ottomanempire-castle.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 The Ottoman Empire 1280 -1918 1
The Ottoman Empire 1280 -1918 1
 The Ottomans were: ·Turkish (capital Istanbul) ·Muslim ·The largest empire in the world
The Ottomans were: ·Turkish (capital Istanbul) ·Muslim ·The largest empire in the world
 Osman I (Othman): 1299 -1326
Osman I (Othman): 1299 -1326
 Tamerlane (1336 -1405) or “Timur, the Lame”
Tamerlane (1336 -1405) or “Timur, the Lame”
 Mehmet I: 1413 -1421
Mehmet I: 1413 -1421
 Mehmet II (“the Conqueror”), who ruled from 1451 -1481 6 http: //home. earthlink. net/ ~snailstales 2/fatih. jpg
Mehmet II (“the Conqueror”), who ruled from 1451 -1481 6 http: //home. earthlink. net/ ~snailstales 2/fatih. jpg

 The Fall of Constantinople: 1453
The Fall of Constantinople: 1453
 The End of the Byzantine Empire
The End of the Byzantine Empire
 Islam and the Ottoman Empire ·Sultan = caliph (head of Islam) ·Divided the empire into Millets (religious groups) ·Divided the world into “the House of Islam” and the “House of War” 10
Islam and the Ottoman Empire ·Sultan = caliph (head of Islam) ·Divided the empire into Millets (religious groups) ·Divided the world into “the House of Islam” and the “House of War” 10
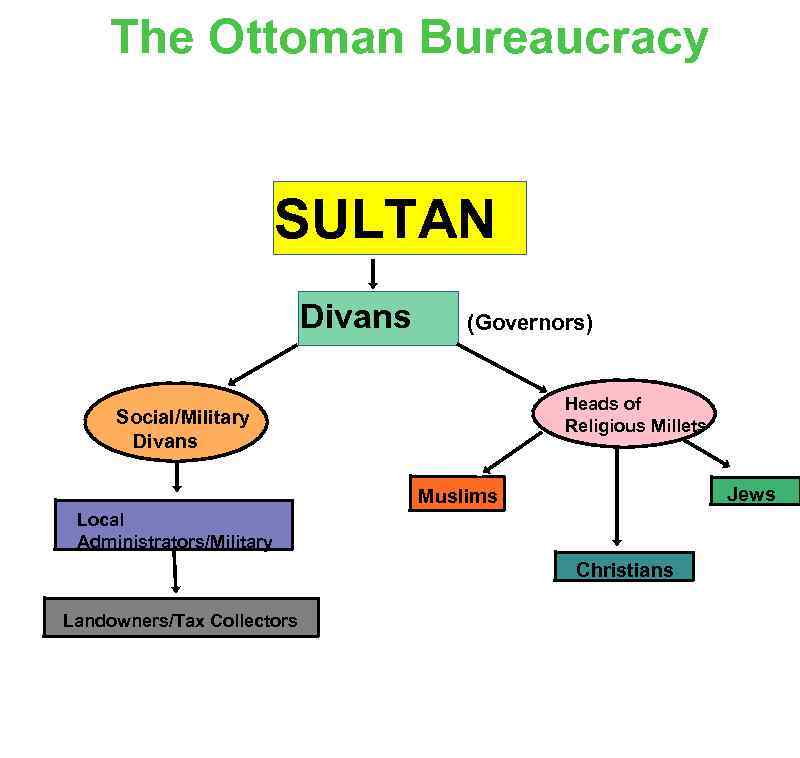 The Ottoman Bureaucracy SULTAN Divans (Governors) Heads of Religious Millets Social/Military Divans Jews Muslims Local Administrators/Military Christians Landowners/Tax Collectors
The Ottoman Bureaucracy SULTAN Divans (Governors) Heads of Religious Millets Social/Military Divans Jews Muslims Local Administrators/Military Christians Landowners/Tax Collectors
 Selim I, ”the Grim”: 1512 -1520
Selim I, ”the Grim”: 1512 -1520
 Suleyman the Magnificent (or “the Law Giver, ” ruled 1520 -1566 12 http: //commons. wikimedia. org/ wiki/Image: Suleyman_young. jpg
Suleyman the Magnificent (or “the Law Giver, ” ruled 1520 -1566 12 http: //commons. wikimedia. org/ wiki/Image: Suleyman_young. jpg
 Summary of the devshirme system: ·Slaves were taken from any non-Muslim areas. Race and language didn’t matter. ·Slaves were given jobs according to their interests and abilities. (Slaves did NOT do agricultural work – as American slaves did. ) 16
Summary of the devshirme system: ·Slaves were taken from any non-Muslim areas. Race and language didn’t matter. ·Slaves were given jobs according to their interests and abilities. (Slaves did NOT do agricultural work – as American slaves did. ) 16
 Devshirme (devşirme) 17 http: //www. pravoslavie. domainbg. com/ images/iljustracii/devshirme. jpg
Devshirme (devşirme) 17 http: //www. pravoslavie. domainbg. com/ images/iljustracii/devshirme. jpg
 Importance of the System: ·Government positions were based on merit, not on birth. ·Slaves were loyal to the sultan. – They owed their rank to him, and they had no powerful families to support them if they rebelled. ·When the system ended in the mid-1600 s, the government and military declined. 18
Importance of the System: ·Government positions were based on merit, not on birth. ·Slaves were loyal to the sultan. – They owed their rank to him, and they had no powerful families to support them if they rebelled. ·When the system ended in the mid-1600 s, the government and military declined. 18
 Three Ottoman Strengths:
Three Ottoman Strengths:
 1. Control of Trade ·Location on the east/west trade route ·Control of the Waterways
1. Control of Trade ·Location on the east/west trade route ·Control of the Waterways


 2. Wealth from trade
2. Wealth from trade
 Sultan’s headpiece, decorated with gold, emeralds, rubies, diamonds, and pearls 27 www. tourism. gov. tr
Sultan’s headpiece, decorated with gold, emeralds, rubies, diamonds, and pearls 27 www. tourism. gov. tr
 Jeweled Dagger 28 www. ee. bilkent. edu. tr/~history/ Pictures 2/topkapi_dagger_1746. jpg
Jeweled Dagger 28 www. ee. bilkent. edu. tr/~history/ Pictures 2/topkapi_dagger_1746. jpg
 Golden cradle 29 www. ee. bilkent. edu. tr/~history/Pictures 2/goldencradle_16 cc. jpg
Golden cradle 29 www. ee. bilkent. edu. tr/~history/Pictures 2/goldencradle_16 cc. jpg
 Gold dishes (for eating sweetmeats) 30 www. ee. bilkent. edu. tr/~history/Pictures 2/Yeni/trea 1. JP G
Gold dishes (for eating sweetmeats) 30 www. ee. bilkent. edu. tr/~history/Pictures 2/Yeni/trea 1. JP G
 The gate of the Topkapi Palace, the oldest and largest of the remaining palaces in the world. 31 http: //www. bibleplaces. com/istanbul. htm
The gate of the Topkapi Palace, the oldest and largest of the remaining palaces in the world. 31 http: //www. bibleplaces. com/istanbul. htm
 It’s a huge palace - the outer wall surrounding it is 3 miles long. 32 http: //www. iconofile. com/events/images/topkapi. jpg
It’s a huge palace - the outer wall surrounding it is 3 miles long. 32 http: //www. iconofile. com/events/images/topkapi. jpg
 The Blue Mosque 33 http: //lloydi. com/travel-writing/turkey/wallpaper/blue-mosque-1 x 7. jpg
The Blue Mosque 33 http: //lloydi. com/travel-writing/turkey/wallpaper/blue-mosque-1 x 7. jpg
 Inside the Blue Mosque 34 http: //cache. eb. com/eb/image? id=95924&rend. Type. Id=4
Inside the Blue Mosque 34 http: //cache. eb. com/eb/image? id=95924&rend. Type. Id=4
 3. Superior technology (the benefit of diffusion)
3. Superior technology (the benefit of diffusion)
 Ottoman Sipahi (cavalry) 21 http: //www. osmanischesreich. com/Geschichte/Armee/Heerwesen_I/Sipahi 1530. jpg
Ottoman Sipahi (cavalry) 21 http: //www. osmanischesreich. com/Geschichte/Armee/Heerwesen_I/Sipahi 1530. jpg
 Janissaries
Janissaries
 Musket Cannon Swords
Musket Cannon Swords
 How did the empire end? The Europeans destroyed their strengths.
How did the empire end? The Europeans destroyed their strengths.
 Ottoman Strength #1: Control of trade. ·Europeans broke this strength by going around Africa and gaining control of trade.
Ottoman Strength #1: Control of trade. ·Europeans broke this strength by going around Africa and gaining control of trade.

 Ottoman Strength #2: Wealth ·Discovery of the New World leads to great wealth for Europe from the gold and silver found there.
Ottoman Strength #2: Wealth ·Discovery of the New World leads to great wealth for Europe from the gold and silver found there.


 Ottoman Strength #3: Technology ·The technology of Europeans surpassed the Ottoman superiority especially in production of guns and munitions and other products necessary for war.
Ottoman Strength #3: Technology ·The technology of Europeans surpassed the Ottoman superiority especially in production of guns and munitions and other products necessary for war.
 Until the 18 century, the Ottoman Empire was one of the greatest empires in the world. th 43
Until the 18 century, the Ottoman Empire was one of the greatest empires in the world. th 43

 Conquerors__Suleyman_the_Magnificent. asf Attachments
Conquerors__Suleyman_the_Magnificent. asf Attachments


