212692218179a3bf9b7f238dcc1f339b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 The Navy has gone full-speed ahead in adapting knowledge practices and processes. There is no company in the world anywhere near it in scope, ” “And it’s a very balanced endeavor. They are talking about people, technology and social relationships that make things work. ” - Larry Prusak, executive director of IBM’s Institute for Knowledge Management in Cambridge, Mass. Building the Knowledge Enterprise Mrs. Karen T. Danis Enterprise Knowledge Management June 2001
The Navy has gone full-speed ahead in adapting knowledge practices and processes. There is no company in the world anywhere near it in scope, ” “And it’s a very balanced endeavor. They are talking about people, technology and social relationships that make things work. ” - Larry Prusak, executive director of IBM’s Institute for Knowledge Management in Cambridge, Mass. Building the Knowledge Enterprise Mrs. Karen T. Danis Enterprise Knowledge Management June 2001
 Briefing Objectives § Provide an overview… – What is Knowledge Management – How we perform Knowledge Management (processes and tools) – Examples of Knowledge Management in the DON § Lay a foundation for partnering, collaboration, and knowledge sharing
Briefing Objectives § Provide an overview… – What is Knowledge Management – How we perform Knowledge Management (processes and tools) – Examples of Knowledge Management in the DON § Lay a foundation for partnering, collaboration, and knowledge sharing
 Today’s Navy – Supporting our National Military Strategy • Mobility & Adaptability • Versatility of Power / Scalability • Presence & Visibility • Cooperative & Independent Capabilities Addressing evolving national security challenges – regional conflicts, peacekeeping, terrorism, & nontraditional asymmetric threats
Today’s Navy – Supporting our National Military Strategy • Mobility & Adaptability • Versatility of Power / Scalability • Presence & Visibility • Cooperative & Independent Capabilities Addressing evolving national security challenges – regional conflicts, peacekeeping, terrorism, & nontraditional asymmetric threats
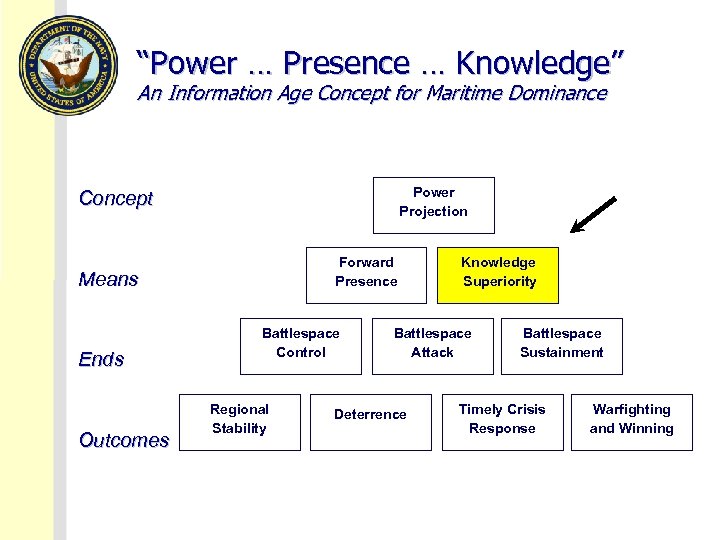 “Power … Presence … Knowledge” An Information Age Concept for Maritime Dominance Power Projection Concept Forward Presence Means Ends Outcomes Battlespace Control Regional Stability Knowledge Superiority Battlespace Attack Deterrence Battlespace Sustainment Timely Crisis Response Warfighting and Winning
“Power … Presence … Knowledge” An Information Age Concept for Maritime Dominance Power Projection Concept Forward Presence Means Ends Outcomes Battlespace Control Regional Stability Knowledge Superiority Battlespace Attack Deterrence Battlespace Sustainment Timely Crisis Response Warfighting and Winning
 The DON Maritime Concept § Real-time shared understanding of battlespace § Rapid synchronization of actions § Mitigates the fog of war E NC SE RE P RD WA OR F Y RIT IO ER P SU GE ED L OW KN GLOBAL POWER PROJECTION “Our Navy will be alive with the fire of shared understanding. ” - KS Project Vision
The DON Maritime Concept § Real-time shared understanding of battlespace § Rapid synchronization of actions § Mitigates the fog of war E NC SE RE P RD WA OR F Y RIT IO ER P SU GE ED L OW KN GLOBAL POWER PROJECTION “Our Navy will be alive with the fire of shared understanding. ” - KS Project Vision
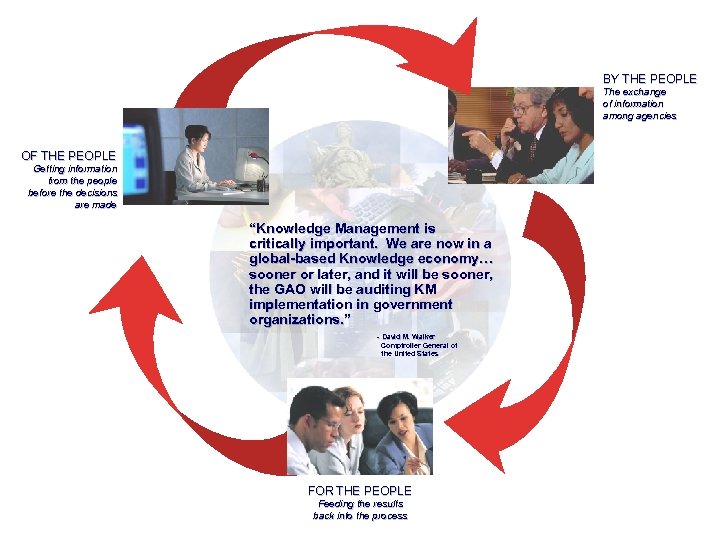 BY THE PEOPLE The exchange of information among agencies OF THE PEOPLE Getting information from the people before the decisions are made “Knowledge Management is critically important. We are now in a global-based Knowledge economy… sooner or later, and it will be sooner, the GAO will be auditing KM implementation in government organizations. ” - David M. Walker Comptroller General of the United States FOR THE PEOPLE Feeding the results back into the process
BY THE PEOPLE The exchange of information among agencies OF THE PEOPLE Getting information from the people before the decisions are made “Knowledge Management is critically important. We are now in a global-based Knowledge economy… sooner or later, and it will be sooner, the GAO will be auditing KM implementation in government organizations. ” - David M. Walker Comptroller General of the United States FOR THE PEOPLE Feeding the results back into the process
 The World is Changing. . . DON IM/IT Environment HISTORICAL Stable Learned Obtrusive technology Presence Activity People support technology Stovepipe mentality Crisis-driven Computation Hardware focus Localized Information chaos Control Standardization Isolated Solutions FUTURE Flexible Learning Invisible technology Virtual Performance Technology supporting people Integrative competency Strategy-driven Communication Client utility focus Ubiquitous Knowledge Centric Point of Action empowerment Open Standards Interoperability
The World is Changing. . . DON IM/IT Environment HISTORICAL Stable Learned Obtrusive technology Presence Activity People support technology Stovepipe mentality Crisis-driven Computation Hardware focus Localized Information chaos Control Standardization Isolated Solutions FUTURE Flexible Learning Invisible technology Virtual Performance Technology supporting people Integrative competency Strategy-driven Communication Client utility focus Ubiquitous Knowledge Centric Point of Action empowerment Open Standards Interoperability
 The DON IM/IT Vision for the Future § An integrated, results-oriented Navy and Marine Corps team characterized by strategic leadership, ubiquitous communication, and invisible technology. § An effective, flexible and sustainable DON enterprisewide information and technology environment that enables our people to make and implement efficient and agile decisions. § A knowledge-centric culture where trust and respect facilitate information sharing and organizational learning. Knowledge management is critical to achieving our IM/IT vision
The DON IM/IT Vision for the Future § An integrated, results-oriented Navy and Marine Corps team characterized by strategic leadership, ubiquitous communication, and invisible technology. § An effective, flexible and sustainable DON enterprisewide information and technology environment that enables our people to make and implement efficient and agile decisions. § A knowledge-centric culture where trust and respect facilitate information sharing and organizational learning. Knowledge management is critical to achieving our IM/IT vision
 Knowledge management can be viewed as a process for optimizing the effective application of intellectual capital to achieve organizational objectives. Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/04/99 v. 1
Knowledge management can be viewed as a process for optimizing the effective application of intellectual capital to achieve organizational objectives. Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/04/99 v. 1
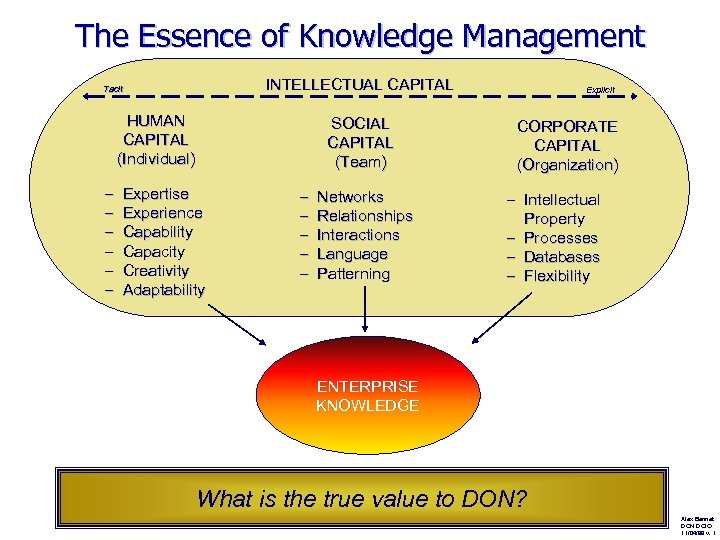 The Essence of Knowledge Management INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL Tacit HUMAN CAPITAL (Individual) – – – SOCIAL CAPITAL (Team) Expertise Experience Capability Capacity Creativity Adaptability – – – Networks Relationships Interactions Language Patterning Explicit CORPORATE CAPITAL (Organization) – Intellectual Property – Processes – Databases – Flexibility ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE What is the true value to DON? Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/04/99 v. 1
The Essence of Knowledge Management INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL Tacit HUMAN CAPITAL (Individual) – – – SOCIAL CAPITAL (Team) Expertise Experience Capability Capacity Creativity Adaptability – – – Networks Relationships Interactions Language Patterning Explicit CORPORATE CAPITAL (Organization) – Intellectual Property – Processes – Databases – Flexibility ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE What is the true value to DON? Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/04/99 v. 1
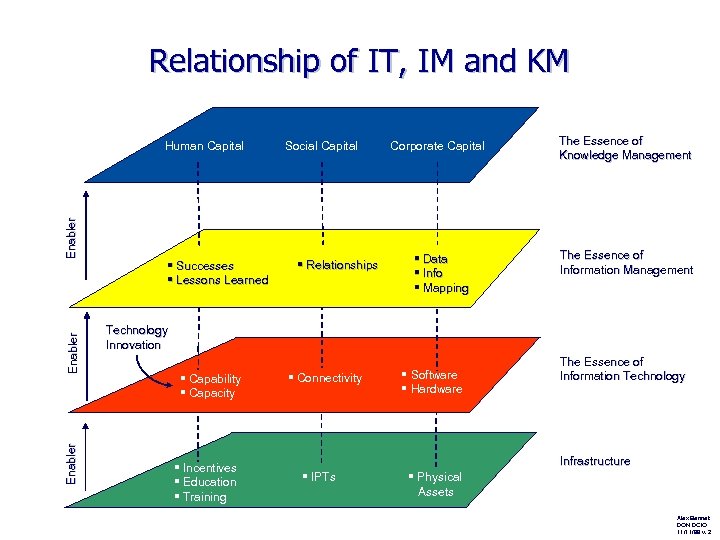 Relationship of IT, IM and KM Enabler Human Capital § Successes § Lessons Learned Social Capital § Relationships Corporate Capital § Data § Info § Mapping The Essence of Knowledge Management The Essence of Information Management Technology Innovation § Capability § Capacity § Incentives § Education § Training § Connectivity § Software § Hardware The Essence of Information Technology Infrastructure § IPTs § Physical Assets Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/11/99 v. 2
Relationship of IT, IM and KM Enabler Human Capital § Successes § Lessons Learned Social Capital § Relationships Corporate Capital § Data § Info § Mapping The Essence of Knowledge Management The Essence of Information Management Technology Innovation § Capability § Capacity § Incentives § Education § Training § Connectivity § Software § Hardware The Essence of Information Technology Infrastructure § IPTs § Physical Assets Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/11/99 v. 2
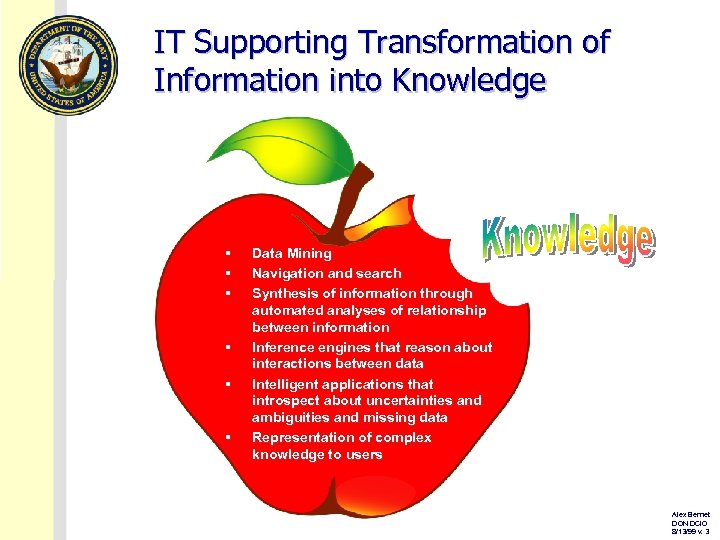 IT Supporting Transformation of Information into Knowledge § § § Data Mining Navigation and search Synthesis of information through automated analyses of relationship between information Inference engines that reason about interactions between data Intelligent applications that introspect about uncertainties and ambiguities and missing data Representation of complex knowledge to users Alex Bennet DON DCIO 8/13/99 v. 3
IT Supporting Transformation of Information into Knowledge § § § Data Mining Navigation and search Synthesis of information through automated analyses of relationship between information Inference engines that reason about interactions between data Intelligent applications that introspect about uncertainties and ambiguities and missing data Representation of complex knowledge to users Alex Bennet DON DCIO 8/13/99 v. 3
 KM Truisms § Perfect information does not equal perfect decisions § Behaviors are not changed by technology alone § Connecting is not sufficient to create value
KM Truisms § Perfect information does not equal perfect decisions § Behaviors are not changed by technology alone § Connecting is not sufficient to create value
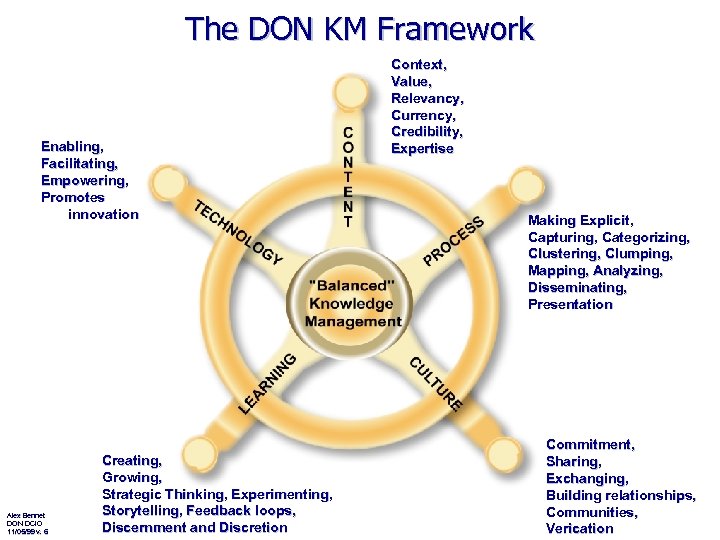 The DON KM Framework Enabling, Facilitating, Empowering, Promotes innovation Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/05/99 v. 6 Creating, Growing, Strategic Thinking, Experimenting, Storytelling, Feedback loops, Discernment and Discretion Context, Value, Relevancy, Currency, Credibility, Expertise Making Explicit, Capturing, Categorizing, Clustering, Clumping, Mapping, Analyzing, Disseminating, Presentation Commitment, Sharing, Exchanging, Building relationships, Communities, Verication
The DON KM Framework Enabling, Facilitating, Empowering, Promotes innovation Alex Bennet DON DCIO 11/05/99 v. 6 Creating, Growing, Strategic Thinking, Experimenting, Storytelling, Feedback loops, Discernment and Discretion Context, Value, Relevancy, Currency, Credibility, Expertise Making Explicit, Capturing, Categorizing, Clustering, Clumping, Mapping, Analyzing, Disseminating, Presentation Commitment, Sharing, Exchanging, Building relationships, Communities, Verication
 NMCI Vision: Building the modern Navy-Marine Corps on the transformational power of networking § Enable connection to the National infrastructure § Extend sharing and creation of knowledge and expertise worldwide § Empower innovative work and training § Enhance the Quality of Life for every Marine, Sailor and DON Civilian Forward…. at the speed of light!
NMCI Vision: Building the modern Navy-Marine Corps on the transformational power of networking § Enable connection to the National infrastructure § Extend sharing and creation of knowledge and expertise worldwide § Empower innovative work and training § Enhance the Quality of Life for every Marine, Sailor and DON Civilian Forward…. at the speed of light!
 Key DON KM Strategy Concepts § Pull, not push § Leadership Alignment, not control § Embed into our business, not the business § Little km, not a “KM” program § Where appropriate, not everywhere § NMCI will be the bridge
Key DON KM Strategy Concepts § Pull, not push § Leadership Alignment, not control § Embed into our business, not the business § Little km, not a “KM” program § Where appropriate, not everywhere § NMCI will be the bridge
 DON Knowledge Fair 2000 § Showcased for facilitating Enterprise sharing. § Event hosted by the UNSECNAV, A/CMC and VCNO § Featured over 80 displays demonstrating successful KM applications § First Knowledge Sharing awards § Virtual Tool e. Business Knowledge Fair August 2001
DON Knowledge Fair 2000 § Showcased for facilitating Enterprise sharing. § Event hosted by the UNSECNAV, A/CMC and VCNO § Featured over 80 displays demonstrating successful KM applications § First Knowledge Sharing awards § Virtual Tool e. Business Knowledge Fair August 2001
 Communities of Practice and Interest § § § § Shared Domain of Practice/Interest Alignment with strategic direction Critical Factors Crosses operational, functional and • Personal organizational boundaries passion • Trust • Sense of Urgency Defined by knowledge, not tasks Managed by making connections • Key thought leaders Focus on value, added mutual exchange and Respect • • Open Communication continuous learning Evolving agenda § Communities emerging across the Department (Collaboration at Sea, Logistics, MC QDR, total ownership cost, KM, Investment Practices, etc. ) “…you cannot force a plant to grow by pulling its leaves… what you can do is create the infrastructure in which it can prosper. ” - Etienne Wegner, 1999
Communities of Practice and Interest § § § § Shared Domain of Practice/Interest Alignment with strategic direction Critical Factors Crosses operational, functional and • Personal organizational boundaries passion • Trust • Sense of Urgency Defined by knowledge, not tasks Managed by making connections • Key thought leaders Focus on value, added mutual exchange and Respect • • Open Communication continuous learning Evolving agenda § Communities emerging across the Department (Collaboration at Sea, Logistics, MC QDR, total ownership cost, KM, Investment Practices, etc. ) “…you cannot force a plant to grow by pulling its leaves… what you can do is create the infrastructure in which it can prosper. ” - Etienne Wegner, 1999
 The DON KM Community of Practice § Forum for furthering the practice of Knowledge Management – Builds on the Fall 1998 and early 1999 KM Senior Leaders’ Forums sponsored by CNO(N 6). – Offers the opportunity to benchmark against best practices and participate in development of Enterprise-wide tools. – Facilitates exchange of successes and lessons learned. – Wide representation from across Enterprise. § Continuing virtual connectivity and quarterly forum meetings. Next meeting: 29 August 2001 in Washington, DC § Sponsors the DON Knowledge Fairs. Next Fair: 30 August 2001 in Washington, DC § To join: www. don-imit. navy. mil/quickplace Facilitates information sharing and organizational learning.
The DON KM Community of Practice § Forum for furthering the practice of Knowledge Management – Builds on the Fall 1998 and early 1999 KM Senior Leaders’ Forums sponsored by CNO(N 6). – Offers the opportunity to benchmark against best practices and participate in development of Enterprise-wide tools. – Facilitates exchange of successes and lessons learned. – Wide representation from across Enterprise. § Continuing virtual connectivity and quarterly forum meetings. Next meeting: 29 August 2001 in Washington, DC § Sponsors the DON Knowledge Fairs. Next Fair: 30 August 2001 in Washington, DC § To join: www. don-imit. navy. mil/quickplace Facilitates information sharing and organizational learning.
 New: PM Community of Practice Navy ARO and DAU Partnership to Support Do. D’s Strategic Goals
New: PM Community of Practice Navy ARO and DAU Partnership to Support Do. D’s Strategic Goals
 PM Co. P Goals • Performance Support • Knowledge Retrieval • Knowledge Capture • Collaboration and Solutions Environment • Generation of New Knowledge
PM Co. P Goals • Performance Support • Knowledge Retrieval • Knowledge Capture • Collaboration and Solutions Environment • Generation of New Knowledge
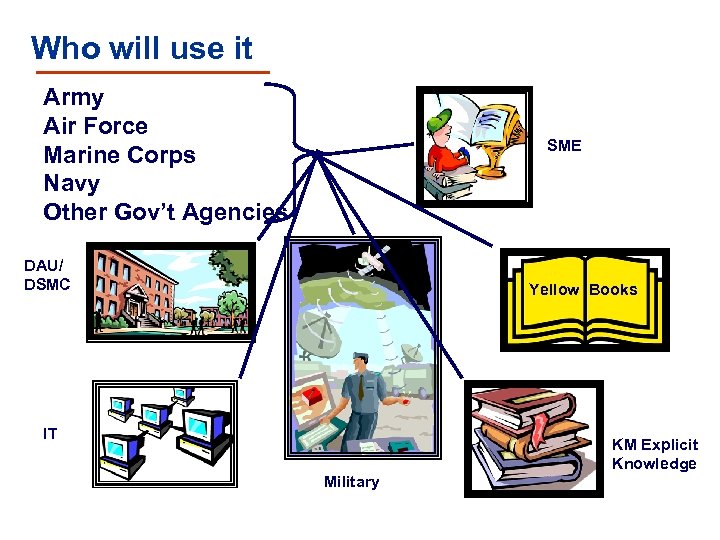 Who will use it Army Air Force Marine Corps Navy Other Gov’t Agencies SME DAU/ DSMC Yellow Books IT KM Explicit Knowledge Military
Who will use it Army Air Force Marine Corps Navy Other Gov’t Agencies SME DAU/ DSMC Yellow Books IT KM Explicit Knowledge Military
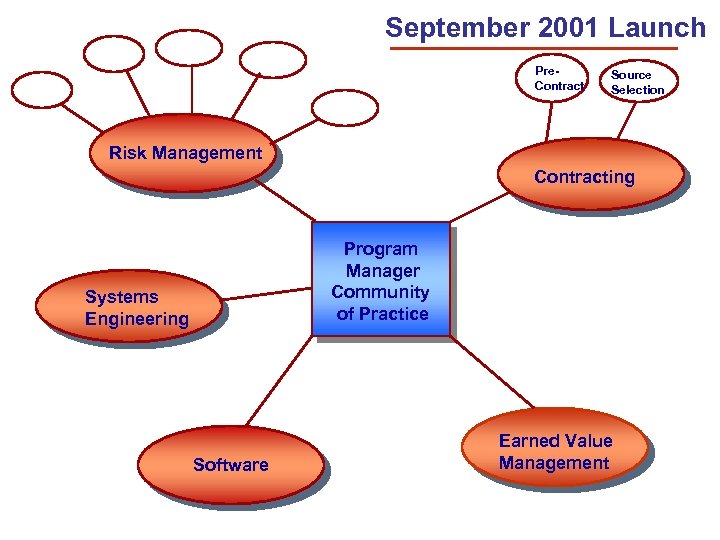 September 2001 Launch Pre. Contract Source Selection Risk Management Contracting Program Manager Community of Practice Systems Engineering Software Earned Value Management
September 2001 Launch Pre. Contract Source Selection Risk Management Contracting Program Manager Community of Practice Systems Engineering Software Earned Value Management
 Knowledge Centric Organization (KCO) Toolkit § Leads organizations through the stages of achieving a KCO § Sponsored by the KM Co. P and developed with Arthur Andersen § Packed with templates, case studies and reference material § Virtual tool available on CD and via DON CIO web site: www. don-imit. navy. mil (Interest Areas>Knowledge Sharing>Knowledge Management) – Over 17, 000 CDs have been distributed government-wide – Next version: August 2001 A KCO learns constantly, connects people and information, and promotes innovation and quality decision-making
Knowledge Centric Organization (KCO) Toolkit § Leads organizations through the stages of achieving a KCO § Sponsored by the KM Co. P and developed with Arthur Andersen § Packed with templates, case studies and reference material § Virtual tool available on CD and via DON CIO web site: www. don-imit. navy. mil (Interest Areas>Knowledge Sharing>Knowledge Management) – Over 17, 000 CDs have been distributed government-wide – Next version: August 2001 A KCO learns constantly, connects people and information, and promotes innovation and quality decision-making
 KCO Implementation Process § Build awareness and spread KM expertise § Identify key knowledge assets § Design projects: determine project focus, feasibility, resources, costs, ROI; and prioritize knowledge assets – Create maps of owners and users of knowledge assets – Define metrics for evaluation of project, e. g. , reliability of knowledge assets; usability of knowledge system; reduction in process cycle time – Design, develop and deploy systems to collect, organize, distill, disseminate – Build Communities of Practice around "hot" topics
KCO Implementation Process § Build awareness and spread KM expertise § Identify key knowledge assets § Design projects: determine project focus, feasibility, resources, costs, ROI; and prioritize knowledge assets – Create maps of owners and users of knowledge assets – Define metrics for evaluation of project, e. g. , reliability of knowledge assets; usability of knowledge system; reduction in process cycle time – Design, develop and deploy systems to collect, organize, distill, disseminate – Build Communities of Practice around "hot" topics
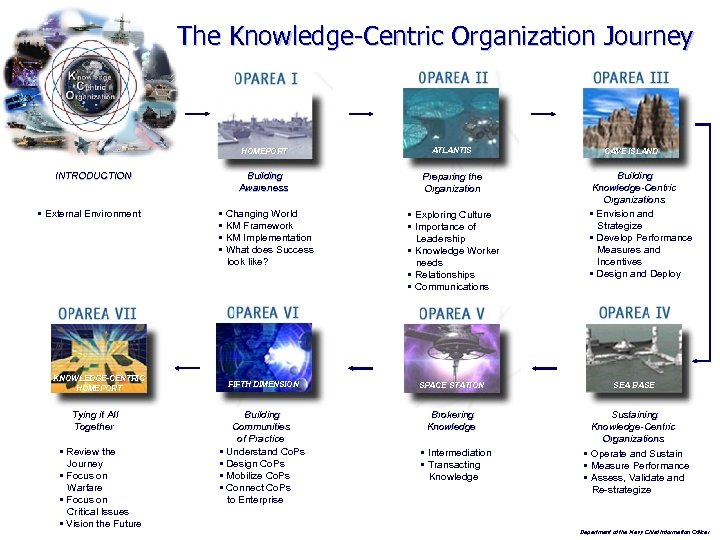 The Knowledge-Centric Organization Journey HOMEPORT INTRODUCTION § External Environment KNOWLEDGE-CENTRIC HOMEPORT Tying it All Together § Review the Journey § Focus on Warfare § Focus on Critical Issues § Vision the Future ATLANTIS Building Awareness Preparing the Organization § Changing World § KM Framework § KM Implementation § What does Success look like? § Exploring Culture § Importance of Leadership § Knowledge Worker needs § Relationships § Communications FIFTH DIMENSION SPACE STATION Building Communities of Practice § Understand Co. Ps § Design Co. Ps § Mobilize Co. Ps § Connect Co. Ps to Enterprise Brokering Knowledge § Intermediation § Transacting Knowledge CAVE ISLAND Building Knowledge-Centric Organizations § Envision and Strategize § Develop Performance Measures and Incentives § Design and Deploy SEA BASE Sustaining Knowledge-Centric Organizations § Operate and Sustain § Measure Performance § Assess, Validate and Re-strategize Department of the Navy Chief Information Officer
The Knowledge-Centric Organization Journey HOMEPORT INTRODUCTION § External Environment KNOWLEDGE-CENTRIC HOMEPORT Tying it All Together § Review the Journey § Focus on Warfare § Focus on Critical Issues § Vision the Future ATLANTIS Building Awareness Preparing the Organization § Changing World § KM Framework § KM Implementation § What does Success look like? § Exploring Culture § Importance of Leadership § Knowledge Worker needs § Relationships § Communications FIFTH DIMENSION SPACE STATION Building Communities of Practice § Understand Co. Ps § Design Co. Ps § Mobilize Co. Ps § Connect Co. Ps to Enterprise Brokering Knowledge § Intermediation § Transacting Knowledge CAVE ISLAND Building Knowledge-Centric Organizations § Envision and Strategize § Develop Performance Measures and Incentives § Design and Deploy SEA BASE Sustaining Knowledge-Centric Organizations § Operate and Sustain § Measure Performance § Assess, Validate and Re-strategize Department of the Navy Chief Information Officer
 KCO Assistance Teams Validating and improving the KCO Toolkit Creating case-studies and capturing KM successes for other commands to follow § First pilot at SPAWAR Systems Center Charleston § Integrated with corporate SPAWAR efforts § Strong leadership support § Effective team addressing culture, learning, process, content, technology and community § Efforts underway in NAVSEA (NUWC Keyport), OPNAV, NAVFAC, Naval Audit Service Creating the Knowledge-Centric Enterprise
KCO Assistance Teams Validating and improving the KCO Toolkit Creating case-studies and capturing KM successes for other commands to follow § First pilot at SPAWAR Systems Center Charleston § Integrated with corporate SPAWAR efforts § Strong leadership support § Effective team addressing culture, learning, process, content, technology and community § Efforts underway in NAVSEA (NUWC Keyport), OPNAV, NAVFAC, Naval Audit Service Creating the Knowledge-Centric Enterprise
 DON IM/IT Workforce Guidance § Knowledge Management embedded in: – IM/IT Inherently Governmental Guidance – IM/IT Workforce Strategic Plan KCO Roles § Chief Knowledge Officer – KM/IM/IT Civilian Career Path Guide § Knowledge Manager – DON CIO Continuous Learning Guidance § Knowledge Process Manager – Knowledge Transfer Engineer – Knowledge Research Engineer – Knowledge Life Cycle Engineer § Knowledge System Engineer § Knowledge Community Leader § Performance Measurement Engineer § Knowledge Assurance Manager § Intellectual Capital Manager § Knowledge Assistant
DON IM/IT Workforce Guidance § Knowledge Management embedded in: – IM/IT Inherently Governmental Guidance – IM/IT Workforce Strategic Plan KCO Roles § Chief Knowledge Officer – KM/IM/IT Civilian Career Path Guide § Knowledge Manager – DON CIO Continuous Learning Guidance § Knowledge Process Manager – Knowledge Transfer Engineer – Knowledge Research Engineer – Knowledge Life Cycle Engineer § Knowledge System Engineer § Knowledge Community Leader § Performance Measurement Engineer § Knowledge Assurance Manager § Intellectual Capital Manager § Knowledge Assistant
 Systems Thinking § MIT-developed methodology for learning organization § Expands individual thinking skills § Integrative core competency for IM/IT § Tool for identifying patterns in decision making § Periodic classes offered through DON CIO § Virtual tool available on CD, and via CNET at: – www. navylearning. com – www. navylearning. navy. mil Provides the opportunity for our Sailors and Marines to transform complex information into effective decision making.
Systems Thinking § MIT-developed methodology for learning organization § Expands individual thinking skills § Integrative core competency for IM/IT § Tool for identifying patterns in decision making § Periodic classes offered through DON CIO § Virtual tool available on CD, and via CNET at: – www. navylearning. com – www. navylearning. navy. mil Provides the opportunity for our Sailors and Marines to transform complex information into effective decision making.
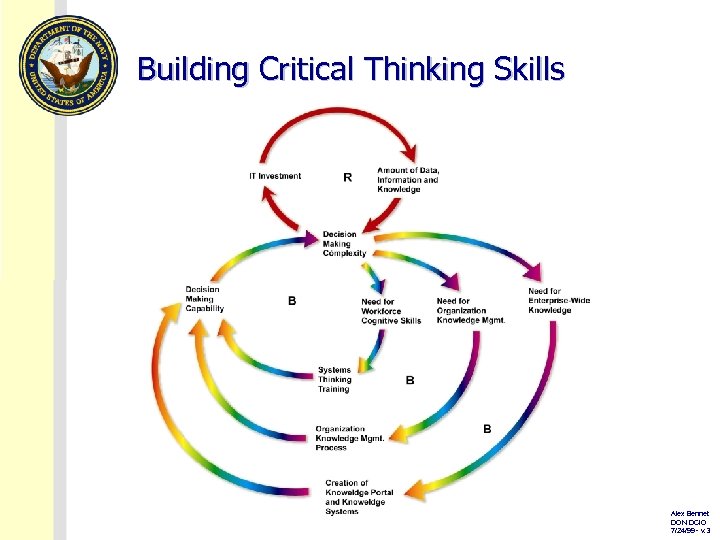 Building Critical Thinking Skills Alex Bennet DON DCIO 7/24/99 - v. 3
Building Critical Thinking Skills Alex Bennet DON DCIO 7/24/99 - v. 3

 Information literacy is a survival skill in the Information Age. Instead of drowning in the abundance of information that floods their lives, information literate people know how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively to solve a particular problem or make a decision… - Presidential Committee on Information Literacy
Information literacy is a survival skill in the Information Age. Instead of drowning in the abundance of information that floods their lives, information literate people know how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively to solve a particular problem or make a decision… - Presidential Committee on Information Literacy
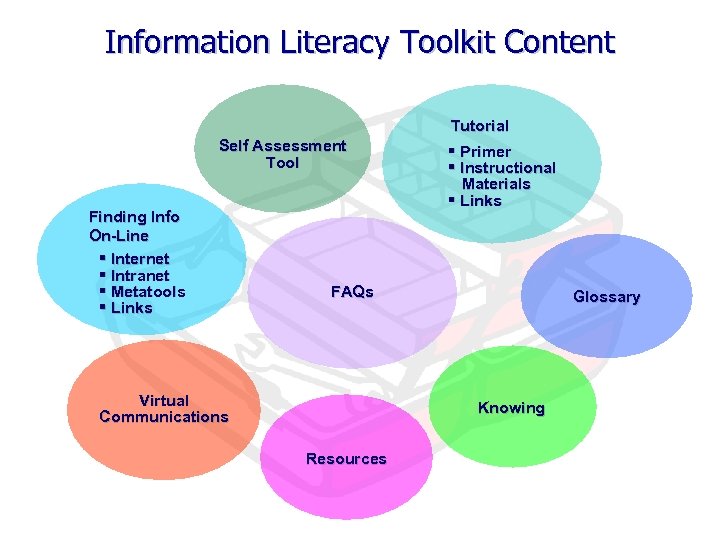 Information Literacy Toolkit Content Tutorial Self Assessment Tool Finding Info On-Line § Internet § Intranet § Metatools § Links § Primer § Instructional Materials § Links FAQs Virtual Communications Glossary Knowing Resources
Information Literacy Toolkit Content Tutorial Self Assessment Tool Finding Info On-Line § Internet § Intranet § Metatools § Links § Primer § Instructional Materials § Links FAQs Virtual Communications Glossary Knowing Resources
 KNOWING is seeing beyond images; hearing beyond words, and sensing beyond appearances. So it is said that if you know others and know yourself, you will not be imperiled in a hundred battles; if you do not know others but know yourself, you win one and lose one; if you do not know others and do not know yourself, you will be imperiled in every single battle. – Sun Tzu, The Art of War
KNOWING is seeing beyond images; hearing beyond words, and sensing beyond appearances. So it is said that if you know others and know yourself, you will not be imperiled in a hundred battles; if you do not know others but know yourself, you win one and lose one; if you do not know others and do not know yourself, you will be imperiled in every single battle. – Sun Tzu, The Art of War
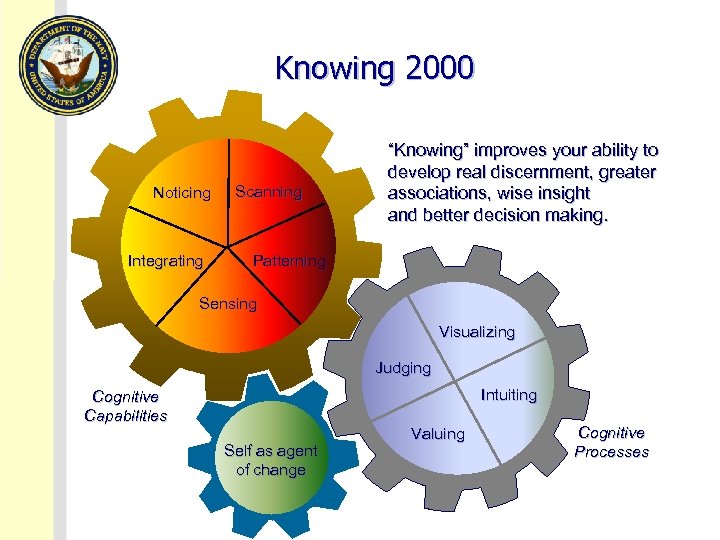 Knowing 2000 Noticing Integrating Scanning “Knowing” improves your ability to develop real discernment, greater associations, wise insight and better decision making. Patterning Sensing Visualizing Judging Intuiting Cognitive Capabilities Self as agent of change Valuing Cognitive Processes
Knowing 2000 Noticing Integrating Scanning “Knowing” improves your ability to develop real discernment, greater associations, wise insight and better decision making. Patterning Sensing Visualizing Judging Intuiting Cognitive Capabilities Self as agent of change Valuing Cognitive Processes
 Dimensions of KM across the Navy and Marine Corps § § § § Knowledge Centric Organization Communities of Practice Tacit Knowledge Capture/Transfer Knowledge Repositories Reachback Collaboration Decision Support/Command Control Knowledge Portals
Dimensions of KM across the Navy and Marine Corps § § § § Knowledge Centric Organization Communities of Practice Tacit Knowledge Capture/Transfer Knowledge Repositories Reachback Collaboration Decision Support/Command Control Knowledge Portals
 CINCPACFLT……. FIRST CKO ……. PORTALS…. COMMUNITIES ACROSS THE PACIFIC FLEET NAVSEA……. SEVENTEEN INITIATIVES AT KM FAIR ………. A TRULY ENTERPRISE APPROACH INTEGRATING E-BUSINESS AND ERP
CINCPACFLT……. FIRST CKO ……. PORTALS…. COMMUNITIES ACROSS THE PACIFIC FLEET NAVSEA……. SEVENTEEN INITIATIVES AT KM FAIR ………. A TRULY ENTERPRISE APPROACH INTEGRATING E-BUSINESS AND ERP
 Current Fleet Support Process Shared data environment facilitating streamlined fleet support processes 38
Current Fleet Support Process Shared data environment facilitating streamlined fleet support processes 38
 NAVFAC HAS 31 COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE WITH TECHNICAL DISCIPLINE LEADERS …. PAVEMENTS, INTERIOR DESIGN, ETC, THE ACQUISITION REFORM OFFICE HAS ESTABLISHED A TOTAL OWNERSHIP COST COMMUNITY OF INTEREST TO SUPPORT THIS NEW CONCEPT
NAVFAC HAS 31 COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE WITH TECHNICAL DISCIPLINE LEADERS …. PAVEMENTS, INTERIOR DESIGN, ETC, THE ACQUISITION REFORM OFFICE HAS ESTABLISHED A TOTAL OWNERSHIP COST COMMUNITY OF INTEREST TO SUPPORT THIS NEW CONCEPT
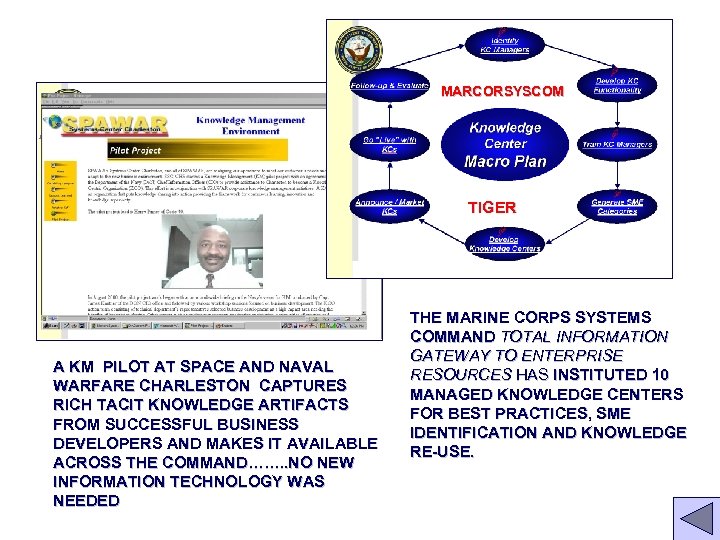 MARCORSYSCOM TIGER A KM PILOT AT SPACE AND NAVAL WARFARE CHARLESTON CAPTURES RICH TACIT KNOWLEDGE ARTIFACTS FROM SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS DEVELOPERS AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE ACROSS THE COMMAND……. . NO NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY WAS NEEDED THE MARINE CORPS SYSTEMS COMMAND TOTAL INFORMATION GATEWAY TO ENTERPRISE RESOURCES HAS INSTITUTED 10 MANAGED KNOWLEDGE CENTERS FOR BEST PRACTICES, SME IDENTIFICATION AND KNOWLEDGE RE-USE.
MARCORSYSCOM TIGER A KM PILOT AT SPACE AND NAVAL WARFARE CHARLESTON CAPTURES RICH TACIT KNOWLEDGE ARTIFACTS FROM SUCCESSFUL BUSINESS DEVELOPERS AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE ACROSS THE COMMAND……. . NO NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY WAS NEEDED THE MARINE CORPS SYSTEMS COMMAND TOTAL INFORMATION GATEWAY TO ENTERPRISE RESOURCES HAS INSTITUTED 10 MANAGED KNOWLEDGE CENTERS FOR BEST PRACTICES, SME IDENTIFICATION AND KNOWLEDGE RE-USE.
 Collaboration @ Sea An Evolutionary Step Towards Network Centric Warfare Share Data & Information More Easily & Rapidly Allow People to Make More Informed Decisions, Faster
Collaboration @ Sea An Evolutionary Step Towards Network Centric Warfare Share Data & Information More Easily & Rapidly Allow People to Make More Informed Decisions, Faster
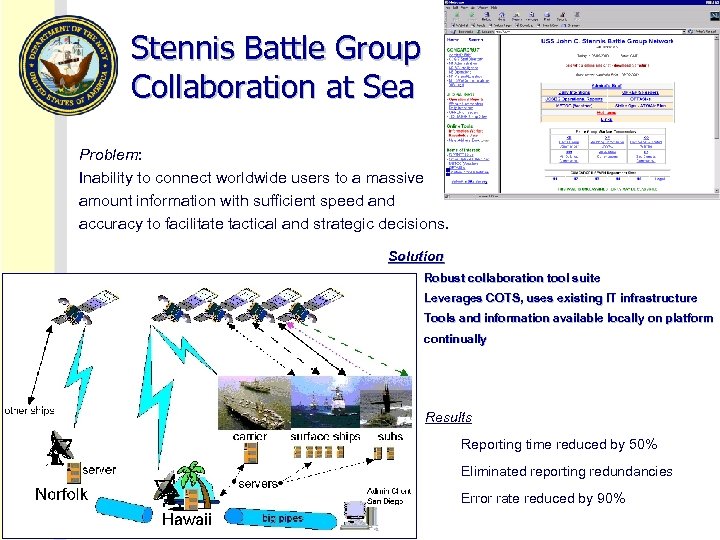 Stennis Battle Group Collaboration at Sea Problem: Inability to connect worldwide users to a massive amount information with sufficient speed and accuracy to facilitate tactical and strategic decisions. Solution Robust collaboration tool suite Leverages COTS, uses existing IT infrastructure Tools and information available locally on platform continually Results Reporting time reduced by 50% Eliminated reporting redundancies Error rate reduced by 90%
Stennis Battle Group Collaboration at Sea Problem: Inability to connect worldwide users to a massive amount information with sufficient speed and accuracy to facilitate tactical and strategic decisions. Solution Robust collaboration tool suite Leverages COTS, uses existing IT infrastructure Tools and information available locally on platform continually Results Reporting time reduced by 50% Eliminated reporting redundancies Error rate reduced by 90%
 Knowledge Centric-Warfare Developing the Aircraft Carrier of the Future Battlespace Representation Human-Computer Interaction Distributed Collaborative Technologies Intelligent Applications & Decision Support Distributed Information Management Seamless, Global Information Access Sensors and Sources
Knowledge Centric-Warfare Developing the Aircraft Carrier of the Future Battlespace Representation Human-Computer Interaction Distributed Collaborative Technologies Intelligent Applications & Decision Support Distributed Information Management Seamless, Global Information Access Sensors and Sources
 The Command 21 “Knowledge Wall” Conceptual CJTF Collaborative “Knowledge Wall”: A “Picture Window” into a “sea of information” displayed using a “data wall” & fed from Anchor Desk DSS’s. “Enabling Knowledge-Centric Warfare for Fleet Decision-makers”
The Command 21 “Knowledge Wall” Conceptual CJTF Collaborative “Knowledge Wall”: A “Picture Window” into a “sea of information” displayed using a “data wall” & fed from Anchor Desk DSS’s. “Enabling Knowledge-Centric Warfare for Fleet Decision-makers”
 Joint Warfare Knowledge Portal Addressing issues concerning target identification, launch, command § Who should take the target § Rules of engagement § Conflicting commands § Loss of time due to a deviation in a computer or sensor system. § Time loss due to a misinterpretation of incoming data from one or more systems. § § Target action with missing or incomplete Target from sensor to decision to engagement
Joint Warfare Knowledge Portal Addressing issues concerning target identification, launch, command § Who should take the target § Rules of engagement § Conflicting commands § Loss of time due to a deviation in a computer or sensor system. § Time loss due to a misinterpretation of incoming data from one or more systems. § § Target action with missing or incomplete Target from sensor to decision to engagement
 Next Steps… § Document Success Stories from Across the Enterprise § Explore KM and Warfighting § Finalize Metrics Guide for KM Initiatives § Sponsor August 30, 2001 e. Business Knowledge Fair; Washington, DC § Leverage NMCI – Portal Integration Office, Content Management – Taxonomy § DON Community of Practice Startup Kit § Reach out to Balance of Navy
Next Steps… § Document Success Stories from Across the Enterprise § Explore KM and Warfighting § Finalize Metrics Guide for KM Initiatives § Sponsor August 30, 2001 e. Business Knowledge Fair; Washington, DC § Leverage NMCI – Portal Integration Office, Content Management – Taxonomy § DON Community of Practice Startup Kit § Reach out to Balance of Navy
 Bringing the Knowledge of the Department to the tip of the spear!
Bringing the Knowledge of the Department to the tip of the spear!
 Back-up Slides
Back-up Slides
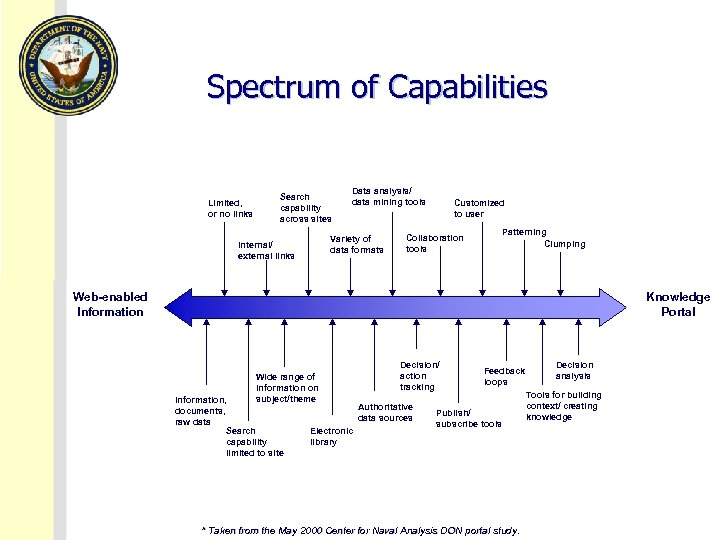 Spectrum of Capabilities Limited, or no links Search capability across sites Data analysis/ data mining tools Variety of data formats Internal/ external links Customized to user Collaboration tools Patterning Clumping Web-enabled Information Knowledge Portal Wide range of information on subject/theme Information, documents, raw data Search capability limited to site Electronic library Decision/ action tracking Authoritative data sources Feedback loops Publish/ subscribe tools * Taken from the May 2000 Center for Naval Analysis DON portal study. Decision analysis Tools for building context/ creating knowledge
Spectrum of Capabilities Limited, or no links Search capability across sites Data analysis/ data mining tools Variety of data formats Internal/ external links Customized to user Collaboration tools Patterning Clumping Web-enabled Information Knowledge Portal Wide range of information on subject/theme Information, documents, raw data Search capability limited to site Electronic library Decision/ action tracking Authoritative data sources Feedback loops Publish/ subscribe tools * Taken from the May 2000 Center for Naval Analysis DON portal study. Decision analysis Tools for building context/ creating knowledge
 Government Learning Objectives for KM Certification 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Have knowledge of the value added by Knowledge Management to the business proposition, including the return on investment, performance measures, and the ability to develop a business case. Have knowledge of the strategies and processes to transfer explicit and tacit knowledge across time, space and organizational boundaries, including retrieval of critical archived information. This transfer has a spiraling nature, i. e. , ideas build on ideas, and old ideas may or may not be of current value. Have knowledge of state-of-the-art and evolving technology solutions that promote KM, including portals and collaborative and distributed learning technologies. Have knowledge of and the ability to facilitate knowledge creation, sharing and reuse. This includes developing partnerships and alliances, designing creative knowledge spaces, and using incentive structures. Have knowledge of learning styles and behaviors, strive for continuous improvement and be actively engaged in exploring new ideas and concepts. Have working knowledge of state-of-the-art research and implementation strategies for knowledge management, information management, document and records management and data management. This includes project management of knowledge initiatives and retrieval of critical archived information.
Government Learning Objectives for KM Certification 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Have knowledge of the value added by Knowledge Management to the business proposition, including the return on investment, performance measures, and the ability to develop a business case. Have knowledge of the strategies and processes to transfer explicit and tacit knowledge across time, space and organizational boundaries, including retrieval of critical archived information. This transfer has a spiraling nature, i. e. , ideas build on ideas, and old ideas may or may not be of current value. Have knowledge of state-of-the-art and evolving technology solutions that promote KM, including portals and collaborative and distributed learning technologies. Have knowledge of and the ability to facilitate knowledge creation, sharing and reuse. This includes developing partnerships and alliances, designing creative knowledge spaces, and using incentive structures. Have knowledge of learning styles and behaviors, strive for continuous improvement and be actively engaged in exploring new ideas and concepts. Have working knowledge of state-of-the-art research and implementation strategies for knowledge management, information management, document and records management and data management. This includes project management of knowledge initiatives and retrieval of critical archived information.
 Government Learning Objectives for KM Certification 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Have understanding of the global and economic importance of developing knowledge-based organizations to meet the challenges of the knowledge era. Have the ability to use systems thinking in implementing solutions. Have the ability to design, develop and sustain communities of interest and practice. Have the ability to design, develop and sustain the flow of knowledge. This includes understanding the breakthrough skills needed to leverage virtual teamwork and the effective use of social networks. Have the ability to perform cultural and ethnographic analyses, develop knowledge taxonomies, facilitate knowledge audits, and perform knowledge mapping and needs assessments. Have the ability to capture, evaluate and use best-known practices, including the use of storytelling to transfer these best practices. Have the ability to manage change and complex knowledge initiatives and projects. Have the ability to identify customers and stakeholders and tie organizational goals to the needs and requirements of those customers and stakeholders.
Government Learning Objectives for KM Certification 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Have understanding of the global and economic importance of developing knowledge-based organizations to meet the challenges of the knowledge era. Have the ability to use systems thinking in implementing solutions. Have the ability to design, develop and sustain communities of interest and practice. Have the ability to design, develop and sustain the flow of knowledge. This includes understanding the breakthrough skills needed to leverage virtual teamwork and the effective use of social networks. Have the ability to perform cultural and ethnographic analyses, develop knowledge taxonomies, facilitate knowledge audits, and perform knowledge mapping and needs assessments. Have the ability to capture, evaluate and use best-known practices, including the use of storytelling to transfer these best practices. Have the ability to manage change and complex knowledge initiatives and projects. Have the ability to identify customers and stakeholders and tie organizational goals to the needs and requirements of those customers and stakeholders.
 The DON KM Community of Practice § Offers the opportunity to benchmark against best practices and participate in development of Enterprise-wide tools. § Facilitates exchange of successes and lessons learned. § Wide representation from across Enterprise. § Shared Opportunities – IKM and APQC § Continuing virtual connectivity and quarterly forum meetings. Next meeting: 29 Aug 2001 in Washington, DC – 8/5/2000 Sponsored the DON Knowledge Fair. Next Fair: 30 Aug 2001 in Washington, DC – 7/31/2000 KMCo. P meeting speakers included World Bank KM Director, Chrysler Daimler KM University Manager, a Navy CKO and Commander NAVSEA. – 11/6/2000 Sponsored IKM Research Session, Washington, DC – 2/1/2001 Sponsored the Development of a Co. P Start-up Kit § To join: www. don-imit. navy. mil/quickplace Facilitates information sharing and organizational learning.
The DON KM Community of Practice § Offers the opportunity to benchmark against best practices and participate in development of Enterprise-wide tools. § Facilitates exchange of successes and lessons learned. § Wide representation from across Enterprise. § Shared Opportunities – IKM and APQC § Continuing virtual connectivity and quarterly forum meetings. Next meeting: 29 Aug 2001 in Washington, DC – 8/5/2000 Sponsored the DON Knowledge Fair. Next Fair: 30 Aug 2001 in Washington, DC – 7/31/2000 KMCo. P meeting speakers included World Bank KM Director, Chrysler Daimler KM University Manager, a Navy CKO and Commander NAVSEA. – 11/6/2000 Sponsored IKM Research Session, Washington, DC – 2/1/2001 Sponsored the Development of a Co. P Start-up Kit § To join: www. don-imit. navy. mil/quickplace Facilitates information sharing and organizational learning.
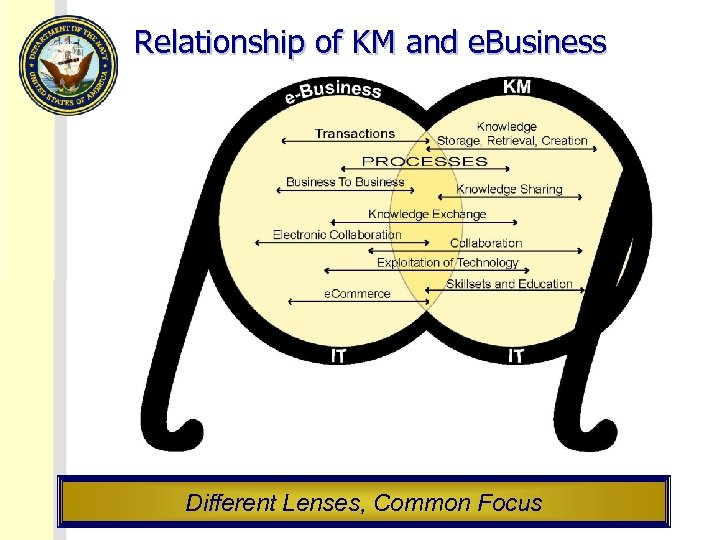 Relationship of KM and e. Business Different Lenses, Common Focus
Relationship of KM and e. Business Different Lenses, Common Focus
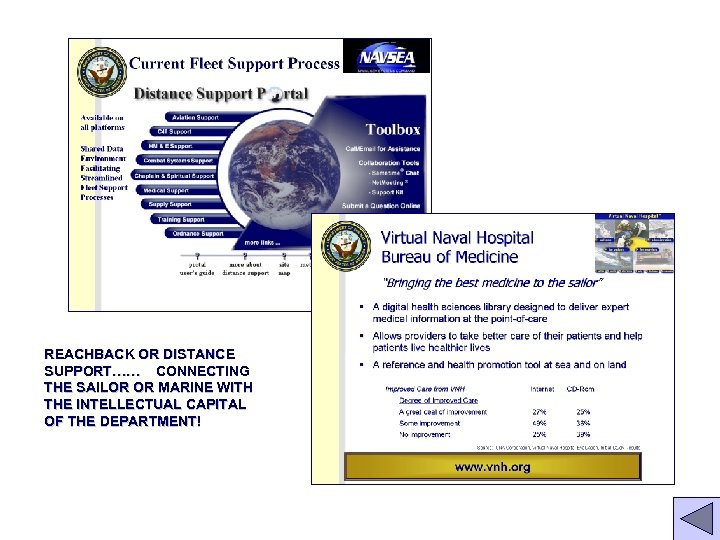 REACHBACK OR DISTANCE SUPPORT…… CONNECTING THE SAILOR OR MARINE WITH THE INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL OF THE DEPARTMENT!
REACHBACK OR DISTANCE SUPPORT…… CONNECTING THE SAILOR OR MARINE WITH THE INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL OF THE DEPARTMENT!
 PORTALS……. MOVING FROM WINDOWS TO INFORMATION………. BECOMING WINDOWS TO THE KNOWLEDGE, APPLICATIONS AND TOOLS THAT AN INDIVIDUAL NEEDS TO DO HIS JOB SUCCESSFULLY…… INCORPORATING NARROWCASTING, INTELLIGENT SEARCH ENGINES, EXPERTISE LOCATORS
PORTALS……. MOVING FROM WINDOWS TO INFORMATION………. BECOMING WINDOWS TO THE KNOWLEDGE, APPLICATIONS AND TOOLS THAT AN INDIVIDUAL NEEDS TO DO HIS JOB SUCCESSFULLY…… INCORPORATING NARROWCASTING, INTELLIGENT SEARCH ENGINES, EXPERTISE LOCATORS
 OPNAV KM Initiative § Leverages N 4 Logistics Portal N-code Web sites & Collaboration Tools Phase 1 § Phased Rollout to all of OPNAV § Evolving tool set to meet Action Officer Needs Tasker Phase 2 Knowledge Portals Phase 3 REPOSITORIES……. . CODIFYING AND RE-USING THE KNOWLEDGE GAINED IN PROJECTS, CONTRACTS……IN THIS CASE OPNAV IS RE-USING THE KNOWLEDGE CREATED BY IT’S ACTION OFFICERS
OPNAV KM Initiative § Leverages N 4 Logistics Portal N-code Web sites & Collaboration Tools Phase 1 § Phased Rollout to all of OPNAV § Evolving tool set to meet Action Officer Needs Tasker Phase 2 Knowledge Portals Phase 3 REPOSITORIES……. . CODIFYING AND RE-USING THE KNOWLEDGE GAINED IN PROJECTS, CONTRACTS……IN THIS CASE OPNAV IS RE-USING THE KNOWLEDGE CREATED BY IT’S ACTION OFFICERS
 At the Doorstep § Document Success Stories from Across the Enterprise § Explore KM and Warfighting § Finalize Metrics Guide for KM Initiatives § Sponsor August 30, 2001 e. Business Knowledge Fair; Washington, DC § Continue KCO Assist Visits § Reach out to Balance of Navy
At the Doorstep § Document Success Stories from Across the Enterprise § Explore KM and Warfighting § Finalize Metrics Guide for KM Initiatives § Sponsor August 30, 2001 e. Business Knowledge Fair; Washington, DC § Continue KCO Assist Visits § Reach out to Balance of Navy
 On the Horizon § Leveraging NMCI – Portal Integration Office, Content Management – Tools – Taxonomy § DON Community of Practice Startup Kit
On the Horizon § Leveraging NMCI – Portal Integration Office, Content Management – Tools – Taxonomy § DON Community of Practice Startup Kit


