3c1684bff8eed87abbe3f63e78c9f6ab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 The play-wright on my right thinks it right that some conventional rite should symbolize the right of every man to write as he pleases 1
The play-wright on my right thinks it right that some conventional rite should symbolize the right of every man to write as he pleases 1
 The play-wright on my right thinks it right that some conventional rite should symbolize the right of every man to write as he pleases 2
The play-wright on my right thinks it right that some conventional rite should symbolize the right of every man to write as he pleases 2
 The problem of differentiating between polysemy and homonymy spring is represented • as two homonyms in V. K. Müller’s and Hornby’s dictionaries: I. a season of the year, II. a) the act of springing, a leap, b) a place where a stream of water comes up out of the earth. • as three homonyms in V. D. Arakin’s dictionary. 3
The problem of differentiating between polysemy and homonymy spring is represented • as two homonyms in V. K. Müller’s and Hornby’s dictionaries: I. a season of the year, II. a) the act of springing, a leap, b) a place where a stream of water comes up out of the earth. • as three homonyms in V. D. Arakin’s dictionary. 3
 Homonyms (Gr. homos “similar” + onoma “name”) are words which have identical sound form and/or spelling but are different in their meaning. E. g. bank (n) – a shore (of the river); bank (n) – an institution for receiving, lending, exchanging and safeguarding money 4
Homonyms (Gr. homos “similar” + onoma “name”) are words which have identical sound form and/or spelling but are different in their meaning. E. g. bank (n) – a shore (of the river); bank (n) – an institution for receiving, lending, exchanging and safeguarding money 4
 Classification of homonyms (1) • Homonyms proper (собственно омонимы): E. g. ball (мяч) – ball (бал); bank (банк) – bank (берег); light, adj. (легкий) – light, n. (свет). • Homophones: E. g. piece – peace; air - heir; knight – night; rose (flower) – rose (Past form of rise). • Homographs: E. g. bow [bəu] (лук) – bow [bau] (поклон); lead [liːd] (лидерство) – lead [led] (свинец); row [rəu] (ряд) – row [rau] (ссора). 5
Classification of homonyms (1) • Homonyms proper (собственно омонимы): E. g. ball (мяч) – ball (бал); bank (банк) – bank (берег); light, adj. (легкий) – light, n. (свет). • Homophones: E. g. piece – peace; air - heir; knight – night; rose (flower) – rose (Past form of rise). • Homographs: E. g. bow [bəu] (лук) – bow [bau] (поклон); lead [liːd] (лидерство) – lead [led] (свинец); row [rəu] (ряд) – row [rau] (ссора). 5
 Classification of homonyms (2) The criterion: whether homonyms belong to the same or to different parts of speech. • Lexical • Lexico-grammatical • Grammatical 6
Classification of homonyms (2) The criterion: whether homonyms belong to the same or to different parts of speech. • Lexical • Lexico-grammatical • Grammatical 6
 Lexical homonyms Belong to the same part of speech. The difference is confined to the lexical meaning only: fair (ярмарка) – fare (плата за проезд); bow [bəu] (лук) - bow [bau] (поклон); match (спичка) – match (матч) 7
Lexical homonyms Belong to the same part of speech. The difference is confined to the lexical meaning only: fair (ярмарка) – fare (плата за проезд); bow [bəu] (лук) - bow [bau] (поклон); match (спичка) – match (матч) 7
 Lexico-grammatical homonyms Belong to different parts of speech and differ in lexical meaning: tear [tɪə], n. (слеза) – to tear, v. [tɛə] (рвать); bear, n. [bɛə] (медведь) – to bare [bɛə], v. (носить) – bare [bɛə], adj. (обнаженный). 8
Lexico-grammatical homonyms Belong to different parts of speech and differ in lexical meaning: tear [tɪə], n. (слеза) – to tear, v. [tɛə] (рвать); bear, n. [bɛə] (медведь) – to bare [bɛə], v. (носить) – bare [bɛə], adj. (обнаженный). 8
 Grammatical homonyms Belong to different parts of speech but there is a link between their lexical meanings: milk – to milk; practice – to practise 9
Grammatical homonyms Belong to different parts of speech but there is a link between their lexical meanings: milk – to milk; practice – to practise 9
 Classification of homonyms (3) The criterion: whether the paradigms of the homonyms coincide completely or partially. • Full homonyms are identical in sound in all their forms and paradigms: • match (матч) - match (спичка); ball (мяч) – ball (бал) • Partial homonyms are identical only in some of the forms: • to found (основывать) – found (Past Indefinite, Past Participle of the verb to find); • to lie (lied, lied) (лгать) – to lie (lay, lain) (лежать); 10
Classification of homonyms (3) The criterion: whether the paradigms of the homonyms coincide completely or partially. • Full homonyms are identical in sound in all their forms and paradigms: • match (матч) - match (спичка); ball (мяч) – ball (бал) • Partial homonyms are identical only in some of the forms: • to found (основывать) – found (Past Indefinite, Past Participle of the verb to find); • to lie (lied, lied) (лгать) – to lie (lay, lain) (лежать); 10
 Sources of homonyms phonetic changes: night – knight (OE kniht); write (OE writan) – right (OE reht and riht). borrowings: • bank (берег): native origin - bank (банк): Italian; • fair (справедливый): native - fair (ярмарка): French. 11
Sources of homonyms phonetic changes: night – knight (OE kniht); write (OE writan) – right (OE reht and riht). borrowings: • bank (берег): native origin - bank (банк): Italian; • fair (справедливый): native - fair (ярмарка): French. 11
 Sources of homonyms shortening of words: flu (from influenza) - flew (Past Indef. of to fly); fan (from fanatic) -fan (вентилятор). conversion: comb, n. – to comb, v. , pale, adj. – to pale, v. , to make, v. – make, n. (grammatical homonyms). 12
Sources of homonyms shortening of words: flu (from influenza) - flew (Past Indef. of to fly); fan (from fanatic) -fan (вентилятор). conversion: comb, n. – to comb, v. , pale, adj. – to pale, v. , to make, v. – make, n. (grammatical homonyms). 12
 Sources of homonyms • Split polysemy: spring (n) – “the act of springing, a leap”; spring (n) – “a place where a stream of water comes up out of the earth”; spring (n) – “a season of the year”. The original word: springan - “to jump, ” “to leap” 13
Sources of homonyms • Split polysemy: spring (n) – “the act of springing, a leap”; spring (n) – “a place where a stream of water comes up out of the earth”; spring (n) – “a season of the year”. The original word: springan - “to jump, ” “to leap” 13
 Split polysemy: BAR • late 12 c. , "stake or rod of iron used to fasten a door or gate, " from Old French barre (12 c. ) • c. 1300, "to fasten (a gate, etc. ) with a bar, " from bar (n. 1) • "tavern, " 1590 s, so called in reference to the bars of the barrier or counter over which drinks or food were served to customers (see bar (n. 1)). • "whole body of lawyers, the legal profession, " 1550 s, a sense which derives ultimately from the railing that separated benchers from the hall in the Inns of Court. 14
Split polysemy: BAR • late 12 c. , "stake or rod of iron used to fasten a door or gate, " from Old French barre (12 c. ) • c. 1300, "to fasten (a gate, etc. ) with a bar, " from bar (n. 1) • "tavern, " 1590 s, so called in reference to the bars of the barrier or counter over which drinks or food were served to customers (see bar (n. 1)). • "whole body of lawyers, the legal profession, " 1550 s, a sense which derives ultimately from the railing that separated benchers from the hall in the Inns of Court. 14
 Definition of synonyms • Synonyms are words with the same denotation (or denotative component) but different in connotations (or connotative components). (semantic approach) • Methods of studying synonyms: definitional, transformational, componential. 15
Definition of synonyms • Synonyms are words with the same denotation (or denotative component) but different in connotations (or connotative components). (semantic approach) • Methods of studying synonyms: definitional, transformational, componential. 15
 Origins of synonyms • to begin (native, neutral) – to commence (French, bookish) – to initiate (Latin, bookish) • bodily (native, neutral) — corporal (Latin, bookish) • brotherly (native, neutral) — fraternal (Latin, bookish). 16
Origins of synonyms • to begin (native, neutral) – to commence (French, bookish) – to initiate (Latin, bookish) • bodily (native, neutral) — corporal (Latin, bookish) • brotherly (native, neutral) — fraternal (Latin, bookish). 16
 SOURCES OF SYNONYMY Native English Words borrowed from French Words borrowed from Latin to ask belly to gather empty to end to rise teaching to question stomach to assemble devoid to finish to mount guidance to interrogate abdomen to collect vacuous to complete to ascend instruction 17
SOURCES OF SYNONYMY Native English Words borrowed from French Words borrowed from Latin to ask belly to gather empty to end to rise teaching to question stomach to assemble devoid to finish to mount guidance to interrogate abdomen to collect vacuous to complete to ascend instruction 17
 Phrasal Verbs • • choose : : pick out, abandon : : give up; continue : : go on; enter : : come in; lift : : pick up; postpone : : put o ff ; quarrel : : fall out; return : : bring back. 18
Phrasal Verbs • • choose : : pick out, abandon : : give up; continue : : go on; enter : : come in; lift : : pick up; postpone : : put o ff ; quarrel : : fall out; return : : bring back. 18
 V. V. Vinogradov’s classification of synonyms • Ideographic synonyms are words conveying the same concept but differing in shades of meaning: power — force — energy; beautiful — handsome — pretty. • Stylistic synonyms have the same denotational components but differ in stylistic characteristics: hearty (neutr. ) – cordial (formal), to imitate (neutr. ) – to monkey (inform. ), to begin (neutr. ) – to commence (formal); to die (neutr. ) – to pass away (formal). 19
V. V. Vinogradov’s classification of synonyms • Ideographic synonyms are words conveying the same concept but differing in shades of meaning: power — force — energy; beautiful — handsome — pretty. • Stylistic synonyms have the same denotational components but differ in stylistic characteristics: hearty (neutr. ) – cordial (formal), to imitate (neutr. ) – to monkey (inform. ), to begin (neutr. ) – to commence (formal); to die (neutr. ) – to pass away (formal). 19
 V. V. Vinogradov’s classification of synonyms • Absolute synonyms coincide in all their shades of meaning and in all their stylistic characteristics: gift - present; homeland – motherland, etc. The phenomenon of absolute synonymy is very rare in the language and very often temporary. 20
V. V. Vinogradov’s classification of synonyms • Absolute synonyms coincide in all their shades of meaning and in all their stylistic characteristics: gift - present; homeland – motherland, etc. The phenomenon of absolute synonymy is very rare in the language and very often temporary. 20
 Classification of synonyms based on the types of connotations • The connotation of degree or intensity: to surprise – to astonish – to amaze – to astound; to shout – to yell – to roar (the rising degree of intensity) • The connotation of duration: to stare – to glare – to gaze – to peep - to peer (a lasting look) - to glance (a brief look) • The emotive connotation: to stare (to look in surprise, curiosity) – to glare (in anger, rage or fury) – to gaze (in tenderness, admiration or wonder) 21
Classification of synonyms based on the types of connotations • The connotation of degree or intensity: to surprise – to astonish – to amaze – to astound; to shout – to yell – to roar (the rising degree of intensity) • The connotation of duration: to stare – to glare – to gaze – to peep - to peer (a lasting look) - to glance (a brief look) • The emotive connotation: to stare (to look in surprise, curiosity) – to glare (in anger, rage or fury) – to gaze (in tenderness, admiration or wonder) 21
 Classification of synonyms based on the types of connotations • The evaluative connotation (conveys the speaker’s attitude towards the referent): wellknown – famous – notorious (-) – celebrated (+) (cf. : a notorious criminal, but a celebrated scientist). • The causative connotation: to shiver (because of the frost) – to shudder (with fear, horror). • The connotation of manner: to stroll – to stride – to pace – to trot – to swagger 22
Classification of synonyms based on the types of connotations • The evaluative connotation (conveys the speaker’s attitude towards the referent): wellknown – famous – notorious (-) – celebrated (+) (cf. : a notorious criminal, but a celebrated scientist). • The causative connotation: to shiver (because of the frost) – to shudder (with fear, horror). • The connotation of manner: to stroll – to stride – to pace – to trot – to swagger 22
 Synonyms that differ in their emotive or evaluative meaning There are words that bear the same meaning but express different emotions of the user, indicating the attitude of the user toward he is using about. 23
Synonyms that differ in their emotive or evaluative meaning There are words that bear the same meaning but express different emotions of the user, indicating the attitude of the user toward he is using about. 23
 Collaborator vs accomplice • Collaborator and accomplice are synonymous as they share the meaning of “a person who helps the other”, but: • Collaborator helps another in doing something good, while • Accomplice helps another in the criminal act. 24
Collaborator vs accomplice • Collaborator and accomplice are synonymous as they share the meaning of “a person who helps the other”, but: • Collaborator helps another in doing something good, while • Accomplice helps another in the criminal act. 24
 Synonyms of the verb to look • to stare: to look + steadily, lastingly + in surprise, curiosity, etc. • to glare: to look + steadily, lastingly + in anger, rage, fury • to gaze: to look + steadily, lastingly + in tenderness, admiration, wonder • to glance: to look + briefly, in passing • to peep: to look + steadily, lastingly + by stealth; through an opening or from a concealed location • to peer: to look + steadily, lastingly + with difficulty or strain 25
Synonyms of the verb to look • to stare: to look + steadily, lastingly + in surprise, curiosity, etc. • to glare: to look + steadily, lastingly + in anger, rage, fury • to gaze: to look + steadily, lastingly + in tenderness, admiration, wonder • to glance: to look + briefly, in passing • to peep: to look + steadily, lastingly + by stealth; through an opening or from a concealed location • to peer: to look + steadily, lastingly + with difficulty or strain 25
 Dialectal synonyms • Dialectal synonyms – synonyms used in different regional dialects. • These are words with more or less the same meaning used in different regional dialects. • British English and American English are the two major geographical varieties of the English language. 26
Dialectal synonyms • Dialectal synonyms – synonyms used in different regional dialects. • These are words with more or less the same meaning used in different regional dialects. • British English and American English are the two major geographical varieties of the English language. 26
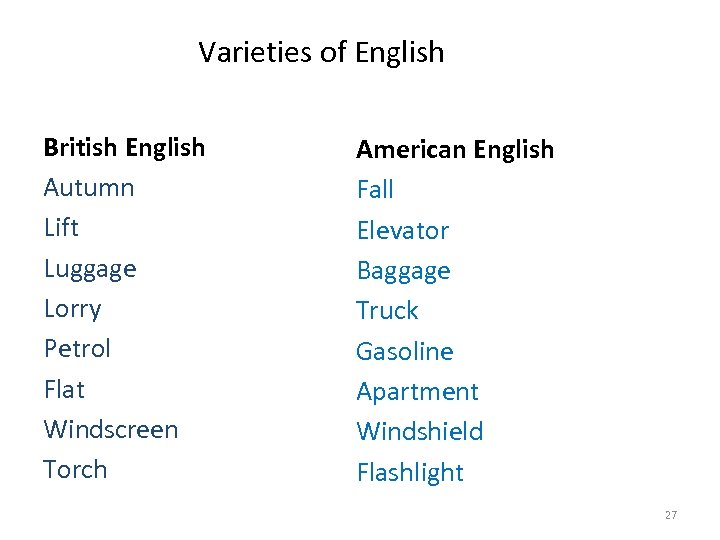 Varieties of English British English Autumn Lift Luggage Lorry Petrol Flat Windscreen Torch American English Fall Elevator Baggage Truck Gasoline Apartment Windshield Flashlight 27
Varieties of English British English Autumn Lift Luggage Lorry Petrol Flat Windscreen Torch American English Fall Elevator Baggage Truck Gasoline Apartment Windshield Flashlight 27
 Collocational synonyms • Some synonyms differ in their collocation, i. e. in the words they go together with. • Accuse, charge, rebuke are followed by different prepositions: accuse of, charge with, rebuke for 28
Collocational synonyms • Some synonyms differ in their collocation, i. e. in the words they go together with. • Accuse, charge, rebuke are followed by different prepositions: accuse of, charge with, rebuke for 28
 The synonymic dominant (the dominant synonym) the most general word in the group belonging to the basic stock of words stylistically neutral having high frequency of usage, vast combinability, lacking connotations. • expresses the notion common to all the members of the group in the most general way without any additional information. to surprise – to astonish – to amaze – to astound; to shout – to yell – to bellow – to roar; to look – to stare – to glare – to gaze – to peer. • • 29
The synonymic dominant (the dominant synonym) the most general word in the group belonging to the basic stock of words stylistically neutral having high frequency of usage, vast combinability, lacking connotations. • expresses the notion common to all the members of the group in the most general way without any additional information. to surprise – to astonish – to amaze – to astound; to shout – to yell – to bellow – to roar; to look – to stare – to glare – to gaze – to peer. • • 29
 Synonyms of a polysemantic word • to close – to finish (e. g. to close a discussion) • to close – to shut (e. g. to close the door). 30
Synonyms of a polysemantic word • to close – to finish (e. g. to close a discussion) • to close – to shut (e. g. to close the door). 30
 Euphemisms • Euphemism (Gr. eu “well” + pheme “speaking”) is a substitution for an expression that may offend or suggest something unpleasant to the receiver, using instead an agreeable or less offensive expression. • E. g. drunk: intoxicated, under the influence (formal), tipsy (colloq. ), boiled, tanked, high as a kite (slang), etc. 31
Euphemisms • Euphemism (Gr. eu “well” + pheme “speaking”) is a substitution for an expression that may offend or suggest something unpleasant to the receiver, using instead an agreeable or less offensive expression. • E. g. drunk: intoxicated, under the influence (formal), tipsy (colloq. ), boiled, tanked, high as a kite (slang), etc. 31
 Targets for euphemistic substitution • • • notions of death, madness, stupidity, drunkenness, certain physiological processes, crimes, etc. 32
Targets for euphemistic substitution • • • notions of death, madness, stupidity, drunkenness, certain physiological processes, crimes, etc. 32
 Euphemisms (examples) To die: to expire, to pass away, to depart, to join the silent majority, to kick the bucket, to breathe one’s last, to be gathered to one’s fathers etc. Lavatory : powder room, washroom, restroom, retiring room, (public) comfort station, ladies' (room), gentlemen's (room), water-closet, w. c. ([d 0 blju: 'si: ]), public conveniences 33
Euphemisms (examples) To die: to expire, to pass away, to depart, to join the silent majority, to kick the bucket, to breathe one’s last, to be gathered to one’s fathers etc. Lavatory : powder room, washroom, restroom, retiring room, (public) comfort station, ladies' (room), gentlemen's (room), water-closet, w. c. ([d 0 blju: 'si: ]), public conveniences 33
 Antonyms • Antonyms are words of the same part of speech having common denotative component of meaning but expressing contrasting points of the same notion. • wide - narrow, admit - deny, produce consume, old - young, etc. 34
Antonyms • Antonyms are words of the same part of speech having common denotative component of meaning but expressing contrasting points of the same notion. • wide - narrow, admit - deny, produce consume, old - young, etc. 34
 Antonyms and parts of speech • Adjectives: high – low, strong – weak, bitter – sweet. • Verbs: to lose – to find, to live – to die, to open – to close. • Nouns: friend – enemy, joy – grief, good – evil. 35
Antonyms and parts of speech • Adjectives: high – low, strong – weak, bitter – sweet. • Verbs: to lose – to find, to live – to die, to open – to close. • Nouns: friend – enemy, joy – grief, good – evil. 35
 Antonyms of a polysemantic word E. g. dull: • Boring – the deficiency in interest: interesting, amusing, entertaining • Stupid - the deficiency in intellect: clever, bright, capable • Not active - the deficiency in activity: active 36
Antonyms of a polysemantic word E. g. dull: • Boring – the deficiency in interest: interesting, amusing, entertaining • Stupid - the deficiency in intellect: clever, bright, capable • Not active - the deficiency in activity: active 36
 Structural classification of antonyms (V. N. Komissarov. Dictionary of English Antonyms) • D e r i v a t i o n a l antonyms (antonyms of the same root): e. g. to do – to undo, cheerful - cheerless; (affixes which help in the formation of antonyms: un-, in-, dis-, -less, etc. ) • antonyms of different roots: e. g. day – night, rich - poor. 37
Structural classification of antonyms (V. N. Komissarov. Dictionary of English Antonyms) • D e r i v a t i o n a l antonyms (antonyms of the same root): e. g. to do – to undo, cheerful - cheerless; (affixes which help in the formation of antonyms: un-, in-, dis-, -less, etc. ) • antonyms of different roots: e. g. day – night, rich - poor. 37
 Semantic classification of antonyms • Contradictories : dead – alive, single – married (contradict each other: not dead = alive, not single = married). • Contraries (gradable) are polar members of a gradual opposition which may have intermediate elements: cold – (cool – warm) - hot. 38
Semantic classification of antonyms • Contradictories : dead – alive, single – married (contradict each other: not dead = alive, not single = married). • Contraries (gradable) are polar members of a gradual opposition which may have intermediate elements: cold – (cool – warm) - hot. 38
 OPPOSITES • Directional opposites involve an opposition in direction with reference to some point (come -go, arrive – depart). • Conversives (or relational opposites) as F. R. Palmer calls them denote one and the same referent or situation as viewed from different points of view, with a reversal of the order of participants and their roles. He gave her flowers. She received flowers from him. husband, wife; doctor, patient; teach, learn 39
OPPOSITES • Directional opposites involve an opposition in direction with reference to some point (come -go, arrive – depart). • Conversives (or relational opposites) as F. R. Palmer calls them denote one and the same referent or situation as viewed from different points of view, with a reversal of the order of participants and their roles. He gave her flowers. She received flowers from him. husband, wife; doctor, patient; teach, learn 39
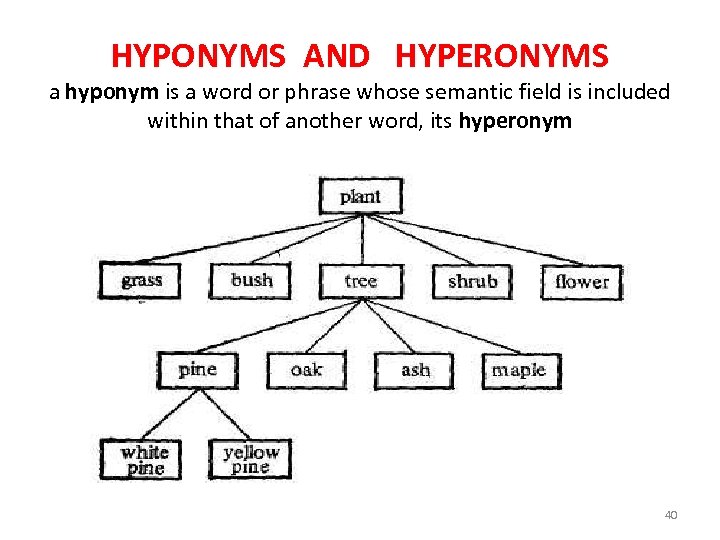 HYPONYMS AND HYPERONYMS a hyponym is a word or phrase whose semantic field is included within that of another word, its hyperonym 40
HYPONYMS AND HYPERONYMS a hyponym is a word or phrase whose semantic field is included within that of another word, its hyperonym 40
 MERONYMS VS. HOLONYMS MERONYM A word that denotes a constituent part or a member of something. For example, apple is a meronym of apple tree. HOLONYM A word that names the whole of which a given word is a part finger ---- hand roof ----- house 41
MERONYMS VS. HOLONYMS MERONYM A word that denotes a constituent part or a member of something. For example, apple is a meronym of apple tree. HOLONYM A word that names the whole of which a given word is a part finger ---- hand roof ----- house 41
 PARONYMS similar-sounding words, related to one part of speech and one semantic field, but having, as a rule, different meanings Politic – acting or judging wisely, prudent. Политичный, расчетливый. Political – of the state, of government, of politics. Политический 42
PARONYMS similar-sounding words, related to one part of speech and one semantic field, but having, as a rule, different meanings Politic – acting or judging wisely, prudent. Политичный, расчетливый. Political – of the state, of government, of politics. Политический 42


