4773b3a13a01988aa8cc2a3e165f03da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 THE NEW CAREER TECH ED Using Career Clusters/Pathways to help ALL students achieve success
THE NEW CAREER TECH ED Using Career Clusters/Pathways to help ALL students achieve success
 Essential Questions Why are we getting involved in using career clusters, career pathways, and programs of study to increase rigor and relevance, and how to we do it?
Essential Questions Why are we getting involved in using career clusters, career pathways, and programs of study to increase rigor and relevance, and how to we do it?
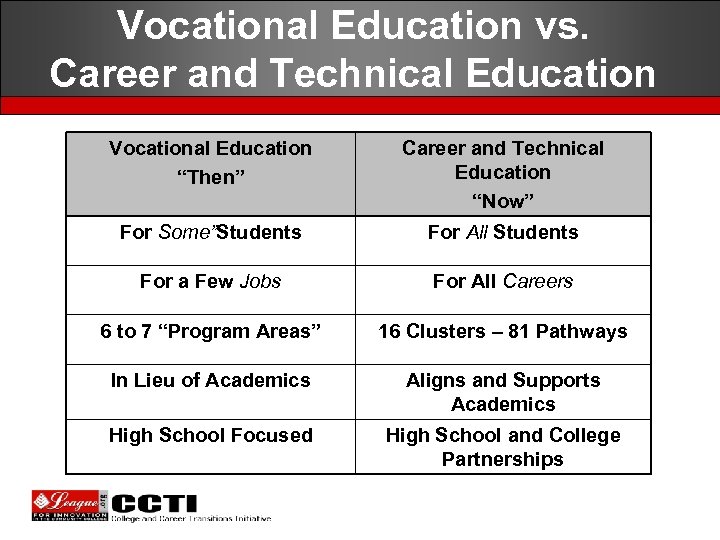 Vocational Education vs. Career and Technical Education Vocational Education “Then” Career and Technical Education “Now” For Some”Students For All Students For a Few Jobs For All Careers 6 to 7 “Program Areas” 16 Clusters – 81 Pathways In Lieu of Academics Aligns and Supports Academics High School Focused High School and College Partnerships
Vocational Education vs. Career and Technical Education Vocational Education “Then” Career and Technical Education “Now” For Some”Students For All Students For a Few Jobs For All Careers 6 to 7 “Program Areas” 16 Clusters – 81 Pathways In Lieu of Academics Aligns and Supports Academics High School Focused High School and College Partnerships
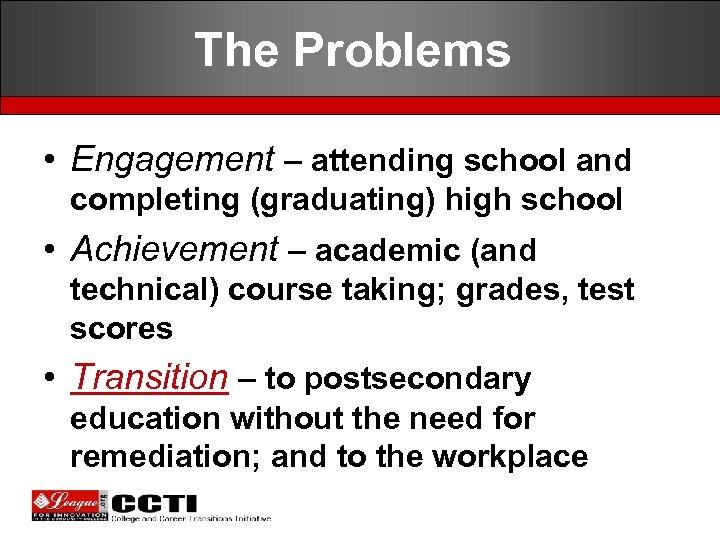 The Problems • Engagement – attending school and completing (graduating) high school • Achievement – academic (and technical) course taking; grades, test scores • Transition – to postsecondary education without the need for remediation; and to the workplace
The Problems • Engagement – attending school and completing (graduating) high school • Achievement – academic (and technical) course taking; grades, test scores • Transition – to postsecondary education without the need for remediation; and to the workplace
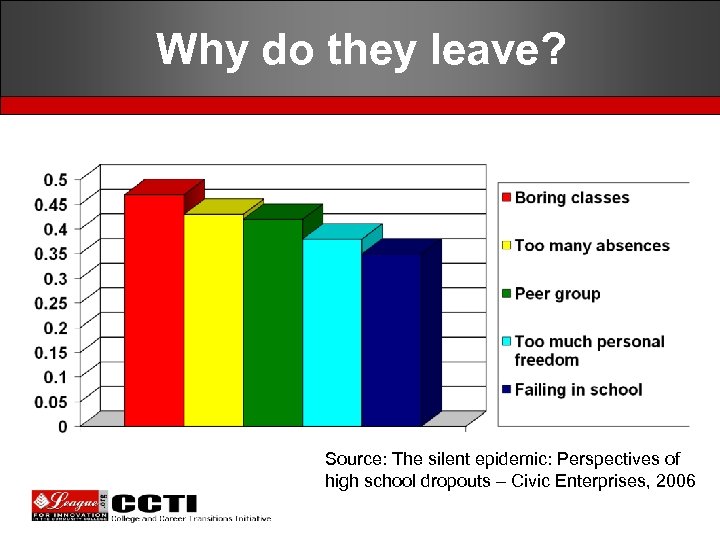 Why do they leave? Source: The silent epidemic: Perspectives of high school dropouts – Civic Enterprises, 2006
Why do they leave? Source: The silent epidemic: Perspectives of high school dropouts – Civic Enterprises, 2006
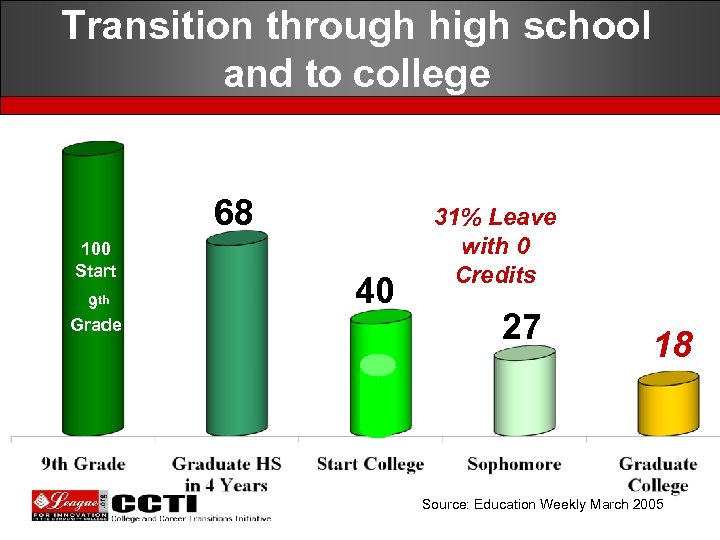 Transition through high school and to college 68 100 Start 9 th Grade 40 31% Leave with 0 Credits 27 18 Source: Education Weekly March 2005
Transition through high school and to college 68 100 Start 9 th Grade 40 31% Leave with 0 Credits 27 18 Source: Education Weekly March 2005
 Transition • 84% of high school students anticipate earning a college degree. • Students who anticipate a degree are unlikely to prepare for a career following high school. • More than 50% of students who begin college do not earn a degree. • For students with the lowest high school performance, 86% do not earn a degree. Rosenbaum, J. E. (2002). Beyond Empty Promises: Policies To Improve Transitions into College and Jobs. U. S. ; Illinois: 42.
Transition • 84% of high school students anticipate earning a college degree. • Students who anticipate a degree are unlikely to prepare for a career following high school. • More than 50% of students who begin college do not earn a degree. • For students with the lowest high school performance, 86% do not earn a degree. Rosenbaum, J. E. (2002). Beyond Empty Promises: Policies To Improve Transitions into College and Jobs. U. S. ; Illinois: 42.
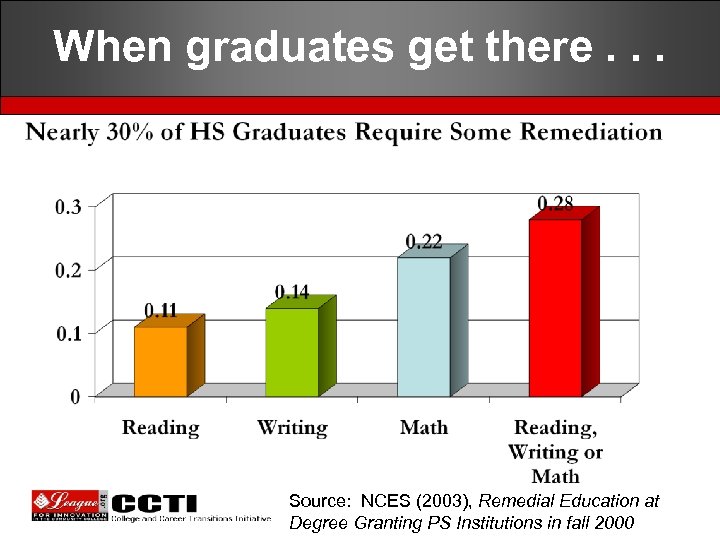 When graduates get there. . . Source: NCES (2003), Remedial Education at Degree Granting PS Institutions in fall 2000
When graduates get there. . . Source: NCES (2003), Remedial Education at Degree Granting PS Institutions in fall 2000
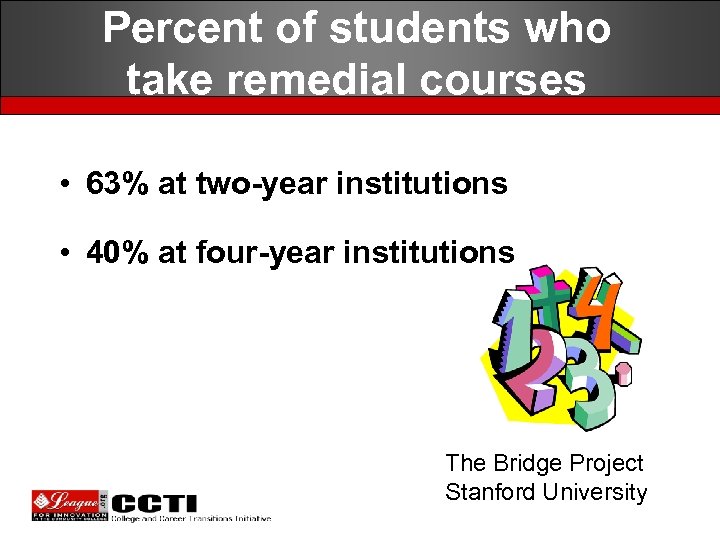 Percent of students who take remedial courses • 63% at two-year institutions • 40% at four-year institutions The Bridge Project Stanford University
Percent of students who take remedial courses • 63% at two-year institutions • 40% at four-year institutions The Bridge Project Stanford University
 Seeking Solutions for Student Success
Seeking Solutions for Student Success
 Career Clusters “An organizing tool defining CTE using 16 broad clusters of occupations and 81 pathways with validated standards that ensure opportunities for all students regardless of their career goals and interests. “
Career Clusters “An organizing tool defining CTE using 16 broad clusters of occupations and 81 pathways with validated standards that ensure opportunities for all students regardless of their career goals and interests. “
 Career Pathway “A career pathway is a coherent, articulated sequence of rigorous academic and career related courses, commencing in ninth grade and leading to an associate degree, and/or an industry-recognized certificate or licensure, and/or a baccalaureate and beyond. ”
Career Pathway “A career pathway is a coherent, articulated sequence of rigorous academic and career related courses, commencing in ninth grade and leading to an associate degree, and/or an industry-recognized certificate or licensure, and/or a baccalaureate and beyond. ”
 Perkins – “Programs of Study” “State approved programs, which may be adopted by local education agencies and postsecondary institutions to be offered as an option to students when planning for and completing future coursework, for career and technical content areas. ”
Perkins – “Programs of Study” “State approved programs, which may be adopted by local education agencies and postsecondary institutions to be offered as an option to students when planning for and completing future coursework, for career and technical content areas. ”
 Perkins – “Programs of Study” 1. Incorporate secondary education and postsecondary education elements;
Perkins – “Programs of Study” 1. Incorporate secondary education and postsecondary education elements;
 Perkins – “Programs of Study” 2. Include coherent and rigorous content aligned with challenging academic standards and relevant career and technical content in a coordinated, nonduplicative progression of courses that align secondary education with postsecondary education to adequately prepare students to succeed in postsecondary education;
Perkins – “Programs of Study” 2. Include coherent and rigorous content aligned with challenging academic standards and relevant career and technical content in a coordinated, nonduplicative progression of courses that align secondary education with postsecondary education to adequately prepare students to succeed in postsecondary education;
 Perkins – “Programs of Study” 3. May include the opportunity for secondary education students to participate in dual or concurrent enrollment programs or other ways to acquire postsecondary education credits; and
Perkins – “Programs of Study” 3. May include the opportunity for secondary education students to participate in dual or concurrent enrollment programs or other ways to acquire postsecondary education credits; and
 Perkins – “Programs of Study” 4. Lead to an industry-recognized credential or certificate at the postsecondary level, or an associate or baccalaureate degree.
Perkins – “Programs of Study” 4. Lead to an industry-recognized credential or certificate at the postsecondary level, or an associate or baccalaureate degree.
 16 Career Clusters
16 Career Clusters
 What are the Programs of Study? • A sequenced listing of courses, both academic and CTE/degree major, that connects student’s high school and postsecondary educational experiences
What are the Programs of Study? • A sequenced listing of courses, both academic and CTE/degree major, that connects student’s high school and postsecondary educational experiences
 www. careerclusters. org
www. careerclusters. org
 College and Career Transitions Initiative (CCTI) Cooperative Agreement between U. S. Department of Education Office of Vocational and Adult Education and The League for Innovation in the Community College Consortium
College and Career Transitions Initiative (CCTI) Cooperative Agreement between U. S. Department of Education Office of Vocational and Adult Education and The League for Innovation in the Community College Consortium
 Purpose of CCTI will contribute to strengthening the role of community and technical colleges in • Easing student transitions between secondary and postsecondary education as well as transitions to employment, and • Improving academic performance at both the secondary and postsecondary levels.
Purpose of CCTI will contribute to strengthening the role of community and technical colleges in • Easing student transitions between secondary and postsecondary education as well as transitions to employment, and • Improving academic performance at both the secondary and postsecondary levels.
 CCTI Outcomes 1. Decrease remediation at the postsecondary level. 2. Increase enrollment and persistence in postsecondary education. 3. Increase academic and skill achievement at both the secondary and postsecondary levels.
CCTI Outcomes 1. Decrease remediation at the postsecondary level. 2. Increase enrollment and persistence in postsecondary education. 3. Increase academic and skill achievement at both the secondary and postsecondary levels.
 CCTI Outcomes 4. Increase attainment of postsecondary degrees, certificates, or other recognized credentials. 5. Increase successful entry into employment or further education.
CCTI Outcomes 4. Increase attainment of postsecondary degrees, certificates, or other recognized credentials. 5. Increase successful entry into employment or further education.
 CCTI Site Partnerships • Education & Training î Anne Arundel Community College (MD) î Lorain County Community College (OH) î Maricopa Community Colleges (AZ) • Health Science î Ivy Tech Community College (IN) î Miami Dade College (FL) î Northern Virginia Community College (VA) • Information Technology î Central Piedmont Community College (NC) î Corning Community College (NY) î Southwestern Oregon Community College (OR)
CCTI Site Partnerships • Education & Training î Anne Arundel Community College (MD) î Lorain County Community College (OH) î Maricopa Community Colleges (AZ) • Health Science î Ivy Tech Community College (IN) î Miami Dade College (FL) î Northern Virginia Community College (VA) • Information Technology î Central Piedmont Community College (NC) î Corning Community College (NY) î Southwestern Oregon Community College (OR)
 CCTI Site Partnerships • Law, Public Safety and Security î Fox Valley Technical College (WI) î Prince George’s Community College (MD) î San Diego Community College District (CA) • Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics î Lehigh Carbon Community College (PA) î Sinclair Community College (OH) î St. Louis Community College (MO)
CCTI Site Partnerships • Law, Public Safety and Security î Fox Valley Technical College (WI) î Prince George’s Community College (MD) î San Diego Community College District (CA) • Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics î Lehigh Carbon Community College (PA) î Sinclair Community College (OH) î St. Louis Community College (MO)
 CCTI Website www. league. org/ccti
CCTI Website www. league. org/ccti
 Toolkit • Career Pathways • Implementation Strategies • Lessons Learned • Improvement Plan • Case Studies
Toolkit • Career Pathways • Implementation Strategies • Lessons Learned • Improvement Plan • Case Studies
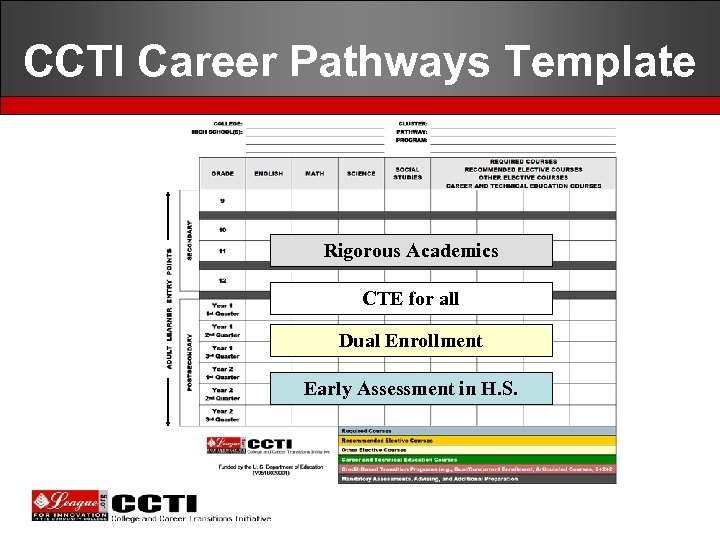 CCTI Career Pathways Template Rigorous Academics CTE for all Dual Enrollment Early Assessment in H. S.
CCTI Career Pathways Template Rigorous Academics CTE for all Dual Enrollment Early Assessment in H. S.
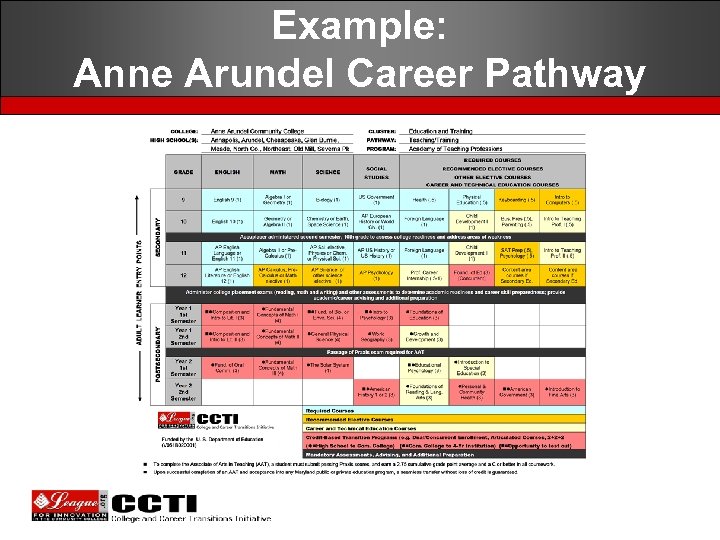 Example: Anne Arundel Career Pathway
Example: Anne Arundel Career Pathway
 Example: Maricopa Career Pathway
Example: Maricopa Career Pathway
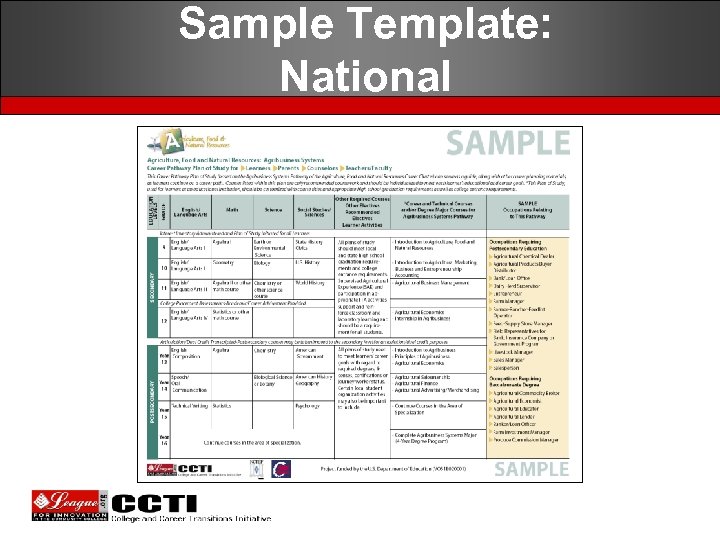 Sample Template: National
Sample Template: National
 CCTI … Is It Working? The Numbers …
CCTI … Is It Working? The Numbers …
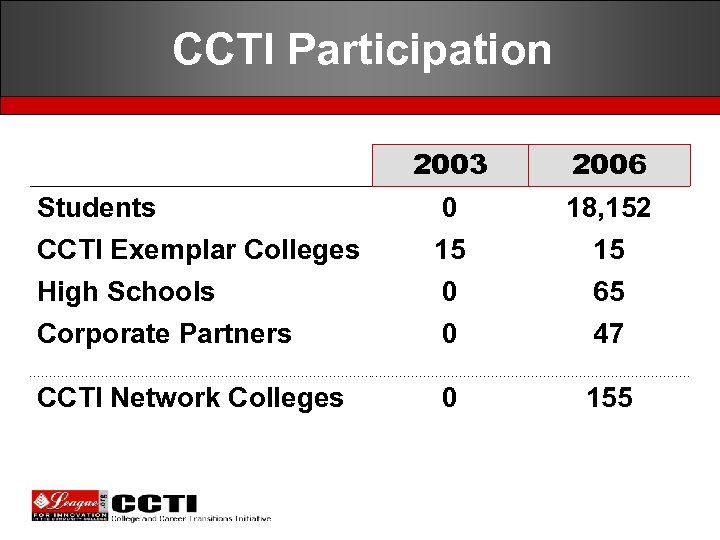 CCTI Participation 2003 2006 Students CCTI Exemplar Colleges 0 15 18, 152 15 High Schools Corporate Partners 0 0 65 47 CCTI Network Colleges 0 155
CCTI Participation 2003 2006 Students CCTI Exemplar Colleges 0 15 18, 152 15 High Schools Corporate Partners 0 0 65 47 CCTI Network Colleges 0 155
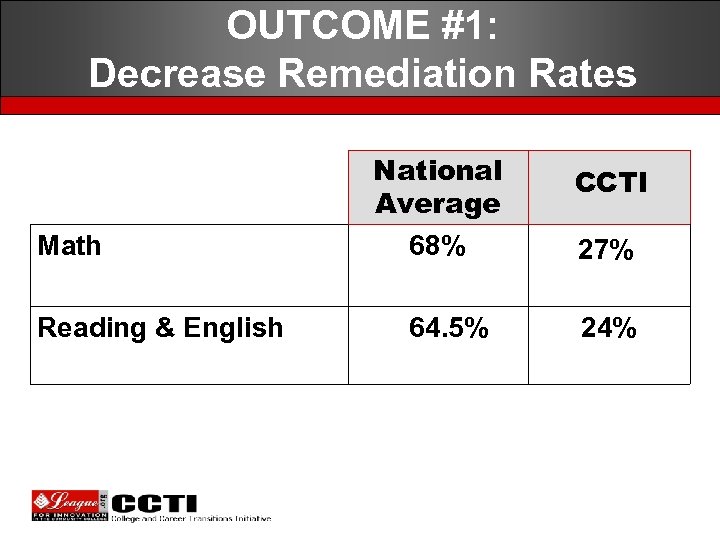 OUTCOME #1: Decrease Remediation Rates Math Reading & English National Average 68% 64. 5% CCTI 27% 24%
OUTCOME #1: Decrease Remediation Rates Math Reading & English National Average 68% 64. 5% CCTI 27% 24%
 OUTCOME #2: Increase Enrollment/Persistence Entrance to postsecondary education rate Persistence National Average 14% CCTI 54% 71% 29%
OUTCOME #2: Increase Enrollment/Persistence Entrance to postsecondary education rate Persistence National Average 14% CCTI 54% 71% 29%
 What We Have Learned • Community Colleges can lead this work. • Partners are anxious to work together. • Communication is key: – Generally among education sectors and business – Between faculty of high school and college • Postsecondary remediation can be reduced. • Enrollment persistence can be increased. • Transformation needs to take place in the context of a P-20 or lifetime framework.
What We Have Learned • Community Colleges can lead this work. • Partners are anxious to work together. • Communication is key: – Generally among education sectors and business – Between faculty of high school and college • Postsecondary remediation can be reduced. • Enrollment persistence can be increased. • Transformation needs to take place in the context of a P-20 or lifetime framework.
 The Most Important Aspects of Plans/Programs of Study • Cluster Foundation Knowledge and Skills • Career Pathway Knowledge and Skills
The Most Important Aspects of Plans/Programs of Study • Cluster Foundation Knowledge and Skills • Career Pathway Knowledge and Skills
 POS Checklist þ Are both academic and degree major courses included? þ Are both secondary and postsecondary courses included? þ Does coursework reflect the K & S? þ Do courses represent a sequence of instruction that leads to a degree, certificate or credential?
POS Checklist þ Are both academic and degree major courses included? þ Are both secondary and postsecondary courses included? þ Does coursework reflect the K & S? þ Do courses represent a sequence of instruction that leads to a degree, certificate or credential?
 POS Checklist (continued) þ Do courses represent a coherent and rigorous program of studies? þ Have courses been cross-referenced against state and national standards? þ Does completion of the high school courses ensure success at the postsecondary level? þ Does the high school plan reflect opportunities for postsecondary enrollment?
POS Checklist (continued) þ Do courses represent a coherent and rigorous program of studies? þ Have courses been cross-referenced against state and national standards? þ Does completion of the high school courses ensure success at the postsecondary level? þ Does the high school plan reflect opportunities for postsecondary enrollment?
 Implementation of the pathways provides: • Consistency for better data (results) and shared opportunities for development • Articulation within and between states • Employer and postsecondary validated standards • Opportunities for “all” students • A “place” for all career goals and interests
Implementation of the pathways provides: • Consistency for better data (results) and shared opportunities for development • Articulation within and between states • Employer and postsecondary validated standards • Opportunities for “all” students • A “place” for all career goals and interests
 Critical Components for Cluster/Pathway Implementation • • Administrative Support Shared Planning Career Development Professional Development Standards-Based Curriculum Parent and Community Support Education Partnerships B&I Partnerships
Critical Components for Cluster/Pathway Implementation • • Administrative Support Shared Planning Career Development Professional Development Standards-Based Curriculum Parent and Community Support Education Partnerships B&I Partnerships
 Critical Components for Cluster/Pathway Implementation • • • Multi-Measure Assessment Inter-Disciplinary Teams Flexible Schedules Integrated Curriculum Creative & Innovative Teaching Strategies • Workplace Learning • Student Centered Learning
Critical Components for Cluster/Pathway Implementation • • • Multi-Measure Assessment Inter-Disciplinary Teams Flexible Schedules Integrated Curriculum Creative & Innovative Teaching Strategies • Workplace Learning • Student Centered Learning
 Cluster/Pathway Approach to Addressing Educational Redesign • Strategy to organize instruction and student experiences around career themes (Focus on an industry cluster of related occupations) • Incorporates existing school reform strategies (career academies, career pathways, small learning communities, Tech Prep) • Connects to business and higher education
Cluster/Pathway Approach to Addressing Educational Redesign • Strategy to organize instruction and student experiences around career themes (Focus on an industry cluster of related occupations) • Incorporates existing school reform strategies (career academies, career pathways, small learning communities, Tech Prep) • Connects to business and higher education
 Laurance J. Warford CCTI Project Director warford@league. org www. league. org/ccti
Laurance J. Warford CCTI Project Director warford@league. org www. league. org/ccti


