3d3903506065739ec9da585532f4f708.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

The Open Group and Manageability: An Overview Presentation December 1999 Karl Schopmeyer Chair TOG Management Program Group k. schopmeyer@opengroup. org

What is Happening Today? l Information is one of the Keys to Management — A common Information Model l The customer wants management in his terms — Applications Management — Service Management — Business Level Management l The Customer wants Enterprise Management, not just Point Management -- Service Management, not just Technology Management l Management is Big Business l The Suppliers are beginning to work together

Enterprise Management (EM) and The Open Group l Open Enterprise Systems Management is a strategic objective for TOG l Technical and program group devoted to Enterprise Management l A meeting forum for suppliers and users l A partner with other Standards forums — Ex. DMTF Service Management Change Management Problem Management Configuration Management Operational Management

ESM Objectives l l l Encourage, support and create EFFECTIVE standards in Enterprise Systems Management Help advance the art of Enterprise Systems Management Communicate between users and suppliers l l l Help the suppliers understand user requirements Help users understand management and open management solutions Help users understand the art, practice, and standards of Distributed Systems Management Technology Business Education

ESM Organization l The Program Group (Open attendance) — Users and suppliers working together to: l advance open enterprise management l Technical Working Groups — Preparation of one technology — Specifications, Reference Code, testing, etc. l Business Working Groups — Business support for a technology area to encourage market adoption l Branding, Certification, Marketing, documentation

Enterprise Management Program Strategy l Build on current program activities, supporting technology deployment — — — l Software license use management (XSLM) Application response management (ARM) Universal management installation agent (UMIA) Application Information and Control (AIC) (Was AMI) Work With WEB Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) New programs with an overall coherence — Manageability (Major New Initiative) — Service Management — Business approach to programs — Concept to market adoption
Current Work l License Management (XSLM Work Group) l Universal Management Installation (UMIA Work Group) l Service Management (Interest Group) l Application Response Monitoring (ARM Business Group) l CIM Schema extensions for UNIX (Work Group) l AIC (Application Instrumentation and Control) Fast Track l Manageability (Interest Group)
Open Manageability l The objective of the Manageability Initiative is to provide: — A set of standard interfaces and standard service definitions for manageability components (interfaces between management agents and the managed entities) such as events, inventory, etc. — A manageability architecture into which these APIs and services can fit and which is based on the use of CIM as the common data

Manageability Background l There are NO effective ways to instrument for most managed entities today — No common SNMP agent instrumentation tools — No API to generate events l l l No way for applications to cooperate in management No real interfaces to get information to and from management systems. Many, multiple and often competing agents Management today tries to work through whatever information it can get through external exploration

Manageability is: l Manageability is the ability to be managed l Manageability defines how managed entities communicate with management functions l Manabeabilitiy is a major interface between different constituencies — Manager – Management Systems — Managee (Managed entity) – Entity to be managed (OS, applications, middleware, components, etc. Manager Managee Manageability
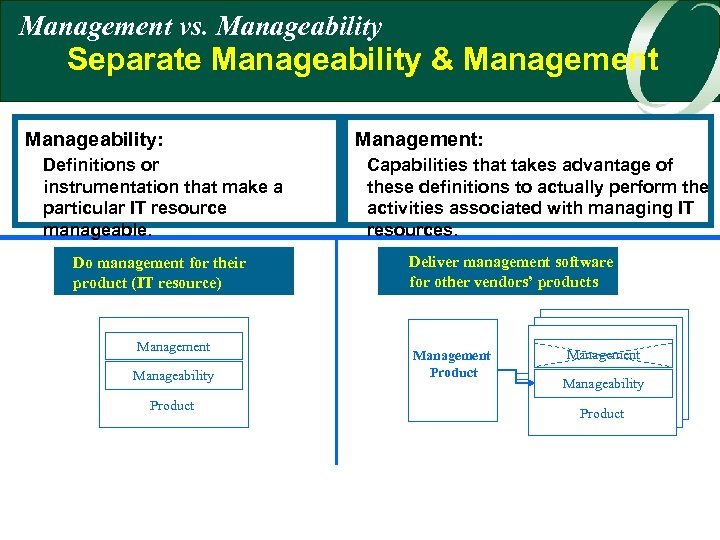
Management vs. Manageability Separate Manageability & Management Manageability: Definitions or instrumentation that make a particular IT resource manageable. Do management for their product (IT resource) Management Manageability Product Management: Capabilities that takes advantage of these definitions to actually perform the activities associated with managing IT resources. Deliver management software for other vendors’ products Management Product Management Manageability Product

Some Rules of Management l Capturing correct information and knowing what to do with it key to good management — Higher level management will require higher level information — Consistent information semantics must be established and preserved l Management is low priority in software development — Management is not important to the app developer — If it is difficult, don’t do it l Management means touching everything in the environment, not just some things l Today we manage in a hostile environment — We take information, it is not given

Manageability brings together: l Management system suppliers — Need information to manage l Software Providers (Applications and Middleware) — Instrument software for management l OS suppliers — OS instrumentation for management — Market advantage through effective application instrumentation l Customers — Need the information – Information not available today — Want simple and effective tools that integrate efficiently But – Why hasn’t this been done before?

We must remember that l Different priorities and objectives — Manageability (Instrumentation) l Simplicity for developers l Stability and long life l Multiple interface paradigms — Management Suppliers l Flexibility – Functionality will grow l Rich information capture — Customers l Interoperability l The Manageability concept lacks an owner — Who feels it is important enough to solve the problem? — Everybody wants something, nobody wants to do it
Some Key Characteristics l Key characteristics — Separate elements with loosely coupled interfaces — Provide interface with major Infrastructure (WEBM) — Extensible interface — Rich information model — Support required for multiple management system architectures (SNMP, WBEM, proprietary, etc. )

Manageability needs l Manageability needs today: — The managed components be instrumented — There should be a common API(s) so that these managed components can communicate with the managing systems independently of management solution — Service definitions so the managed components and management system have common understanding of service management offers — Common mechanism to define the information (CIM)
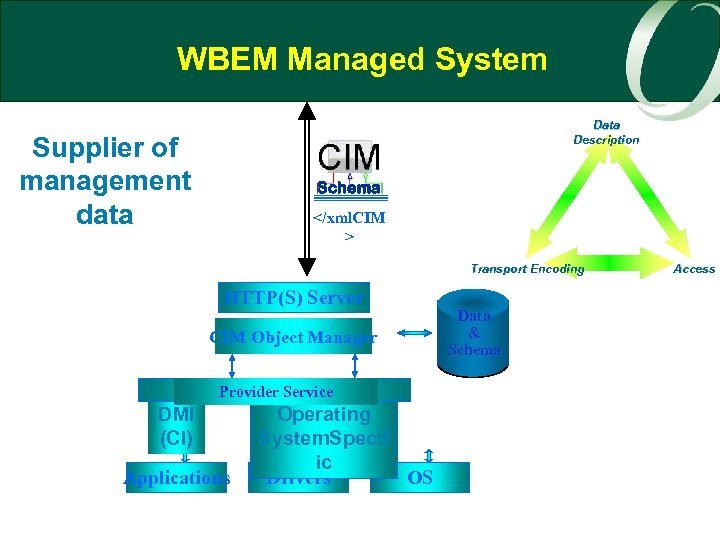
WBEM Managed System Data Description Supplier of management data Schema </xml. CIM > Transport Encoding HTTP(S) Server CIM Object Manager Provider Service DMI (CI) Applications Operating System. Specif ic Drivers OS Data & Schema Access
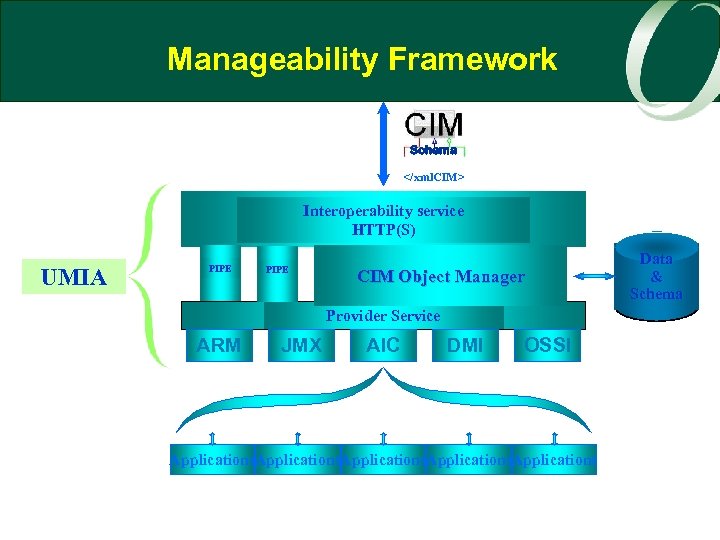
Manageability Framework Schema </xml. CIM> Interoperability service HTTP(S) UMIA PIPE CIM Object Manager Provider Service ARM JMX AIC DMI OSSI Applications Data & Schema
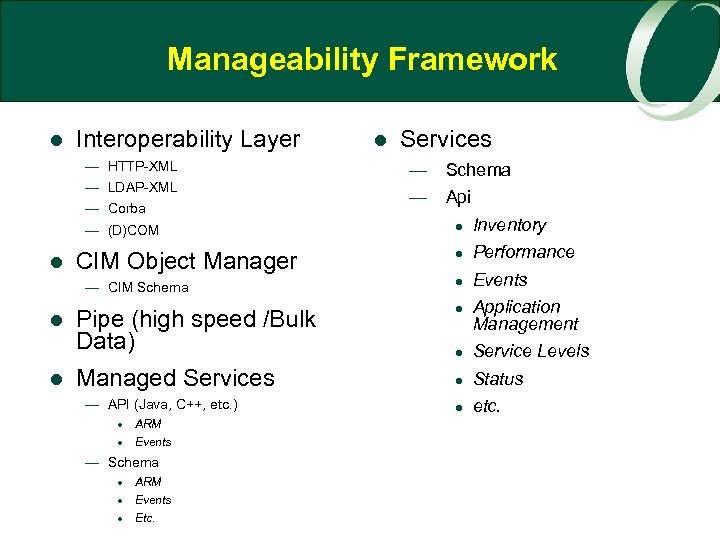
Manageability Framework l Interoperability Layer — — l HTTP-XML LDAP-XML Corba (D)COM CIM Object Manager — CIM Schema l Pipe (high speed /Bulk Data) l Managed Services — API (Java, C++, etc. ) l ARM l Events — Schema l ARM l Events l Etc. l Services — Schema — Api l Inventory l Performance l Events l Application Management l Service Levels l Status l etc.

Manageability needs l Manageability needs today: — The managed components be instrumented — Their be standard API sets so that the managed components can communicate independent of management solution — Service definitions so the managed components and management system have common understanding of services management offers — Common mechanism to use the information (ex. CIM)

Disjoint pieces of Manageability l No “APIs” that can provide the interface(s) that an applications can instrument to — ex. Never established a common API even for Events l No clear definition of manageability services l No clear statement and business case for manageability l Multitude of competing agents that are often incompatible l No clear roadmap l No buy in from all vendors

Manageability Framework Goals l An optioned framework that covers all pervasive, mobile, desktop, servers computing systems l Provides for at least the minimal managed capabilities that allows any of the target systems to be managed l Framework must allow for a range of capabilities to cover all devices with a variety of capabilities

Objectives of the TOG Initiative l Define an architecture that will drive effective manageability l Establish standards for a Management Service Provider layer l Integrate existing specifications into a larger whole l Provide an effective interface with Common Management Infrastructures (ex. WBEM) l Provide specifications for specific components of the manageability instrumentation
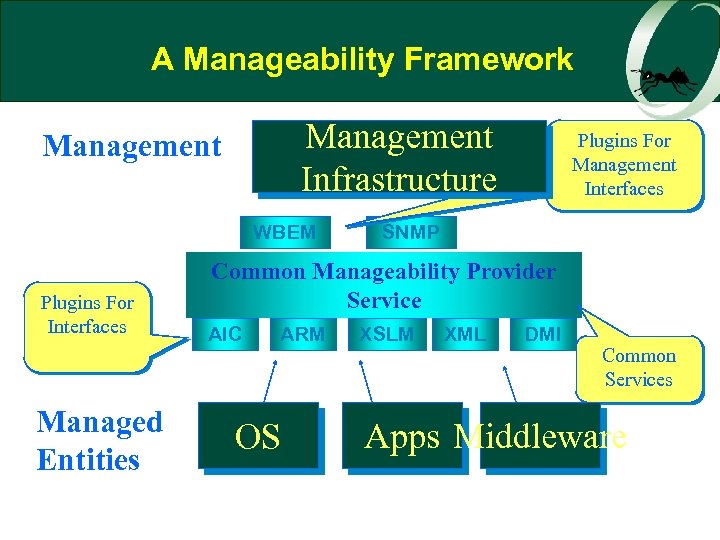
A Manageability Framework Management Infrastructure Management WBEM Plugins For Interfaces Managed Entities Plugins For Management Interfaces SNMP Common Manageability Provider Service AIC ARM OS XSLM XML DMI Common Services Apps Middleware

Manageability Challenges l Get all parties to the table — Major Management Suppliers — Smaller Management suppliers — Application suppliers — OS suppliers — Users l Figure out who can drive this program — Management suppliers, App suppliers, etc. ? l Management of existing apps is still high value solution

Manageability in TOG Today l Already delivering Manageability pieces — XSLM – Client APIs for license management — ARM – Client APIs for transaction information — UMIA – Tool to aid agent installation l BUT — Not coherent — There is no architecture — There is no industry leadership for the concepts

How can we Accomplish This? l Green. Field – Create new standards — Positive – We get exactly what we want — Negative - Long and difficult l Fast. Track existing technologies — Positive – Moves them into the TOG domain — Negative – Minimum possibility to integrate l Work from existing donated base technologies and specifications — Positive – We can modify the starting points together — Negative – There is a real work effort — Note: We can control what we get through RFIs
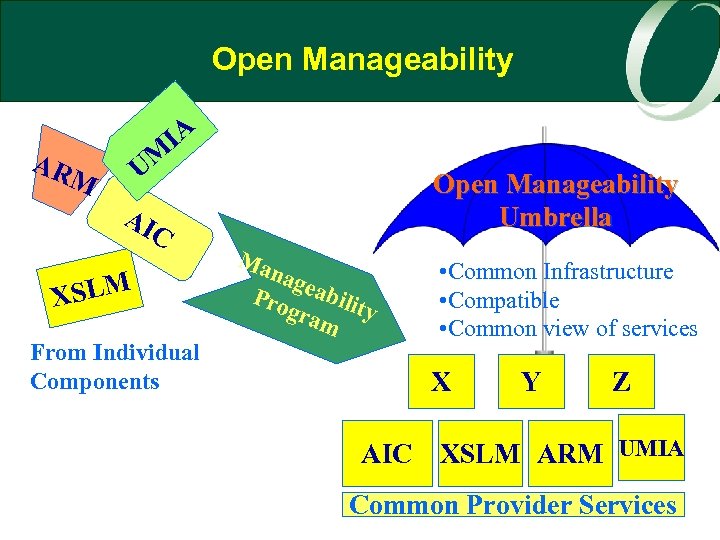
Open Manageability IA UM AR M Open Manageability Umbrella AI C XSLM From Individual Components Ma nag Pro eabilit y gra m • Common Infrastructure • Compatible • Common view of services X Y Z AIC XSLM ARM UMIA Common Provider Services

Initiative Status today l Agreement on the need and base requirements l Looking at alternate technologies l Initiating architecture l Working with several technologies — Java JMX — XML based instrumentation l Integrating Manageability with — Application run-time CIM Schema development — TOG AIC extension to integrate with CIM, etc.
3d3903506065739ec9da585532f4f708.ppt