0521ec51c82b45e16551040fe8b2695f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 The physical parts of a computer system are known as the hardware. A single item of hardware is called a device. A computer system can be drawn in a block diagram as follows: Main Memory ROM and RAM Output Input Devices Processor Devices Backing Storage Devices Version 1 1
The physical parts of a computer system are known as the hardware. A single item of hardware is called a device. A computer system can be drawn in a block diagram as follows: Main Memory ROM and RAM Output Input Devices Processor Devices Backing Storage Devices Version 1 1
 The Processor - where all the sorting, searching, calculating and decision making goes on. Modern computer systems have two or more processors working together to make the system work better. You will find systems with duo-processors, with two processors working together, and quad processors, with four processors working together, and even a hexa-core processor with six processors. Clock speed is one simple measure of how powerful a processor is. Processors have different clock speeds measured in Giga. Hertz (1 Gigahertz(GHz)= 1000 million pulses per second). Faster clock speeds can improve performance. HP Pavilion P 6 -2178 EA Desktop PC Intel Core i 5 3. 3 GHz, 6 GB RAM 3 TB Hard disk drive Version 1 2
The Processor - where all the sorting, searching, calculating and decision making goes on. Modern computer systems have two or more processors working together to make the system work better. You will find systems with duo-processors, with two processors working together, and quad processors, with four processors working together, and even a hexa-core processor with six processors. Clock speed is one simple measure of how powerful a processor is. Processors have different clock speeds measured in Giga. Hertz (1 Gigahertz(GHz)= 1000 million pulses per second). Faster clock speeds can improve performance. HP Pavilion P 6 -2178 EA Desktop PC Intel Core i 5 3. 3 GHz, 6 GB RAM 3 TB Hard disk drive Version 1 2
 Main memory is located inside the computer system. Main memory can hold either RAM or ROM. Data can flow from main memory to the processor (RAM and ROM) and data can flow from the processor to main memory (RAM only). ROM (Read Only Memory) is system memory. It holds vital systems information like start-up instructions. Key points about ROM v. Data is stored permanently in ROM, it is not lost when the power goes off. v. Data in the ROM cannot be changed. v. Holds vital systems data and programs. v. Data flows from ROM to the processor but not from the processor to ROM since this memory is read only. Version 1 3
Main memory is located inside the computer system. Main memory can hold either RAM or ROM. Data can flow from main memory to the processor (RAM and ROM) and data can flow from the processor to main memory (RAM only). ROM (Read Only Memory) is system memory. It holds vital systems information like start-up instructions. Key points about ROM v. Data is stored permanently in ROM, it is not lost when the power goes off. v. Data in the ROM cannot be changed. v. Holds vital systems data and programs. v. Data flows from ROM to the processor but not from the processor to ROM since this memory is read only. Version 1 3
 RAM ( Random Access Memory) is the working space of the computer. It holds all the programs and data files currently in use by the system and the user. Key points about RAM v. The processor can write to, or read from, RAM at high speed. v. Data held in RAM can be changed. v. All data in RAM is lost when the power is switched off. v. RAM holds all the data and programs currently in use. v. Data flows from RAM to the processor and from the processor to RAM. Measuring the size of memory Bit Binary Digit: a single 1 or 0 Byte 8 bits e. g. 1100 Kilobyte 1024 bytes Megabyte 1024 Kilobytes Gigabyte 1024 Megabytes Terabyte 1024 Gigabytes Petabyte 1024 Terabytes Version 1 Converting between units: To change: Bits to bytes, divide by 8 Bytes to bits, multiply by 8 Byes to KB, divide by 1024 KB to bytes, multiply by 1024. 4
RAM ( Random Access Memory) is the working space of the computer. It holds all the programs and data files currently in use by the system and the user. Key points about RAM v. The processor can write to, or read from, RAM at high speed. v. Data held in RAM can be changed. v. All data in RAM is lost when the power is switched off. v. RAM holds all the data and programs currently in use. v. Data flows from RAM to the processor and from the processor to RAM. Measuring the size of memory Bit Binary Digit: a single 1 or 0 Byte 8 bits e. g. 1100 Kilobyte 1024 bytes Megabyte 1024 Kilobytes Gigabyte 1024 Megabytes Terabyte 1024 Gigabytes Petabyte 1024 Terabytes Version 1 Converting between units: To change: Bits to bytes, divide by 8 Bytes to bits, multiply by 8 Byes to KB, divide by 1024 KB to bytes, multiply by 1024. 4
 Input Devices (needed to put information into the computer) 1. Keyboard Virtual (software) keyboards are also available - an image of a keyboard is displayed on the screen. Advantage; this can be very helpful to users with limited hand movement. Laser keyboards are available where an image of a keyboard is projected onto the desk. Disadvantage; keyboard entry can be slow and sometimes errors can be made. 2. Mouse Used to point to and select items on the screen. 3. Trackpad As you move your finger over a touch sensitive pad the cursor moves on screen. Often found on Laptop computers instead of a mouse. Advantage; no desk space required to move a mouse. Version 1 5
Input Devices (needed to put information into the computer) 1. Keyboard Virtual (software) keyboards are also available - an image of a keyboard is displayed on the screen. Advantage; this can be very helpful to users with limited hand movement. Laser keyboards are available where an image of a keyboard is projected onto the desk. Disadvantage; keyboard entry can be slow and sometimes errors can be made. 2. Mouse Used to point to and select items on the screen. 3. Trackpad As you move your finger over a touch sensitive pad the cursor moves on screen. Often found on Laptop computers instead of a mouse. Advantage; no desk space required to move a mouse. Version 1 5
 4. Joystick/Gamepad or Game Controller These types of controllers are mostly used to play computer games. 5. Graphics Tablet Consists of a flat surface covered with sensors. The user “draws”with a special pen called a stylus. The image is then shown on screen. Advantage; drawings created with a graphics tablet are much more accurate than using a mouse or any other pointing device. 6. Touch Sensitive Screen The user can make a selection or position the cursor by touching the screen. Advantages; vtouch screens are simple to operate vusually found where normal keyboards would be difficult to use like information points in public places vless likely to be damaged compared to mouse/keyboard. Version 1 6
4. Joystick/Gamepad or Game Controller These types of controllers are mostly used to play computer games. 5. Graphics Tablet Consists of a flat surface covered with sensors. The user “draws”with a special pen called a stylus. The image is then shown on screen. Advantage; drawings created with a graphics tablet are much more accurate than using a mouse or any other pointing device. 6. Touch Sensitive Screen The user can make a selection or position the cursor by touching the screen. Advantages; vtouch screens are simple to operate vusually found where normal keyboards would be difficult to use like information points in public places vless likely to be damaged compared to mouse/keyboard. Version 1 6
 7. Scanner A scanner is used to turn a picture on paper into a digital image in the computer’s memory. v. A light beam passes over the page and a sensor detects the light being reflected. v. The image is then stored in the computer as binary numbers. v. Using character recognition software, text can be scanned in and put in a word processing document and then edited. The resolution (dpi-dots per inch) of a scanner is one measurement used to determine how good it is. 8. Digital Camera A digital camera captures images (pictures) and stores them as digital files which can be transferred to a computer for editing and printing. You measure how good they are by looking at the number of megapixels they have (resolution) and how much memory they have (capacity). The amount of data that can be stored on the camera is usually measured in megabytes or gigabytes. Version 1 7
7. Scanner A scanner is used to turn a picture on paper into a digital image in the computer’s memory. v. A light beam passes over the page and a sensor detects the light being reflected. v. The image is then stored in the computer as binary numbers. v. Using character recognition software, text can be scanned in and put in a word processing document and then edited. The resolution (dpi-dots per inch) of a scanner is one measurement used to determine how good it is. 8. Digital Camera A digital camera captures images (pictures) and stores them as digital files which can be transferred to a computer for editing and printing. You measure how good they are by looking at the number of megapixels they have (resolution) and how much memory they have (capacity). The amount of data that can be stored on the camera is usually measured in megabytes or gigabytes. Version 1 7
 9. Digital Video Camera Digital video (DV) is a method of recording moving pictures in a digital format. A digital video camera captures these very high quality images. These images can be transferred directly to a computer’s memory for editing. 10. Webcam A webcam is a low cost, low quality video camera, used on the web to provide online video. 11. Microphone Used for sound recording on a computer system to use in presentations, websites or podcasts. Version 1 8
9. Digital Video Camera Digital video (DV) is a method of recording moving pictures in a digital format. A digital video camera captures these very high quality images. These images can be transferred directly to a computer’s memory for editing. 10. Webcam A webcam is a low cost, low quality video camera, used on the web to provide online video. 11. Microphone Used for sound recording on a computer system to use in presentations, websites or podcasts. Version 1 8
 Output Devices (needed to display the results of processing) 1. Ink Jet Printer This sprays tiny drops of ink onto the paper to form characters or graphics. Printouts can be black and white or in colour. Advantages: v. Produces high quality pictures. v. Fairly cheap to buy. v. Portable versions are available. Disadvantages: v. Running costs (The cost per page) are high as it is expensive to replace the ink cartridges and they only hold enough ink for a few hundred pages. v. They are also slow to print. v. Printouts can easily become smudged if they are handled too quickly after printing or allowed to get wet. Version 1 9
Output Devices (needed to display the results of processing) 1. Ink Jet Printer This sprays tiny drops of ink onto the paper to form characters or graphics. Printouts can be black and white or in colour. Advantages: v. Produces high quality pictures. v. Fairly cheap to buy. v. Portable versions are available. Disadvantages: v. Running costs (The cost per page) are high as it is expensive to replace the ink cartridges and they only hold enough ink for a few hundred pages. v. They are also slow to print. v. Printouts can easily become smudged if they are handled too quickly after printing or allowed to get wet. Version 1 9
 2. Laser Printer A laser printer puts very fine powdered plastic (called toner) onto the paper to make its image. Advantages: vvery fast vhigh quality output vtext and graphics can both be printed. vcost per page is low as each toner cartridge can produce thousands of pages. Disadvantages: vlaser printers are more expensive than inkjet printers to buy vnot portable. Colour laser printers are also available but can be expensive to buy and to run. You can compare printers according to the following characteristics: Speed: how fast they print, measured in pages per minute (ppm) Resolution: the higher the resolution the better the quality. Resolution is measured in dots per inch (dpi). Cost: the initial cost of buying a printer/ running costs: cost of toner or ink. Version 1 10
2. Laser Printer A laser printer puts very fine powdered plastic (called toner) onto the paper to make its image. Advantages: vvery fast vhigh quality output vtext and graphics can both be printed. vcost per page is low as each toner cartridge can produce thousands of pages. Disadvantages: vlaser printers are more expensive than inkjet printers to buy vnot portable. Colour laser printers are also available but can be expensive to buy and to run. You can compare printers according to the following characteristics: Speed: how fast they print, measured in pages per minute (ppm) Resolution: the higher the resolution the better the quality. Resolution is measured in dots per inch (dpi). Cost: the initial cost of buying a printer/ running costs: cost of toner or ink. Version 1 10
 3. Monitor The screen used to display computer output. The screen is made up of picture elements or pixels. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) are light, compact screens that don’t need a lot of power and can easily be run on batteries. They are used on desktops, laptops, palmtops and smartphones. Thin Film Transistors (TFT) is a type of LCD screen that uses lots of transistors to produce a high quality display. A TFT screen can display animations and 3 D graphics much more clearly than ordinary LCD screens. 4. Loudspeakers/Headphones Speakers/ headphones on your computer enable you to play and hear sound. They can be separate devices or are built into the computer. Version 1 11
3. Monitor The screen used to display computer output. The screen is made up of picture elements or pixels. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) are light, compact screens that don’t need a lot of power and can easily be run on batteries. They are used on desktops, laptops, palmtops and smartphones. Thin Film Transistors (TFT) is a type of LCD screen that uses lots of transistors to produce a high quality display. A TFT screen can display animations and 3 D graphics much more clearly than ordinary LCD screens. 4. Loudspeakers/Headphones Speakers/ headphones on your computer enable you to play and hear sound. They can be separate devices or are built into the computer. Version 1 11
 5. Graphics Card v. A graphics card is a device which controls the quality of output on a monitor. v. Graphics cards often contain a large quantity of RAM and can support different types of screen displays at a variety of resolutions. v. They have their own processor which then frees up the main processor so that it can get on with other tasks. Advantage; a good graphics card can speed up game play on a PC, as the processor no longer has to work out what the screen should look like and display it. Version 1 12
5. Graphics Card v. A graphics card is a device which controls the quality of output on a monitor. v. Graphics cards often contain a large quantity of RAM and can support different types of screen displays at a variety of resolutions. v. They have their own processor which then frees up the main processor so that it can get on with other tasks. Advantage; a good graphics card can speed up game play on a PC, as the processor no longer has to work out what the screen should look like and display it. Version 1 12
 6. Sound Card A sound card is a device used to take in sound and for outputting sound. Sound cards are capable of outputting a number of sound channels in high quality formats. They have a dedicated processor which then frees up the main processor so that it can get on with other tasks Advantage; sound cards improve the quality of sound output from games and multimedia applications. Sound is analogue in nature, it is a continuously varying quantity. Computers work in digital quantities. In order to input sound into a computer the sound must be changed from analogue into digital. This process is called analogue to digital conversion. A microphone or another sound source is connected to the computer’s sound card in order to capture the sound. The sound carries out the ADC in the process called sampling. In order to output sound from a computer the sound must be changed from digital to analogue. This process is called digital to analogue conversion. Version 1 13
6. Sound Card A sound card is a device used to take in sound and for outputting sound. Sound cards are capable of outputting a number of sound channels in high quality formats. They have a dedicated processor which then frees up the main processor so that it can get on with other tasks Advantage; sound cards improve the quality of sound output from games and multimedia applications. Sound is analogue in nature, it is a continuously varying quantity. Computers work in digital quantities. In order to input sound into a computer the sound must be changed from analogue into digital. This process is called analogue to digital conversion. A microphone or another sound source is connected to the computer’s sound card in order to capture the sound. The sound carries out the ADC in the process called sampling. In order to output sound from a computer the sound must be changed from digital to analogue. This process is called digital to analogue conversion. Version 1 13
 Backing Storage Devices We store things we want to use again using a backing storage device. Backing storage is used to store programs and data permanently. Remember that RAM is the working area of the computer but all contents of RAM are lost when the computer is switched off so we need to store our work on backing storage. USB Flash drives, Hard disks, CD-ROMs and DVDs are examples of backing storage media and the hardware that uses or holds the media is known as a backing storage device. Version 1 14
Backing Storage Devices We store things we want to use again using a backing storage device. Backing storage is used to store programs and data permanently. Remember that RAM is the working area of the computer but all contents of RAM are lost when the computer is switched off so we need to store our work on backing storage. USB Flash drives, Hard disks, CD-ROMs and DVDs are examples of backing storage media and the hardware that uses or holds the media is known as a backing storage device. Version 1 14
 Magnetic Storage 1. Hard Disk Drive A sealed metal disk inside the drive which stores data on its surfaces using magnetic charge. They are usually fixed inside a computer, but you can get external drives that you plug into the computer usually via a USB port. Advantages v. You can read and write data to a hard disk v. Fast access times v. Fast data transfer rates v. Cheap per Gigabyte. 2. Portable Hard Disk Drive v. A portable hard it is small enough to carry with you. v. Portable hard drives can be easily used by multiple PC’s for file sharing. v. A portable hard drive allows for backups of files ( a backup is a second copy of a file). v. A portable drive allows for quick and easy storage of data. Version 1 15
Magnetic Storage 1. Hard Disk Drive A sealed metal disk inside the drive which stores data on its surfaces using magnetic charge. They are usually fixed inside a computer, but you can get external drives that you plug into the computer usually via a USB port. Advantages v. You can read and write data to a hard disk v. Fast access times v. Fast data transfer rates v. Cheap per Gigabyte. 2. Portable Hard Disk Drive v. A portable hard it is small enough to carry with you. v. Portable hard drives can be easily used by multiple PC’s for file sharing. v. A portable hard drive allows for backups of files ( a backup is a second copy of a file). v. A portable drive allows for quick and easy storage of data. Version 1 15
 3. Magnetic tape Unit Tape storage can be used as a form of backing storage. Tapes store data in binary using magnetic spots to encode the data. Key Features: v. They have a large capacity. v. They are ideally suited for making backups. However magnetic tape drives are being used less and less now. Many companies are backing up their data on to a mirror disk. This is basically another hard disk drive that takes an exact copy of the current drive and therefore acts as a backup of the system. 4. Cloud Computing (external storage) Cloud computing is the use of the Internet to provide computing services. Cloud computing customers can rent storage space on servers. Customers can have a contract which enables them to decide how much storage space they need for their data. This arrangement can be very flexible and customers can easily scale their storage up or down as required. They can also access a wide range of application software. As soon as the contract is signed a customer can have access to all the software it needs without having to buy the hardware or pay for and install the software. Version 1 16
3. Magnetic tape Unit Tape storage can be used as a form of backing storage. Tapes store data in binary using magnetic spots to encode the data. Key Features: v. They have a large capacity. v. They are ideally suited for making backups. However magnetic tape drives are being used less and less now. Many companies are backing up their data on to a mirror disk. This is basically another hard disk drive that takes an exact copy of the current drive and therefore acts as a backup of the system. 4. Cloud Computing (external storage) Cloud computing is the use of the Internet to provide computing services. Cloud computing customers can rent storage space on servers. Customers can have a contract which enables them to decide how much storage space they need for their data. This arrangement can be very flexible and customers can easily scale their storage up or down as required. They can also access a wide range of application software. As soon as the contract is signed a customer can have access to all the software it needs without having to buy the hardware or pay for and install the software. Version 1 16
 Optical Storage Optical disk drives use laser technology to read data from the disks or write data to the disks. The drive for optical media uses a low powered laser to read the data from the disk. If it is a writeable disk then it uses a higher powered laser to write to it. The speed of an optical CD ROM drive is given as a number, for example 52 x ( 52 times 150 kilobits per second where 1 kilobit equals 1024 bits). This speed refers to the transfer of data from the disk to the computer’s main memory. Version 1 17
Optical Storage Optical disk drives use laser technology to read data from the disks or write data to the disks. The drive for optical media uses a low powered laser to read the data from the disk. If it is a writeable disk then it uses a higher powered laser to write to it. The speed of an optical CD ROM drive is given as a number, for example 52 x ( 52 times 150 kilobits per second where 1 kilobit equals 1024 bits). This speed refers to the transfer of data from the disk to the computer’s main memory. Version 1 17
 1. CD-ROM (Compact Disc – Read Only) This means the information can be read by a computer but cannot be added to or altered. A standard CD-ROM can store up to 700 Mb of data. Advantages v. Capable of storing a large amount of data. v. Fast access. Disadvantage v. Cannot be used to store new documents or to make changes to old ones 2. CD-R (Compact Disc – Recordable) This is a CD-recordable, it allows you to record or write data once. Once data has been recorded on it, it works just like a CD-ROM, it is read only. The speed of a CD-R drive is given as two numbers, the read speed and the write speed. Version 1 18
1. CD-ROM (Compact Disc – Read Only) This means the information can be read by a computer but cannot be added to or altered. A standard CD-ROM can store up to 700 Mb of data. Advantages v. Capable of storing a large amount of data. v. Fast access. Disadvantage v. Cannot be used to store new documents or to make changes to old ones 2. CD-R (Compact Disc – Recordable) This is a CD-recordable, it allows you to record or write data once. Once data has been recorded on it, it works just like a CD-ROM, it is read only. The speed of a CD-R drive is given as two numbers, the read speed and the write speed. Version 1 18
 3. CD-RW (Compact Disc Re-Writable) The contents of the disk can be erased and replaced with new data. A CD-RW has three speeds, one for writing the data, one for re-writing and one for reading. For example write 52 X, re-write 24 X, and read 52 X. 4. DVD-ROM (Digital Versatile Disk-Read Only Memory) A DVD is similar to a CD-ROM but has much greater storage capacity. The capacity is big enough to store digital video of full-length feature films or huge amounts of data. A single-sided single- layered DVD can store 4. 7 Gigabytes. Double-sided multi-layered DVDs have a capacity of 17 Gigabytes. The speed of a DVD-ROM drive is given as a number, e. g. 16 X. This is different from a CD, as each 1 x is 1250 kilobits per second (kbps), so 16 x is 16 x 1250 kbps. 5. DVD-R (Digital Versatile Disk-Recordable) A DVD –R allows you to record data once. After recording the data cannot be changed. They have the same capacity as DVDs but have two speeds, one for writing and one for reading data e. g. write 6 x, read 12 x. 6. DVD-RW (Digital Versatile Disk-Re-Writable) Similar to a CD-RW, these come blank and its contents are written with a DVD re-writer. The whole disk can be erased and re-used many times over. A DVD-RW has three speeds, one for writing data, one for re-writing and one for reading. Eg. Write 6 x, re-write 2. 4 x and read 12 x. Version 1 19
3. CD-RW (Compact Disc Re-Writable) The contents of the disk can be erased and replaced with new data. A CD-RW has three speeds, one for writing the data, one for re-writing and one for reading. For example write 52 X, re-write 24 X, and read 52 X. 4. DVD-ROM (Digital Versatile Disk-Read Only Memory) A DVD is similar to a CD-ROM but has much greater storage capacity. The capacity is big enough to store digital video of full-length feature films or huge amounts of data. A single-sided single- layered DVD can store 4. 7 Gigabytes. Double-sided multi-layered DVDs have a capacity of 17 Gigabytes. The speed of a DVD-ROM drive is given as a number, e. g. 16 X. This is different from a CD, as each 1 x is 1250 kilobits per second (kbps), so 16 x is 16 x 1250 kbps. 5. DVD-R (Digital Versatile Disk-Recordable) A DVD –R allows you to record data once. After recording the data cannot be changed. They have the same capacity as DVDs but have two speeds, one for writing and one for reading data e. g. write 6 x, read 12 x. 6. DVD-RW (Digital Versatile Disk-Re-Writable) Similar to a CD-RW, these come blank and its contents are written with a DVD re-writer. The whole disk can be erased and re-used many times over. A DVD-RW has three speeds, one for writing data, one for re-writing and one for reading. Eg. Write 6 x, re-write 2. 4 x and read 12 x. Version 1 19
 Solid State Storage USB Flash Drive (pen drive, memory stick) This is a small portable backing storage device. An easy way of making backups and transferring data between computers. Digital cameras use solid state storage in the form of flash cards to store images captured by the camera. Solid State devices are: v Small - flash cards can fit inside a camera, USB flash drives can fit on a key ring and in watches. v Robust because they have no moving parts. v Use less power than a hard disk drive v Have a range of capacities. Over time the cost of these devices has decreased and the capacity of them has increased. Version 1 20
Solid State Storage USB Flash Drive (pen drive, memory stick) This is a small portable backing storage device. An easy way of making backups and transferring data between computers. Digital cameras use solid state storage in the form of flash cards to store images captured by the camera. Solid State devices are: v Small - flash cards can fit inside a camera, USB flash drives can fit on a key ring and in watches. v Robust because they have no moving parts. v Use less power than a hard disk drive v Have a range of capacities. Over time the cost of these devices has decreased and the capacity of them has increased. Version 1 20
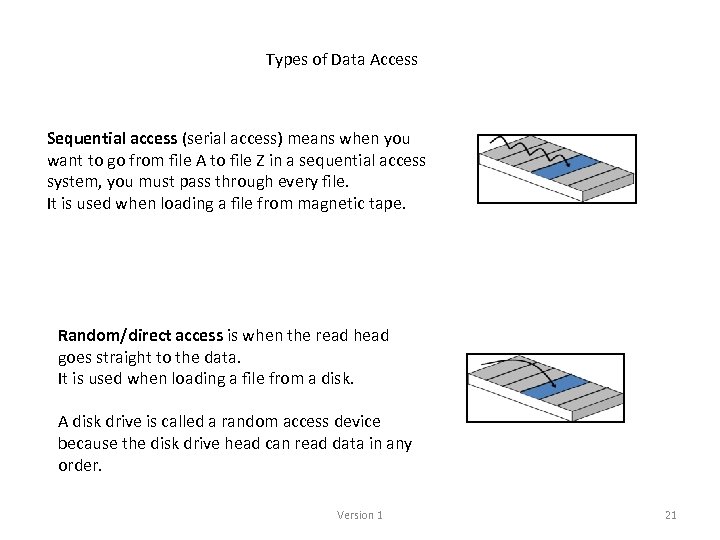 Types of Data Access Sequential access (serial access) means when you want to go from file A to file Z in a sequential access system, you must pass through every file. It is used when loading a file from magnetic tape. Random/direct access is when the read head goes straight to the data. It is used when loading a file from a disk. A disk drive is called a random access device because the disk drive head can read data in any order. Version 1 21
Types of Data Access Sequential access (serial access) means when you want to go from file A to file Z in a sequential access system, you must pass through every file. It is used when loading a file from magnetic tape. Random/direct access is when the read head goes straight to the data. It is used when loading a file from a disk. A disk drive is called a random access device because the disk drive head can read data in any order. Version 1 21
 Software is the name given to the programs that run in a computer. A program is a set of instructions that tell the computer what to do eg. MS Word, i. Tunes. v. The operating system is a program or set of programs that controls the hardware and software running on the computer allowing the user to communicate with the application software and hardware devices. v. When a computer is switched on the first task is to load the operating system into RAM. There a number of different operating systems eg. Mac. OS X, Windows 7, Android. Version 1 22
Software is the name given to the programs that run in a computer. A program is a set of instructions that tell the computer what to do eg. MS Word, i. Tunes. v. The operating system is a program or set of programs that controls the hardware and software running on the computer allowing the user to communicate with the application software and hardware devices. v. When a computer is switched on the first task is to load the operating system into RAM. There a number of different operating systems eg. Mac. OS X, Windows 7, Android. Version 1 22
 There are different ways that an operating system helps us: Error reporting When we use the mouse, keyboard, trackpad or trackball, the operating system looks at what we have asked and tries to do it. If we ask for something that is not possible then it will report an error. e. g. trying to save a file with a filename being used by another file that is still open. File management This organises and manages the saving and loading of program files and data files between the backing storage device and the main memory. It decides which tracks on the Hard disk a file should be stored on. Memory management This organises the programs and data in the main memory of the computer. It makes sure that there is enough space in the RAM to store a file and decides where the files should be stored. Version 1 23
There are different ways that an operating system helps us: Error reporting When we use the mouse, keyboard, trackpad or trackball, the operating system looks at what we have asked and tries to do it. If we ask for something that is not possible then it will report an error. e. g. trying to save a file with a filename being used by another file that is still open. File management This organises and manages the saving and loading of program files and data files between the backing storage device and the main memory. It decides which tracks on the Hard disk a file should be stored on. Memory management This organises the programs and data in the main memory of the computer. It makes sure that there is enough space in the RAM to store a file and decides where the files should be stored. Version 1 23
 Representation of Data Storing Numbers A single unit in Binary is called a bit. The word bit is made up from the two words BInary and digi. T. It can have a value of 1 or 0. For example: Binary number with 8 bits - 1011 0011 To change this number to decimal use the place values for binary; 128 s 1 64 s 0 32 s 1 16 s 1 8 s 0 4 s 0 2 s 1 1 s (units) 1 This would be 128 + 0 + 32 + 16 + 0 + 2 + 1 = 179 in decimal Largest 8 bit number is 1111 which is 255 in decimal Range of Integers - If 2 bytes (16 bits) are used to store numbers then numbers from 0000 up to 1111 may be stored (0 to 65, 535 in decimal- a total of 65, 536 different numbers. ) Version 1 24
Representation of Data Storing Numbers A single unit in Binary is called a bit. The word bit is made up from the two words BInary and digi. T. It can have a value of 1 or 0. For example: Binary number with 8 bits - 1011 0011 To change this number to decimal use the place values for binary; 128 s 1 64 s 0 32 s 1 16 s 1 8 s 0 4 s 0 2 s 1 1 s (units) 1 This would be 128 + 0 + 32 + 16 + 0 + 2 + 1 = 179 in decimal Largest 8 bit number is 1111 which is 255 in decimal Range of Integers - If 2 bytes (16 bits) are used to store numbers then numbers from 0000 up to 1111 may be stored (0 to 65, 535 in decimal- a total of 65, 536 different numbers. ) Version 1 24
 Storing Text A character is a symbol or letter eg. digits 0 to 9, letters and punctuation marks. The character set is a list of all the characters which a computer can process and store. A byte is the space in a computer’s memory which is used to hold one character. Each character is stored using a different binary code number eg. 0100 0001 is the letter A. One form of code is the American Standard Code for Information Interchange or ASCII. Each ASCII character takes up one byte of storage. Many different computers use ASCII to represent text. Advantage; this makes it easier for text to be transferred between different computer systems. Version 1 25
Storing Text A character is a symbol or letter eg. digits 0 to 9, letters and punctuation marks. The character set is a list of all the characters which a computer can process and store. A byte is the space in a computer’s memory which is used to hold one character. Each character is stored using a different binary code number eg. 0100 0001 is the letter A. One form of code is the American Standard Code for Information Interchange or ASCII. Each ASCII character takes up one byte of storage. Many different computers use ASCII to represent text. Advantage; this makes it easier for text to be transferred between different computer systems. Version 1 25
 Some ASCII characters do not print on the screen in the normal way. They are known as control characters because they control certain operations of the computer system. In ASCII, codes from 0 to 31 are used as control characters. The table below shows an example of ASCII codes. Character Enable printer Return Binary 000 0010 0000 1101 2 13 Decimal Unicode is another code to represent letters but uses 16 bits. This allows more characters to be represented eg. Different languages have lots of different symbols. Version 1 26
Some ASCII characters do not print on the screen in the normal way. They are known as control characters because they control certain operations of the computer system. In ASCII, codes from 0 to 31 are used as control characters. The table below shows an example of ASCII codes. Character Enable printer Return Binary 000 0010 0000 1101 2 13 Decimal Unicode is another code to represent letters but uses 16 bits. This allows more characters to be represented eg. Different languages have lots of different symbols. Version 1 26
 A program is a set of instructions that a computer can understand. A High Level Language program is a program written in everyday language eg. PRINT “Hello” Machine Code is a the computer’s own language. Machine code is a program written using binary eg. 000011011 11010111 Version 1 27
A program is a set of instructions that a computer can understand. A High Level Language program is a program written in everyday language eg. PRINT “Hello” Machine Code is a the computer’s own language. Machine code is a program written using binary eg. 000011011 11010111 Version 1 27
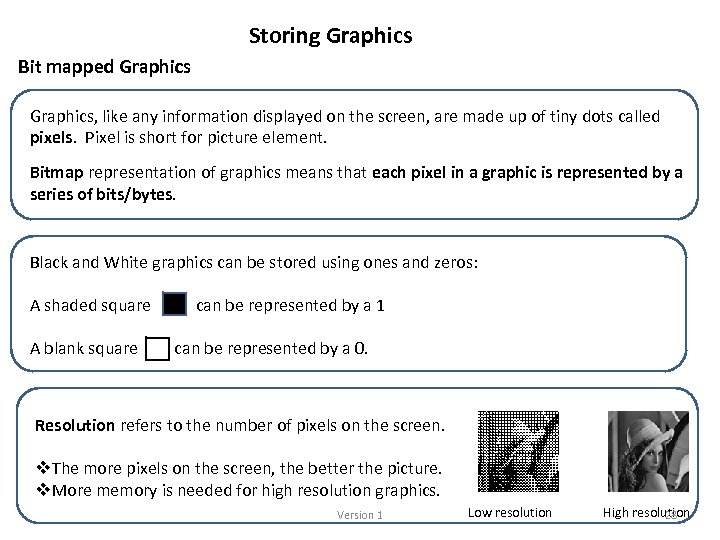 Storing Graphics Bit mapped Graphics, like any information displayed on the screen, are made up of tiny dots called pixels. Pixel is short for picture element. Bitmap representation of graphics means that each pixel in a graphic is represented by a series of bits/bytes. Black and White graphics can be stored using ones and zeros: A shaded square can be represented by a 1 A blank square can be represented by a 0. Resolution refers to the number of pixels on the screen. v. The more pixels on the screen, the better the picture. v. More memory is needed for high resolution graphics. Version 1 Low resolution High resolution 28
Storing Graphics Bit mapped Graphics, like any information displayed on the screen, are made up of tiny dots called pixels. Pixel is short for picture element. Bitmap representation of graphics means that each pixel in a graphic is represented by a series of bits/bytes. Black and White graphics can be stored using ones and zeros: A shaded square can be represented by a 1 A blank square can be represented by a 0. Resolution refers to the number of pixels on the screen. v. The more pixels on the screen, the better the picture. v. More memory is needed for high resolution graphics. Version 1 Low resolution High resolution 28


