841e7abcb0d6e1423e51ed730995f3ed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 The Physics Education Technology Project Kathy Perkins & the rest of the Ph. ET Team University of Colorado at Boulder http: //phet. colorado. edu
The Physics Education Technology Project Kathy Perkins & the rest of the Ph. ET Team University of Colorado at Boulder http: //phet. colorado. edu
 Ph. ET Project Physics faculty: Michael Dubson Noah Finkelstein Kathy Perkins Carl Wieman (Director) Postdocs: Sam Mc. Kagan Linda Koch Teacher collaborators: Trish Loeblein Staff: Krista Beck Linda Wellmann Ph. D. students: Wendy Adams Chris Keller Noah Podolefsky Pat Kohl Danielle Harlow Programmers: Ron Le. Master Sam Reid Chris Malley Michael Dubson Website: Chris Maytag ~5 -6 full time equivalents
Ph. ET Project Physics faculty: Michael Dubson Noah Finkelstein Kathy Perkins Carl Wieman (Director) Postdocs: Sam Mc. Kagan Linda Koch Teacher collaborators: Trish Loeblein Staff: Krista Beck Linda Wellmann Ph. D. students: Wendy Adams Chris Keller Noah Podolefsky Pat Kohl Danielle Harlow Programmers: Ron Le. Master Sam Reid Chris Malley Michael Dubson Website: Chris Maytag ~5 -6 full time equivalents
 Ph. ET Funding NSF Kavli Foundation Hewlett Foundation University of Colorado Alfred Nobel
Ph. ET Funding NSF Kavli Foundation Hewlett Foundation University of Colorado Alfred Nobel
 Outline • Introduction to Ph. ET • Design Process and Role of Research/Assessment • Research and Assessment of ØDesign: • User interface: interpretation / effectiveness • For learning & engagement in exploration/discovery ØUse: • Where and how: lecture, lab, recitation, homework • Assessment: When these work (and don’t)
Outline • Introduction to Ph. ET • Design Process and Role of Research/Assessment • Research and Assessment of ØDesign: • User interface: interpretation / effectiveness • For learning & engagement in exploration/discovery ØUse: • Where and how: lecture, lab, recitation, homework • Assessment: When these work (and don’t)
 Physics Education Techn Project • Suite of interactive simulations (~60) • Covering intro physics, modern physics, bit of chemistry • Research-based and user-tested • Free! Online or downloadable. (~70 Mbytes) • Easy to use and incorporate in class Show website http: //phet. colorado. edu
Physics Education Techn Project • Suite of interactive simulations (~60) • Covering intro physics, modern physics, bit of chemistry • Research-based and user-tested • Free! Online or downloadable. (~70 Mbytes) • Easy to use and incorporate in class Show website http: //phet. colorado. edu
 Accessibility ØUniversal, web-based languages Java or Flash Ø 3 ways to run sims: • directly from web • download whole website to local computer for offline use • (new) download selected sims for offline use • In last year: 1 Million sims launched; 50, 000 site downloads ØEasy to translate into other languages • Mirror site in Spanish
Accessibility ØUniversal, web-based languages Java or Flash Ø 3 ways to run sims: • directly from web • download whole website to local computer for offline use • (new) download selected sims for offline use • In last year: 1 Million sims launched; 50, 000 site downloads ØEasy to translate into other languages • Mirror site in Spanish
 Ease of use Ø Flexible use • Pick and choose which sims to use • Customize use to your environment Ø Facilitate effective use with Activities Database • Community of users share ideas/activities • Over 50 Ph. ET and user-contributed activities
Ease of use Ø Flexible use • Pick and choose which sims to use • Customize use to your environment Ø Facilitate effective use with Activities Database • Community of users share ideas/activities • Over 50 Ph. ET and user-contributed activities
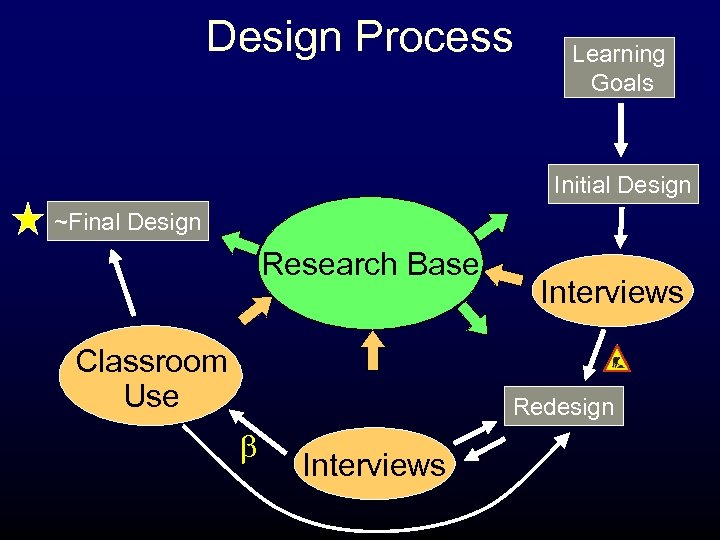 Design Process Learning Goals Initial Design ~Final Design Research Base Classroom Use Interviews Redesign b Interviews
Design Process Learning Goals Initial Design ~Final Design Research Base Classroom Use Interviews Redesign b Interviews
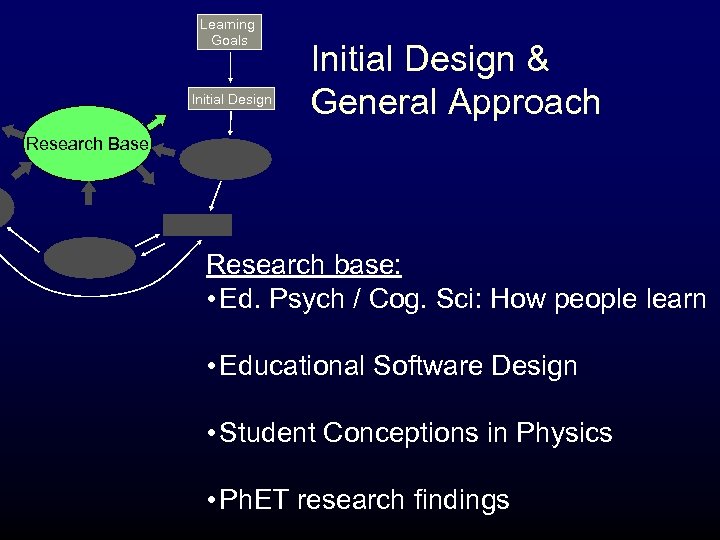 Learning Goals Initial Design & General Approach Research Base Research base: • Ed. Psych / Cog. Sci: How people learn • Educational Software Design • Student Conceptions in Physics • Ph. ET research findings
Learning Goals Initial Design & General Approach Research Base Research base: • Ed. Psych / Cog. Sci: How people learn • Educational Software Design • Student Conceptions in Physics • Ph. ET research findings
 Initial Design & General Approach • • Fun and engaging w/ open-style play area Highly interactive Dynamic feedback. Interaction links to animation. Explore and discover (constructivist) Connection to real world Explicit visual & conceptual models (that experts use) Productive constraints K. K. Perkins, et al, “Ph. ET: Interactive Simulations for Teaching and Learning Physics”, Physics Teacher (Jan 2006)
Initial Design & General Approach • • Fun and engaging w/ open-style play area Highly interactive Dynamic feedback. Interaction links to animation. Explore and discover (constructivist) Connection to real world Explicit visual & conceptual models (that experts use) Productive constraints K. K. Perkins, et al, “Ph. ET: Interactive Simulations for Teaching and Learning Physics”, Physics Teacher (Jan 2006)
 Visual Models
Visual Models
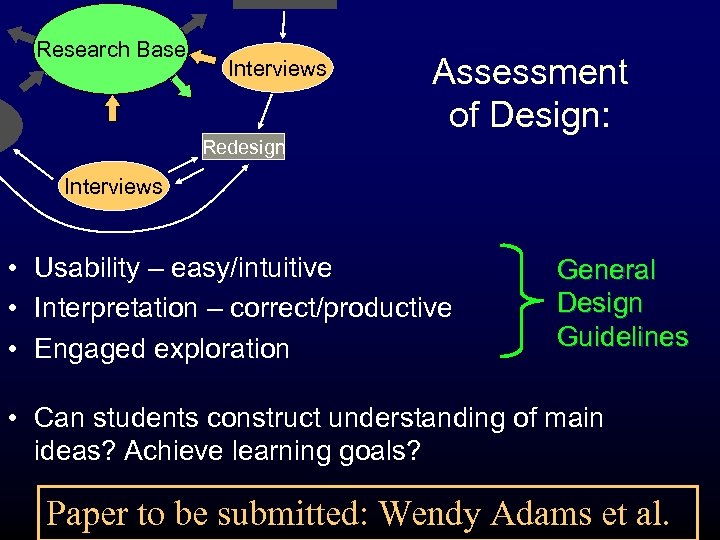 Research Base Interviews Assessment of Design: Redesign Interviews • Usability – easy/intuitive • Interpretation – correct/productive • Engaged exploration General Design Guidelines • Can students construct understanding of main ideas? Achieve learning goals? Paper to be submitted: Wendy Adams et al.
Research Base Interviews Assessment of Design: Redesign Interviews • Usability – easy/intuitive • Interpretation – correct/productive • Engaged exploration General Design Guidelines • Can students construct understanding of main ideas? Achieve learning goals? Paper to be submitted: Wendy Adams et al.
 Research Base Interviews Redesign Interviews Assessment of Design: Interviews • Think-aloud style • Either no guidance or limited to one or two conceptual questions. • 30 to 60 minutes (1 -3 simulations) • 4 -6 interviews per version of simulation
Research Base Interviews Redesign Interviews Assessment of Design: Interviews • Think-aloud style • Either no guidance or limited to one or two conceptual questions. • 30 to 60 minutes (1 -3 simulations) • 4 -6 interviews per version of simulation
 Research Base Interviews Redesign Interviews Assessment of Design: Findings from Interviews • Intuitive Controls – Click and Drag – Grab-able Objects • Representations – Cartoon-like features • Limited Text - Students do not read • Start-up for engagement – Little or no animation – “Wiggle me’s” Full listing of guidelines will be in Adams et al.
Research Base Interviews Redesign Interviews Assessment of Design: Findings from Interviews • Intuitive Controls – Click and Drag – Grab-able Objects • Representations – Cartoon-like features • Limited Text - Students do not read • Start-up for engagement – Little or no animation – “Wiggle me’s” Full listing of guidelines will be in Adams et al.
 Research Base Use of Sims: Classroom Use ü Well honed tool for learning Ø Doesn’t guarantee its effectiveness: Depends on context Frames of Context Course (Level & Goals) Setting (Lecture/Lab) Task / Activity Student
Research Base Use of Sims: Classroom Use ü Well honed tool for learning Ø Doesn’t guarantee its effectiveness: Depends on context Frames of Context Course (Level & Goals) Setting (Lecture/Lab) Task / Activity Student
 Research Base Use of Sims: Classroom Use Pre-class or pre-lab Activity Lecture/classroom Visual Aids, Interactive Lecture Demos, & Concept tests Labs/Recitations Group activities Homework Frames of Context Course (Level & Goals) Setting (Lecture/Lab) Task / Activity Student
Research Base Use of Sims: Classroom Use Pre-class or pre-lab Activity Lecture/classroom Visual Aids, Interactive Lecture Demos, & Concept tests Labs/Recitations Group activities Homework Frames of Context Course (Level & Goals) Setting (Lecture/Lab) Task / Activity Student
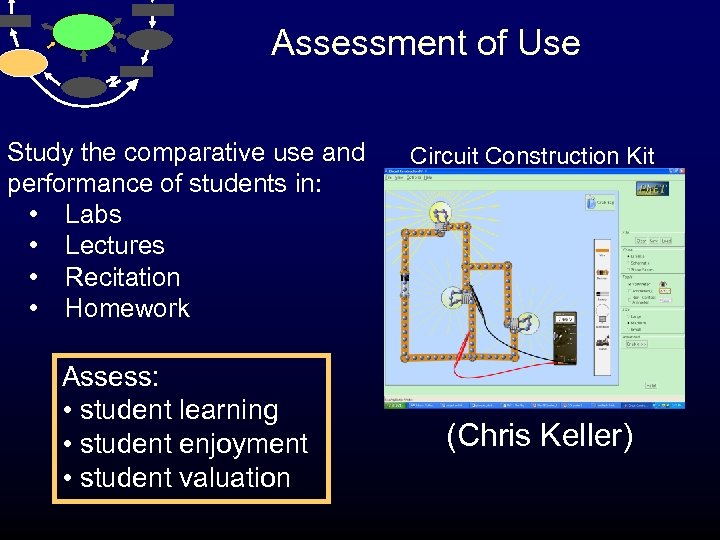 Assessment of Use Study the comparative use and performance of students in: • Labs • Lectures • Recitation • Homework Assess: • student learning • student enjoyment • student valuation Circuit Construction Kit (Chris Keller)
Assessment of Use Study the comparative use and performance of students in: • Labs • Lectures • Recitation • Homework Assess: • student learning • student enjoyment • student valuation Circuit Construction Kit (Chris Keller)
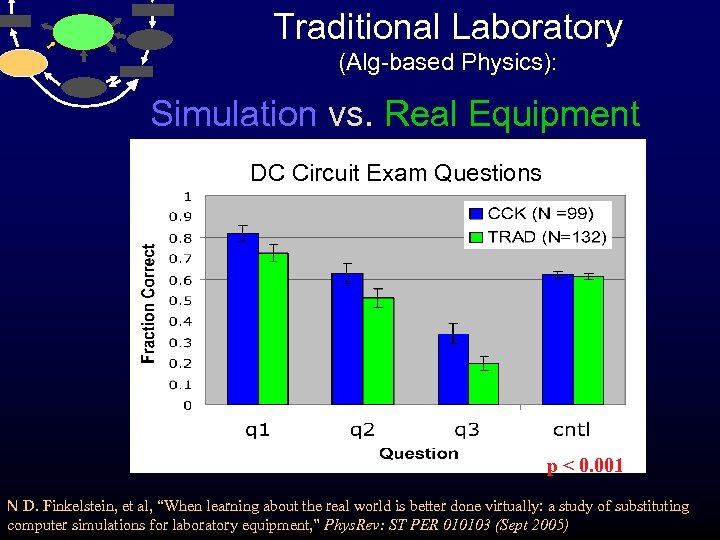 Traditional Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Simulation vs. Real Equipment DC Circuit Exam Questions vs. p < 0. 001 N D. Finkelstein, et al, “When learning about the real world is better done virtually: a study of substituting computer simulations for laboratory equipment, ” Phys. Rev: ST PER 010103 (Sept 2005)
Traditional Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Simulation vs. Real Equipment DC Circuit Exam Questions vs. p < 0. 001 N D. Finkelstein, et al, “When learning about the real world is better done virtually: a study of substituting computer simulations for laboratory equipment, ” Phys. Rev: ST PER 010103 (Sept 2005)
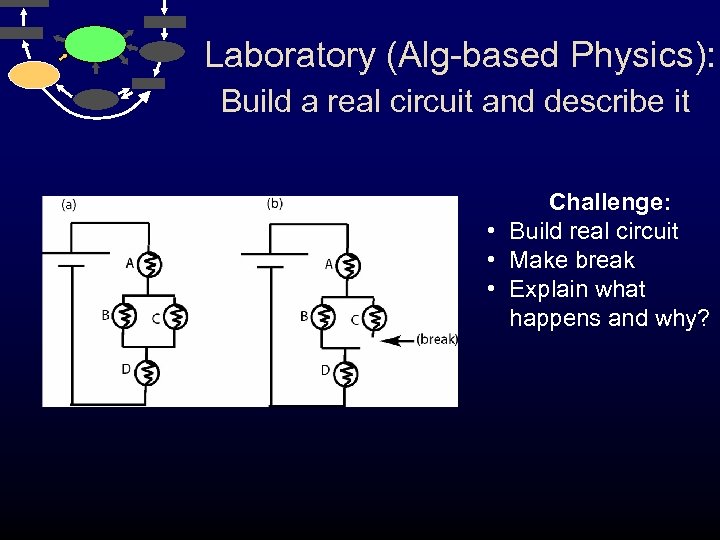 Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Build a real circuit and describe it Challenge: • Build real circuit • Make break • Explain what happens and why?
Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Build a real circuit and describe it Challenge: • Build real circuit • Make break • Explain what happens and why?
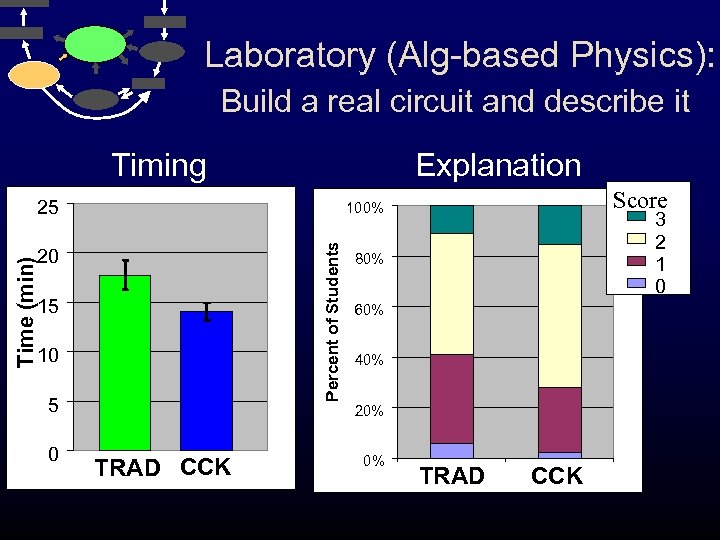 Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Build a real circuit and describe it Timing Explanation 25 Percent of Students Time (min) 20 15 10 5 0 Score 100% 3 2 1 0 80% 60% 40% 20% TRAD CCK
Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Build a real circuit and describe it Timing Explanation 25 Percent of Students Time (min) 20 15 10 5 0 Score 100% 3 2 1 0 80% 60% 40% 20% TRAD CCK
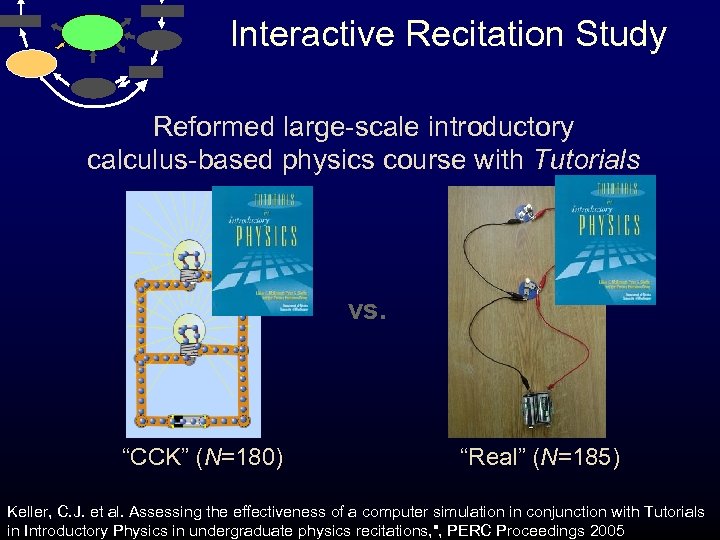 Interactive Recitation Study Reformed large-scale introductory calculus-based physics course with Tutorials vs. “CCK” (N=180) “Real” (N=185) Keller, C. J. et al. Assessing the effectiveness of a computer simulation in conjunction with Tutorials in Introductory Physics in undergraduate physics recitations, ", PERC Proceedings 2005
Interactive Recitation Study Reformed large-scale introductory calculus-based physics course with Tutorials vs. “CCK” (N=180) “Real” (N=185) Keller, C. J. et al. Assessing the effectiveness of a computer simulation in conjunction with Tutorials in Introductory Physics in undergraduate physics recitations, ", PERC Proceedings 2005
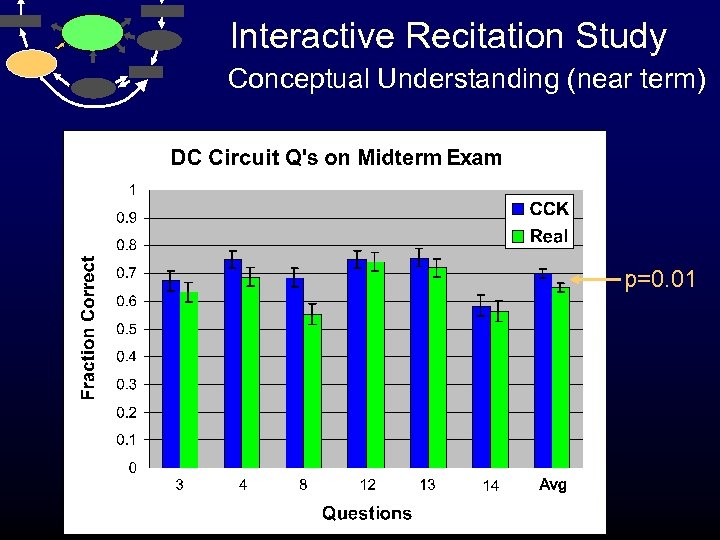 Interactive Recitation Study Conceptual Understanding (near term) p=0. 01
Interactive Recitation Study Conceptual Understanding (near term) p=0. 01
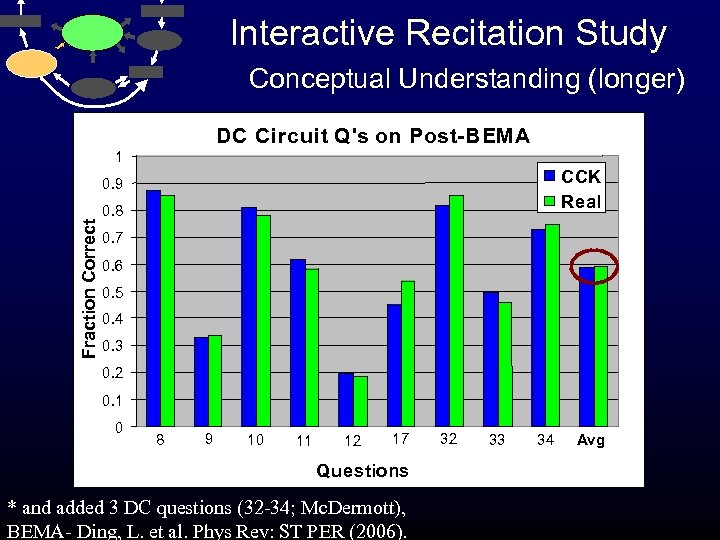 Interactive Recitation Study Conceptual Understanding (longer) DC Circuit Q's on Post-BEMA 1 CCK Real Fraction Correct 0. 9 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 8 9 10 11 12 17 Questions * and added 3 DC questions (32 -34; Mc. Dermott), BEMA- Ding, L. et al. Phys Rev: ST PER (2006). 32 33 34 Avg
Interactive Recitation Study Conceptual Understanding (longer) DC Circuit Q's on Post-BEMA 1 CCK Real Fraction Correct 0. 9 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 8 9 10 11 12 17 Questions * and added 3 DC questions (32 -34; Mc. Dermott), BEMA- Ding, L. et al. Phys Rev: ST PER (2006). 32 33 34 Avg
 Context dependence? • Different populations Alg-based vs. Calc-based • Different activities Traditional vs PER-based • Different courses Instruction: More traditional vs More interactive HW/Exams: More traditional vs More conceptual Our Research Goal: • Assess use across these sorts of dimensions • Characterize and understand. Identify where use is effective at improving learning
Context dependence? • Different populations Alg-based vs. Calc-based • Different activities Traditional vs PER-based • Different courses Instruction: More traditional vs More interactive HW/Exams: More traditional vs More conceptual Our Research Goal: • Assess use across these sorts of dimensions • Characterize and understand. Identify where use is effective at improving learning
 Lecture (Calc-based w/ peer instruction) Sims vs. Pictures/Words/Demo Influence on Environment & Learning vs.
Lecture (Calc-based w/ peer instruction) Sims vs. Pictures/Words/Demo Influence on Environment & Learning vs.
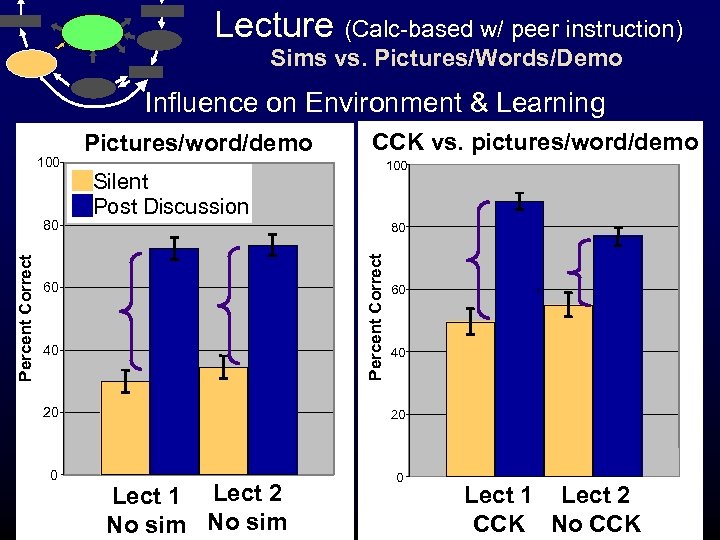 Lecture (Calc-based w/ peer instruction) Sims vs. Pictures/Words/Demo Influence on Environment & Learning Percent Correct 80 CCK vs. pictures/word/demo 100 Silent Post Discussion 80 Percent Correct 100 Pictures/word/demo 60 40 60 c 40 20 20 0 0 Lect 1 Lect 2 No sim Lect 1 Lect 2 CCK No CCK
Lecture (Calc-based w/ peer instruction) Sims vs. Pictures/Words/Demo Influence on Environment & Learning Percent Correct 80 CCK vs. pictures/word/demo 100 Silent Post Discussion 80 Percent Correct 100 Pictures/word/demo 60 40 60 c 40 20 20 0 0 Lect 1 Lect 2 No sim Lect 1 Lect 2 CCK No CCK
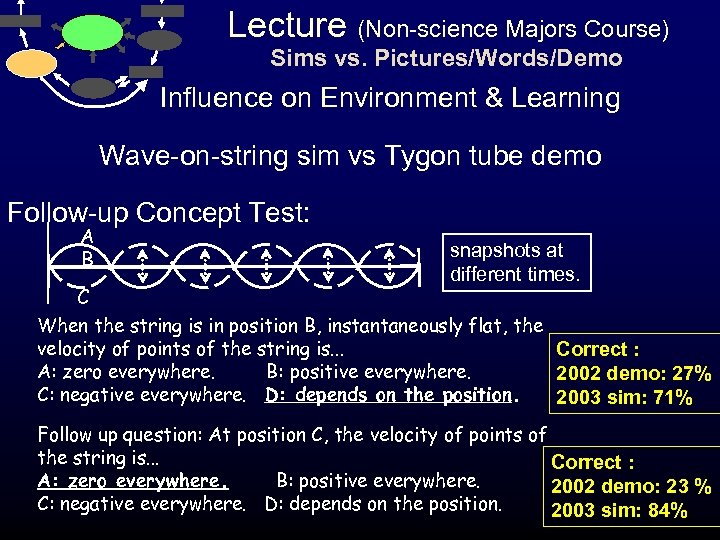 Lecture (Non-science Majors Course) Sims vs. Pictures/Words/Demo Influence on Environment & Learning Wave-on-string sim vs Tygon tube demo Follow-up Concept Test: A B C snapshots at different times. When the string is in position B, instantaneously flat, the velocity of points of the string is. . . Correct : A: zero everywhere. B: positive everywhere. 2002 demo: 27% C: negative everywhere. D: depends on the position. 2003 sim: 71% Follow up question: At position C, the velocity of points of the string is. . . Correct : A: zero everywhere. B: positive everywhere. 2002 demo: 23 % C: negative everywhere. D: depends on the position. 2003 sim: 84%
Lecture (Non-science Majors Course) Sims vs. Pictures/Words/Demo Influence on Environment & Learning Wave-on-string sim vs Tygon tube demo Follow-up Concept Test: A B C snapshots at different times. When the string is in position B, instantaneously flat, the velocity of points of the string is. . . Correct : A: zero everywhere. B: positive everywhere. 2002 demo: 27% C: negative everywhere. D: depends on the position. 2003 sim: 71% Follow up question: At position C, the velocity of points of the string is. . . Correct : A: zero everywhere. B: positive everywhere. 2002 demo: 23 % C: negative everywhere. D: depends on the position. 2003 sim: 84%
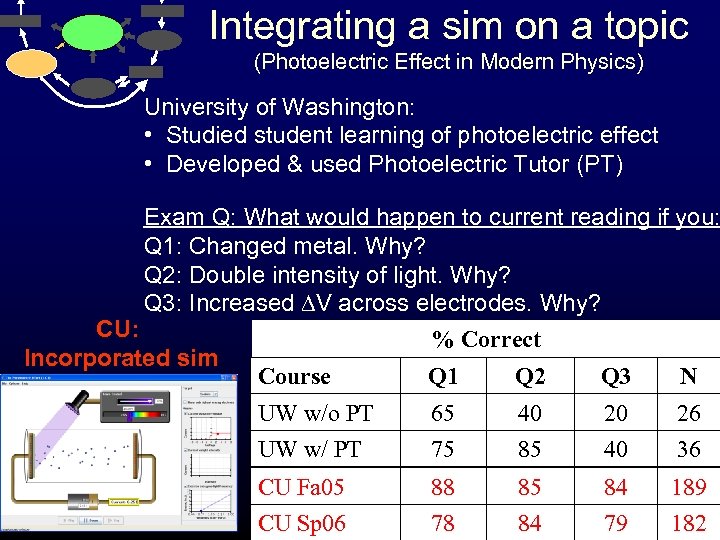 Integrating a sim on a topic (Photoelectric Effect in Modern Physics) University of Washington: • Studied student learning of photoelectric effect • Developed & used Photoelectric Tutor (PT) Exam Q: What would happen to current reading if you: Q 1: Changed metal. Why? Q 2: Double intensity of light. Why? Q 3: Increased DV across electrodes. Why? CU: % Correct Incorporated sim Course Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 N UW w/o PT 65 40 20 26 UW w/ PT 75 85 40 36 CU Fa 05 88 85 84 189 CU Sp 06 78 84 79 182
Integrating a sim on a topic (Photoelectric Effect in Modern Physics) University of Washington: • Studied student learning of photoelectric effect • Developed & used Photoelectric Tutor (PT) Exam Q: What would happen to current reading if you: Q 1: Changed metal. Why? Q 2: Double intensity of light. Why? Q 3: Increased DV across electrodes. Why? CU: % Correct Incorporated sim Course Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 N UW w/o PT 65 40 20 26 UW w/ PT 75 85 40 36 CU Fa 05 88 85 84 189 CU Sp 06 78 84 79 182
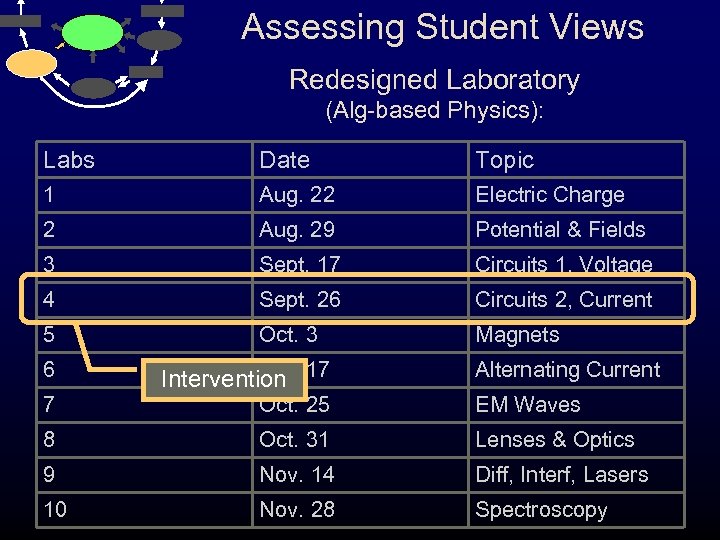 Assessing Student Views Redesigned Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Labs Date Topic 1 Aug. 22 Electric Charge 2 Aug. 29 Potential & Fields 3 Sept. 17 Circuits 1, Voltage 4 Sept. 26 Circuits 2, Current 5 Oct. 3 Magnets 6 Oct. Intervention 17 Alternating Current 7 Oct. 25 EM Waves 8 Oct. 31 Lenses & Optics 9 Nov. 14 Diff, Interf, Lasers 10 Nov. 28 Spectroscopy
Assessing Student Views Redesigned Laboratory (Alg-based Physics): Labs Date Topic 1 Aug. 22 Electric Charge 2 Aug. 29 Potential & Fields 3 Sept. 17 Circuits 1, Voltage 4 Sept. 26 Circuits 2, Current 5 Oct. 3 Magnets 6 Oct. Intervention 17 Alternating Current 7 Oct. 25 EM Waves 8 Oct. 31 Lenses & Optics 9 Nov. 14 Diff, Interf, Lasers 10 Nov. 28 Spectroscopy
 Assessing Student Views Pre-Lab Questions 1. I thought this lab was _____ USEFUL for learning about. . . (very, pretty, somewhat, barely, not at all) 2. I thought this lab was ____ ENJOYABLE for a physics lab. (very, pretty, somewhat, barely, not at all)
Assessing Student Views Pre-Lab Questions 1. I thought this lab was _____ USEFUL for learning about. . . (very, pretty, somewhat, barely, not at all) 2. I thought this lab was ____ ENJOYABLE for a physics lab. (very, pretty, somewhat, barely, not at all)
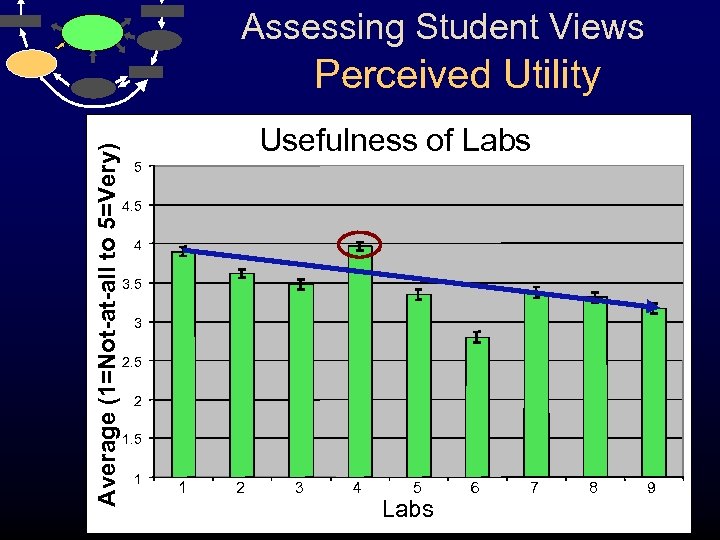 Assessing Student Views Average (1=Not-at-all to 5=Very) Perceived Utility Usefulness of Labs 5 4 3. 5 3 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 1 2 3 4 5 Labs 6 7 8 9
Assessing Student Views Average (1=Not-at-all to 5=Very) Perceived Utility Usefulness of Labs 5 4 3. 5 3 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 1 2 3 4 5 Labs 6 7 8 9
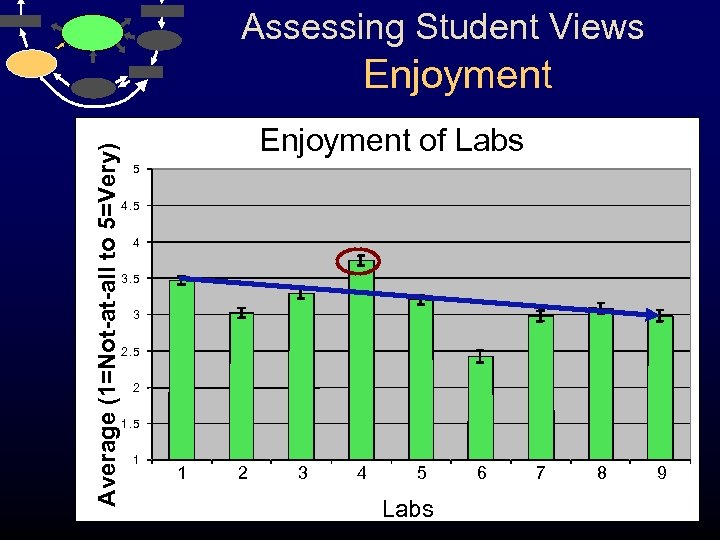 Assessing Student Views Average (1=Not-at-all to 5=Very) Enjoyment of Labs 5 4 3. 5 3 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 1 2 3 4 5 Labs 6 7 8 9
Assessing Student Views Average (1=Not-at-all to 5=Very) Enjoyment of Labs 5 4 3. 5 3 2. 5 2 1. 5 1 1 2 3 4 5 Labs 6 7 8 9
 Assessing Student Views Whole course integration Perceived Utility of sims for learning (1=Not useful; 5=A great deal…) Physics of Everyday Life: 3. 7 Modern Physics for Engineers: 4. 0 “Great sims, I can't imagine QM without them. ”
Assessing Student Views Whole course integration Perceived Utility of sims for learning (1=Not useful; 5=A great deal…) Physics of Everyday Life: 3. 7 Modern Physics for Engineers: 4. 0 “Great sims, I can't imagine QM without them. ”
 Conclusions Get Ph. ET: http: //phet. colorado. edu • Ph. ET: suite of interactive sims, free, easy to use. • Assessment is critical for evaluating effectiveness of design and use any tools. • Findings from the design of Ph. ET sims may be useful for others designing online tools. • While sims are designed for productive/effective learning, critical to attend to how we use them. • Research needs to identify, characterize, and understand what makes use of Ph. ET sims effective at improving learning and how this depends on context.
Conclusions Get Ph. ET: http: //phet. colorado. edu • Ph. ET: suite of interactive sims, free, easy to use. • Assessment is critical for evaluating effectiveness of design and use any tools. • Findings from the design of Ph. ET sims may be useful for others designing online tools. • While sims are designed for productive/effective learning, critical to attend to how we use them. • Research needs to identify, characterize, and understand what makes use of Ph. ET sims effective at improving learning and how this depends on context.
 Extra slides below
Extra slides below
 So what’s in activity design? Ph. ET Team Approach to Curriculum Design: Guided Inquiry Approach Does the activity … • Address all of your learning goals? • Require active thinking? • Require sense making / reasoning? • Build on prior knowledge? • Connect to real world? • Help students monitor their understanding?
So what’s in activity design? Ph. ET Team Approach to Curriculum Design: Guided Inquiry Approach Does the activity … • Address all of your learning goals? • Require active thinking? • Require sense making / reasoning? • Build on prior knowledge? • Connect to real world? • Help students monitor their understanding?
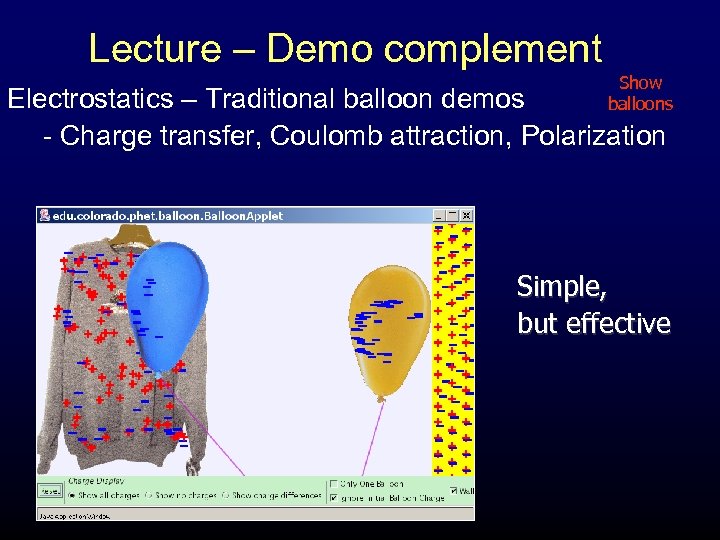 Lecture – Demo complement Show balloons Electrostatics – Traditional balloon demos - Charge transfer, Coulomb attraction, Polarization Simple, but effective
Lecture – Demo complement Show balloons Electrostatics – Traditional balloon demos - Charge transfer, Coulomb attraction, Polarization Simple, but effective
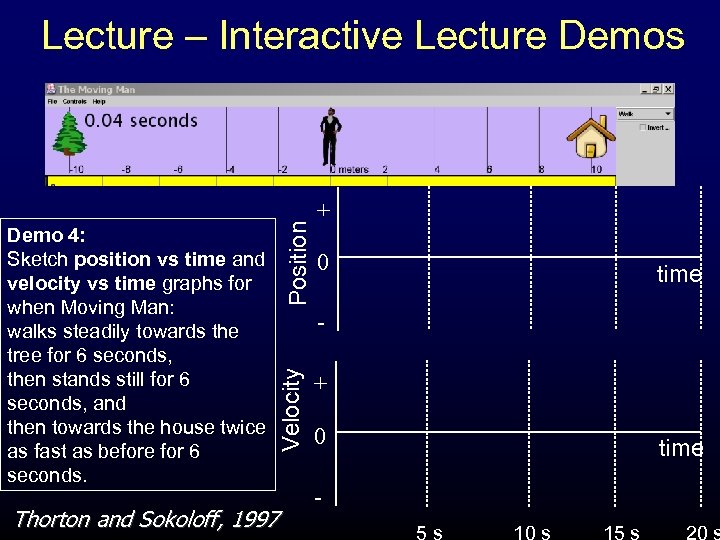 + 0 time Velocity Demo 4: Sketch position vs time and velocity vs time graphs for when Moving Man: walks steadily towards the tree for 6 seconds, then stands still for 6 seconds, and then towards the house twice as fast as before for 6 seconds. Position Lecture – Interactive Lecture Demos Thorton and Sokoloff, 1997 + 0 - time
+ 0 time Velocity Demo 4: Sketch position vs time and velocity vs time graphs for when Moving Man: walks steadily towards the tree for 6 seconds, then stands still for 6 seconds, and then towards the house twice as fast as before for 6 seconds. Position Lecture – Interactive Lecture Demos Thorton and Sokoloff, 1997 + 0 - time
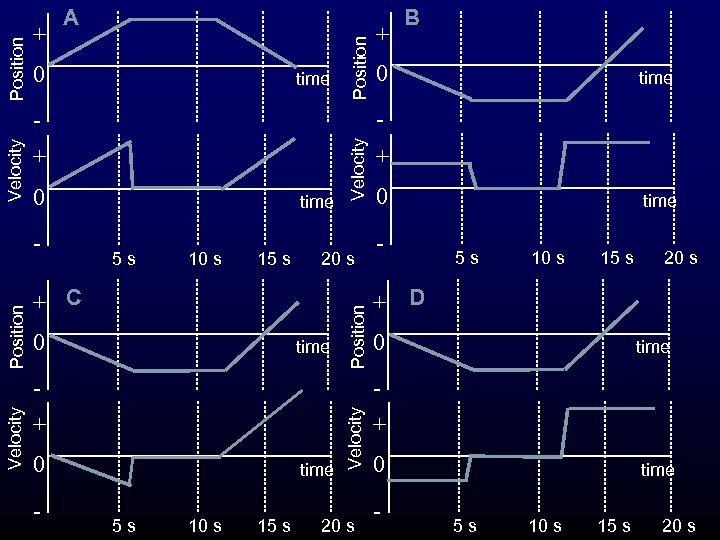 0 time Position + A Position time 5 s 10 s 15 s 20 s + C 0 Velocity 0 time Position Velocity + time + 0 - time 5 s 10 s 15 s 20 s + D 0 time - + 0 time 5 s 10 s 15 s Velocity - - 0 - - - + B 20 s + 0 - time 5 s 10 s 15 s 20 s
0 time Position + A Position time 5 s 10 s 15 s 20 s + C 0 Velocity 0 time Position Velocity + time + 0 - time 5 s 10 s 15 s 20 s + D 0 time - + 0 time 5 s 10 s 15 s Velocity - - 0 - - - + B 20 s + 0 - time 5 s 10 s 15 s 20 s
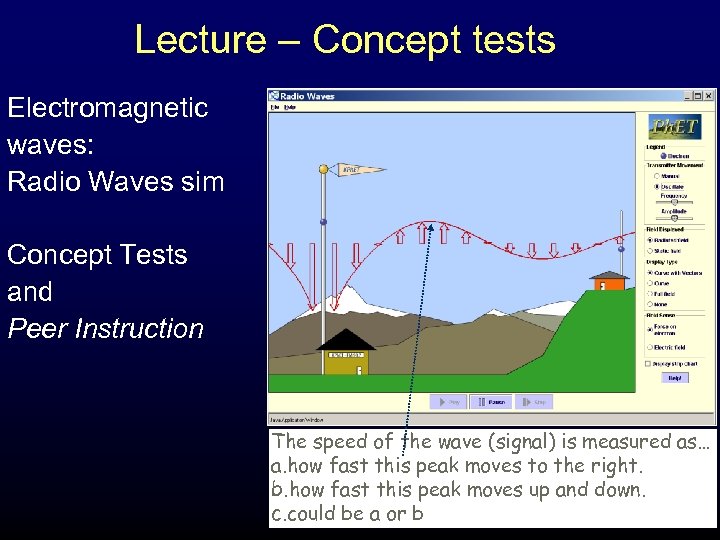 Lecture – Concept tests Electromagnetic waves: Radio Waves sim Concept Tests and Peer Instruction The speed of the wave (signal) is measured as… a. how fast this peak moves to the right. b. how fast this peak moves up and down. c. could be a or b
Lecture – Concept tests Electromagnetic waves: Radio Waves sim Concept Tests and Peer Instruction The speed of the wave (signal) is measured as… a. how fast this peak moves to the right. b. how fast this peak moves up and down. c. could be a or b


