The Nobel Prize in


The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1953 "for his discovery of the citric acid cycle" 1/2 of the prize United Kingdom b. 1900 Sheffield University (in Hildesheim, , United Kingdom Germany) d. 1981 Sir Hans Adolf Krebs Cancer claims There have been erroneous reports that E 330 is a major cause of cancer. It is thought that this has been brought about by misunderstanding and confusion over the word Krebs. In this case, it refers to Sir Hans Adolf Krebs, discoverer of the Krebs cycle, and not the German word for cancer. Citric acid is not known to be harmful to the body when taken alone.
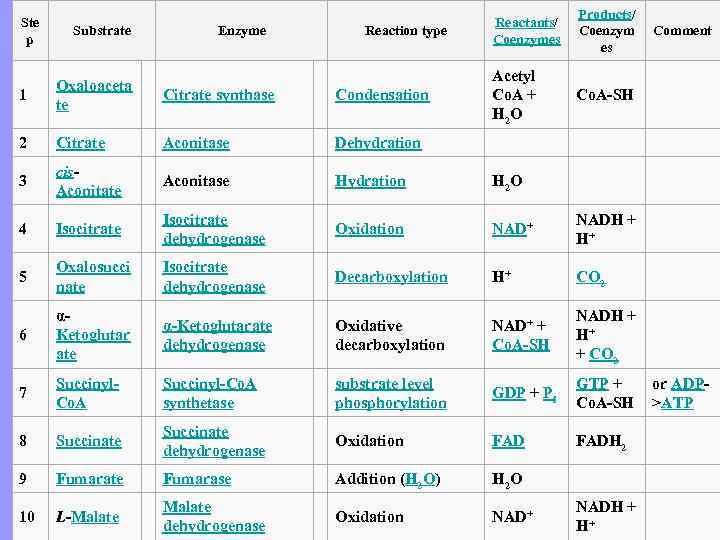
Products/ Ste Reactants/ Substrate Enzyme Reaction type Coenzym Comment p Coenzymes Acetyl Oxaloaceta 1 Citrate synthase Condensation Co. A + Co. A-SH te H 2 O 2 Citrate Aconitase Dehydration cis- 3 Aconitase Hydration H 2 O Aconitate Isocitrate NADH + 4 Isocitrate Oxidation NAD+ dehydrogenase H+ Oxalosucci Isocitrate 5 Decarboxylation H+ CO 2 nate dehydrogenase α- NADH + α-Ketoglutarate Oxidative NAD+ + 6 Ketoglutar H+ dehydrogenase decarboxylation Co. A-SH ate + CO 2 Succinyl-Co. A substrate level GTP + or ADP- 7 GDP + Pi Co. A synthetase phosphorylation Co. A-SH >ATP Succinate 8 Succinate Oxidation FADH 2 dehydrogenase 9 Fumarate Fumarase Addition (H 2 O) H 2 O Malate NADH + 10 L-Malate Oxidation NAD+ dehydrogenase H+
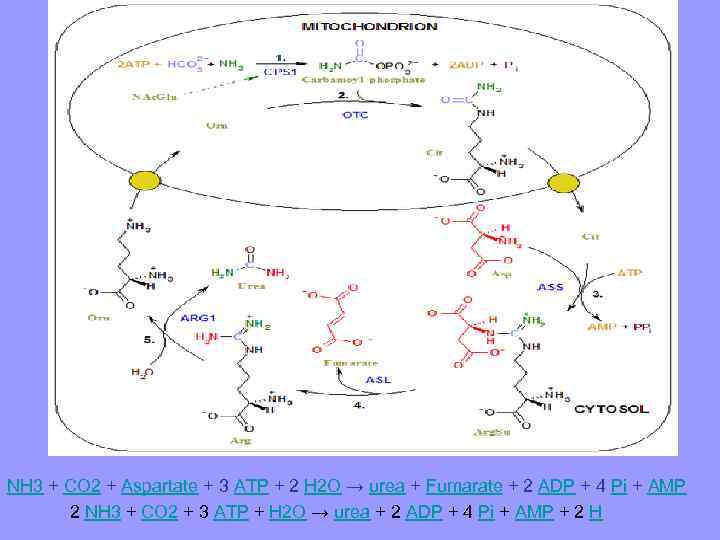
NH 3 + CO 2 + Aspartate + 3 ATP + 2 H 2 O → urea + Fumarate + 2 ADP + 4 Pi + AMP 2 NH 3 + CO 2 + 3 ATP + H 2 O → urea + 2 ADP + 4 Pi + AMP + 2 H
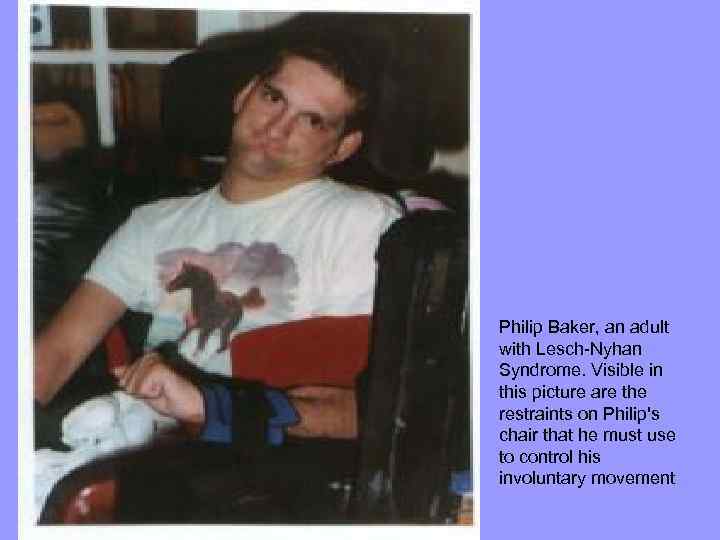
Philip Baker, an adult with Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome. Visible in this picture are the restraints on Philip's chair that he must use to control his involuntary movement

