39fcd6c22b367499dcd1e5aeff6147e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

THE NITROGEN CYCLE © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
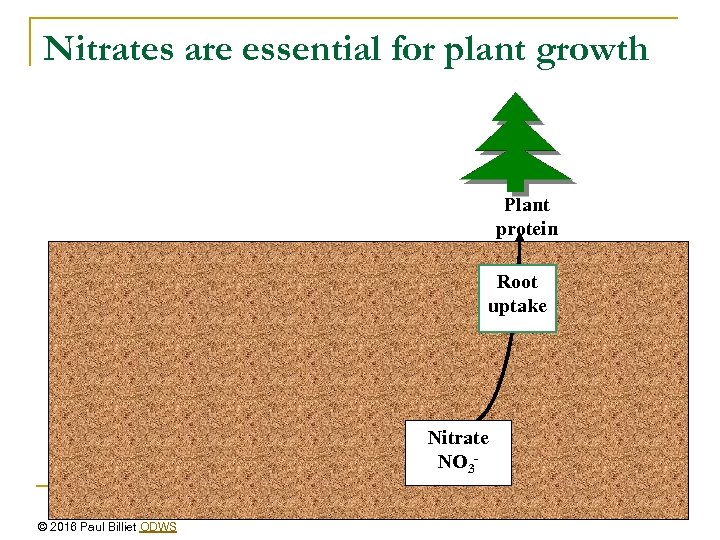
Nitrates are essential for plant growth Plant protein Root uptake Nitrate NO 3© 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
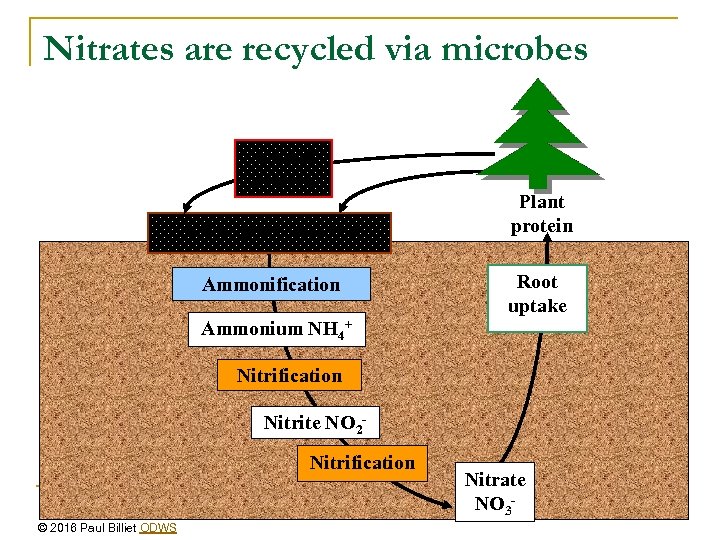
Nitrates are recycled via microbes Animal protein Soil organic nitrogen Ammonification Plant protein Root uptake Ammonium NH 4+ Nitrification Nitrite NO 2 Nitrification © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS Nitrate NO 3 -
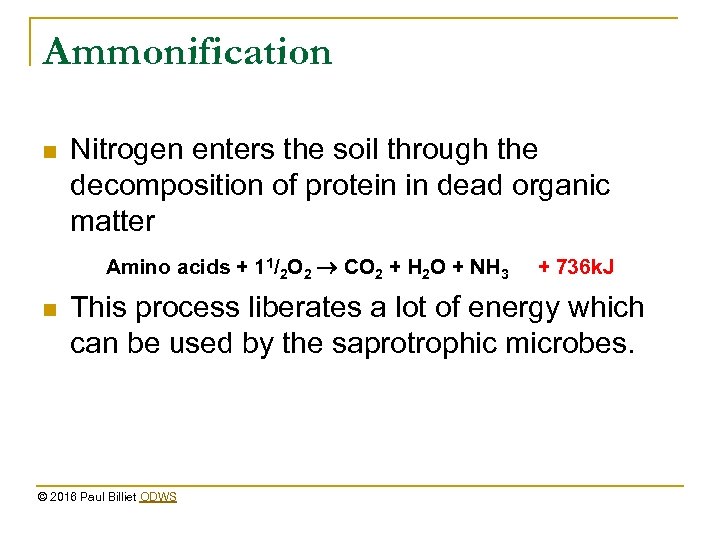
Ammonification n Nitrogen enters the soil through the decomposition of protein in dead organic matter Amino acids + 11/2 O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O + NH 3 n + 736 k. J This process liberates a lot of energy which can be used by the saprotrophic microbes. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
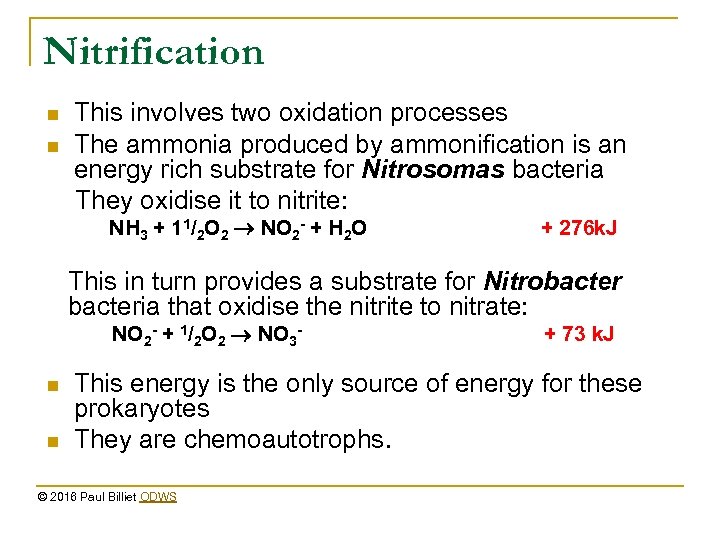
Nitrification n n This involves two oxidation processes The ammonia produced by ammonification is an energy rich substrate for Nitrosomas bacteria They oxidise it to nitrite: NH 3 + 11/2 O 2 NO 2 - + H 2 O + 276 k. J This in turn provides a substrate for Nitrobacteria that oxidise the nitrite to nitrate: NO 2 - + 1/2 O 2 NO 3 - n n + 73 k. J This energy is the only source of energy for these prokaryotes They are chemoautotrophs. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
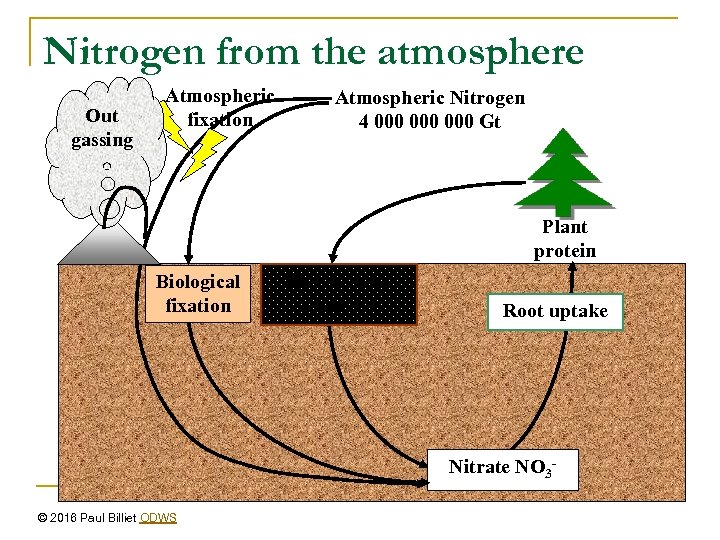
Nitrogen from the atmosphere Out gassing Atmospheric fixation Atmospheric Nitrogen 4 000 000 Gt Plant protein Biological fixation Soil organic nitrogen Root uptake Nitrate NO 3© 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Atmospheric nitrogen fixation n Electrical storms Lightning provides sufficient energy to split the nitrogen atoms of nitrogen gas, Forming oxides of nitrogen NOx and NO 2 © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Atmospheric Pollution n n n This also happens inside the engines of cars The exhaust emissions of cars contribute to atmospheric pollution in the form of NOx form photochemical smogs NOx are green house gases NOx dissolve in rain to contribute to acid rain in the form of nitric acid The rain falling on soil and running into rivers NOx contribute to the eutrophication of water bodies. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
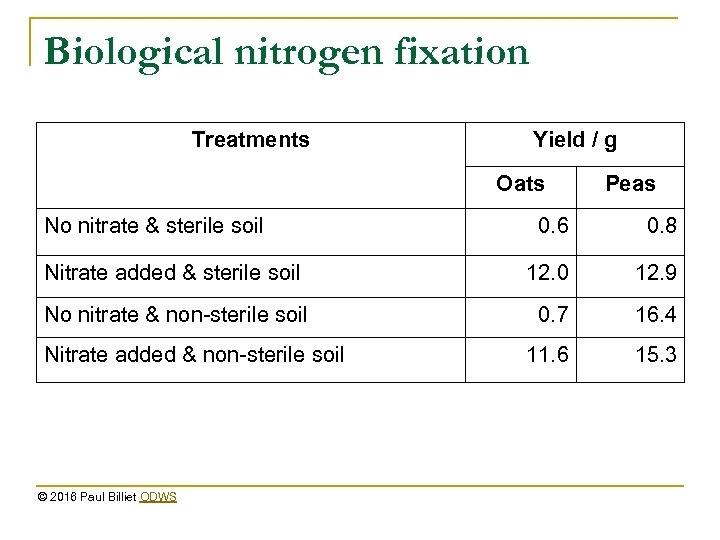
Biological nitrogen fixation Treatments Yield / g Oats No nitrate & sterile soil Peas 0. 6 0. 8 Nitrate added & sterile soil 12. 0 12. 9 No nitrate & non-sterile soil 0. 7 16. 4 11. 6 15. 3 Nitrate added & non-sterile soil © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Conclusion n n Adding nitrate fertiliser helps the growth of both plants The presence of microbes permits the peas to grow much better than the oats The peas grow better in the presence of the microbes than they do with nitrate fertiliser added The difference is due to the present of mutualistic nitrogen fixing bacteria which live in the pea roots. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
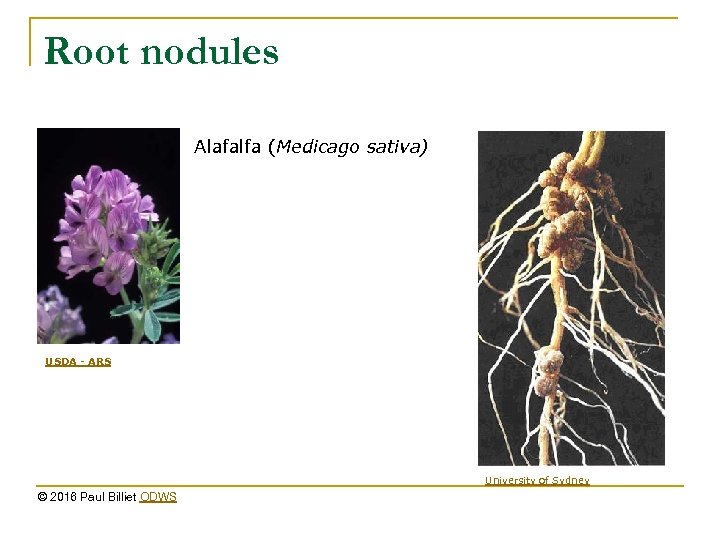
Root nodules Alafalfa (Medicago sativa) USDA - ARS University of Sydney © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
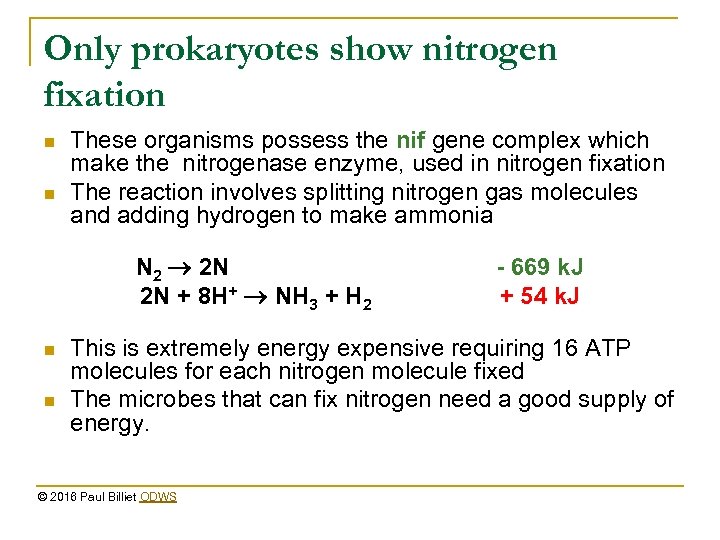
Only prokaryotes show nitrogen fixation n n These organisms possess the nif gene complex which make the nitrogenase enzyme, used in nitrogen fixation The reaction involves splitting nitrogen gas molecules and adding hydrogen to make ammonia N 2 2 N 2 N + 8 H+ NH 3 + H 2 n n - 669 k. J + 54 k. J This is extremely energy expensive requiring 16 ATP molecules for each nitrogen molecule fixed The microbes that can fix nitrogen need a good supply of energy. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
The nitrogen fixers n n Cyanobacteria are nitrogen fixers that also fix carbon (these are photosynthetic) Rhizobium bacteria are mutualistic with certain plant species e. g. Legumes They grow in root nodules Azotobacter are bacteria associated with the rooting zone (the rhizosphere) of plants in grasslands. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
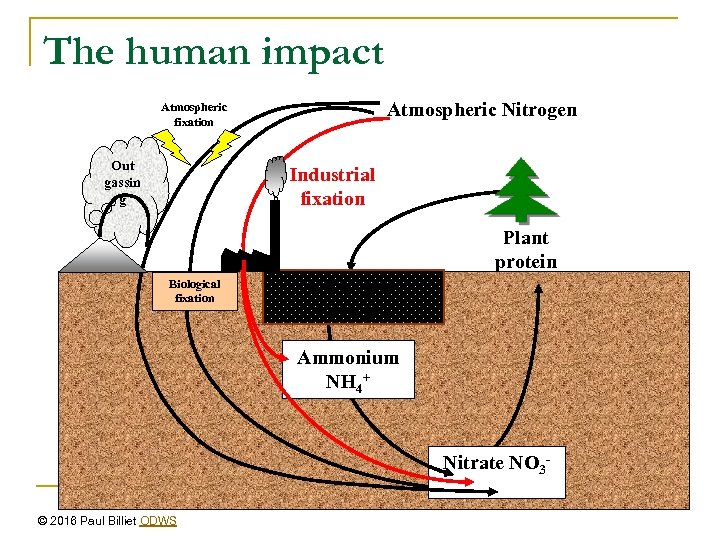
The human impact Atmospheric Nitrogen Atmospheric fixation Out gassin g Industrial fixation Plant protein Biological fixation Soil organic nitrogen Ammonium NH 4+ Nitrate NO 3© 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
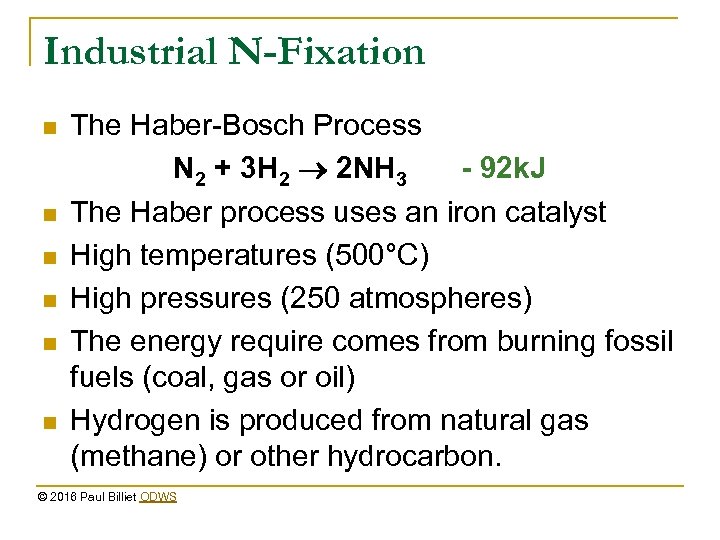
Industrial N-Fixation n n n The Haber-Bosch Process N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 - 92 k. J The Haber process uses an iron catalyst High temperatures (500°C) High pressures (250 atmospheres) The energy require comes from burning fossil fuels (coal, gas or oil) Hydrogen is produced from natural gas (methane) or other hydrocarbon. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
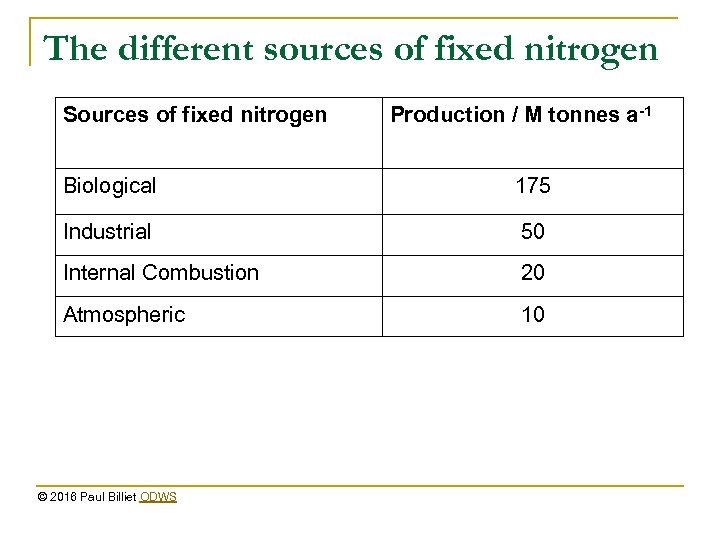
The different sources of fixed nitrogen Sources of fixed nitrogen Production / M tonnes a-1 Biological 175 Industrial 50 Internal Combustion 20 Atmospheric 10 © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Eutrophication n n n Nutrient enrichment of water bodies Nitrates and ammonia are very soluble in water They are easily washed (leached) from free draining soils These soils tend to be deficient in nitrogen When fertiliser is added to these soils it too will be washed out into water bodies There algae benefit from the extra nitrogen This leads to a serious form of water pollution. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
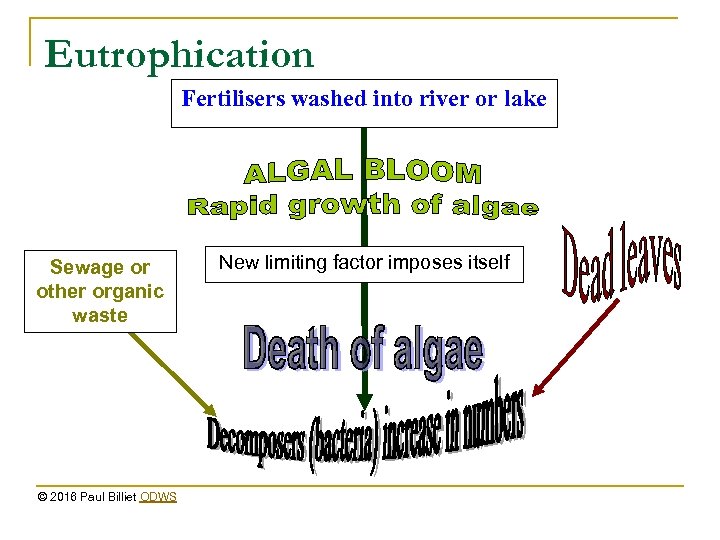
Eutrophication Fertilisers washed into river or lake Sewage or other organic waste © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS New limiting factor imposes itself
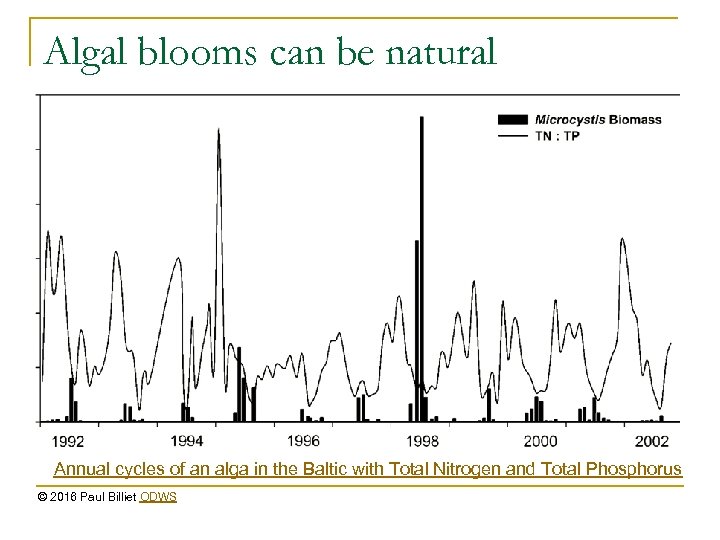
Algal blooms can be natural Annual cycles of an alga in the Baltic with Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorus © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Controlling algal blooms Lake Erie n n n Limit nutrients Control pollution Increase number of herbivores © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
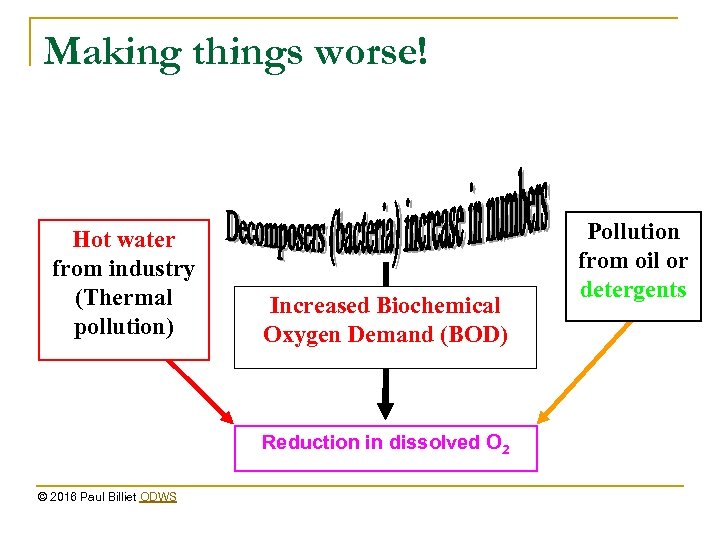
Making things worse! Hot water from industry (Thermal pollution) Increased Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) Reduction in dissolved O 2 © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS Pollution from oil or detergents
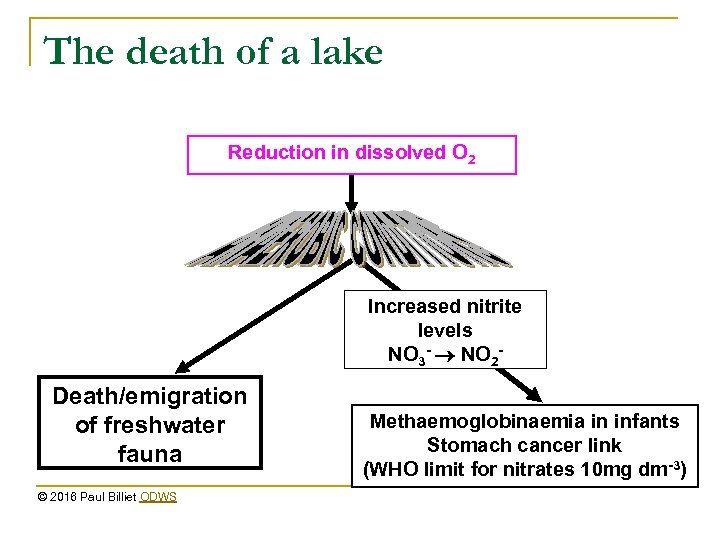
The death of a lake Reduction in dissolved O 2 Increased nitrite levels NO 3 - NO 2 - Death/emigration of freshwater fauna © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS Methaemoglobinaemia in infants Stomach cancer link (WHO limit for nitrates 10 mg dm-3)

The future of industrial nitrogen fixation n n Food production relies heavily upon synthetic fertilisers made by consuming a lot of fossil energy Food will become more expensive to produce Nitrogen fixing microbes, using an enzyme system, do the same process at standard temperatures and pressures essentially using solar energy Answer: Genetically engineered biological nitrogen fixation? © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Making things better n n n The need for synthetic fertilisers can be reduced by cultural practices Avoiding the use of soluble fertilisers in sandy (free draining soil) prevents leaching Rotating crops permits the soil to recover from nitrogen hungry crops (e. g. wheat) Adding a nitrogen fixing crop into the rotation cycle Ploughing aerates the soil and reduces denitrification Draining water logged soil also helps reduce denitrification. © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Return to the atmosphere: Denitrification Nitrates and nitrites can be used a source of oxygen for Pseudomonas bacteria n Favourable conditions: Cold waterlogged (anaerobic) soils 2 NO 3 - 3 O 2 + N 2 providing up to 2385 k. J 2 NO 2 - 2 O 2 + N 2 n The liberated oxygen is used as an electron acceptor in the processes that oxidise organic molecules, such as glucose n These microbes are, therefore, heterotrophs n © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Insectivorous plants Drosera rotundifolia © P Billiet © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS

Insectivorous plants Drosera rotundifolia © P Billiet n n n Carnivorous plants trap insects They digest their bodies Insect proteins provide a source of nitrogen These plants have found a niche in nitrogen deficient soils E. g. peat bogs © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
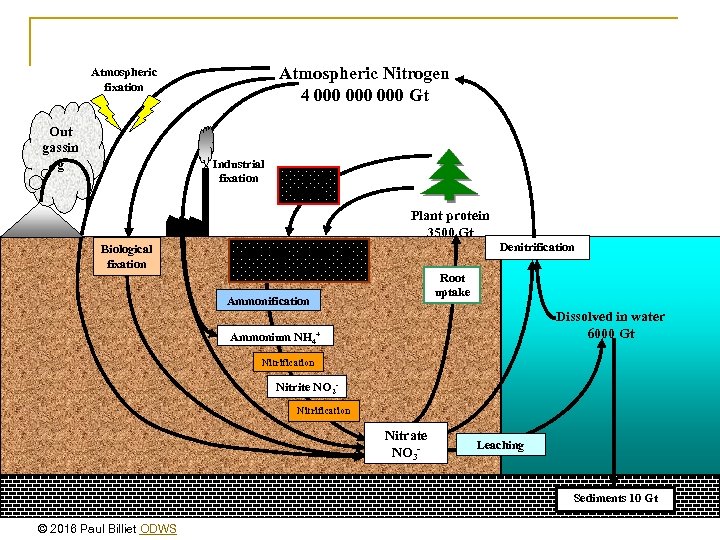
Atmospheric Nitrogen 4 000 000 Gt Atmospheric fixation Out gassin g Industrial fixation Animal protein Plant protein 3500 Gt Biological fixation Denitrification Soil organic nitrogen 9500 Gt Root uptake Ammonification Dissolved in water 6000 Gt Ammonium NH 4+ Nitrification Nitrite NO 2 Nitrification Nitrate NO 3 - Leaching Sediments 10 Gt © 2016 Paul Billiet ODWS
39fcd6c22b367499dcd1e5aeff6147e5.ppt