f58ab28353eaa1a57aee6cb2e0701822.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF BELARUS ID CENTER www. ids. by Traceability from the point of view of standarizers and regulators Victor Dravitsa Director of Center for Identification systems and e-business operations, Vice-Chairman of the Bureau UN Centre for Trade Facilitation and E-business (UN/CEFACT) 1*
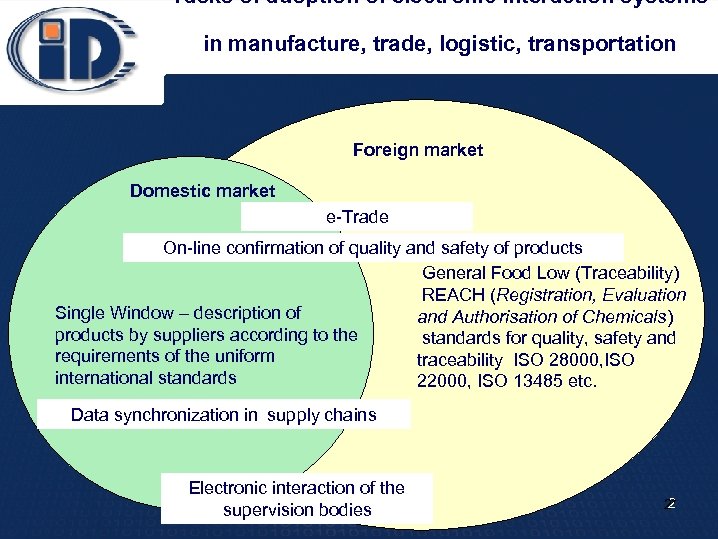
Tasks of adoption of electronic interaction systems in manufacture, trade, logistic, transportation Foreign market Domestic market e-Trade On-line confirmation of quality and safety of products General Food Low (Traceability) REACH (Registration, Evaluation Single Window – description of and Authorisation of Chemicals) products by suppliers according to the standards for quality, safety and requirements of the uniform traceability ISO 28000, ISO international standards 22000, ISO 13485 etc. Data synchronization in supply chains Electronic interaction of the supervision bodies 2 2*

TRACEABILITY Traceability - the ability to trace the history, application or location of materials and components, manufacturing processes and finished goods ISO 9000: 2005 Quality Management Systems. Fundamentals and vocabulary 3

SUPPLY CHAIN • Ensures safety Maintains Traceability of products supplied • Supports the continuity of production activities • Protects against counterfeit products Allows copyright protection of manufacturer and brand protection 4

Traceability in Supply Chain The traceability system allows to: • reduce the risk of hazards in the production process, quickly respond to unusual situations • Identify all potentially hazardous products, to simplify the review and withdrawal at any stage of its life cycle • much faster track in the opposite direction of the stepwise movement of goods to the source of potentially hazardous substances that have led to negative consequences • to strengthen the control on identified high risk areas to prevent similar problems in the future • to minimize financial losses from product recall, as only certain batches may be reviewed 5

The system of product identification and Traceability provides the following tasks: • Identification of incoming materials and components, labeling of materials and components in accordance with the rules of identification set at the enterprise • Tracking the usage of materials and components in order to eliminate the production of products and materials that do not meet the requirements • Marking the finished product a unique label - products, packaging, party • Tracking of shipment and usage of finished products at the consumer market Requirement for traceability of products at any stage of the production is an integral part of quality management system in accordance with ISO 9001 6*

ECE Working Group on Standardization Policies and Cooperation on regulatory issues (WP 6) Recommendations. Usage of market surveillance infrastructure as an additional tool for consumers and users protection against counterfeit goods and products • Health protection • Public safety • Protection of Intellectual Property Rights "Providing opportunities for market surveillance authorities to fulfil regulatory functions by applying technical regulations and international standards, including the creation of safety management and traceability system of the supply chain of goods, identification, assessment of security threats and risks, as well as Electronic Data Interchange for administrative, commercial and transportation purposes. . . " Proposal of Belarus 7*
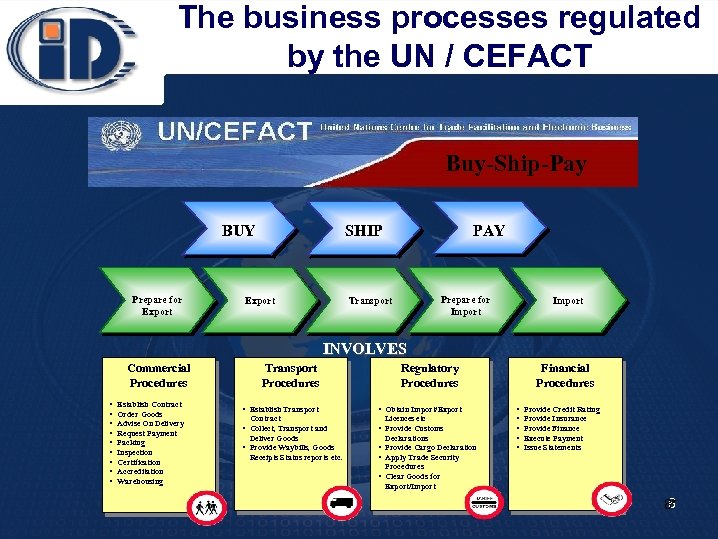
The business processes regulated by the UN / CEFACT Buy-Ship-Pay BUY Prepare for Export PAY SHIP Export Prepare for Import Transport Import INVOLVES Commercial Procedures • • • Establish Contract Order Goods Advise On Delivery Request Payment Packing Inspection Certification Accreditation Warehousing Transport Procedures • Establish Transport Contract • Collect, Transport and Deliver Goods • Provide Waybills, Goods Receipts Status reports etc. Regulatory Procedures • Obtain Import/Export • • Licences etc Provide Customs Declarations Provide Cargo Declaration Apply Trade Security Procedures Clear Goods for Export/Import Financial Procedures • • • Provide Credit Rating Provide Insurance Provide Finance Execute Payment Issue Statements 8 8*

Multiplicity of approaches to traceability – complicated interaction and huge total expenditure • Multiplicity of approaches to identification of objects and products of various economic fields (agriculture, industrial production, food, pharmaceutical production, etc. ) impedes traceability in the chain “manufacture-shipmentdistribution-sale-realization-utilization”, makes it difficult to create unified national and international on-line platforms for Tracking and Tracing of production and generates complicated interaction of the regulatory bodies and business which causes huge total expenditure. 9*
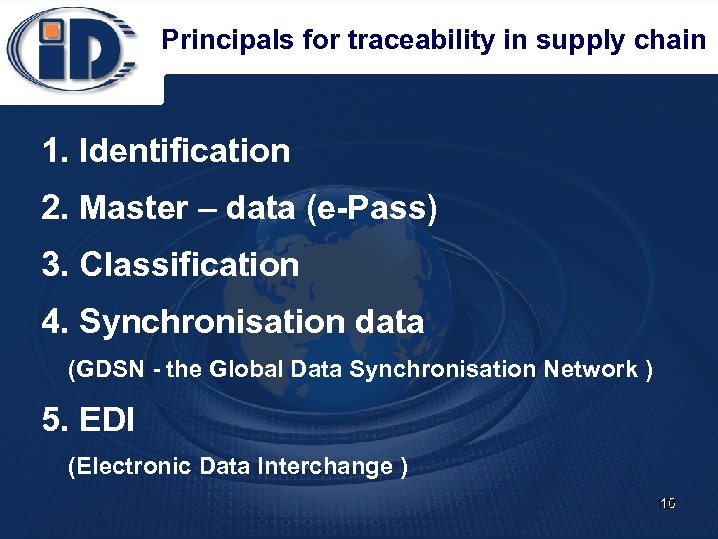
Principals for traceability in supply chain 1. Identification 2. Master – data (e-Pass) 3. Classification 4. Synchronisation data (GDSN - the Global Data Synchronisation Network ) 5. EDI (Electronic Data Interchange ) 10 10*
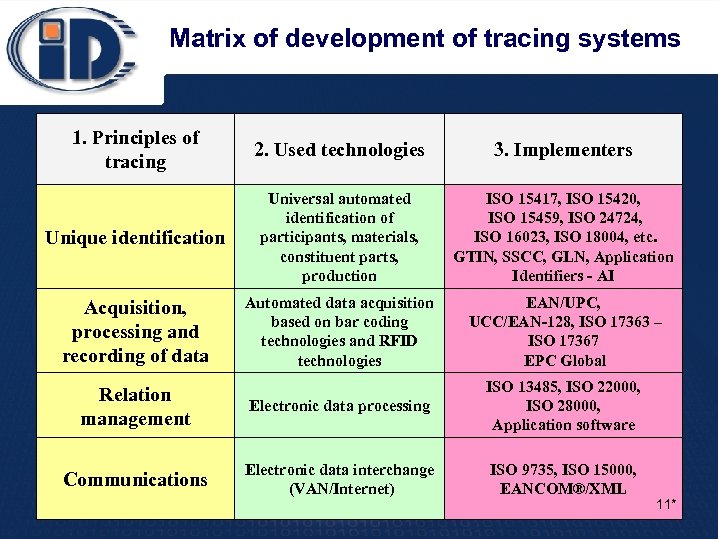
Matrix of development of tracing systems 1. Principles of tracing 2. Used technologies 3. Implementers Unique identification Universal automated identification of participants, materials, constituent parts, production ISO 15417, ISO 15420, ISO 15459, ISO 24724, ISO 16023, ISO 18004, etc. GTIN, SSCC, GLN, Application Identifiers - AI Acquisition, processing and recording of data Automated data acquisition based on bar coding technologies and RFID technologies EAN/UPC, UCC/EAN-128, ISO 17363 – ISO 17367 EPC Global Relation management Electronic data processing ISO 13485, ISO 22000, ISO 28000, Application software Communications Electronic data interchange (VAN/Internet) ISO 9735, ISO 15000, EANCOM®/XML 11*
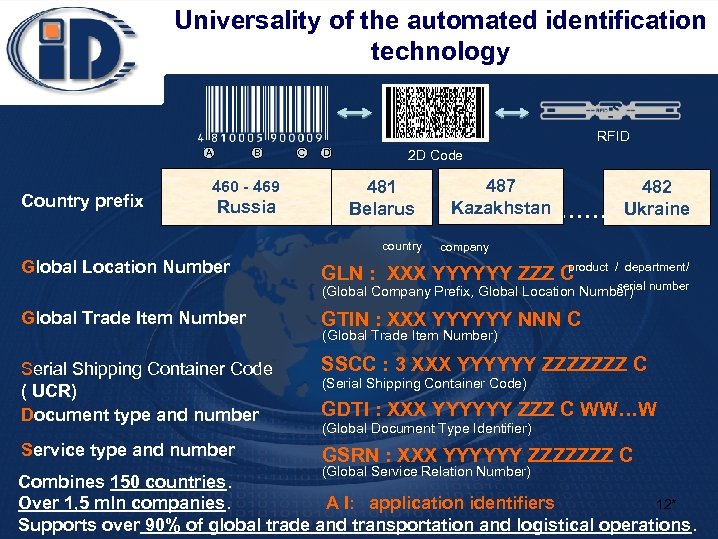
Universality of the automated identification technology RFID A Country prefix B 460 - 469 Russia C D 2 D Code 481 Belarus country Global Location Number 487 Kazakhstan …… 482 Ukraine company product GLN : ХХХ YYYYYY ZZZ C / department/ serial (Global Company Prefix, Global Location Number) number Global Trade Item Number GTIN : XXX YYYYYY NNN C Serial Shipping Container Code ( UCR) Document type and number SSCC : 3 XXX YYYYYY ZZZZZZZ C Service type and number (Global Trade Item Number) (Serial Shipping Container Code) GDTI : XXX YYYYYY ZZZ C WW…W (Global Document Type Identifier) GSRN : XXX YYYYYY ZZZZZZZ C (Global Service Relation Number) Combines 150 countries. 12* Over 1, 5 mln companies. A I: application identifiers Supports over 90% of global trade and transportation and logistical operations.

Objectives of the Belarus project «e. Pass» • Form a public electronic resource containing identification and description of the products formed in accordance with the international standards using “Single window”, which will provide all participants of goods distribution networks including regulatory bodies, enterprises and final customers with the necessary and sufficient information about the product, its quality and safety • Create national information and technology platform for interaction of partners in the chain “manufactureshipment-distribution-sale-realization-utilization”, which will allow product traceability • Systemize approaches and accelerate large-scale implementation of the e-commerce systems based on the unified formats and standards of the electronic data interchange recommended by the UN/CEFACT. 13*
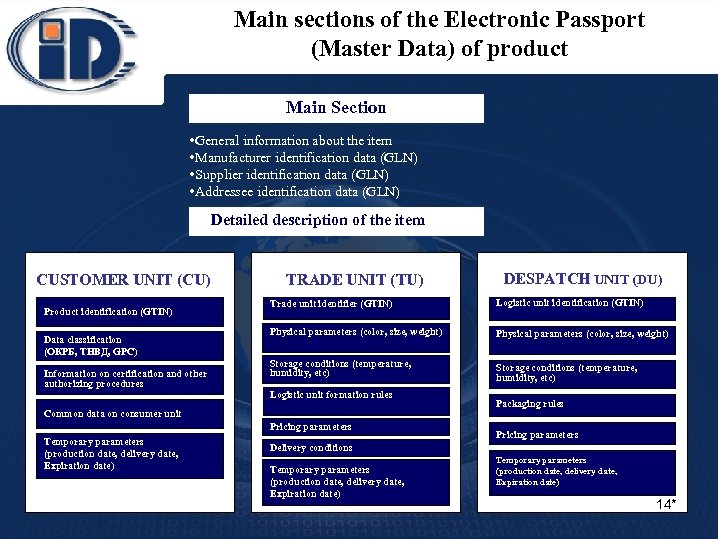
Main sections of the Electronic Passport (Master Data) of product Main Section • General information about the item • Manufacturer identification data (GLN) • Supplier identification data (GLN) • Addressee identification data (GLN) Detailed description of the item CUSTOMER UNIT (CU) Product identification (GTIN) Data classification (ОКРБ, ТНВД, GPC) Information on certification and other authorizing procedures TRADE UNIT (TU) Trade unit identifier (GTIN) Logistic unit identification (GTIN) Physical parameters (color, size, weight) Storage conditions (temperature, humidity, etc) Logistic unit formation rules Common data on consumer unit Pricing parameters Temporary parameters (production date, delivery date, Expiration date) DESPATCH UNIT (DU) Packaging rules Pricing parameters Delivery conditions Temporary parameters (production date, delivery date, Expiration date) 14 14*
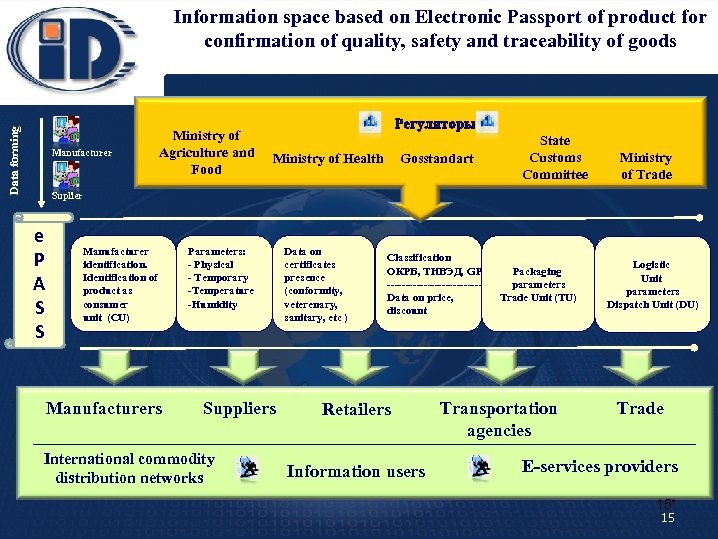
Data forming Information space based on Electronic Passport of product for confirmation of quality, safety and traceability of goods Manufacturer Ministry of Agriculture and Food Ministry of Health Gosstandart State Customs Committee Ministry of Trade Suplier e P A S S Manufacturer identification. Identification of product as consumer unit (CU) Manufacturers Parameters: - Physical - Temporary -Temperature -Humidity Suppliers International commodity distribution networks Data on certificates presence (conformity, veterenary, sanitary, etc ) Classification ОКРБ, ТНВЭД, GPC Packaging -------------parameters Data on price, Trade Unit (TU) discount Retailers Information users Transportation agencies Logistic Unit parameters Dispatch Unit (DU) Trade E-services providers 15* 15
16*
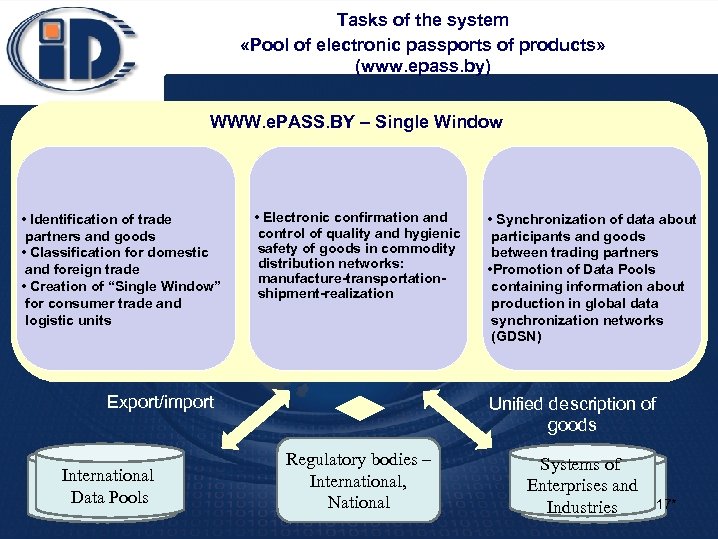
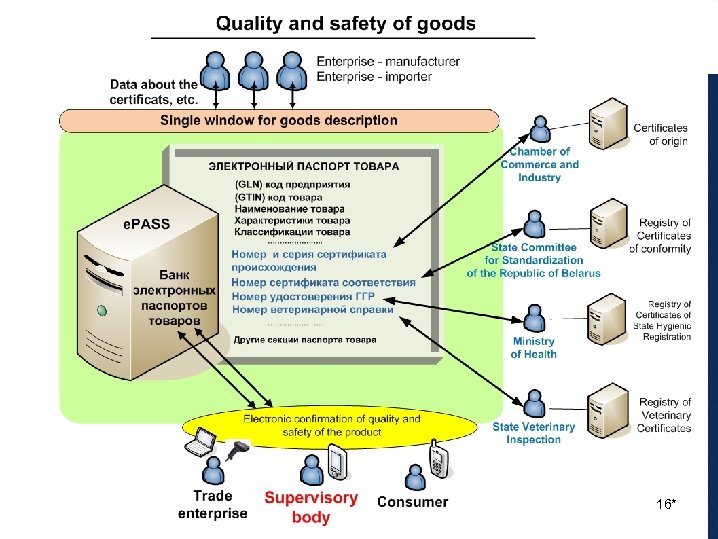
Tasks of the system «Pool of electronic passports of products» (www. epass. by) WWW. e. PASS. BY – Single Window • Identification of trade partners and goods • Classification for domestic and foreign trade • Creation of “Single Window” for consumer trade and logistic units • Electronic confirmation and control of quality and hygienic safety of goods in commodity distribution networks: manufacture-transportationshipment-realization Export/import International Data Pools • Synchronization of data about participants and goods between trading partners • Promotion of Data Pools containing information about production in global data synchronization networks (GDSN) Unified description of goods Regulatory bodies – International, National Systems of Enterprises and Industries 17*
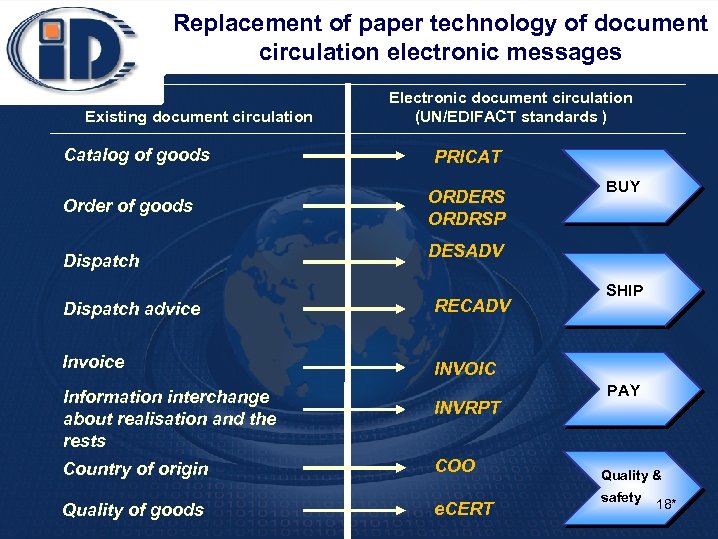
Replacement of paper technology of document circulation electronic messages Existing document circulation Catalog of goods Order of goods Dispatch Electronic document circulation (UN/EDIFACT standards ) PRICAT ORDERS ORDRSP BUY DESADV Dispatch advice RECADV Invoice SHIP INVOIC Information interchange about realisation and the rests INVRPT Country of origin СОО Quality of goods e. CERT PAY Quality & safety 18*
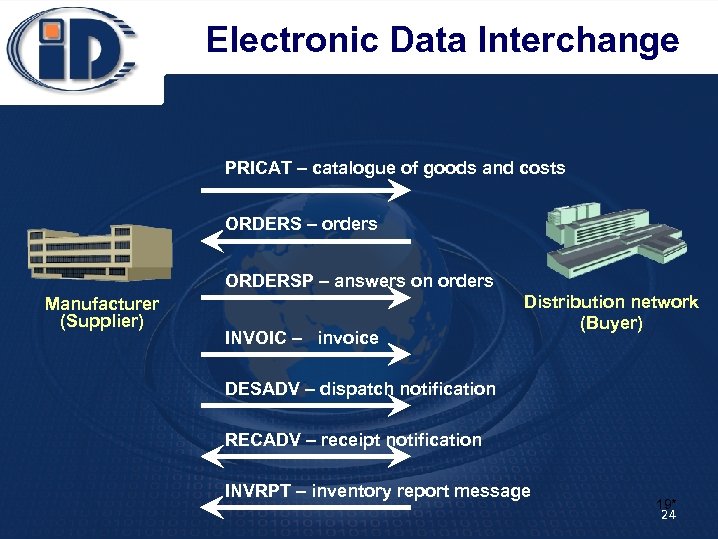
Electronic Data Interchange PRICAT – catalogue of goods and costs ORDERS – orders ORDERSP – answers on orders Manufacturer (Supplier) INVOIC – invoice Distribution network (Buyer) DESADV – dispatch notification RECADV – receipt notification INVRPT – inventory report message 19* 24

THE INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION • UNECE - Committee on Trade UN/CEFACT, WP 6, WP 7 • GS 1 (Automatic identification) • ISO/IEC JTC 1 Information technologies 20

Thank You Victor Dravitsa Director of Center for Identification systems and e-business operations, Vice-Chairman of the Bureau UN Centre for Trade Facilitation and E-business (UN/CEFACT) info@ids. by 21*
f58ab28353eaa1a57aee6cb2e0701822.ppt