8c30d1dc3bec60d0d1a853f8ac0516b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

The Philippines’ Performance in Doing Business 2008 Kim S. Jacinto-Henares September 26, 2007

IFC and the World Bank: Part of the World Bank Group IFC is owned by its 179 member countries, which collectively determine policies. International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD or World Bank), 1945 International Development Association, 1960 International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes, 1966 International Finance Corporation Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency, 1988 2

Doing Business project 2007 2008 • Starting a business • Update of 2006 • Update of 2007 • Dealing with licenses • Add 20 countries • 3 new countries 2006 • Employing workers • Registering property • Enforcing contracts • Getting credit • Trading across borders • Protecting investors 10 topics 178 economies • Paying taxes • Closing a business www. doingbusiness. org 3

What is the Doing Business report? • Presents quantitative indicators, empirical data set on business regulations & their enforcement • Highlights the extent of obstacles to doing business • Helps identifies the source of those obstacles • Helps identifies what reforms are needed and provides advice on how to start the process • Highlights best practices in how to reform • An objective benchmark against which to measure regulatory performance in comparison to other economies 4

Doing Business indicators measure • Degree of regulation (e. g. no. of procedures to start a business or register commercial property) • Regulatory outcomes (e. g. time & cost to enforce a contract, go through bankruptcy or trade across borders) • Extent of legal protections of property (e. g. protections of investors against looting by company directors or the range of assets that can be used as collateral) • Flexibility of employment regulation • Tax burden on businesses 5

What Doing Business indicators don’t measure • Macroeconomic policy • Investor perceptions • Currency volatility • Crime rate • Ease of access to markets • Security of property from theft & looting • Proximity to large markets • Transparency of government procurement • Quality of infrastructure services (other than those related to ‘Trading across borders’) • Bribes • Underlying strength of institutions 6
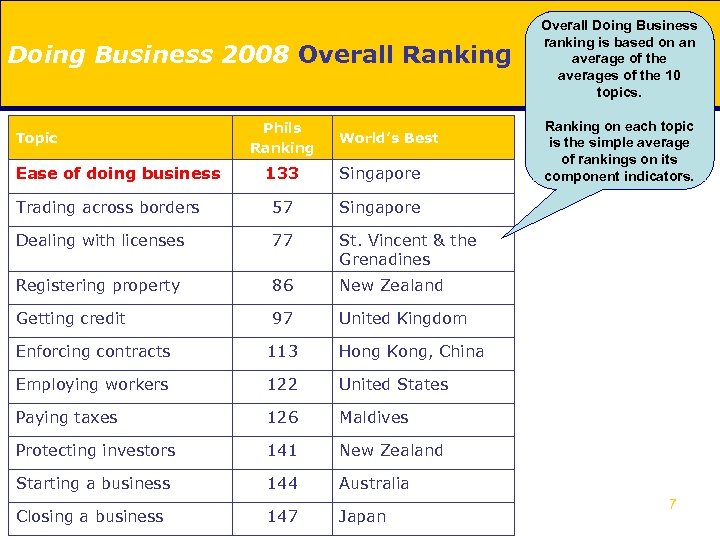
Doing Business 2008 Overall Ranking Topic Ease of doing business Phils Ranking World’s Best 133 Singapore Trading across borders 57 77 St. Vincent & the Grenadines Registering property 86 New Zealand Getting credit 97 Ranking on each topic is the simple average of rankings on its component indicators. Singapore Dealing with licenses Overall Doing Business ranking is based on an average of the averages of the 10 topics. United Kingdom Enforcing contracts 113 Hong Kong, China Employing workers 122 United States Paying taxes 126 Maldives Protecting investors 141 New Zealand Starting a business 144 Australia Closing a business 147 Japan 7
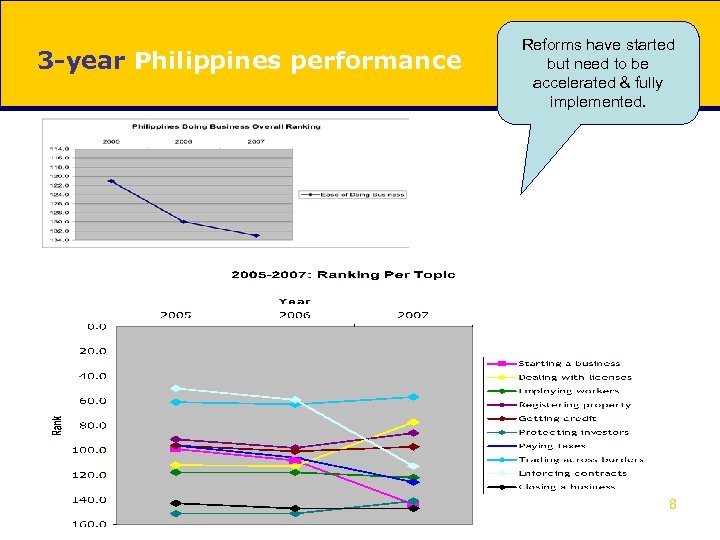
3 -year Philippines performance Reforms have started but need to be accelerated & fully implemented. 8
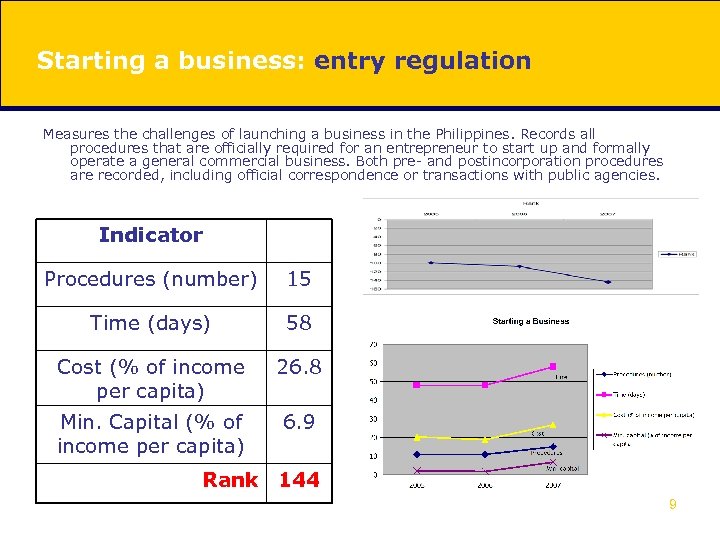
Starting a business: entry regulation Measures the challenges of launching a business in the Philippines. Records all procedures that are officially required for an entrepreneur to start up and formally operate a general commercial business. Both pre- and postincorporation procedures are recorded, including official correspondence or transactions with public agencies. Indicator Procedures (number) 15 Time (days) 58 Cost (% of income per capita) 26. 8 Min. Capital (% of income per capita) 6. 9 Rank 144 9
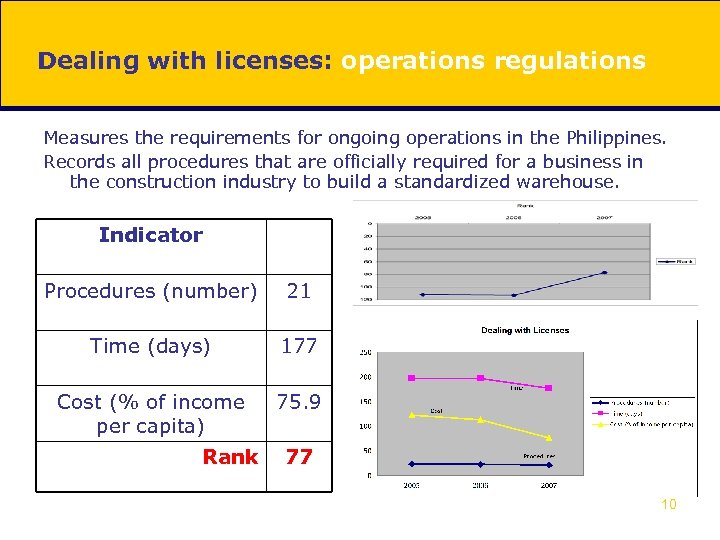
Dealing with licenses: operations regulations Measures the requirements for ongoing operations in the Philippines. Records all procedures that are officially required for a business in the construction industry to build a standardized warehouse. Indicator Procedures (number) 21 Time (days) 177 Cost (% of income per capita) 75. 9 Rank 77 10
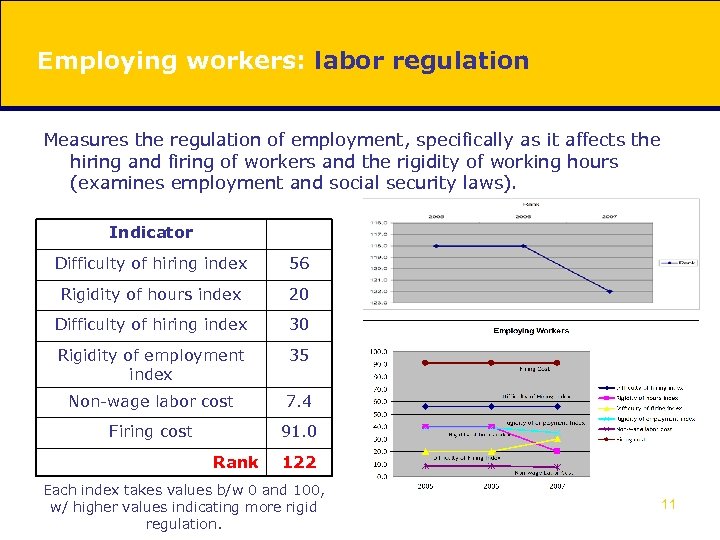
Employing workers: labor regulation Measures the regulation of employment, specifically as it affects the hiring and firing of workers and the rigidity of working hours (examines employment and social security laws). Indicator Difficulty of hiring index 56 Rigidity of hours index 20 Difficulty of hiring index 30 Rigidity of employment index 35 Non-wage labor cost 7. 4 Firing cost 91. 0 Rank 122 Each index takes values b/w 0 and 100, w/ higher values indicating more rigid regulation. 11
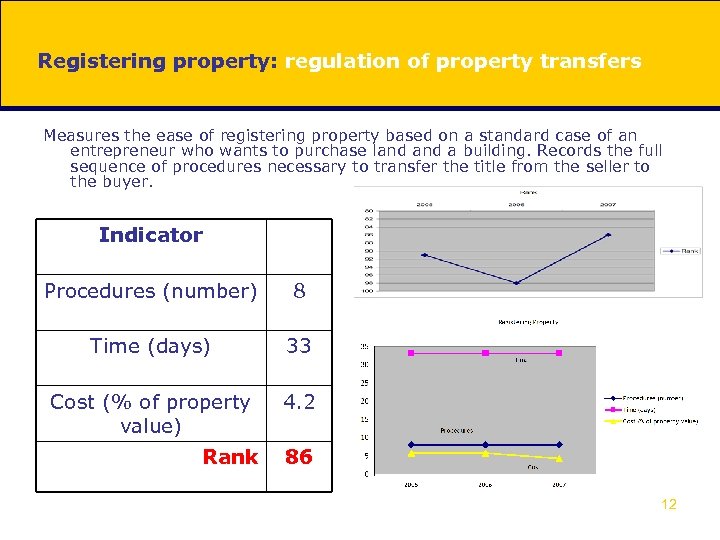
Registering property: regulation of property transfers Measures the ease of registering property based on a standard case of an entrepreneur who wants to purchase land a building. Records the full sequence of procedures necessary to transfer the title from the seller to the buyer. Indicator Procedures (number) 8 Time (days) 33 Cost (% of property value) 4. 2 Rank 86 12
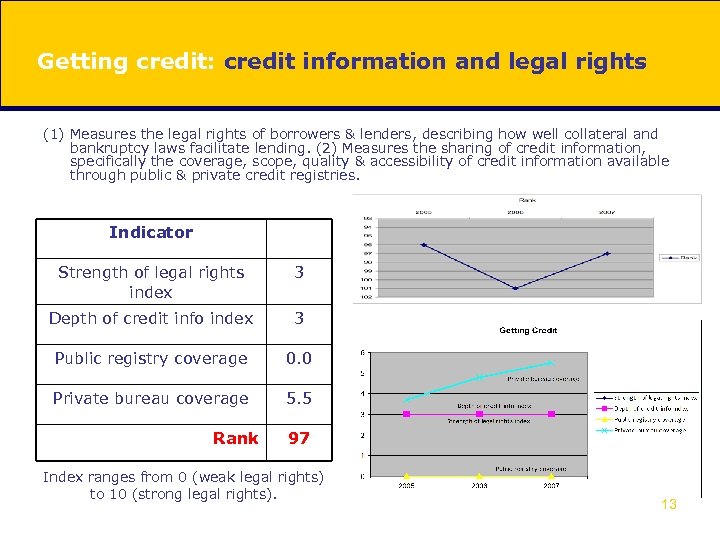
Getting credit: credit information and legal rights (1) Measures the legal rights of borrowers & lenders, describing how well collateral and bankruptcy laws facilitate lending. (2) Measures the sharing of credit information, specifically the coverage, scope, quality & accessibility of credit information available through public & private credit registries. Indicator Strength of legal rights index 3 Depth of credit info index 3 Public registry coverage 0. 0 Private bureau coverage 5. 5 Rank 97 Index ranges from 0 (weak legal rights) to 10 (strong legal rights). 13
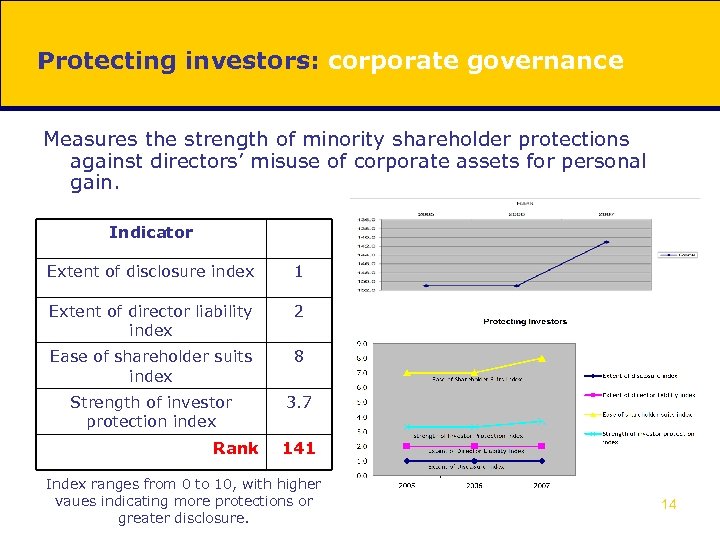
Protecting investors: corporate governance Measures the strength of minority shareholder protections against directors’ misuse of corporate assets for personal gain. Indicator Extent of disclosure index 1 Extent of director liability index 2 Ease of shareholder suits index 8 Strength of investor protection index 3. 7 Rank 141 Index ranges from 0 to 10, with higher vaues indicating more protections or greater disclosure. 14
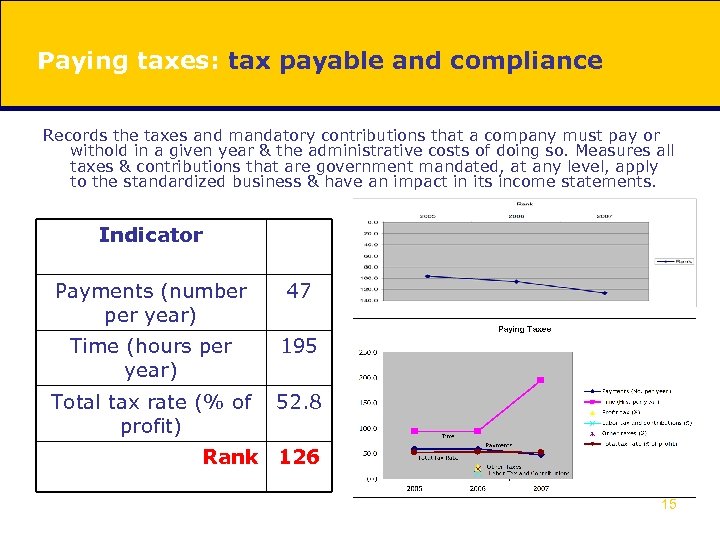
Paying taxes: tax payable and compliance Records the taxes and mandatory contributions that a company must pay or withold in a given year & the administrative costs of doing so. Measures all taxes & contributions that are government mandated, at any level, apply to the standardized business & have an impact in its income statements. Indicator Payments (number per year) 47 Time (hours per year) 195 Total tax rate (% of profit) 52. 8 Rank 126 15
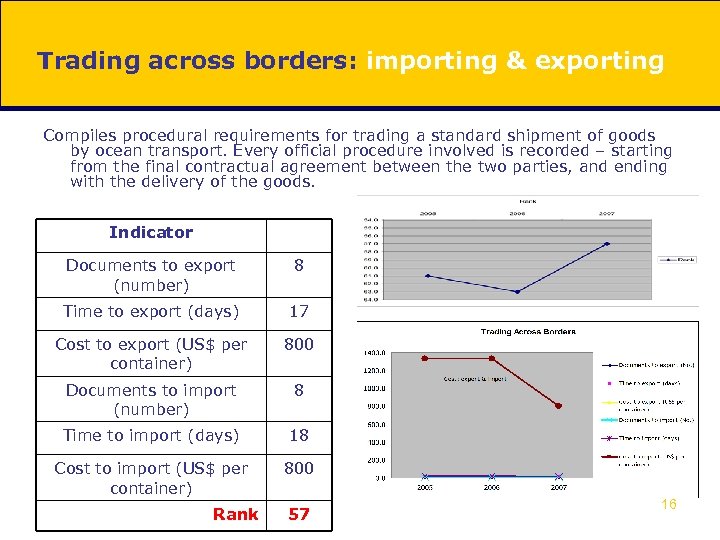
Trading across borders: importing & exporting Compiles procedural requirements for trading a standard shipment of goods by ocean transport. Every official procedure involved is recorded – starting from the final contractual agreement between the two parties, and ending with the delivery of the goods. Indicator Documents to export (number) 8 Time to export (days) 17 Cost to export (US$ per container) 800 Documents to import (number) 8 Time to import (days) 18 Cost to import (US$ per container) 800 Rank 57 16
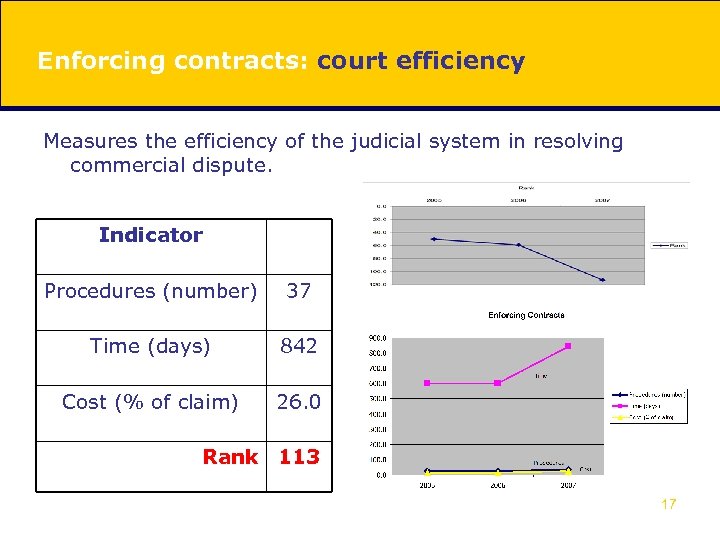
Enforcing contracts: court efficiency Measures the efficiency of the judicial system in resolving commercial dispute. Indicator Procedures (number) 37 Time (days) 842 Cost (% of claim) 26. 0 Rank 113 17
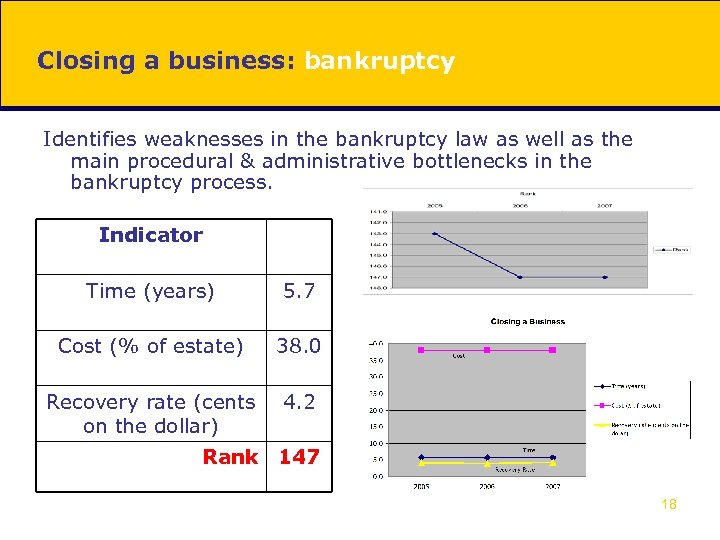
Closing a business: bankruptcy Identifies weaknesses in the bankruptcy law as well as the main procedural & administrative bottlenecks in the bankruptcy process. Indicator Time (years) 5. 7 Cost (% of estate) 38. 0 Recovery rate (cents on the dollar) 4. 2 Rank 147 18
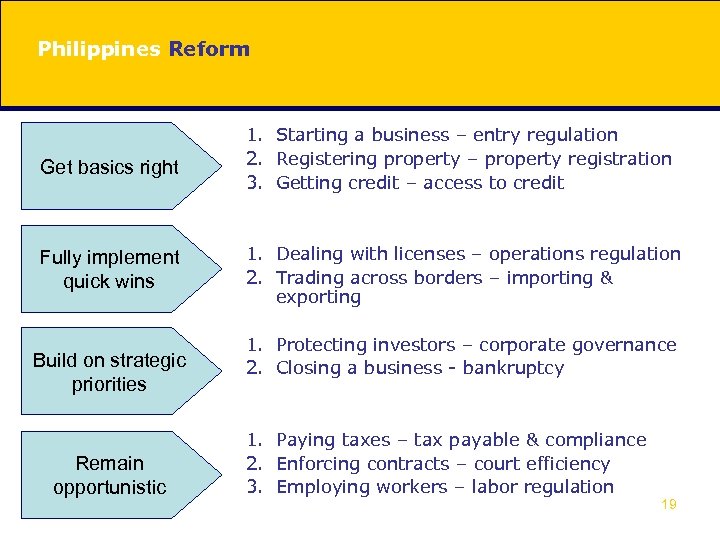
Philippines Reform Get basics right 1. Starting a business – entry regulation 2. Registering property – property registration 3. Getting credit – access to credit Fully implement quick wins 1. Dealing with licenses – operations regulation 2. Trading across borders – importing & exporting Build on strategic priorities Remain opportunistic 1. Protecting investors – corporate governance 2. Closing a business - bankruptcy 1. Paying taxes – tax payable & compliance 2. Enforcing contracts – court efficiency 3. Employing workers – labor regulation 19
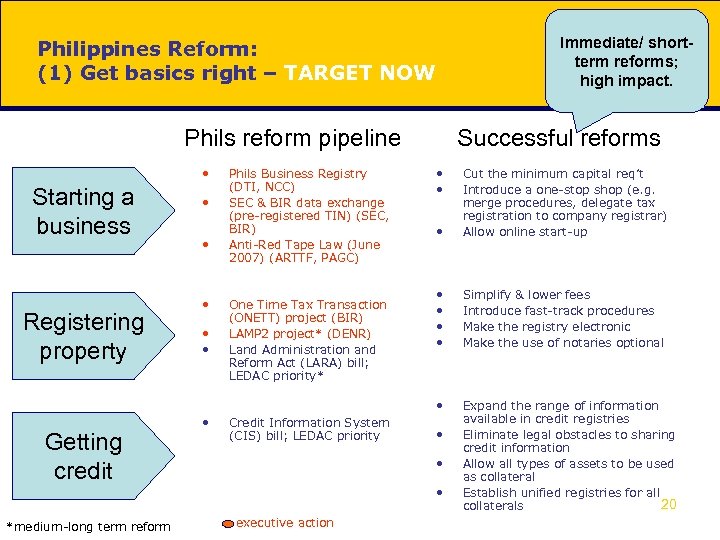
Immediate/ shortterm reforms; high impact. Philippines Reform: (1) Get basics right – TARGET NOW Phils reform pipeline • • • Registering property Getting credit *medium-long term reform • • • One Time Tax Transaction (ONETT) project (BIR) LAMP 2 project* (DENR) Land Administration and Reform Act (LARA) bill; LEDAC priority* Credit Information System (CIS) bill; LEDAC priority • Cut the minimum capital req’t Introduce a one-stop shop (e. g. merge procedures, delegate tax registration to company registrar) Allow online start-up • • Simplify & lower fees Introduce fast-track procedures Make the registry electronic Make the use of notaries optional • Starting a business Phils Business Registry (DTI, NCC) SEC & BIR data exchange (pre-registered TIN) (SEC, BIR) Anti-Red Tape Law (June 2007) (ARTTF, PAGC) Successful reforms Expand the range of information available in credit registries Eliminate legal obstacles to sharing credit information Allow all types of assets to be used as collateral Establish unified registries for all 20 collaterals • • • executive action
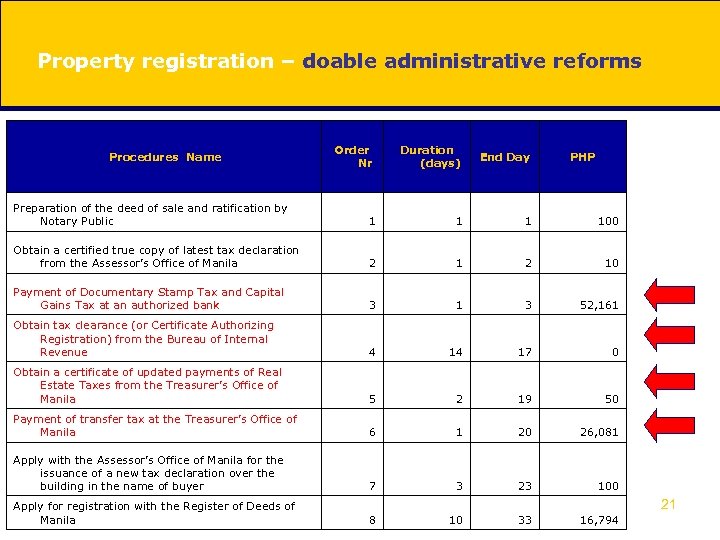
Property registration – doable administrative reforms Order Nr Duration (days) End Day Preparation of the deed of sale and ratification by Notary Public 1 100 Obtain a certified true copy of latest tax declaration from the Assessor’s Office of Manila 2 10 Payment of Documentary Stamp Tax and Capital Gains Tax at an authorized bank 3 1 3 52, 161 Obtain tax clearance (or Certificate Authorizing Registration) from the Bureau of Internal Revenue 4 14 17 0 Obtain a certificate of updated payments of Real Estate Taxes from the Treasurer’s Office of Manila 5 2 19 50 Payment of transfer tax at the Treasurer’s Office of Manila 6 1 20 26, 081 Apply with the Assessor’s Office of Manila for the issuance of a new tax declaration over the building in the name of buyer 7 3 23 100 Apply for registration with the Register of Deeds of Manila 8 10 33 16, 794 Procedures Name PHP 21
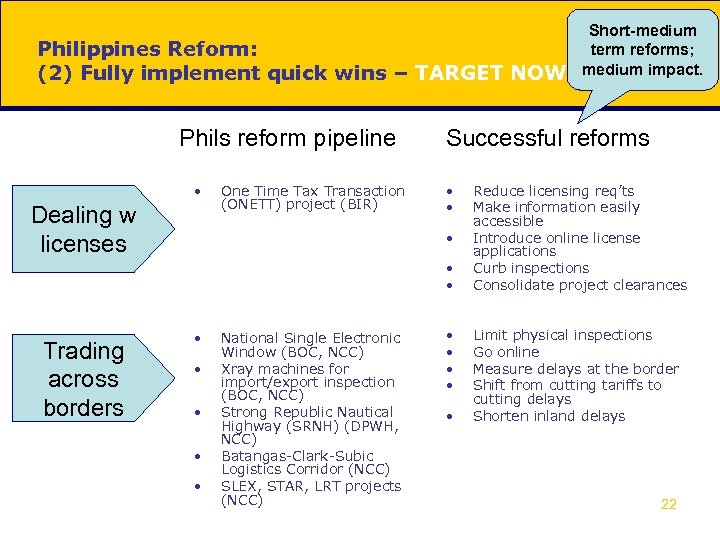
Philippines Reform: (2) Fully implement quick wins – TARGET NOW Phils reform pipeline • Dealing w licenses One Time Tax Transaction (ONETT) project (BIR) Successful reforms • • • Trading across borders • • • National Single Electronic Window (BOC, NCC) Xray machines for import/export inspection (BOC, NCC) Strong Republic Nautical Highway (SRNH) (DPWH, NCC) Batangas-Clark-Subic Logistics Corridor (NCC) SLEX, STAR, LRT projects (NCC) Short-medium term reforms; medium impact. • • • Reduce licensing req’ts Make information easily accessible Introduce online license applications Curb inspections Consolidate project clearances Limit physical inspections Go online Measure delays at the border Shift from cutting tariffs to cutting delays Shorten inland delays 22

Philippines Reform Agenda: (3) Build on strategic priorities – HIGH IMPACT Successful reforms Phils reform pipeline Protecting investors Closing a business Medium-long term reforms; high impact. • • Anti-trust bill; LEDAC priority Good Corporate Governance Training for BOD (BSP) • • Judicial Reform Support Project (JRSP) (SC) • • Open company activities to investor scrutiny Require disinterested shareholder approval Minimize dependence on the courts Shift power to creditors Limit appeals Introduce time limits Use the internet to post decisions & publicize auctions Introduce floating charges Develop the trustee profession 23
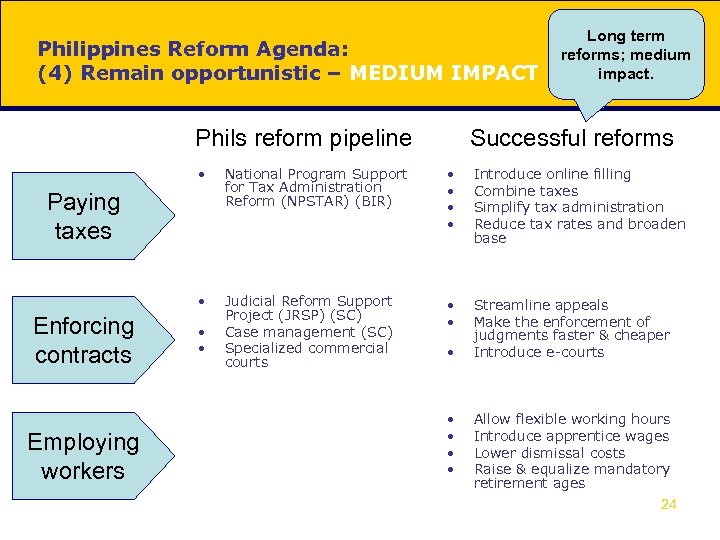
Philippines Reform Agenda: (4) Remain opportunistic – MEDIUM IMPACT Phils reform pipeline Long term reforms; medium impact. Successful reforms • National Program Support for Tax Administration Reform (NPSTAR) (BIR) • • Introduce online filling Combine taxes Simplify tax administration Reduce tax rates and broaden base • Judicial Reform Support Project (JRSP) (SC) Case management (SC) Specialized commercial courts • • Streamline appeals Make the enforcement of judgments faster & cheaper Introduce e-courts Paying taxes Enforcing contracts Employing workers • • Allow flexible working hours Introduce apprentice wages Lower dismissal costs Raise & equalize mandatory retirement ages 24

Doing Business 2008 September 26, 2007

Doing Business methodology - some basics 1. Gather all the relevant laws, regulations, decrees, fee schedules 2. Follow the entrepreneur from the beginning to the end of a transaction 3. Record every step of the process, and its time and cost 4. The data set for all sets of indicators in Doing Business 2008 are for June 2007 5. The standardized survey uses a simple business case to ensure comparability across countries and over time 6. Assumptions about the legal form of the business, its size, location and the nature of its operations 7. Surveys are administered through local intermediaries 26

“The need to make assumptions” ‘Starting a Business’ • • • Considers SME (between 10 and 50 employees) 100% domestically owned Start-up capital of 10 times income per capita Turnover of at least 100 times income per capita Operates in country’s most populous city Legal form: limited liability company (LLC) Simple business operation – general commercial activity Does not qualify for any special benefits Does not own real estate All requirements to incorporate and commence operations are recorded 27
8c30d1dc3bec60d0d1a853f8ac0516b1.ppt