7f6d6800ac54d21e6c738393110bd5fc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

The Price/Earnings Ratio P/E Ratio

What everybody knows about the P/E ratio • Widely used stock measure • Definition: P/E = Price (in dollars /share) divided by Earnings (in dollars/share) – Example: Exxon. Mobil (XOM) costs $84. 26/share and earned $6. 80/share. – P/E = $84. 26/$6. 80 = 12. 4 – Often called “Price Multiple” or “Earnings Multiple” • Used for valuing and comparing stocks • Relatively Simple!!! 2

But wait: there’s more… • Which P/E did you have in mind? – There are lots of definitions, and they are different – What share price to use? Which earnings to use? • What’s a good P/E? – How do I know if a P/E is too high, low, or just right? • How do I use it? • What if E bounces around a lot? – What about one-time windfalls? – What if the company is losing money? • What’s the P/E of the whole stock market? – Is it safe to go into the water yet? 3

What is a good P/E for a Stock? In general, it depends … – Fast growing companies trade at higher P/E, but often risky. – Slow growing companies trade at lower P/E, but often safer. – The higher the P/E, the more “speculative” the investment. – Exceptions: Intel (P/E=22), GM (P/E=7). Which is safer? Super Big Caveat – Stockholders may never enjoy earnings squandered or expropriated by management 4
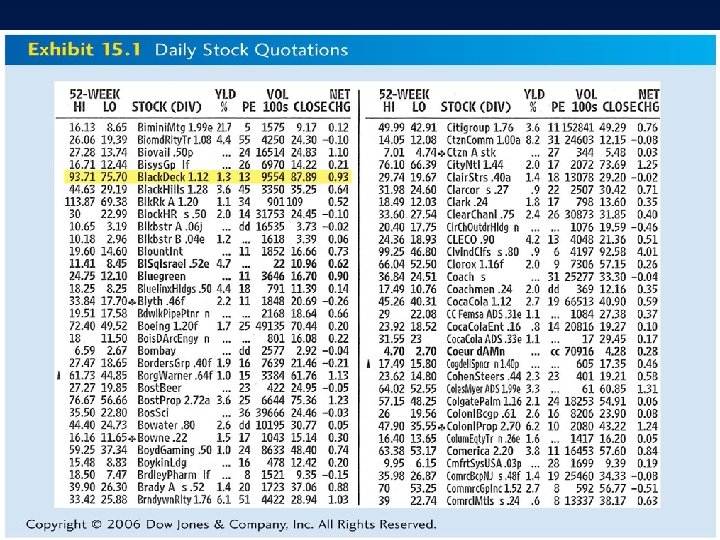
5

Price Earnings Valuation Method • The price earning ratio (PE) is a widely watched measure of how much the market is willing to pay for $1 of earnings from a firm. • A high PE has two interpretations: – A higher than average PE may mean that the market expects earnings to rise in the future. – A high PE may indicate that the market thinks the firm’s earnings are very low risk and is therefore willing to pay a premium for them.

Price Earnings Valuation Method • The PE ratio can be used to estimate the value of a firm’s stock. • Firms in the same industry are expected to have similar PE ratios in the long run. • The value of a firm’s stock can be found by multiplying the average industry PE times the expected earnings per share. P/E x E = P

Price Earnings Model: Example • The average industry PE ratio for restaurants similar to Applebee’s is 23. What is the current price of Applebee’s if earnings per share projected to be $1. 13? – P 0 = P/E x E – P 0 + 23 x $1. 13 = $26.

Price Earnings Valuation Method • Advantages: – Useful for valuing privately held firms and firms that do not pay dividends. • Disadvantages: – By using an industry average PE ratio, firmspecific factors that might contribute to a longterm PE ratio above or below the average are ignored.

Using the P/E • P/E normalizes price and earnings, allowing direct comparison - How would you like to price apples? Dollars per basket? Or dollars per pound? • Compare a stock to… – its history – its future – its close peers – its industry – the market • Compare the entire market to reality 10
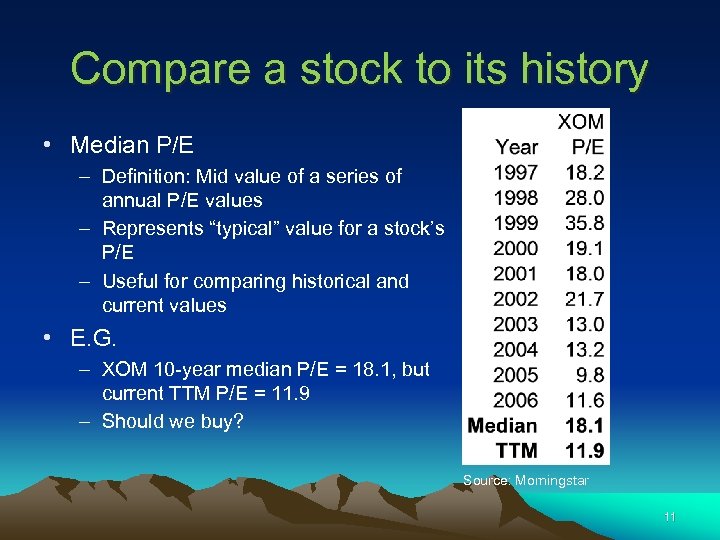
Compare a stock to its history • Median P/E – Definition: Mid value of a series of annual P/E values – Represents “typical” value for a stock’s P/E – Useful for comparing historical and current values • E. G. – XOM 10 -year median P/E = 18. 1, but current TTM P/E = 11. 9 – Should we buy? Source: Morningstar 11

Compare a stock to its future • What will XOM trade for in 5 years? – (If I knew, I wouldn’t tell you) – Hard to forecast Price all by itself – Easier if we separate into 2 parts: Earnings, and P/E ratio • Forecast from Value Line – XOM earnings will grow slower in the future, 6%/year vs. 14%/year over last 10 years – XOM P/E will be 12. 5, lower than historic 18. 1 • Therefore, in 5 years, XOM will price will be P = Present Earnings x Earnings Growth x future P/E = $5. 40 x (1. 06)**5 x 12. 5 = $90 Corresponds to 3% annualized total return • Is XOM expensive or cheap? • Note: Value. Line “normalizes” or smoothes current E by averaging over last 3 years beforecasting future E 12

Using the P/E cont. • Compare a stock to its peers – XOM P/E = $84. 26/$6. 80 = 12. 4 – Shell Oil P/E = $76. 70/$8. 30 = 9. 2 – Is Shell “cheaper” than XOM? • Compare a stock to its industry – Average current P/E of oil cos. is 10. 0 (Value. Line) • Compare a stock to the market – Relative P/E: Divide a stock’s P/E by P/E of overall market (as represented by S&P 500 or other index) – Allows for comparison with market at present and over time – E. G. XOM P/E (12. 5) / Market P/E (19. 5) = 0. 64 13
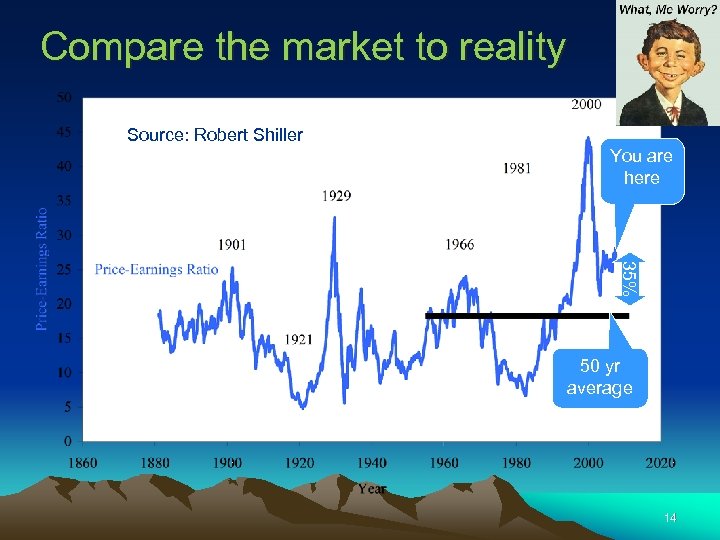
Compare the market to reality Source: Robert Shiller You are here 35% 50 yr average 14

What Drives P/E? • • • Earnings growth Business cycle Inflation Interest rates Investor exuberance/depression It is all about perceived future expectations! 15

The End 16
7f6d6800ac54d21e6c738393110bd5fc.ppt