unfair business practices. • The FTC protects consumers from business fraud.
Federal Trade Commission • The FTC was formed in 1914 to serve as a “watchdog” agency to end unfair business practices. • The FTC protects consumers from business fraud.
 Federal Income Tax • Wilson worked hard to lower tariffs, however, the lost revenue had to be made up. • The 16 th Amendment instituted a graduated federal income tax.
Federal Income Tax • Wilson worked hard to lower tariffs, however, the lost revenue had to be made up. • The 16 th Amendment instituted a graduated federal income tax.
 Rise of U. S. Imperialism! Hawaii, Cuba, the Philippines, and Latin America
Rise of U. S. Imperialism! Hawaii, Cuba, the Philippines, and Latin America
 Anti-Imperial Sentiment • From the Civil War until the 1890 s, most Americans had little interest in territorial expansion: • Imperial rule was inconsistent with America's Republican Principles. • Many Americans did not welcome people with different cultures, languages, & religions.
Anti-Imperial Sentiment • From the Civil War until the 1890 s, most Americans had little interest in territorial expansion: • Imperial rule was inconsistent with America's Republican Principles. • Many Americans did not welcome people with different cultures, languages, & religions.
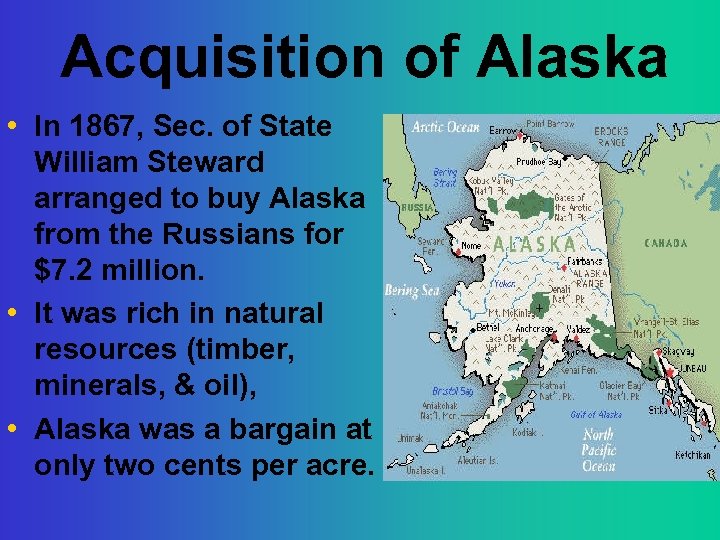 Acquisition of Alaska • In 1867, Sec. of State William Steward arranged to buy Alaska from the Russians for $7. 2 million. • It was rich in natural resources (timber, minerals, & oil), • Alaska was a bargain at only two cents per acre.
Acquisition of Alaska • In 1867, Sec. of State William Steward arranged to buy Alaska from the Russians for $7. 2 million. • It was rich in natural resources (timber, minerals, & oil), • Alaska was a bargain at only two cents per acre.
 European Imperialism • Between 1870 and 1900, the European powers seized territory in Africa and Asia. • In the US, a large number of policy makers, bankers, manufacturers, and trade unions grew fearful that the country might be closed out in the struggle for global markets & raw materials.
European Imperialism • Between 1870 and 1900, the European powers seized territory in Africa and Asia. • In the US, a large number of policy makers, bankers, manufacturers, and trade unions grew fearful that the country might be closed out in the struggle for global markets & raw materials.
 Darwinian Struggle • The world's nations were engaged in a struggle for survival & that countries that failed to compete were doomed to fail. • During the late 1880 s, the US began to display a new assertiveness. • The United States came close to declaring war on Germany, Chile, and Great Britain.
Darwinian Struggle • The world's nations were engaged in a struggle for survival & that countries that failed to compete were doomed to fail. • During the late 1880 s, the US began to display a new assertiveness. • The United States came close to declaring war on Germany, Chile, and Great Britain.
 Dependency on Trade • By the 1890 s, the US economy was dependent on foreign trade. • 1/4 of the nation's farm products & half its oil were sold overseas. • AT Mahan argued that US prosperity & power depended on control of the world's sea-lanes. • "Whoever rules the waves rules the world, "
Dependency on Trade • By the 1890 s, the US economy was dependent on foreign trade. • 1/4 of the nation's farm products & half its oil were sold overseas. • AT Mahan argued that US prosperity & power depended on control of the world's sea-lanes. • "Whoever rules the waves rules the world, "
 Annexation of Hawaii • In 1893, a group of sugar & pineapple businessmen deposed Hawaii's queen with the aid of the military. • They seized 1. 75 million acres and conspired for U. S. annexation. • Some Americans protested but it was annexed in 1898 & became a state in 1959.
Annexation of Hawaii • In 1893, a group of sugar & pineapple businessmen deposed Hawaii's queen with the aid of the military. • They seized 1. 75 million acres and conspired for U. S. annexation. • Some Americans protested but it was annexed in 1898 & became a state in 1959.
 Spanish American War! • The Tariff of 1894, placed restrictions on sugar imported from Cuba. • Angry nationalists began a revolt against the Spanish colonial regime. • The US had investment interests in Cuba so they dispatched the USS Maine to rescue citizens who might be in danger from the conflict.
Spanish American War! • The Tariff of 1894, placed restrictions on sugar imported from Cuba. • Angry nationalists began a revolt against the Spanish colonial regime. • The US had investment interests in Cuba so they dispatched the USS Maine to rescue citizens who might be in danger from the conflict.
 Yellow Journalism • Feb. 15, 1898 the Maine blew up & the US blamed it on a Spanish mine. • The US public was stirred into an anti-Spain frenzy by Hearst and Pulitzer. • President Mc. Kinley gave the OK for war. • Congress agreed after the Teller Amendment (No ambitions in Cuba)
Yellow Journalism • Feb. 15, 1898 the Maine blew up & the US blamed it on a Spanish mine. • The US public was stirred into an anti-Spain frenzy by Hearst and Pulitzer. • President Mc. Kinley gave the OK for war. • Congress agreed after the Teller Amendment (No ambitions in Cuba)
 The Outcome • The US defeated Spanish forces in Cuba & other Spanish colonies in 144 days. • The US took control of the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam. (protectorate) • The Platt Amendment gave the US the right to intervene in Cuba to protect "life, property, and individual liberties. “
The Outcome • The US defeated Spanish forces in Cuba & other Spanish colonies in 144 days. • The US took control of the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam. (protectorate) • The Platt Amendment gave the US the right to intervene in Cuba to protect "life, property, and individual liberties. “
 Philippine American War • As a result war Spain ceded the Philippines to the US for $20 million. • Former Pilipino ally Emilio Aguinaldo led troops against US occupation. • Victory (1902) was costly for both side but in the end the US maintained bases on the Islands. • Philippines Indep. 1946
Philippine American War • As a result war Spain ceded the Philippines to the US for $20 million. • Former Pilipino ally Emilio Aguinaldo led troops against US occupation. • Victory (1902) was costly for both side but in the end the US maintained bases on the Islands. • Philippines Indep. 1946
 Roosevelt Corollary • In 1904, Germany pressed the Dominican Republic for a port on its shores in compensation for an unpaid loan. • President Roosevelt announced the Monroe Doctrines was still in effect. • The US would intervene in the affairs of any Caribbean or Central American Nation. • Panama Canal (1903) “Speak softly and carry a big stick”
Roosevelt Corollary • In 1904, Germany pressed the Dominican Republic for a port on its shores in compensation for an unpaid loan. • President Roosevelt announced the Monroe Doctrines was still in effect. • The US would intervene in the affairs of any Caribbean or Central American Nation. • Panama Canal (1903) “Speak softly and carry a big stick”


