723d9cb615853c746bc086d9187a086c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 The New NRP Algorithm NRP 2006 – Western Canada Launch Vancouver, BC
The New NRP Algorithm NRP 2006 – Western Canada Launch Vancouver, BC
 Objectives n n Show the new 2006 Resuscitation algorithm Discuss the NRP 2006 Initial Steps What has changed since NRP 2000 How specific Canadian Expert Committee recommendations affect the algorithm
Objectives n n Show the new 2006 Resuscitation algorithm Discuss the NRP 2006 Initial Steps What has changed since NRP 2000 How specific Canadian Expert Committee recommendations affect the algorithm
 Objectives n The Initial Steps n Decide if resuscitation is needed n Provide initial steps of resuscitation n Decide if / when oxygen should be given n Exception to “dry the baby” n Resuscitate a newborn when meconium is present
Objectives n The Initial Steps n Decide if resuscitation is needed n Provide initial steps of resuscitation n Decide if / when oxygen should be given n Exception to “dry the baby” n Resuscitate a newborn when meconium is present
 The Canadian Expert Committee n n National guidelines to neonatal resuscitation across several continents are based on the consensus statements of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR). Each country is expected to develop guidelines that reflect their own context.
The Canadian Expert Committee n n National guidelines to neonatal resuscitation across several continents are based on the consensus statements of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR). Each country is expected to develop guidelines that reflect their own context.

 Is resuscitation needed? Routine Care
Is resuscitation needed? Routine Care
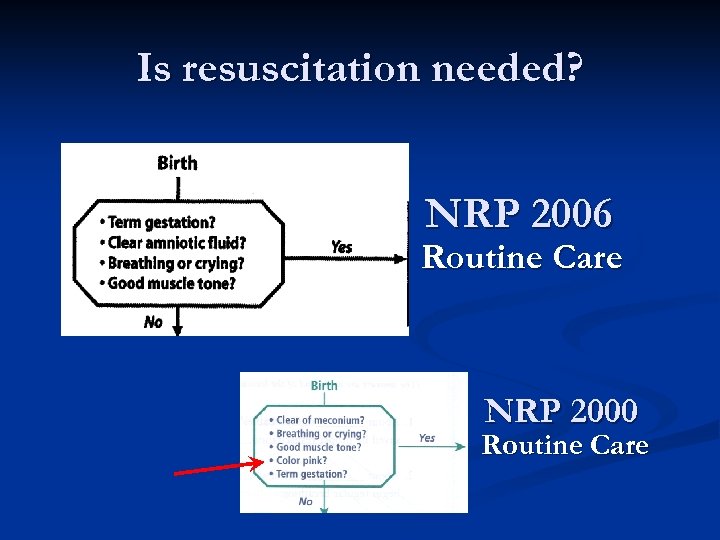 Is resuscitation needed? NRP 2006 Routine Care NRP 2000 Routine Care
Is resuscitation needed? NRP 2006 Routine Care NRP 2000 Routine Care
 Is resuscitation needed? NRP 2006 Routine Care Oxygen is gone …
Is resuscitation needed? NRP 2006 Routine Care Oxygen is gone …
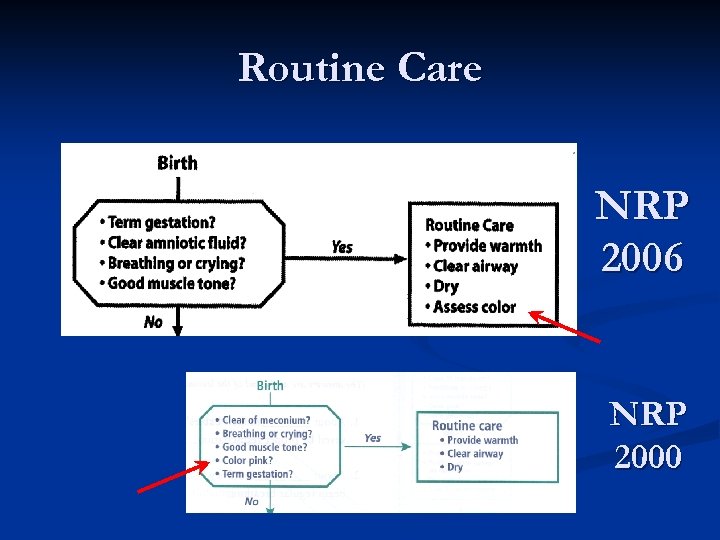 Routine Care NRP 2006 NRP 2000
Routine Care NRP 2006 NRP 2000
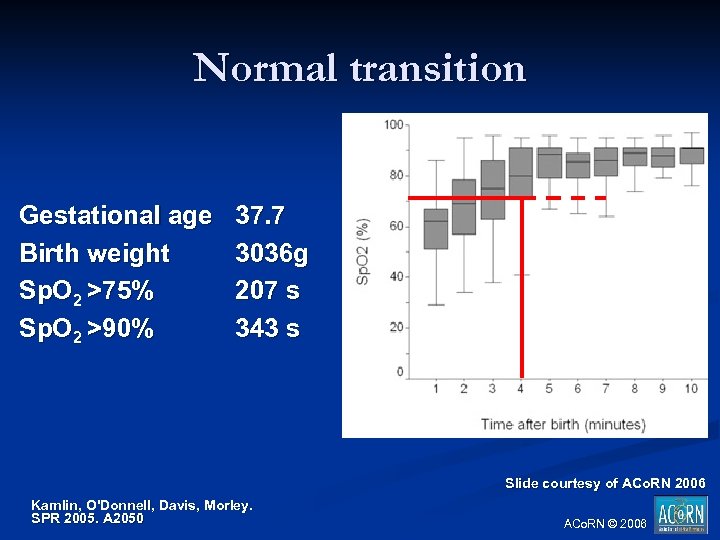 Normal transition Gestational age Birth weight Sp. O 2 >75% Sp. O 2 >90% 37. 7 3036 g 207 s 343 s . Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 Kamlin, O'Donnell, Davis, Morley. SPR 2005. A 2050 ACo. RN © 2006
Normal transition Gestational age Birth weight Sp. O 2 >75% Sp. O 2 >90% 37. 7 3036 g 207 s 343 s . Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 Kamlin, O'Donnell, Davis, Morley. SPR 2005. A 2050 ACo. RN © 2006
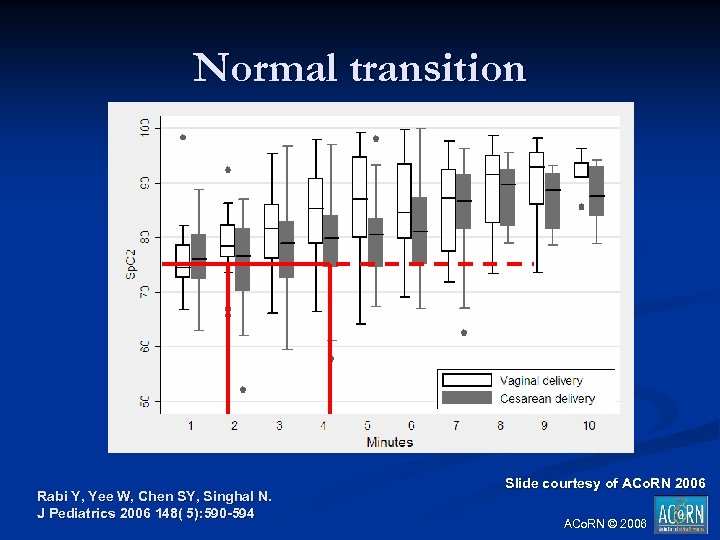 Normal transition Rabi Y, Yee W, Chen SY, Singhal N. J Pediatrics 2006 148( 5): 590 -594 Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 ACo. RN © 2006
Normal transition Rabi Y, Yee W, Chen SY, Singhal N. J Pediatrics 2006 148( 5): 590 -594 Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 ACo. RN © 2006
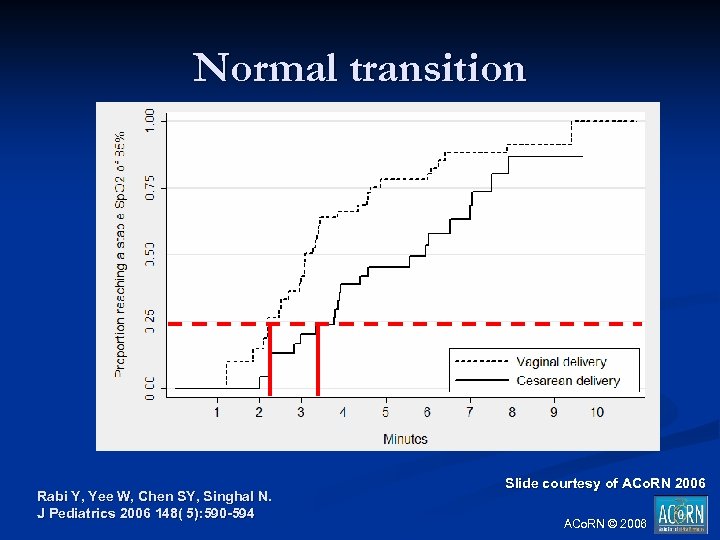 Normal transition Rabi Y, Yee W, Chen SY, Singhal N. J Pediatrics 2006 148( 5): 590 -594 Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 ACo. RN © 2006
Normal transition Rabi Y, Yee W, Chen SY, Singhal N. J Pediatrics 2006 148( 5): 590 -594 Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 ACo. RN © 2006
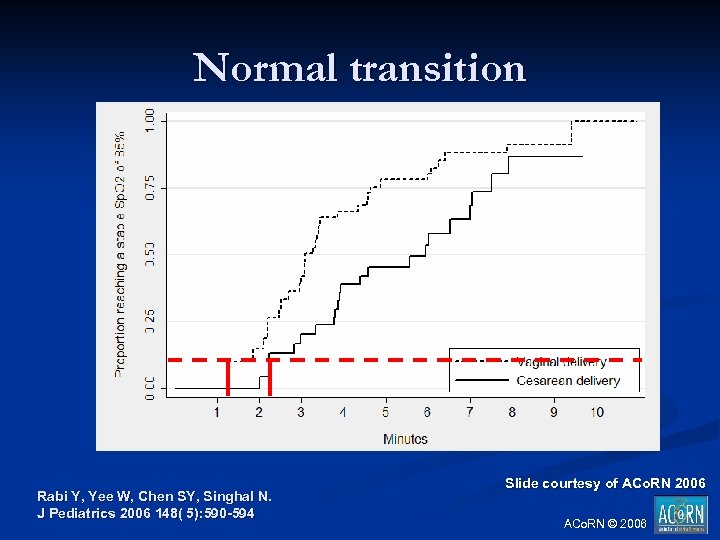 Normal transition Rabi Y, Yee W, Chen SY, Singhal N. J Pediatrics 2006 148( 5): 590 -594 Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 ACo. RN © 2006
Normal transition Rabi Y, Yee W, Chen SY, Singhal N. J Pediatrics 2006 148( 5): 590 -594 Slide courtesy of ACo. RN 2006 ACo. RN © 2006
 Canadian Expert Committee n “Oxygen should be administered to babies who remain cyanotic at 90 seconds of age”
Canadian Expert Committee n “Oxygen should be administered to babies who remain cyanotic at 90 seconds of age”
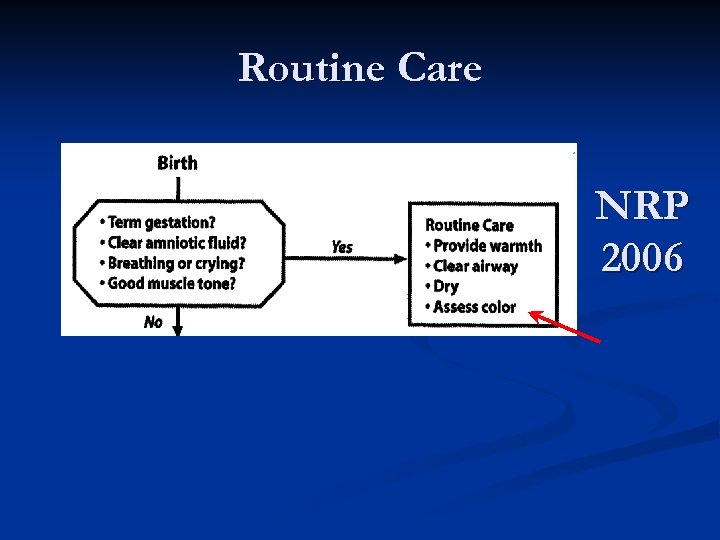 Routine Care NRP 2006
Routine Care NRP 2006
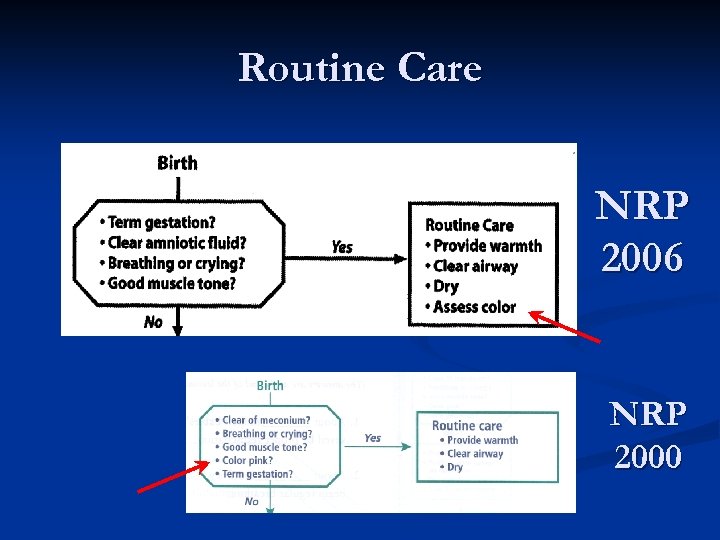 Routine Care NRP 2006 NRP 2000
Routine Care NRP 2006 NRP 2000
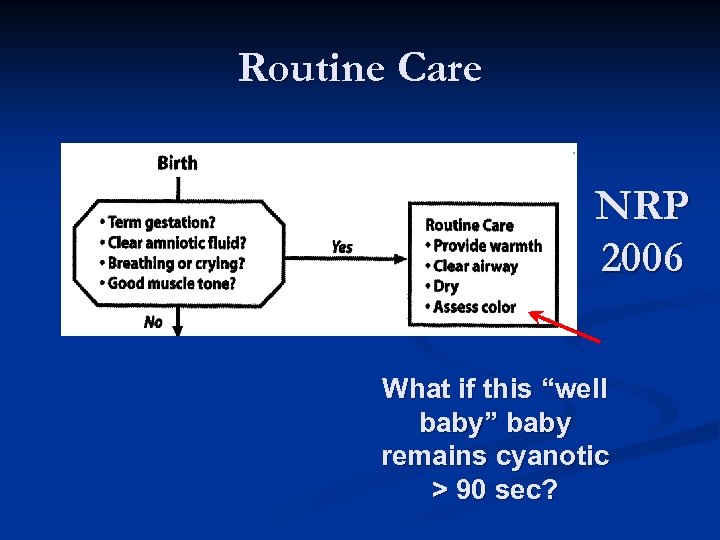 Routine Care NRP 2006 What if this “well baby” baby remains cyanotic > 90 sec?
Routine Care NRP 2006 What if this “well baby” baby remains cyanotic > 90 sec?
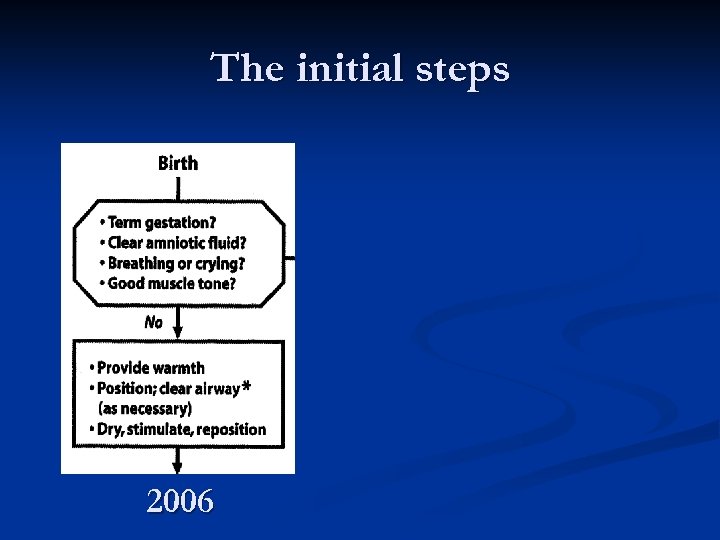 The initial steps 2006
The initial steps 2006
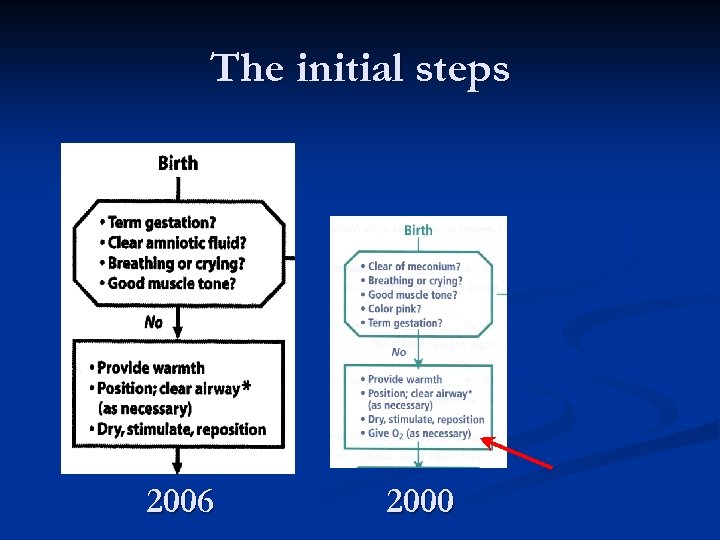 The initial steps 2006 2000
The initial steps 2006 2000
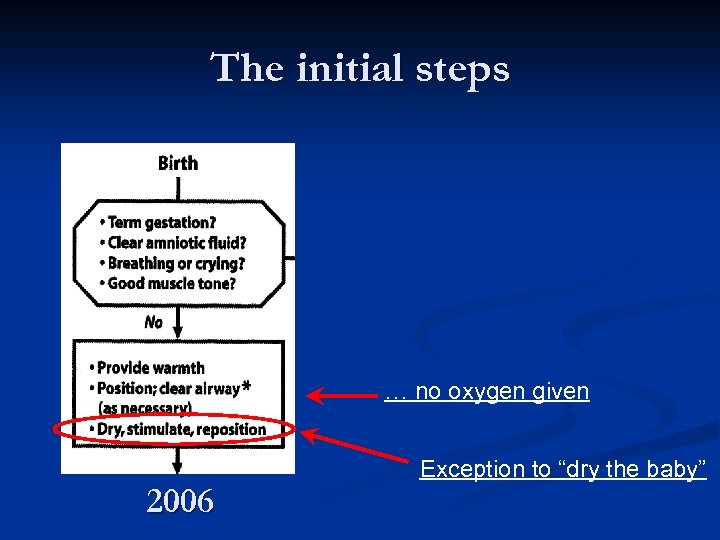 The initial steps … no oxygen given 2006 Exception to “dry the baby”
The initial steps … no oxygen given 2006 Exception to “dry the baby”
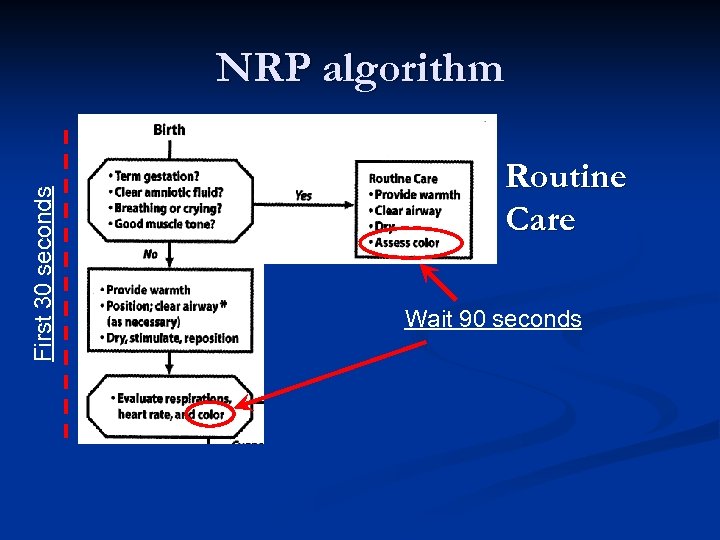 First 30 seconds NRP algorithm Routine Care Wait 90 seconds
First 30 seconds NRP algorithm Routine Care Wait 90 seconds
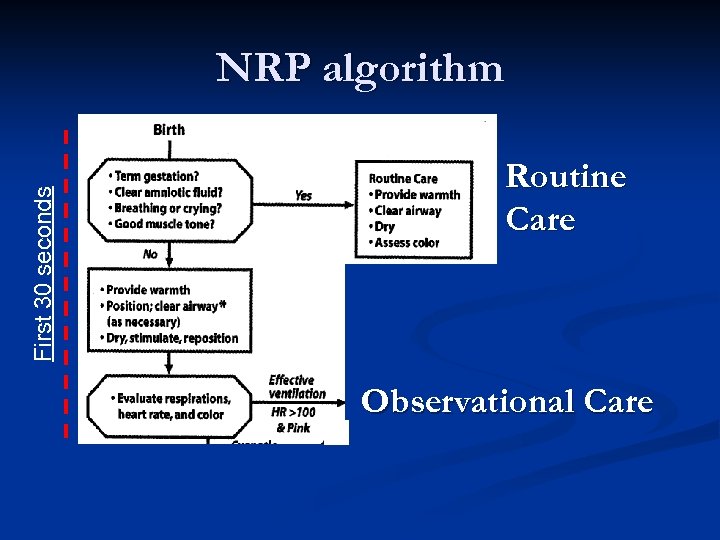 First 30 seconds NRP algorithm Routine Care Observational Care
First 30 seconds NRP algorithm Routine Care Observational Care
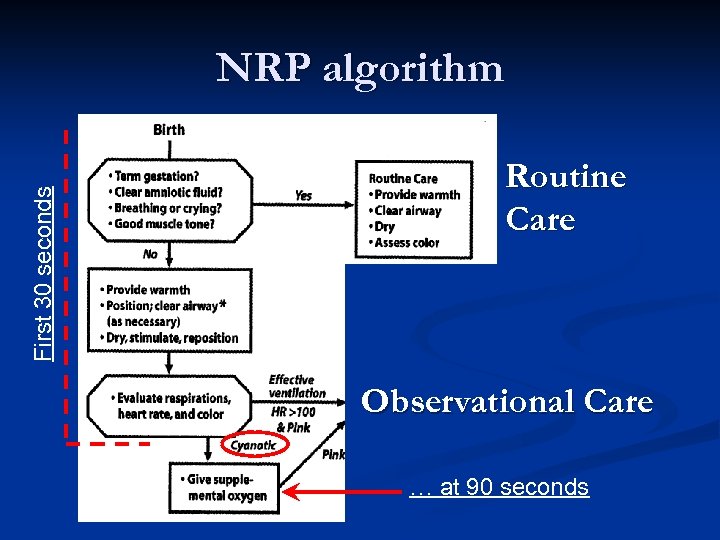 First 30 seconds NRP algorithm Routine Care Observational Care … at 90 seconds
First 30 seconds NRP algorithm Routine Care Observational Care … at 90 seconds
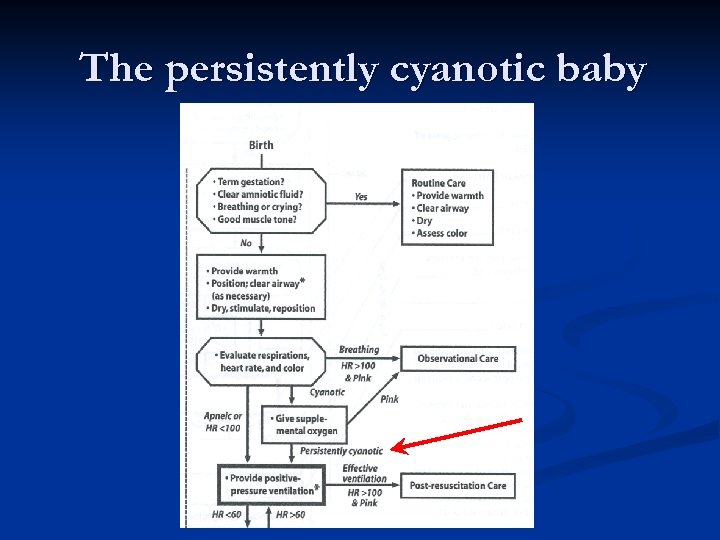 The persistently cyanotic baby
The persistently cyanotic baby
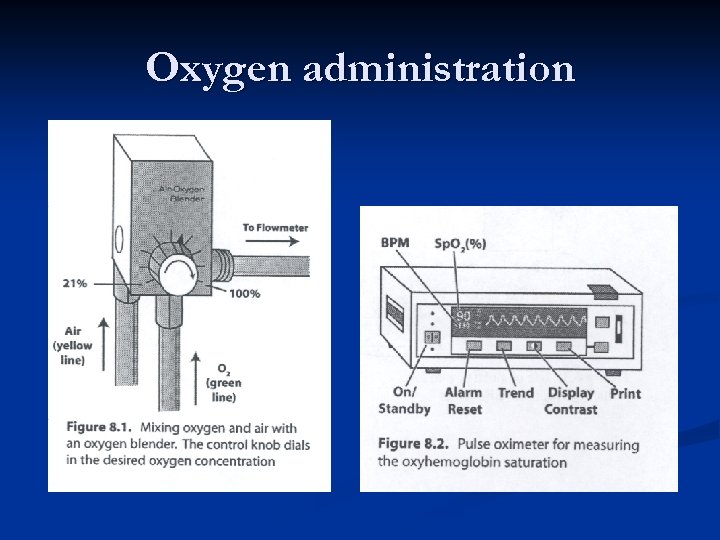
 Oxygen administration n n Only central cyanosis requires intervention. Acrocyanosis does not indicate hypoxemia. “If the baby is breathing but appears blue, administration of supplemental oxygen is indicated” at 90 seconds… “Supplemental oxygen also may be needed when respirations are being assisted” at 90 seconds… “There is evidence that resuscitation with air is as effective as with 100% oxygen …”
Oxygen administration n n Only central cyanosis requires intervention. Acrocyanosis does not indicate hypoxemia. “If the baby is breathing but appears blue, administration of supplemental oxygen is indicated” at 90 seconds… “Supplemental oxygen also may be needed when respirations are being assisted” at 90 seconds… “There is evidence that resuscitation with air is as effective as with 100% oxygen …”
 Oxygen administration
Oxygen administration
 Blending oxygen
Blending oxygen
 Blending oxygen
Blending oxygen
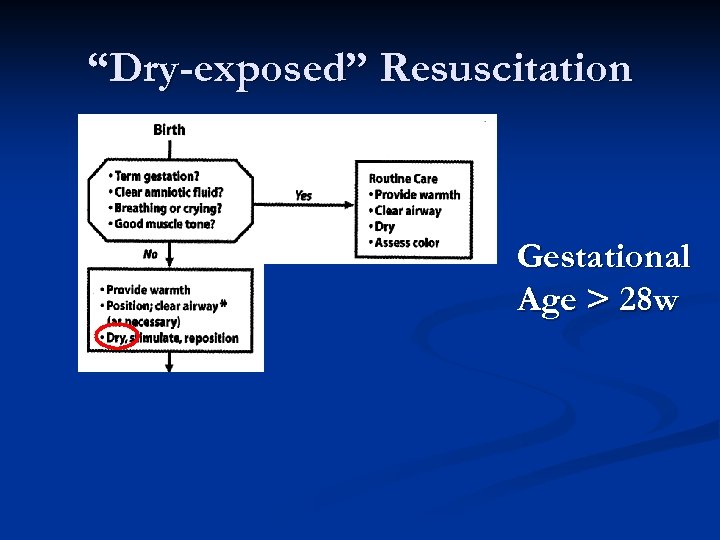 “Dry-exposed” Resuscitation Gestational Age > 28 w
“Dry-exposed” Resuscitation Gestational Age > 28 w
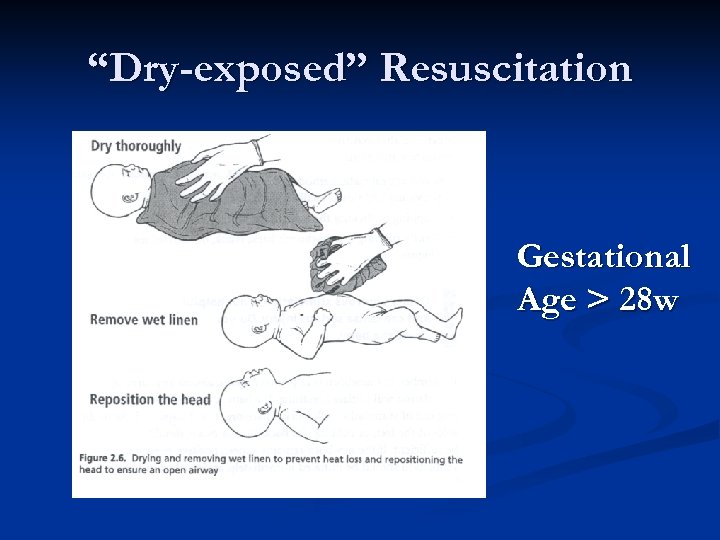 “Dry-exposed” Resuscitation Gestational Age > 28 w
“Dry-exposed” Resuscitation Gestational Age > 28 w
 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
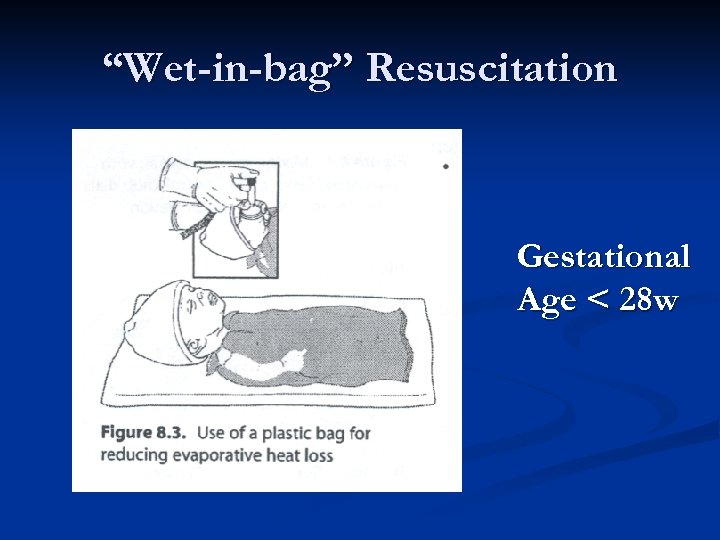 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
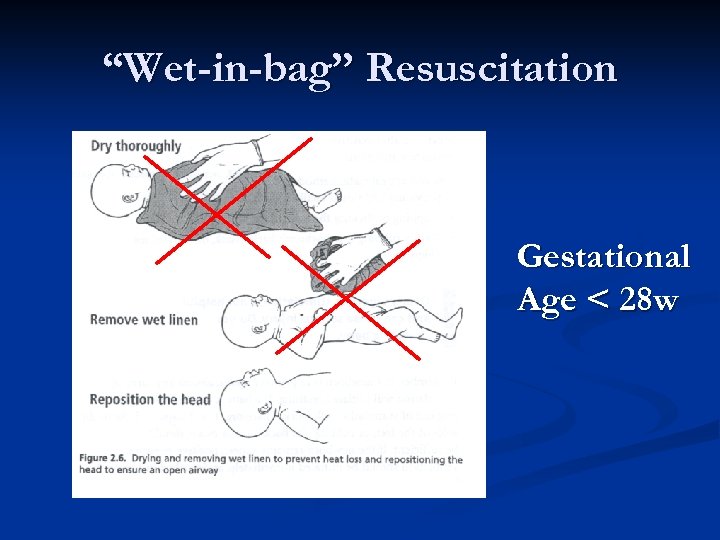 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation Gestational Age < 28 w
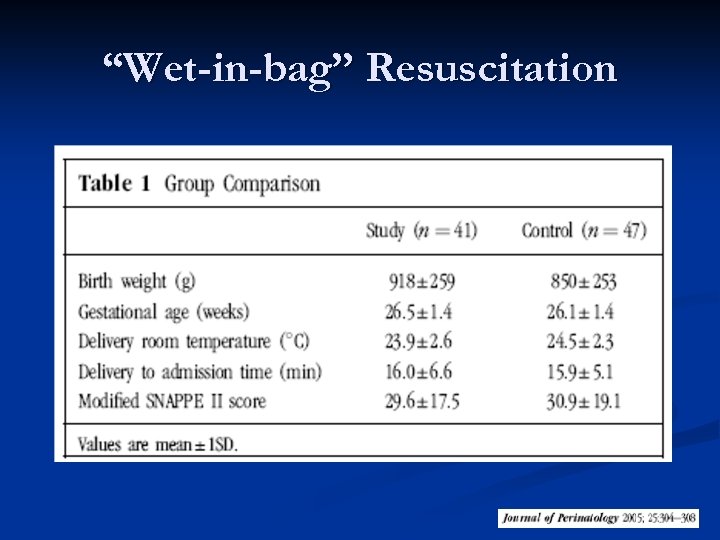
 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation n n 88 infants Infants placed in the polyurethane bags were less likely to have a temp <36. 40 C on admission 44 vs. 70% (p<0. 001) Better if room at 25 -26 o. C Gestational Age ≤ 28 w Knobel et al. Heat loss prevention for preterm infants in the delivery room. J Perinat 2005; 25: 304 -308
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation n n 88 infants Infants placed in the polyurethane bags were less likely to have a temp <36. 40 C on admission 44 vs. 70% (p<0. 001) Better if room at 25 -26 o. C Gestational Age ≤ 28 w Knobel et al. Heat loss prevention for preterm infants in the delivery room. J Perinat 2005; 25: 304 -308
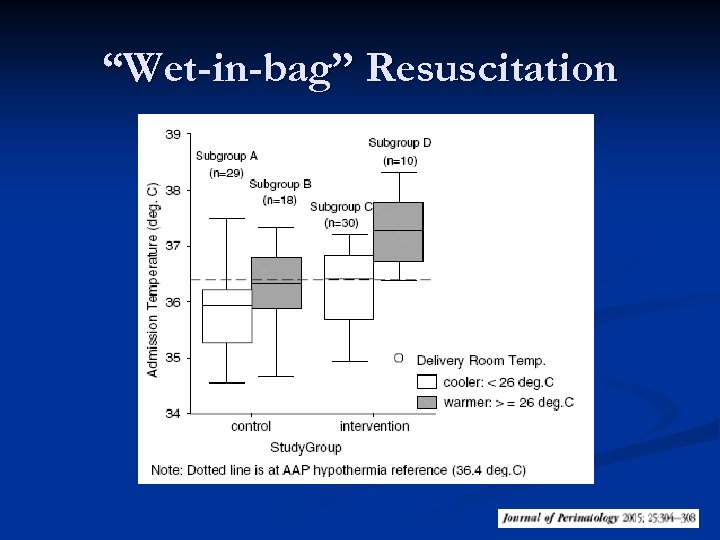 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation
 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation
 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation n Polyethylene bags significantly reduce the risk of hypothermia in infants <28 weeks on admission to NICU n RR 0. 63 (C. I. 0. 42 -0. 93) NNT 4 n
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation n Polyethylene bags significantly reduce the risk of hypothermia in infants <28 weeks on admission to NICU n RR 0. 63 (C. I. 0. 42 -0. 93) NNT 4 n
 “Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation CPS n n n Maintenance of DR at 25 to 26 o. C will diminish heat loss If GA < 28 w place him below the neck in a polyethylene bag All babies (term/preterm) under radiant warmer by 10 min should have servocontrol probe Gestational Age < 28 w
“Wet-in-bag” Resuscitation CPS n n n Maintenance of DR at 25 to 26 o. C will diminish heat loss If GA < 28 w place him below the neck in a polyethylene bag All babies (term/preterm) under radiant warmer by 10 min should have servocontrol probe Gestational Age < 28 w
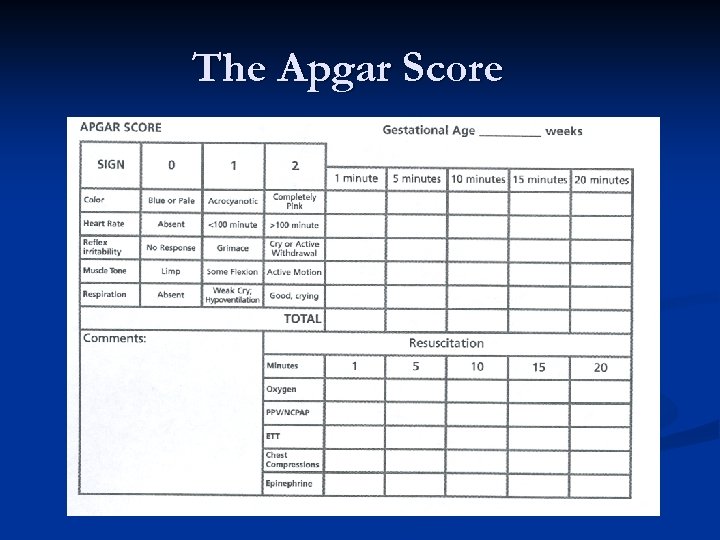 The Apgar Score
The Apgar Score
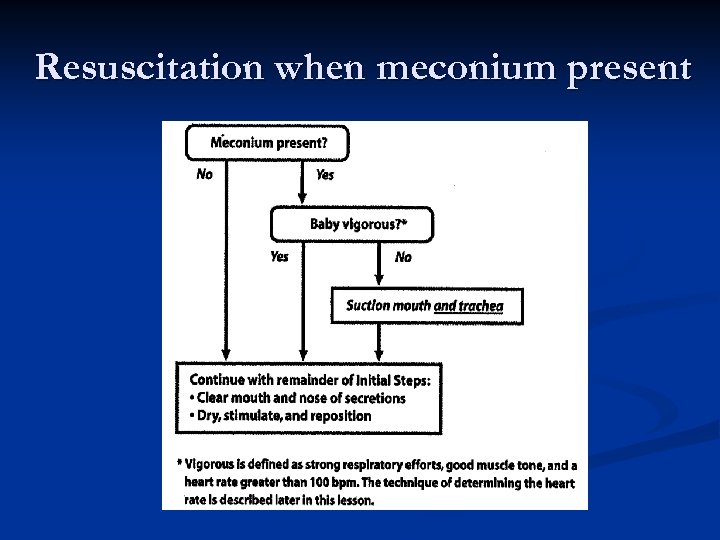 Resuscitation when meconium present
Resuscitation when meconium present
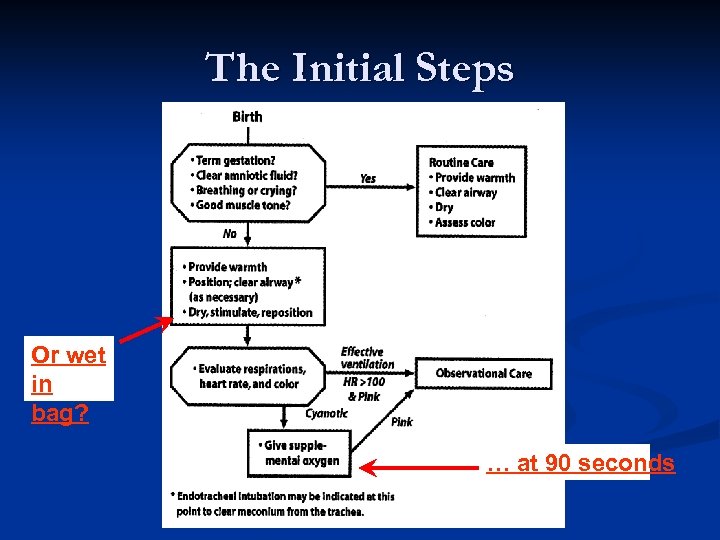 The Initial Steps Or wet in bag? … at 90 seconds
The Initial Steps Or wet in bag? … at 90 seconds
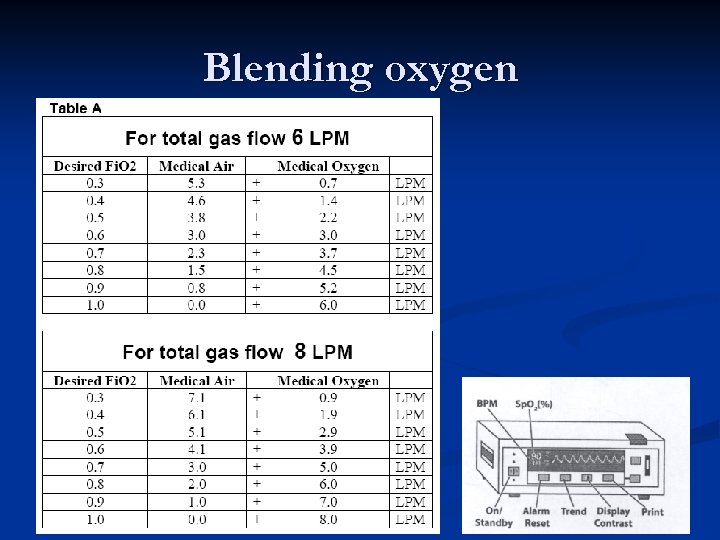
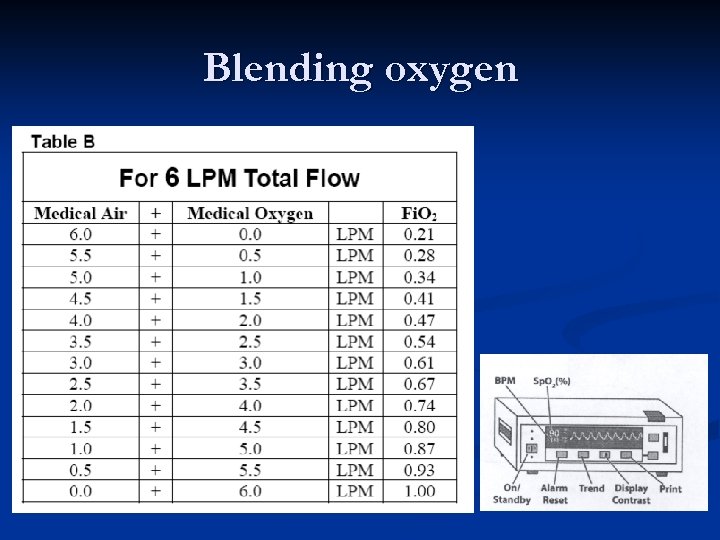
 Preterm < 32 weeks n n Use blended oxygen and air, and a pulse oximeter Begin PPV with Fi. O 2 between 0. 21 and 1. 00. Studies are lacking to be more precise. Adjust Fi. O 2 to achieve Sp. O 2 gradually increasing towards 90%. Decrease the Fi. O 2 as Sp. O 2 rises over 95% If the heart rate does not respond by increasing rapidly to > 100 bpm, correct any ventilation problem and use Fi. O 2 1. 00.
Preterm < 32 weeks n n Use blended oxygen and air, and a pulse oximeter Begin PPV with Fi. O 2 between 0. 21 and 1. 00. Studies are lacking to be more precise. Adjust Fi. O 2 to achieve Sp. O 2 gradually increasing towards 90%. Decrease the Fi. O 2 as Sp. O 2 rises over 95% If the heart rate does not respond by increasing rapidly to > 100 bpm, correct any ventilation problem and use Fi. O 2 1. 00.
 n Should oxygen be administered to babies receiving chest compressions?
n Should oxygen be administered to babies receiving chest compressions?

 Medications NRP 2006 St. John’s - Newfoundland
Medications NRP 2006 St. John’s - Newfoundland
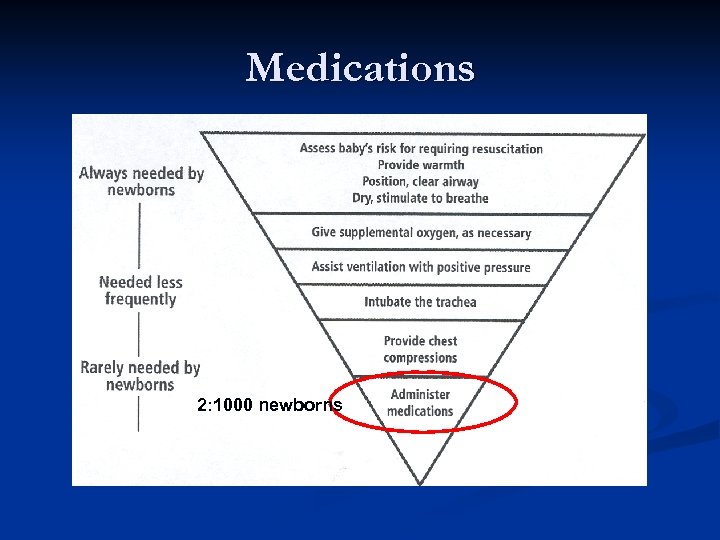 Medications 2: 1000 newborns
Medications 2: 1000 newborns
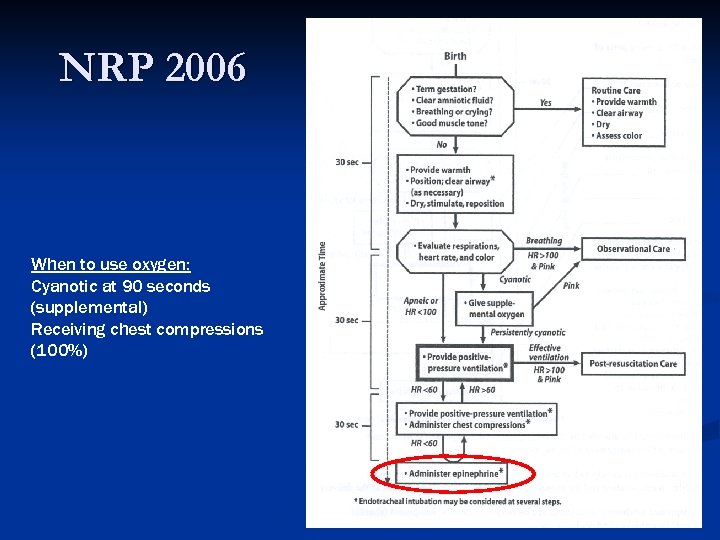 NRP 2006 When to use oxygen: Cyanotic at 90 seconds (supplemental) Receiving chest compressions (100%)
NRP 2006 When to use oxygen: Cyanotic at 90 seconds (supplemental) Receiving chest compressions (100%)
 Epinephrine ! “If the heart rate remains below 60 bpm despite administration of ventilation and chest compressions your first action is to ensure that ventilation and chest compressions are being given optimally and that you are using 100% oxygen”
Epinephrine ! “If the heart rate remains below 60 bpm despite administration of ventilation and chest compressions your first action is to ensure that ventilation and chest compressions are being given optimally and that you are using 100% oxygen”
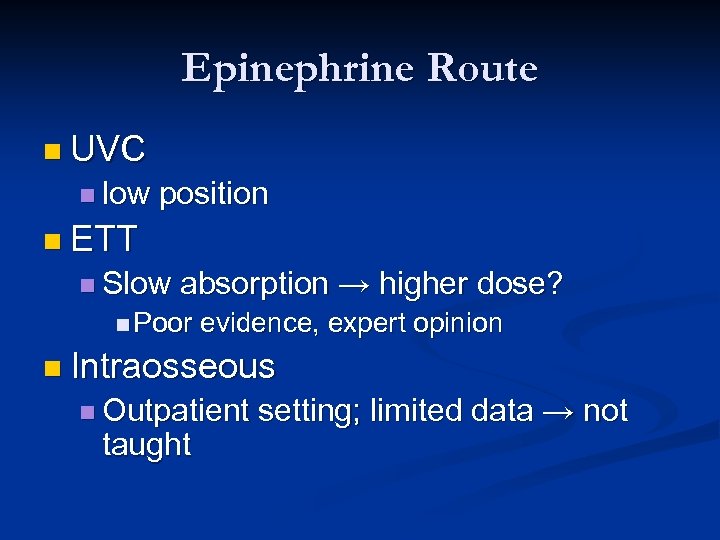 Epinephrine Route n UVC n low position n ETT n Slow absorption → higher dose? n Poor evidence, expert opinion n Intraosseous n Outpatient taught setting; limited data → not
Epinephrine Route n UVC n low position n ETT n Slow absorption → higher dose? n Poor evidence, expert opinion n Intraosseous n Outpatient taught setting; limited data → not
 Epinephrine - Administration CPS: n “First dose via ETT while preparing for insertion of UVC” 3 m. L syringe n 1 m. L/kg of 1: 10, 000 epinephrine n n “When given via UVC …” 1 m. L syringe n 0. 1 m. L/kg of 1: 10, 000 epinephrine n Follow with 5 m. L of 0. 9& saline flush n
Epinephrine - Administration CPS: n “First dose via ETT while preparing for insertion of UVC” 3 m. L syringe n 1 m. L/kg of 1: 10, 000 epinephrine n n “When given via UVC …” 1 m. L syringe n 0. 1 m. L/kg of 1: 10, 000 epinephrine n Follow with 5 m. L of 0. 9& saline flush n
 Epinephrine Administration Shows recommendation in CPS NRP addendum, 2006
Epinephrine Administration Shows recommendation in CPS NRP addendum, 2006
 Epinephrine Administration Can repeat after 3 -5 minutes
Epinephrine Administration Can repeat after 3 -5 minutes
 Shock / hypovolemia ! “If the baby appears in shock and is not responding to resuscitation administration of a volume expander may be indicated”
Shock / hypovolemia ! “If the baby appears in shock and is not responding to resuscitation administration of a volume expander may be indicated”
 If no improvement
If no improvement



