f109837d5fa5fb66bc7c2d15cbf11d7c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 The Procurement Conundrum… ? • How do I solve my procurement problem using technology ? • Is technology going to change the way industry operates ? on t. C os C gic rate g St rcin sou ol tr SCM Negotiations Outsourcing Automation e- et og rn ol te n In ch Te Extended ERP’s s tion Auc EDI s ie
The Procurement Conundrum… ? • How do I solve my procurement problem using technology ? • Is technology going to change the way industry operates ? on t. C os C gic rate g St rcin sou ol tr SCM Negotiations Outsourcing Automation e- et og rn ol te n In ch Te Extended ERP’s s tion Auc EDI s ie
 Electronic Procurement by Chandrashekar T S Electronic Enterprises Laboratory Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Electronic Procurement by Chandrashekar T S Electronic Enterprises Laboratory Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Topics of Discussion Ø Part 1: Procurement Fundamentals Ø Business and Technology Drivers Ø Scope of Procurement Ø Procurement Processes Ø Part 2: Procurement Mechanisms Ø Overview Ø Pointers to more resources Ø Part 3: Procurement Automation Ø Introduction and challenges Ø Conclusion
Topics of Discussion Ø Part 1: Procurement Fundamentals Ø Business and Technology Drivers Ø Scope of Procurement Ø Procurement Processes Ø Part 2: Procurement Mechanisms Ø Overview Ø Pointers to more resources Ø Part 3: Procurement Automation Ø Introduction and challenges Ø Conclusion
 Procurement Fundamentals Business & Technology Drivers • Businesses spend over $20 trillion on external goods and services annually. • Continuous competitive cost pressures in a weak global economy. • INTERNET - Cheap communications medium. • Maturity of complementary technologies – Software agents, data interchange standards, decision technologies.
Procurement Fundamentals Business & Technology Drivers • Businesses spend over $20 trillion on external goods and services annually. • Continuous competitive cost pressures in a weak global economy. • INTERNET - Cheap communications medium. • Maturity of complementary technologies – Software agents, data interchange standards, decision technologies.
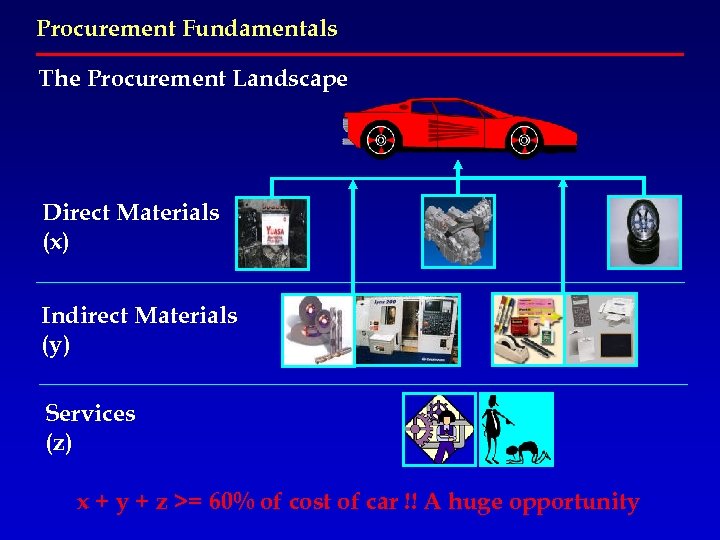 Procurement Fundamentals The Procurement Landscape Direct Materials (x) Indirect Materials (y) Services (z) x + y + z >= 60% of cost of car !! A huge opportunity
Procurement Fundamentals The Procurement Landscape Direct Materials (x) Indirect Materials (y) Services (z) x + y + z >= 60% of cost of car !! A huge opportunity
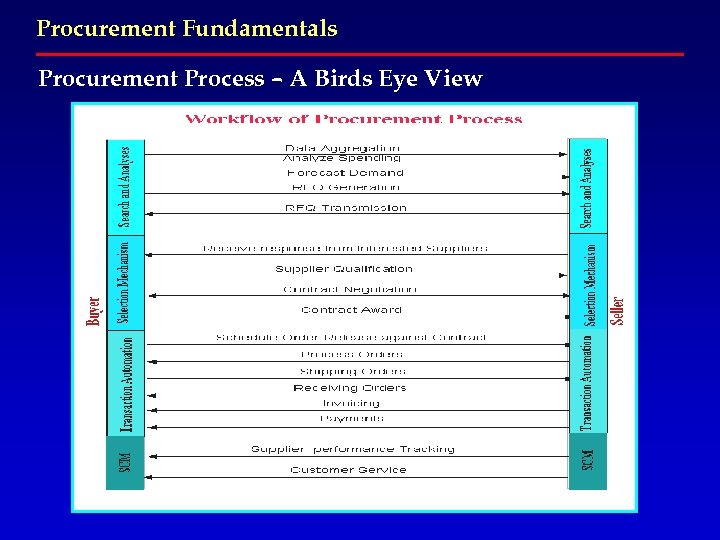 Procurement Fundamentals Procurement Process – A Birds Eye View
Procurement Fundamentals Procurement Process – A Birds Eye View
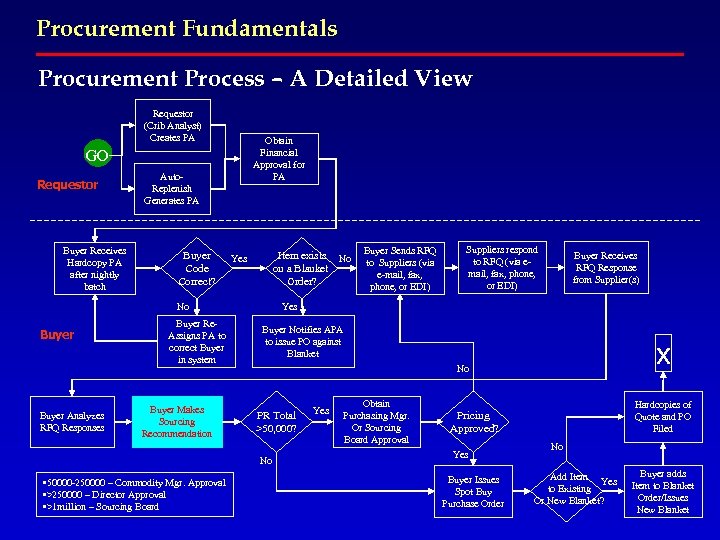 Procurement Fundamentals Procurement Process – A Detailed View Requestor (Crib Analyst) Creates PA Obtain Financial Approval for PA GO Requestor Buyer Receives Hardcopy PA after nightly batch Auto. Replenish Generates PA Buyer Code Correct? Item exists No on a Blanket Order? Yes No Buyer Analyzes RFQ Responses Buyer Re. Assigns PA to correct Buyer in system Buyer Makes Sourcing Recommendation Suppliers respond to RFQ (via email, fax, phone, or EDI) Buyer Receives RFQ Response from Supplier(s) Yes Buyer Notifies APA to issue PO against Blanket x No PR Total >50, 000? No • 50000 -250000 – Commodity Mgr. Approval • >250000 – Director Approval • >1 million – Sourcing Board Buyer Sends RFQ to Suppliers (via e-mail, fax, phone, or EDI) Yes Obtain Purchasing Mgr. Or Sourcing Board Approval Hardcopies of Quote and PO Filed Pricing Approved? Yes Buyer Issues Spot Buy Purchase Order No Add Item Yes to Existing Or New Blanket? Buyer adds Item to Blanket Order/Issues New Blanket
Procurement Fundamentals Procurement Process – A Detailed View Requestor (Crib Analyst) Creates PA Obtain Financial Approval for PA GO Requestor Buyer Receives Hardcopy PA after nightly batch Auto. Replenish Generates PA Buyer Code Correct? Item exists No on a Blanket Order? Yes No Buyer Analyzes RFQ Responses Buyer Re. Assigns PA to correct Buyer in system Buyer Makes Sourcing Recommendation Suppliers respond to RFQ (via email, fax, phone, or EDI) Buyer Receives RFQ Response from Supplier(s) Yes Buyer Notifies APA to issue PO against Blanket x No PR Total >50, 000? No • 50000 -250000 – Commodity Mgr. Approval • >250000 – Director Approval • >1 million – Sourcing Board Buyer Sends RFQ to Suppliers (via e-mail, fax, phone, or EDI) Yes Obtain Purchasing Mgr. Or Sourcing Board Approval Hardcopies of Quote and PO Filed Pricing Approved? Yes Buyer Issues Spot Buy Purchase Order No Add Item Yes to Existing Or New Blanket? Buyer adds Item to Blanket Order/Issues New Blanket
 Part 2 Procurement Mechanisms
Part 2 Procurement Mechanisms
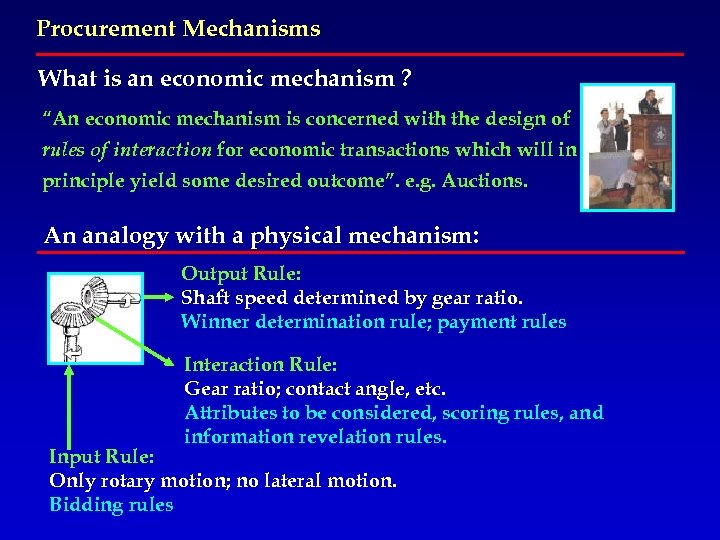 Procurement Mechanisms What is an economic mechanism ? “An economic mechanism is concerned with the design of rules of interaction for economic transactions which will in principle yield some desired outcome”. e. g. Auctions. An analogy with a physical mechanism: Output Rule: Shaft speed determined by gear ratio. Winner determination rule; payment rules Interaction Rule: Gear ratio; contact angle, etc. Attributes to be considered, scoring rules, and information revelation rules. Input Rule: Only rotary motion; no lateral motion. Bidding rules
Procurement Mechanisms What is an economic mechanism ? “An economic mechanism is concerned with the design of rules of interaction for economic transactions which will in principle yield some desired outcome”. e. g. Auctions. An analogy with a physical mechanism: Output Rule: Shaft speed determined by gear ratio. Winner determination rule; payment rules Interaction Rule: Gear ratio; contact angle, etc. Attributes to be considered, scoring rules, and information revelation rules. Input Rule: Only rotary motion; no lateral motion. Bidding rules
 Auction Mechanisms: A Preview • Four basic mechanisms to choose from: • English: First price, ascending auction. • Dutch: First price, descending auction. • Sealed Bid: First price, single round auction. • Vickrey: Second price, ascending auction. • Complications arise because of: • Logistical and capacity concerns. • Cost curves (volume discounts, overtime costs, etc. ). • Exposure, aggregation, and exclusion constraints. • Multiple attributes.
Auction Mechanisms: A Preview • Four basic mechanisms to choose from: • English: First price, ascending auction. • Dutch: First price, descending auction. • Sealed Bid: First price, single round auction. • Vickrey: Second price, ascending auction. • Complications arise because of: • Logistical and capacity concerns. • Cost curves (volume discounts, overtime costs, etc. ). • Exposure, aggregation, and exclusion constraints. • Multiple attributes.
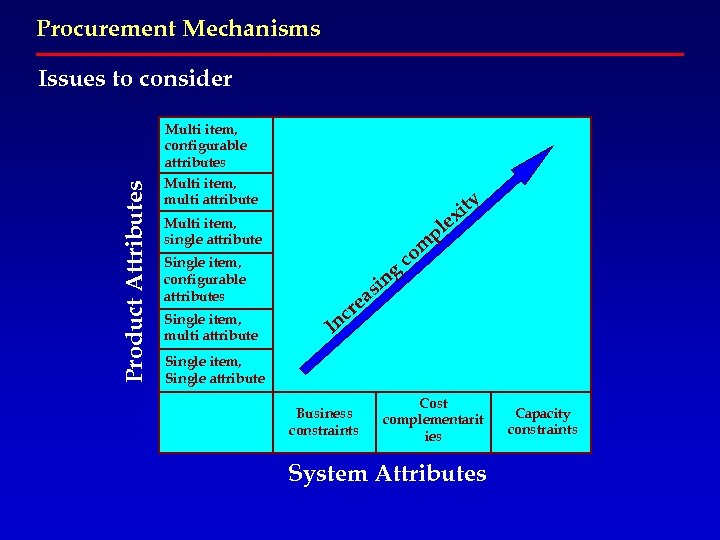 Procurement Mechanisms Product Attributes Issues to consider Multi item, configurable attributes Multi item, multi attribute e Multi item, single attribute Single item, configurable attributes Single item, multi attribute ity x ng i s ea r pl om c c In Single item, Single attribute Business constraints Cost complementarit ies System Attributes Capacity constraints
Procurement Mechanisms Product Attributes Issues to consider Multi item, configurable attributes Multi item, multi attribute e Multi item, single attribute Single item, configurable attributes Single item, multi attribute ity x ng i s ea r pl om c c In Single item, Single attribute Business constraints Cost complementarit ies System Attributes Capacity constraints
 Design criteria for automated auctions • Economic criteria • Efficient mechanisms v/s optimal mechanisms • Incentive compatibility • Budget balance • Solution equilibrium • Computational criteria • At the agents level • Strategic complexity • Valuation complexity • At the mechanism level • Winner determination complexity • Communication complexity
Design criteria for automated auctions • Economic criteria • Efficient mechanisms v/s optimal mechanisms • Incentive compatibility • Budget balance • Solution equilibrium • Computational criteria • At the agents level • Strategic complexity • Valuation complexity • At the mechanism level • Winner determination complexity • Communication complexity
 Automated Procurement Mechanisms Elements of an effective procurement platform: Ø Negotiation Ø Collaboration Ø Project Management Ø Knowledge Management Ø Document Management Ø Analytics
Automated Procurement Mechanisms Elements of an effective procurement platform: Ø Negotiation Ø Collaboration Ø Project Management Ø Knowledge Management Ø Document Management Ø Analytics
 Automated Procurement Mechanisms To probe further: http: //lcm. csa. iisc. ernet. in http: //www. market-design. com http: //task. stanford. edu http: //www. cs. huji. ac. il/~mosheb http: //www. cs. huji. ac. il/~noam http: //www. cs. huji. ac. il/~lehmann http: //www. cs. brown. edu/people/amygreen http: //www. sims. berkeley. edu/resources http: //www. robotics. stanford. edu/resources http: //kasbah. media. mit. edu http: //auction. eecs. umich. edu http: //ecommerce. media. mit. edu http: //www. media. mit. edu/ http: //www. ibm. com/iac
Automated Procurement Mechanisms To probe further: http: //lcm. csa. iisc. ernet. in http: //www. market-design. com http: //task. stanford. edu http: //www. cs. huji. ac. il/~mosheb http: //www. cs. huji. ac. il/~noam http: //www. cs. huji. ac. il/~lehmann http: //www. cs. brown. edu/people/amygreen http: //www. sims. berkeley. edu/resources http: //www. robotics. stanford. edu/resources http: //kasbah. media. mit. edu http: //auction. eecs. umich. edu http: //ecommerce. media. mit. edu http: //www. media. mit. edu/ http: //www. ibm. com/iac
 Part 3 Procurement Automation
Part 3 Procurement Automation
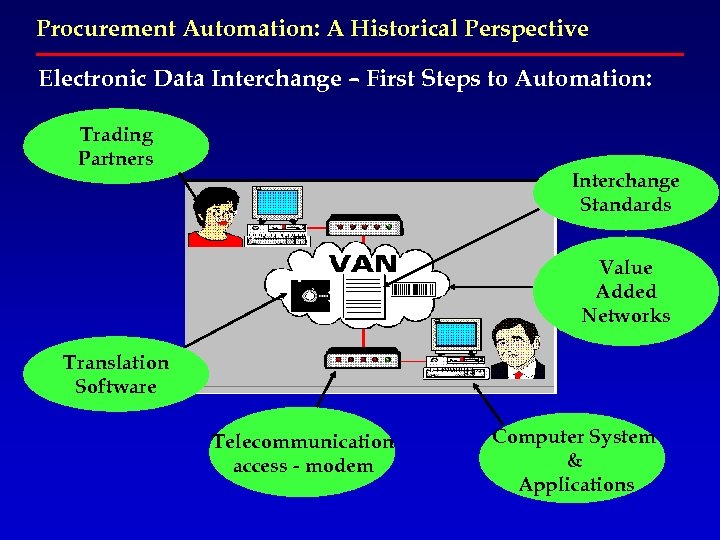 Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange – First Steps to Automation: Trading Partners Interchange Standards Value Added Networks Translation Software Telecommunication access - modem Computer System & Applications
Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange – First Steps to Automation: Trading Partners Interchange Standards Value Added Networks Translation Software Telecommunication access - modem Computer System & Applications
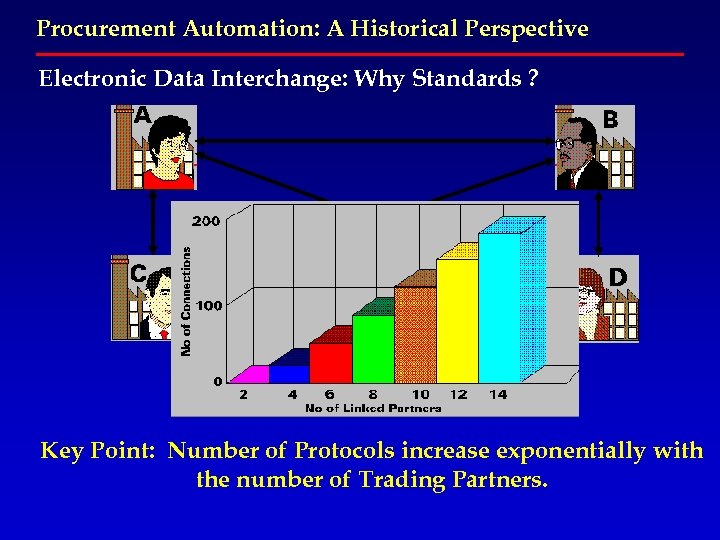 Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: Why Standards ? Key Point: Number of Protocols increase exponentially with the number of Trading Partners.
Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: Why Standards ? Key Point: Number of Protocols increase exponentially with the number of Trading Partners.
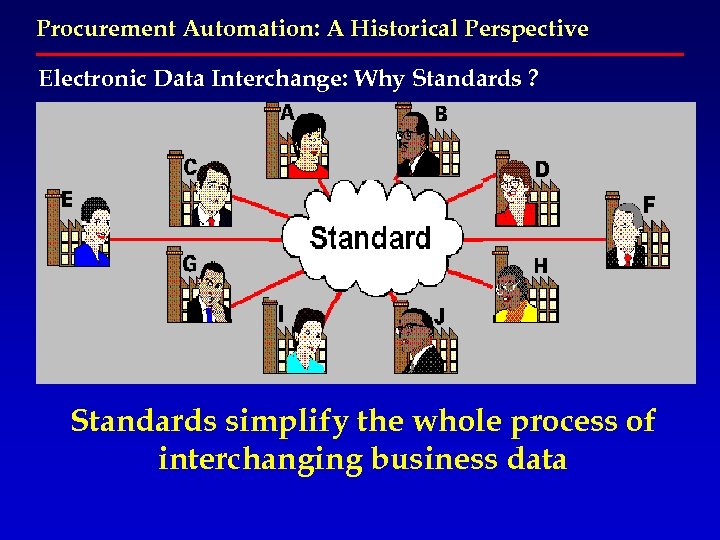 Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: Why Standards ? Standards simplify the whole process of interchanging business data
Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: Why Standards ? Standards simplify the whole process of interchanging business data
 Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: How many Standards ? Electronic Data Interchange for Administration Commerce and Trade
Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: How many Standards ? Electronic Data Interchange for Administration Commerce and Trade
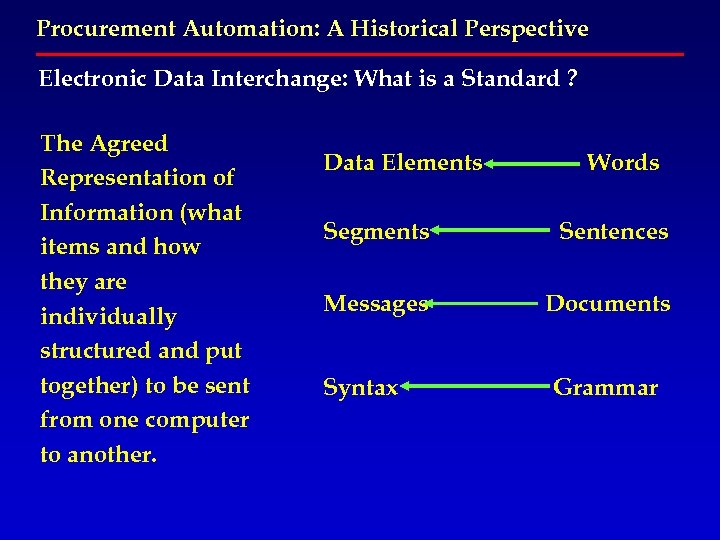 Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: What is a Standard ? The Agreed Representation of Information (what items and how they are individually structured and put together) to be sent from one computer to another. Data Elements Words Segments Sentences Messages Documents Syntax Grammar
Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: What is a Standard ? The Agreed Representation of Information (what items and how they are individually structured and put together) to be sent from one computer to another. Data Elements Words Segments Sentences Messages Documents Syntax Grammar
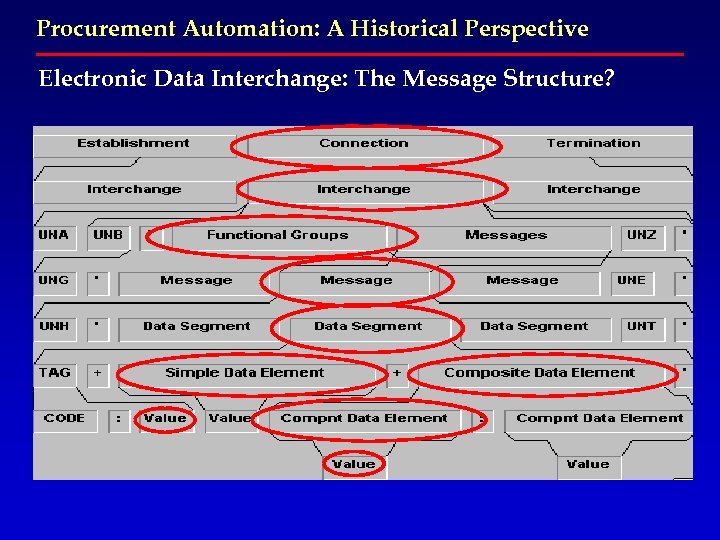 Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: The Message Structure?
Procurement Automation: A Historical Perspective Electronic Data Interchange: The Message Structure?
 Procurement Automation Electronic Data Interchange: Consequences • Industry wide standards • Formalized process flows • Open standards • Secure and legal interchanges • Available tools and service providers • Proven business benefits • Version control • Implementation Mechanics • Maintaining and Updating the Standards • Cost of Implementation, steep on-ramp • Change Management difficult because of distributed maps and translation software
Procurement Automation Electronic Data Interchange: Consequences • Industry wide standards • Formalized process flows • Open standards • Secure and legal interchanges • Available tools and service providers • Proven business benefits • Version control • Implementation Mechanics • Maintaining and Updating the Standards • Cost of Implementation, steep on-ramp • Change Management difficult because of distributed maps and translation software
 Procurement Automation Alternatives to EDI: INTERNET based Technologies • No software installation required at the supplier • only the Internet browser • Easy and quick connection possible • Hub determines the information contents • Pre-entry of fixed data possible • No Data transmission charges - Only Internet access costs • No translator costs • Centralisation of Administration effort • Management of changes is easier.
Procurement Automation Alternatives to EDI: INTERNET based Technologies • No software installation required at the supplier • only the Internet browser • Easy and quick connection possible • Hub determines the information contents • Pre-entry of fixed data possible • No Data transmission charges - Only Internet access costs • No translator costs • Centralisation of Administration effort • Management of changes is easier.
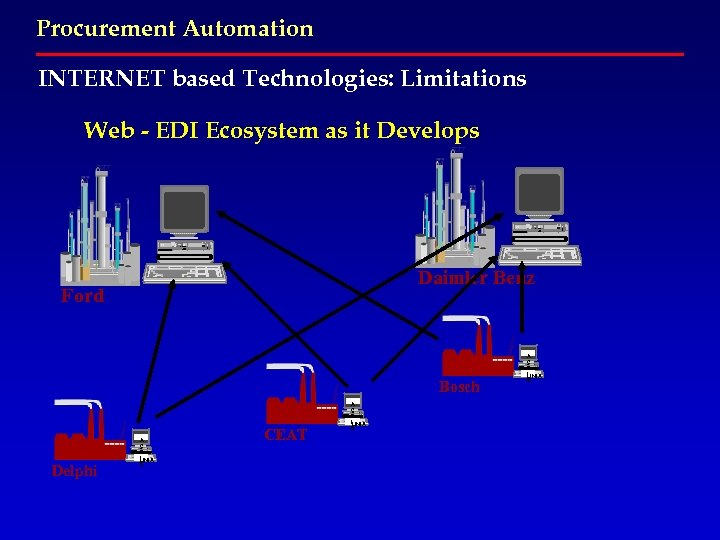 Procurement Automation INTERNET based Technologies: Limitations Web - EDI Ecosystem as it Develops Daimler Benz Ford Bosch Delphi A C T I UNIX S CEAT A C T I UNIX S
Procurement Automation INTERNET based Technologies: Limitations Web - EDI Ecosystem as it Develops Daimler Benz Ford Bosch Delphi A C T I UNIX S CEAT A C T I UNIX S
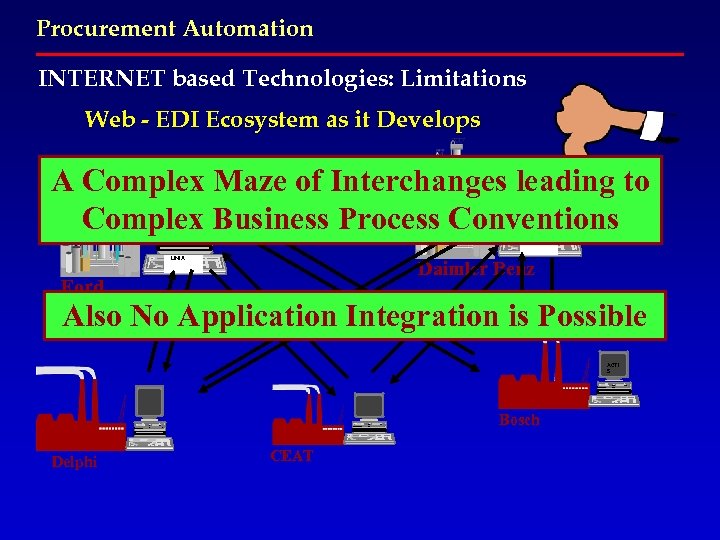 Procurement Automation INTERNET based Technologies: Limitations Web - EDI Ecosystem as it Develops A Complex Maze of Interchanges leading to Complex Business Process Conventions ACTIS UNIX Daimler Benz Ford Also No Application Integration is Possible ACTI S Bosch Delphi CEAT
Procurement Automation INTERNET based Technologies: Limitations Web - EDI Ecosystem as it Develops A Complex Maze of Interchanges leading to Complex Business Process Conventions ACTIS UNIX Daimler Benz Ford Also No Application Integration is Possible ACTI S Bosch Delphi CEAT
 Procurement Automation INTERNET based Technologies: Is There a Solution ? Yes XML (e. Xtensible Markup Language) Over to VKV ….
Procurement Automation INTERNET based Technologies: Is There a Solution ? Yes XML (e. Xtensible Markup Language) Over to VKV ….
 Conclusion To probe further: http: //www. edifact. org http: //www. uncefact. org http: //www. monkeyweb. com http: //www. xml-edi. org http: //www. ediint. org http: //www. vcm. tatamotors. co. in Thank You !
Conclusion To probe further: http: //www. edifact. org http: //www. uncefact. org http: //www. monkeyweb. com http: //www. xml-edi. org http: //www. ediint. org http: //www. vcm. tatamotors. co. in Thank You !



