Дополнение_новая.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

The Object Дополнение

The Object The secondary part of the sentence referring to some other part of the sentence that is usually expressed by a verb (rarely - an adjective or a stative, and, very seldom, an adverb). • She has bought a car. • She was afraid of the dog. • He did it unexpectedly to himself.

The object can be expressed by: • a noun in the common case • a nominal phrase • a substantivised adjective or a participle I saw the boys two hours ago. • We met a lot of people there. • First of all she attended to the sick. •

The object can be expressed by: • A noun-pronoun I don’t know anybody here. What will you do with these? • A numeral or a phrase with a numeral At last he found three of them high up in the hills.

The object can be expressed by: • A gerund or a gerundial construction He insists on coming here. The boys denied their stealing the gold chain. • An infinitive or an infinitive phrase or construction Every day I had to learn how to spell new words. Do you expect our team to win?

The object can be expressed by: • Various predicative constructions • She felt her hands trembling. (With a participle I) • I want it done at once. (With a participle II) • She will let you know about the decision. (With an infinitive) • A clause (an object clause) • I don’t know who it was.
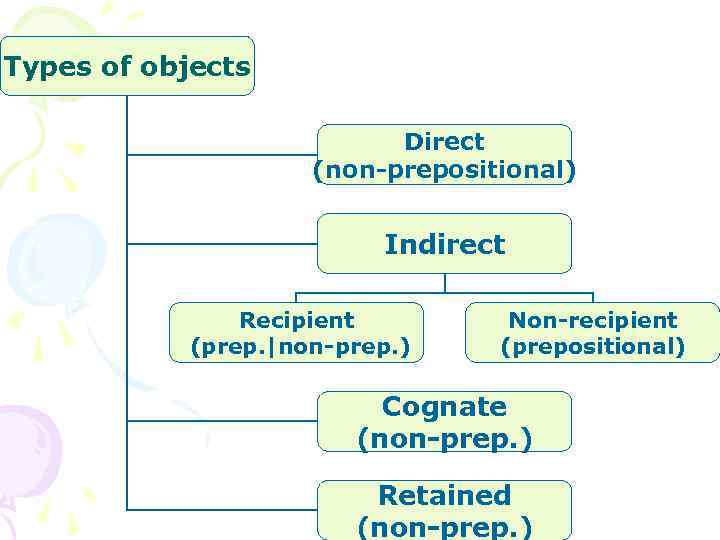
Types of objects Direct (non-prepositional) Indirect Recipient (prep. |non-prep. ) Non-recipient (prepositional) Cognate (non-prep. ) Retained (non-prep. )

The direct object прямое дополнение • Non-prepositional, follows transitive verbs, adjectives or statives and completes their meaning (винительный падеж - кого? что? ). • I wrote a poem. • Who saw him leave? • I find it exciting to watch such films.

These verbs take the direct object To address smb To follow smb, sth To affect smb, sth To join smb, sth To answer sth To mount sth To approach smb, sth To need smb, sth To attend sth To play sth To enjoy sth To reach sth To enter sth To watch smb, sth The use of prepositions with these verbs is not be the same in Russian and in English

The indirect object косвенное дополнение • Follows both transitive and intransitive verbs, adjectives and statives. • Is subdivided into recipient (обозначает адресата действия) and non-recipient object (не имеет значения «адресат действия» ).

The indirect recipient object • Is expressed by a noun/pronoun which denotes the addressee (the recipient) of the action of the verb (дательный падеж - кому? чему? ). • May be prepositional (to, for) or non -prepositional. • He gave the kid two dollars. • Will you bring a cup of coffee for me?

The indirect non-recipient object • Its semantics is various but it never denotes the addressee of the action. • Always prepositional. • One must always hope for the best. • She’s not happy about her new friend.

The cognate object грамматическое дополнение, образованное от того же корня, что и глагол • Non-prepositional, is attached to intransitive verbs. • Is always expressed by nouns derived from, or semantically close to the governing verb. • The child smiled a happy smile. • He struck him a heavy blow.

Cognate objects: examples To live a life To sleep a sleep To smile a smile To dream a dream To laugh a laugh To run a race To die a death To fight a fight To sigh a sigh To fight a battle

The retained object прямое дополнение при глаголе в пассивном залоге • An object in a passive construction that is identical to the object in the corresponding active construction (this object keeps its position after the transformation). They gave Mary the prize (here it is a direct object). Mary was given the prize object). (here it is a retained

References Н. А. Кобрина, Е. А. Корнеева, М. И. Оссовская, К. А. Гузеева Грамматика английского языка: Морфология. Синтаксис. Учебное пособие для студентов педагогических институтов и университетов по специальности № 2103 "Иностранные языки". - СПб. , СОЮЗ, 1999. - 496 с.
Дополнение_новая.ppt