Precedent.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

The problem of precedent in the court proceedings Dr. Tomas Žilinskas Mykolas Romeris University Institute of Constitutional and Administrative Law

Contact Information for Questions n zilinskas@cab. lt
Doctrine of the Court Precedent n STARE n Ratio DECISIS decidenti n Obiter dictum

Doctrine of the Court Precedent and n Common Law System. n Civil Law System.
The of the precedent – UK (I) n The n Horizontal court hierarchy and vertical bindingness

The of the precedent – UK (II) n AVOIDING PRECEDENTS: n Distinguishing n Overruling

The of the precedent – UK (III) n STATUTE V PRECEDENT Statutes, as a form of parliamentary legislation, are therefore the primary source of English Law. However the case law created by judges that constitutes the cornerstone of the English Legal system, for English law has never been generally codified.
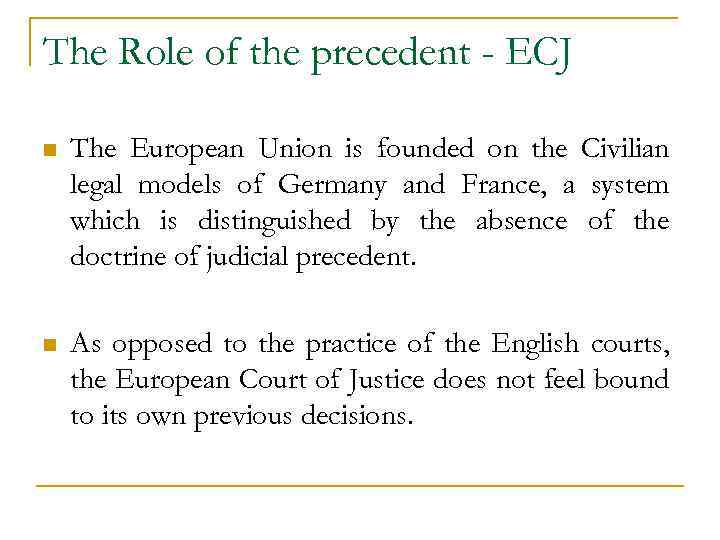
The Role of the precedent - ECJ n The European Union is founded on the Civilian legal models of Germany and France, a system which is distinguished by the absence of the doctrine of judicial precedent. n As opposed to the practice of the English courts, the European Court of Justice does not feel bound to its own previous decisions.

The role of precedent – case of the Lithuania n Legal regulation (I): n When hearing cases courts shall be guided by the Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania, statutes, international agreements to which the Republic of Lithuania is a party, resolutions of the Government, other legal acts in force in the Republic of Lithuania which are not in conflict with the statutes.

The role of precedent – case of the Lithuania n Legal regulation (II): n When hearing cases courts shall also be guided by the officially reported decisions of the Constitutional Court of the Republic of Lithuania and shall take account of the orders of the Supreme Court published in the bulletin of the this court and the decisions, rulings and orders of the Supreme Administrative Court published in the bulletin of the Supreme Administrative Court.

The role of precedent – case of the Lithuania n Legal regulation (III): n When hearing cases courts shall apply the legislation of the European Union and be guided by the resolutions of judicial institutions of the European Union as well as their prejudicial decisions on the issues of interpretation and validity of legal acts of the European Union.

The role of precedent – case of the Lithuania n n Legal regulation (III): When taking decisions in cases of appropriate categories the courts shall be bound by the rules of interpretation of law created by them, formed in analogous or similar cases. The courts of lower instance when taking decisions in cases of appropriate categories shall be bound by the rules of interpretation formulated in analogous or conceptually similar cases. The court practice in cases of appropriate categories must be amended and new rules for the interpretation of law in analogous or similar cases may be created only in cases when it is inevitable or objectively necessary.

The role of precedent – case of the Lithuania n Decision of The Constitutional Court: n The Constitutional Court has explicitly indicated that judicial precedents are sources of law and that by following previous decisions uniform and consistent practice of courts would be achieved. Therefore the courts of lower instance are bound by their own decisions and the decisions of the higher courts, whereas the higher courts, including the Court of Appeal and the Supreme Court, are bound also by their own earlier decisions.

The role of precedent – case of the Lithuania n After The Decision of The Constitutional Court: n The Lithuanian law doctrine emphasises that the reason of increasing importance of court practice is the changing attitude towards a judge: he is no longer expected to merely formally apply the law, he is expected to apply and interpret the law creatively or even to act as a quasi-legislative body. The aim of interpretation and application of law is to ensure succession, predictability and stability of courts’ practice, which are the core maxims guaranteeing the proper implementation of the rule of law, based on justice and equality of all persons before the law.

The rules of application of judicial precedent- Lithuania n n First, with regard to the argument that derogation from the established practice of courts is a ground of cassation appeal, it is important to justify reasonably and in detail on what questions of law the courts did not follow the proposed interpretations of law in previous decisions of the Supreme Court. Second, only those prior judicial decisions which were made in analogous cases are binding as precedent, i. e. the precedent is applied only in those cases which contain factual circumstances identical or very similar to the factual circumstances of the cases which established the precedent and in which the same rule of law, as in the case with the established precedent, should be applied.

The rules of application of judicial precedent- Lithuania n Third, it is essential to consider other significant circumstances: the time of the establishment of the precedent; whether the precedent reflects the existing court practice or whether it is only a sporadic occurrence; persuasion of reasoning; important social, economic and other changes resulting from the decision of the court binding as a precedent. n Fourth, after the aforesaid decisions of the Constitutional Court it is argued in the judicial practice that only those decisions of the Supreme Court of Lithuania are binding as precedents where cassation issues have been raised. n Fifth, the Supreme Court pays a lot of attention on whether the corresponding precedent reflects the established court practice, or whether it is a single occurrence.

The Conditions for Correction of the Court Practice n Constitutional Court explained that the practice of the courts of general competence in the cases of corresponding categories may be modified and new judicial precedents in the cases of those categories may be established only when it is unavoidably and objectively necessary and when it may be grounded and justified constitutionally.

Conclusions n n Advantages of The Court Precedent Disadvantages of The Court Precedent

Topics for the upcoming (04/12/2013) seminar n Please prepare written presentations (duration ~ 20 min. ) on these topics: n The sources of law in civil court proceedings (the role of the precedent) in Ukraine (please provide examples); n The sources of law in criminal court proceedings (the role of the precedent) in Ukraine (please provide examples); n The sources of law in administrative court proceedings (the role of the precedent) in Ukraine (please provide examples).

Literature for Self-Studies n n n A Theory Of Precident. From Analytical Positivism to a Post-analytical Philosophy of Law / by. R. Siltala, Oxford, 2000. Randy J. Kozel. Stare Decisis as Judicial Doctrine. Washington and Lee Law Review, Vol. 67, No. 2, 2010. Vincy Fon, Francesco Parisi. Judicial precedents in civil law systems: A dynamic analysis. International Review of Law and Economics 26 (2006). Markesinis, B. Judicial style and judicial reasoning in English and Germany. Cambridge Law Journal. 2000, 59(2): 305– 320. Rorive, I. Diverging legal culture but Similar Jurisprudence of overruling: the case of the House of Lords and the Belgian Cour de cassation. European Preview of Private law. 2004, 3.

Thank You for the Attention! See You on Wednesday
Precedent.ppt