493b82c3bed18c98bf8f6303f774b42d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 The Monetary Policy Framework of the Eurosystem, liquidity and Collateral Management De Nederlandsche Bank Richard Derksen Conference Financial Sector of Macedonia on Payments and Securities Settlement Systems Ohrid 24 June 2008 De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
The Monetary Policy Framework of the Eurosystem, liquidity and Collateral Management De Nederlandsche Bank Richard Derksen Conference Financial Sector of Macedonia on Payments and Securities Settlement Systems Ohrid 24 June 2008 De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Topics Contents • The ESCB (Euro System of Central Banks) monetary policy framework • Collateral management framework • Trends in collateral: European and NL • Mobilising collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Topics Contents • The ESCB (Euro System of Central Banks) monetary policy framework • Collateral management framework • Trends in collateral: European and NL • Mobilising collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Monetary policy strategy: Ø Ø Ø Why central banks? What targets have central banks? Why to fight inflation? Monetary policy implementation: Ø How to implement these strategies? Ø Role and functions of official interest rates? Ø How can a central bank generate stable interest rate movements? De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Monetary policy strategy: Ø Ø Ø Why central banks? What targets have central banks? Why to fight inflation? Monetary policy implementation: Ø How to implement these strategies? Ø Role and functions of official interest rates? Ø How can a central bank generate stable interest rate movements? De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Monetary policy strategy: The monetary strategy determines which money market interest rate level is required to maintain price stability. Monetary policy implementation: The operational framework determines how to achieve this interest rate level using the available monetary instruments. De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Monetary policy strategy: The monetary strategy determines which money market interest rate level is required to maintain price stability. Monetary policy implementation: The operational framework determines how to achieve this interest rate level using the available monetary instruments. De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Functions of the operational framework Eurosystem sets and stabilises interest rates in the short term money market in two ways: ØSignalling its monetary policy stance to the money market ØManaging the liquidity situation in the money market De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Functions of the operational framework Eurosystem sets and stabilises interest rates in the short term money market in two ways: ØSignalling its monetary policy stance to the money market ØManaging the liquidity situation in the money market De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 How to set (money market) interest rates? Step 1: determine official interest rates Step 2: make banks dependent on credit by the ECB Step 3: extend credit to banks with the appropriate interest rate Step 4: design framework to stabilise very short-term interest rates De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
How to set (money market) interest rates? Step 1: determine official interest rates Step 2: make banks dependent on credit by the ECB Step 3: extend credit to banks with the appropriate interest rate Step 4: design framework to stabilise very short-term interest rates De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Monetary policy instruments: • Minimum reserve requirements Credit extension to banks via • Open Market Operations Main refinancing operations Long-term refinancing operations Fine-tuning operations Structural operations • Standing facilities Marginal lending facility Deposit facility De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Monetary policy instruments: • Minimum reserve requirements Credit extension to banks via • Open Market Operations Main refinancing operations Long-term refinancing operations Fine-tuning operations Structural operations • Standing facilities Marginal lending facility Deposit facility De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Basic requirements for successful monetary policy implementation: ØConfidence market players ØDemand supply ØRegulatory framework Ø…… De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Basic requirements for successful monetary policy implementation: ØConfidence market players ØDemand supply ØRegulatory framework Ø…… De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Liquidity management Eurosystem: Demand Supply - Reserve – Open market operations requirements - MROs (policy rate) - Excess reserves - LTROs - Autonomous factors - Fine tuning factors (net) - Structural operations - deposit facility – marginal lending facility De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Liquidity management Eurosystem: Demand Supply - Reserve – Open market operations requirements - MROs (policy rate) - Excess reserves - LTROs - Autonomous factors - Fine tuning factors (net) - Structural operations - deposit facility – marginal lending facility De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Liquidity management Eurosystem: Demand Supply = - Reserve (over – Open market operations requirements - MROs (policy rate) a - Excess reserves - LTROs reserve - Autonomous factors mainte- Fine tuning factors (net) nance - Structural operations period) - deposit facility – marginal lending facility De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Liquidity management Eurosystem: Demand Supply = - Reserve (over – Open market operations requirements - MROs (policy rate) a - Excess reserves - LTROs reserve - Autonomous factors mainte- Fine tuning factors (net) nance - Structural operations period) - deposit facility – marginal lending facility De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
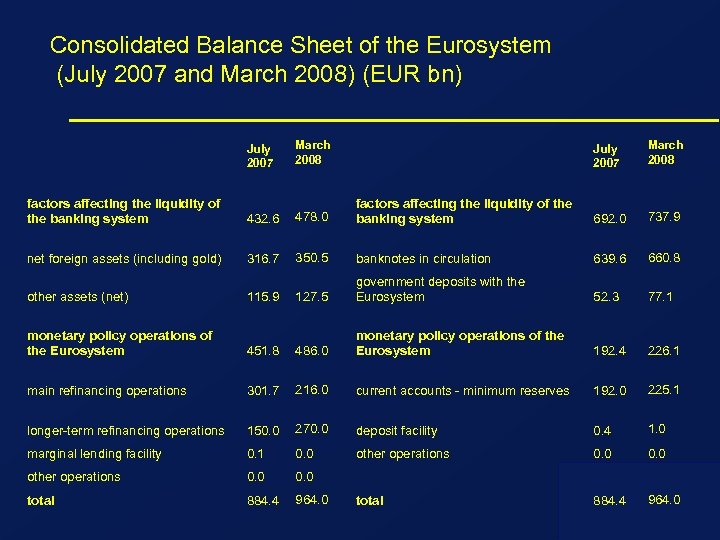 Consolidated Balance Sheet of the Eurosystem (July 2007 and March 2008) (EUR bn) July 2007 March 2008 692. 0 737. 9 factors affecting the liquidity of the banking system 432. 6 478. 0 factors affecting the liquidity of the banking system net foreign assets (including gold) 316. 7 350. 5 banknotes in circulation 639. 6 660. 8 127. 5 government deposits with the Eurosystem 52. 3 77. 1 192. 4 226. 1 other assets (net) 115. 9 monetary policy operations of the Eurosystem 451. 8 486. 0 monetary policy operations of the Eurosystem main refinancing operations 301. 7 216. 0 current accounts - minimum reserves 192. 0 225. 1 longer-term refinancing operations 150. 0 270. 0 deposit facility 0. 4 1. 0 marginal lending facility 0. 1 0. 0 other operations 0. 0 total 884. 4 964. 0 total 964. 0 884. 4 De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Consolidated Balance Sheet of the Eurosystem (July 2007 and March 2008) (EUR bn) July 2007 March 2008 692. 0 737. 9 factors affecting the liquidity of the banking system 432. 6 478. 0 factors affecting the liquidity of the banking system net foreign assets (including gold) 316. 7 350. 5 banknotes in circulation 639. 6 660. 8 127. 5 government deposits with the Eurosystem 52. 3 77. 1 192. 4 226. 1 other assets (net) 115. 9 monetary policy operations of the Eurosystem 451. 8 486. 0 monetary policy operations of the Eurosystem main refinancing operations 301. 7 216. 0 current accounts - minimum reserves 192. 0 225. 1 longer-term refinancing operations 150. 0 270. 0 deposit facility 0. 4 1. 0 marginal lending facility 0. 1 0. 0 other operations 0. 0 total 884. 4 964. 0 total 964. 0 884. 4 De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Future challenges: a) the management of the volatility of short term interest rates b) determining the optimal size and composition of central bank balance sheet c) the appropriate level of communication with the financial markets d) contribute to further integration of financial markets by harmonising and expanding collateral instruments De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Future challenges: a) the management of the volatility of short term interest rates b) determining the optimal size and composition of central bank balance sheet c) the appropriate level of communication with the financial markets d) contribute to further integration of financial markets by harmonising and expanding collateral instruments De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Topics Contents • The ESCB (Euro System of Central Banks) monetary policy framework • Collateral management framework • Trends in collateral: European and NL • Mobilising collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Topics Contents • The ESCB (Euro System of Central Banks) monetary policy framework • Collateral management framework • Trends in collateral: European and NL • Mobilising collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Guiding Principles of the Collateral Framework • Article 18. 1 of the Statute requires all credit operations by the Eurosystem to be “based on adequate collateral”. The concept of adequacy has 2 notions: 1. Collateral must be able to protect the Eurosystem from incurring losses in its credit operations 2. There must be sufficient collateral potentially available to ensure that the Eurosystem can carry out its tasks • To reconcile both notions of “adequate collateral” may not be easy: 1. The range of assets must be broad to ensure the sufficiency of collateral 2. This may be in conflict with the desire for operational efficiency and transparency To what extent compromises on the principle of operational efficiency need to be made depends on the structure of financial markets De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Guiding Principles of the Collateral Framework • Article 18. 1 of the Statute requires all credit operations by the Eurosystem to be “based on adequate collateral”. The concept of adequacy has 2 notions: 1. Collateral must be able to protect the Eurosystem from incurring losses in its credit operations 2. There must be sufficient collateral potentially available to ensure that the Eurosystem can carry out its tasks • To reconcile both notions of “adequate collateral” may not be easy: 1. The range of assets must be broad to ensure the sufficiency of collateral 2. This may be in conflict with the desire for operational efficiency and transparency To what extent compromises on the principle of operational efficiency need to be made depends on the structure of financial markets De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Single list of collateral l l Operational on January 1 st, 2007 Drawbacks 2 -tiers list (1999 -2006): heterogeneity and no transparency 2 asset classes: l marketable assets and l non-marketable assets (no quality difference) Marketable assets: high credit standards (single A↑), located in the euro area, denomination euro De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Single list of collateral l l Operational on January 1 st, 2007 Drawbacks 2 -tiers list (1999 -2006): heterogeneity and no transparency 2 asset classes: l marketable assets and l non-marketable assets (no quality difference) Marketable assets: high credit standards (single A↑), located in the euro area, denomination euro De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Single list of collateral l Marketable assets: listed on regulated markets or certain accepted non-regulated markets Non-marketable assets: credit claims and Irish non-marketable retail mortgage backed debt instruments, no market criterion For both asset classes -> Eurosystem credit assessment framework De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Single list of collateral l Marketable assets: listed on regulated markets or certain accepted non-regulated markets Non-marketable assets: credit claims and Irish non-marketable retail mortgage backed debt instruments, no market criterion For both asset classes -> Eurosystem credit assessment framework De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
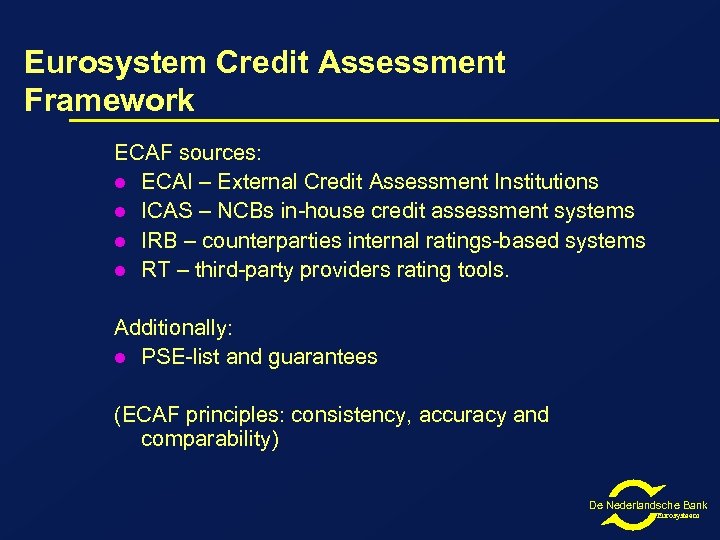 Eurosystem Credit Assessment Framework ECAF sources: l ECAI – External Credit Assessment Institutions l ICAS – NCBs in-house credit assessment systems l IRB – counterparties internal ratings-based systems l RT – third-party providers rating tools. Additionally: l PSE-list and guarantees (ECAF principles: consistency, accuracy and comparability) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Eurosystem Credit Assessment Framework ECAF sources: l ECAI – External Credit Assessment Institutions l ICAS – NCBs in-house credit assessment systems l IRB – counterparties internal ratings-based systems l RT – third-party providers rating tools. Additionally: l PSE-list and guarantees (ECAF principles: consistency, accuracy and comparability) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
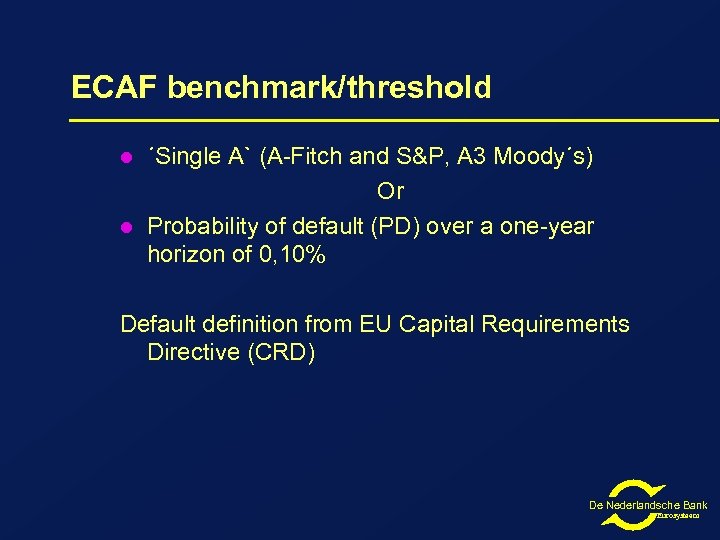 ECAF benchmark/threshold l l ´Single A` (A-Fitch and S&P, A 3 Moody´s) Or Probability of default (PD) over a one-year horizon of 0, 10% Default definition from EU Capital Requirements Directive (CRD) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
ECAF benchmark/threshold l l ´Single A` (A-Fitch and S&P, A 3 Moody´s) Or Probability of default (PD) over a one-year horizon of 0, 10% Default definition from EU Capital Requirements Directive (CRD) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Valuation principles l Marketable assets l l Rules for non-availability of prices l l Define the most representative price source Treatment of income flows Non-marketable assets l Theoretical price or outstanding amount De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Valuation principles l Marketable assets l l Rules for non-availability of prices l l Define the most representative price source Treatment of income flows Non-marketable assets l Theoretical price or outstanding amount De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Present collateral framework (NL) l l l Legal technique: pledge Pool of collateral - total market value minus haircut (+interest) = credit line - integrated use of the collateral pool on request of credit institutions like supporting services, e. g. CCP margin and guarantees for special purposes Legal setting credit claims: public pledge, physical delivery loan documentation, ex ante notification of debtor [Situation before EMU/1999: extensive collateral list: equities, private loans, loans in other currencies] De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Present collateral framework (NL) l l l Legal technique: pledge Pool of collateral - total market value minus haircut (+interest) = credit line - integrated use of the collateral pool on request of credit institutions like supporting services, e. g. CCP margin and guarantees for special purposes Legal setting credit claims: public pledge, physical delivery loan documentation, ex ante notification of debtor [Situation before EMU/1999: extensive collateral list: equities, private loans, loans in other currencies] De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Stabilising features of the Eurosystem’s collateral framework Key features of the Eurosystem’s collateral framework: l l l Acceptance of a broad range of debt instruments as collateral No collateral differentiation between tender operations and standing facilities Single auction rate applicable to different types of collateral in tender operations Performance during the turmoil: l l l Sufficiency of collateral ensured, facilitating broad access to central bank money Low consumption of high opportunity cost collateral Mitigation of asset refinancing risk through large scale acceptance of ABS in the main refinancing operations De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Stabilising features of the Eurosystem’s collateral framework Key features of the Eurosystem’s collateral framework: l l l Acceptance of a broad range of debt instruments as collateral No collateral differentiation between tender operations and standing facilities Single auction rate applicable to different types of collateral in tender operations Performance during the turmoil: l l l Sufficiency of collateral ensured, facilitating broad access to central bank money Low consumption of high opportunity cost collateral Mitigation of asset refinancing risk through large scale acceptance of ABS in the main refinancing operations De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Topics Contents • The ESCB (Euro System of Central Banks) monetary policy framework • Collateral management framework • Trends in collateral: European and NL • Mobilising collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Topics Contents • The ESCB (Euro System of Central Banks) monetary policy framework • Collateral management framework • Trends in collateral: European and NL • Mobilising collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
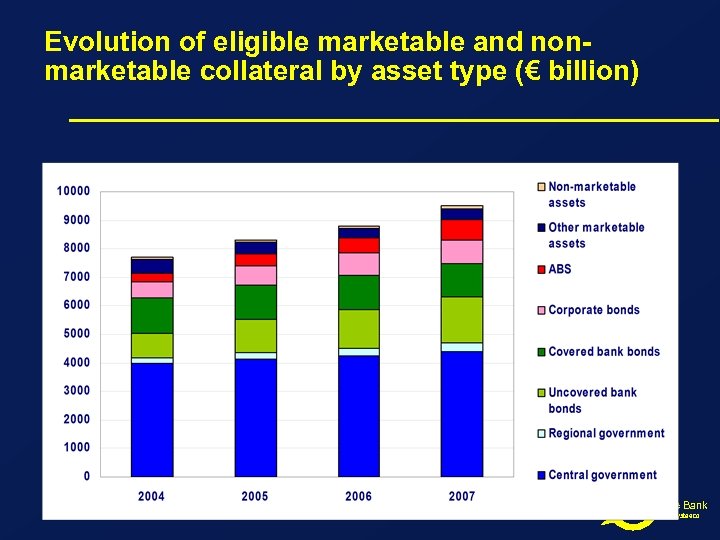 Evolution of eligible marketable and nonmarketable collateral by asset type (€ billion) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Evolution of eligible marketable and nonmarketable collateral by asset type (€ billion) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
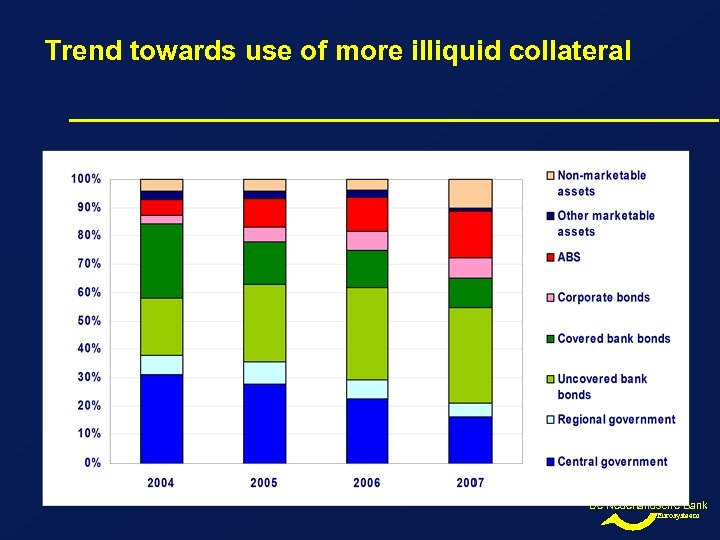 Trend towards use of more illiquid collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Trend towards use of more illiquid collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
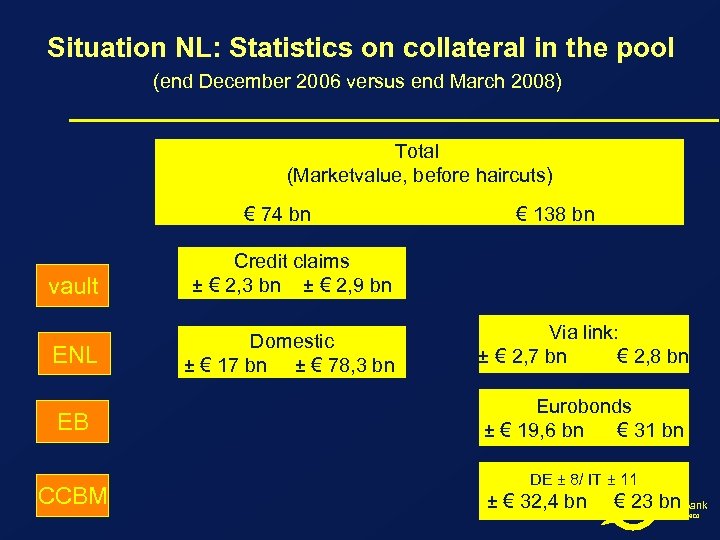 Situation NL: Statistics on collateral in the pool (end December 2006 versus end March 2008) Total (Marketvalue, before haircuts) € 74 bn € 138 bn vault Credit claims ± € 2, 3 bn ± € 2, 9 bn ENL Domestic ± € 17 bn ± € 78, 3 bn EB CCBM Via link: ± € 2, 7 bn € 2, 8 bn Eurobonds ± € 19, 6 bn € 31 bn DE ± 8/ IT ± 11 ± € 32, 4 bn € 23 bn De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Situation NL: Statistics on collateral in the pool (end December 2006 versus end March 2008) Total (Marketvalue, before haircuts) € 74 bn € 138 bn vault Credit claims ± € 2, 3 bn ± € 2, 9 bn ENL Domestic ± € 17 bn ± € 78, 3 bn EB CCBM Via link: ± € 2, 7 bn € 2, 8 bn Eurobonds ± € 19, 6 bn € 31 bn DE ± 8/ IT ± 11 ± € 32, 4 bn € 23 bn De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
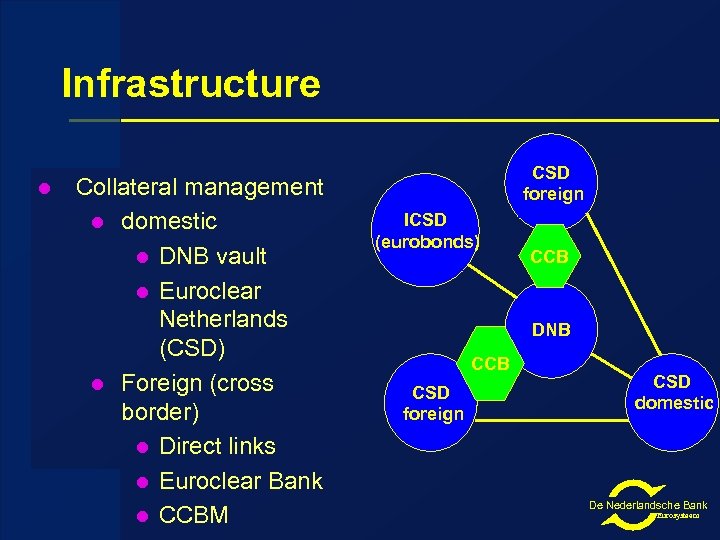 Infrastructure l Collateral management l domestic l DNB vault l Euroclear Netherlands (CSD) l Foreign (cross border) l Direct links l Euroclear Bank l CCBM CSD foreign ICSD (eurobonds) CCB DNB CCB CSD foreign CSD domestic De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Infrastructure l Collateral management l domestic l DNB vault l Euroclear Netherlands (CSD) l Foreign (cross border) l Direct links l Euroclear Bank l CCBM CSD foreign ICSD (eurobonds) CCB DNB CCB CSD foreign CSD domestic De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
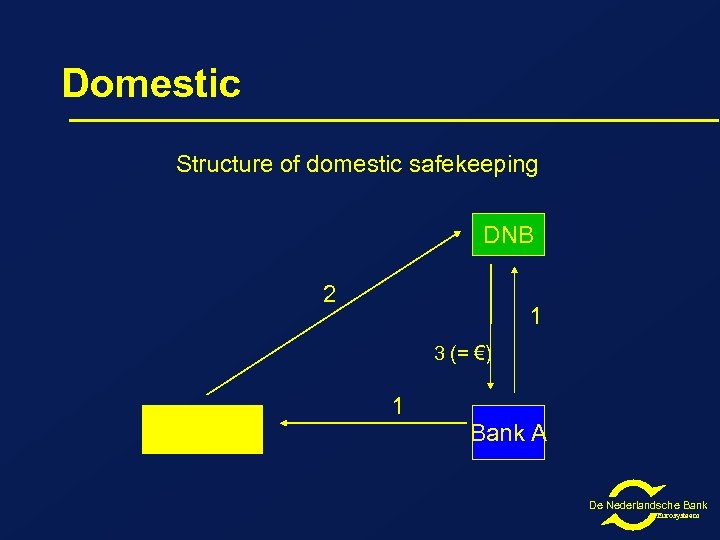 Domestic Structure of domestic safekeeping DNB 2 1 3 (= €) Euroclear Netherlands 1 Bank A De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Domestic Structure of domestic safekeeping DNB 2 1 3 (= €) Euroclear Netherlands 1 Bank A De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
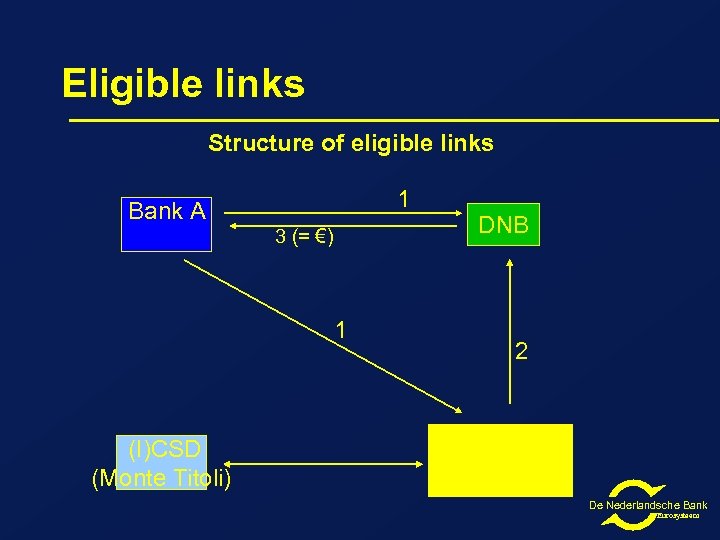 Eligible links Structure of eligible links 1 Bank A 3 (= €) 1 (I)CSD (Monte Titoli) DNB 2 Euroclear Netherlands De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Eligible links Structure of eligible links 1 Bank A 3 (= €) 1 (I)CSD (Monte Titoli) DNB 2 Euroclear Netherlands De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 CCBM l l Dutch Eurosystem counterparty sends Swift MT 540 to DNB (and MT 542 to its own custodian) DNB sends MT 540 to the respective CCB Upon receipt of the securities, the CCB sends an MT 544 to DNB updates its collateral management system and increases the credit facility for the Dutch Eurosystem counterparty De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
CCBM l l Dutch Eurosystem counterparty sends Swift MT 540 to DNB (and MT 542 to its own custodian) DNB sends MT 540 to the respective CCB Upon receipt of the securities, the CCB sends an MT 544 to DNB updates its collateral management system and increases the credit facility for the Dutch Eurosystem counterparty De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
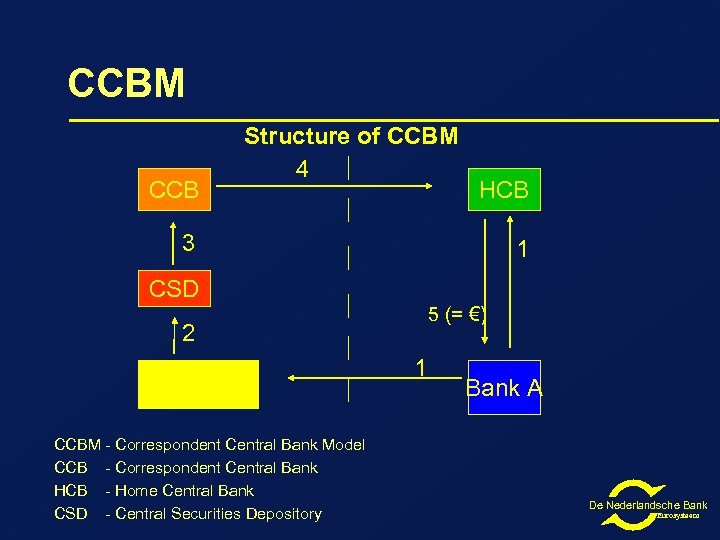 CCBM CCB Structure of CCBM 4 HCB 3 1 CSD 5 (= €) 2 Custodian/ Agent CCBM - Correspondent Central Bank Model CCB - Correspondent Central Bank HCB - Home Central Bank CSD - Central Securities Depository 1 Bank A De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
CCBM CCB Structure of CCBM 4 HCB 3 1 CSD 5 (= €) 2 Custodian/ Agent CCBM - Correspondent Central Bank Model CCB - Correspondent Central Bank HCB - Home Central Bank CSD - Central Securities Depository 1 Bank A De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
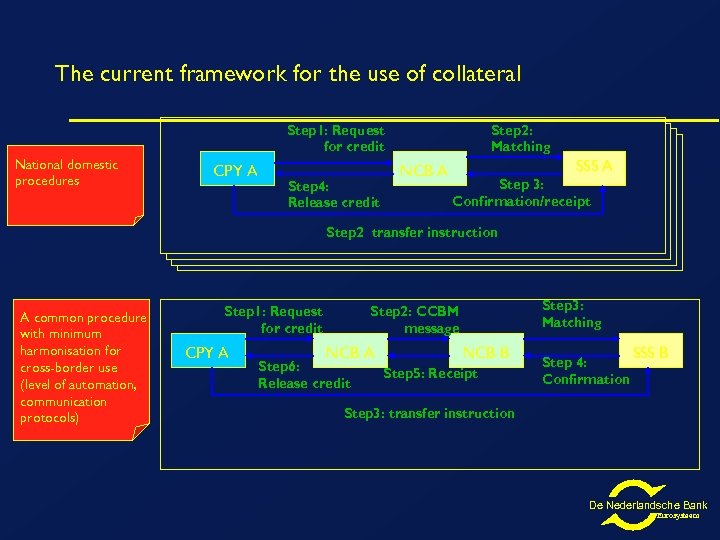 The current framework for the use of collateral Step 1: Request for credit National domestic procedures CPY A Step 4: Release credit Step 2: Matching NCB A SSS A Step 3: Confirmation/receipt Step 2: transfer instruction A common procedure with minimum harmonisation for cross-border use (level of automation, communication protocols) Step 1: Request for credit CPY A Step 3: Matching Step 2: CCBM message NCB A Step 6: Release credit NCB B Step 5: Receipt Step 4: Confirmation SSS B Step 3: transfer instruction De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
The current framework for the use of collateral Step 1: Request for credit National domestic procedures CPY A Step 4: Release credit Step 2: Matching NCB A SSS A Step 3: Confirmation/receipt Step 2: transfer instruction A common procedure with minimum harmonisation for cross-border use (level of automation, communication protocols) Step 1: Request for credit CPY A Step 3: Matching Step 2: CCBM message NCB A Step 6: Release credit NCB B Step 5: Receipt Step 4: Confirmation SSS B Step 3: transfer instruction De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
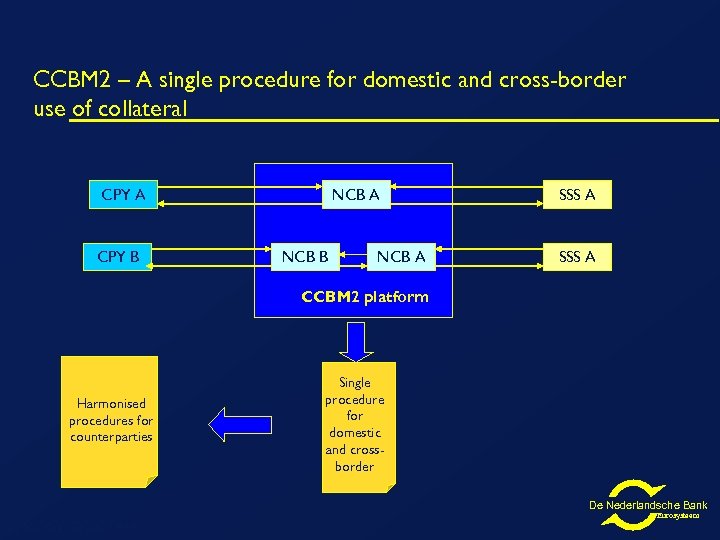 CCBM 2 – A single procedure for domestic and cross-border use of collateral CPY A CPY B NCB A NCB B NCB A SSS A CCBM 2 platform Harmonised procedures for counterparties Single procedure for domestic and crossborder De Nederlandsche Bank PSSC/SWG/2007/414 Eurosysteem
CCBM 2 – A single procedure for domestic and cross-border use of collateral CPY A CPY B NCB A NCB B NCB A SSS A CCBM 2 platform Harmonised procedures for counterparties Single procedure for domestic and crossborder De Nederlandsche Bank PSSC/SWG/2007/414 Eurosysteem
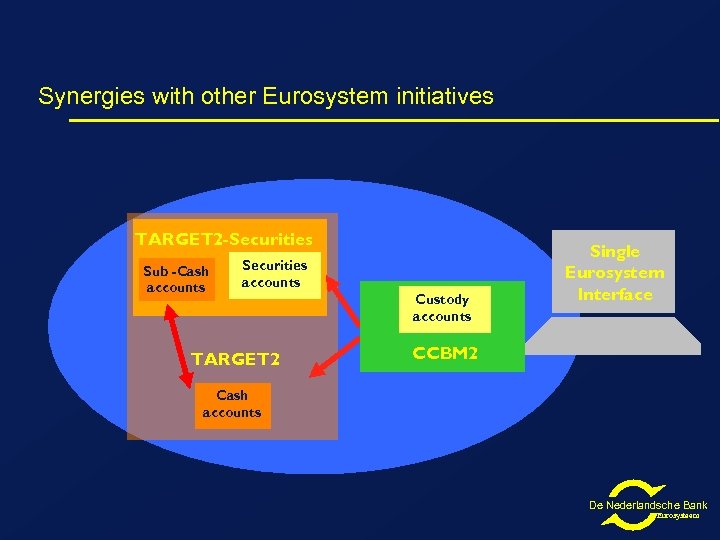 Synergies with other Eurosystem initiatives TARGET 2 -Securities Sub -Cash accounts Securities accounts TARGET 2 Custody accounts Single Eurosystem Interface CCBM 2 Cash accounts De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Synergies with other Eurosystem initiatives TARGET 2 -Securities Sub -Cash accounts Securities accounts TARGET 2 Custody accounts Single Eurosystem Interface CCBM 2 Cash accounts De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Summing up l l Basics on monetary and collateral framework Single list and ECAF NL situation Collateral mobilisation De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Summing up l l Basics on monetary and collateral framework Single list and ECAF NL situation Collateral mobilisation De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Thank you very much ! Qu€stions? De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Thank you very much ! Qu€stions? De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Some detailed slides De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Some detailed slides De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Minimum reserve requirements: ØDuring a reserve maintenance period banks have on average to maintain a certain percentage of certain banks’ balance sheet items (2%) on an account at the central banks ØCreate / increase money market shortage (counterparties vis à vis Eurosystem) ØAveraging feature helps stabilising overnight and intraday money market rates De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Minimum reserve requirements: ØDuring a reserve maintenance period banks have on average to maintain a certain percentage of certain banks’ balance sheet items (2%) on an account at the central banks ØCreate / increase money market shortage (counterparties vis à vis Eurosystem) ØAveraging feature helps stabilising overnight and intraday money market rates De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Minimum reserve requirements: ØInterest paid over required reserves ØExcess reserves not remunerated, giving incentive to go to the market ØPenalty in case of non-compliance ØBanks with large payment flows prefer large reserve requirements De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Minimum reserve requirements: ØInterest paid over required reserves ØExcess reserves not remunerated, giving incentive to go to the market ØPenalty in case of non-compliance ØBanks with large payment flows prefer large reserve requirements De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Minimum reserve requirements: ØCurrent amount reserve requirements for the Eurosystem ± EUR 202 billion (The Netherlands ± EUR 20 billion, largest 5 counterparties account for ± 90% in NL) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Minimum reserve requirements: ØCurrent amount reserve requirements for the Eurosystem ± EUR 202 billion (The Netherlands ± EUR 20 billion, largest 5 counterparties account for ± 90% in NL) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Open markt operations: ØMain refinancing operations (MROs) about 70% of total credit extension ØLong term refinancing transactions (LTROs) about 30% of total credit extension ØFine-tuning operations (FTOs) nowadays last day of the reserve maintenance period ØStructural operations De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Open markt operations: ØMain refinancing operations (MROs) about 70% of total credit extension ØLong term refinancing transactions (LTROs) about 30% of total credit extension ØFine-tuning operations (FTOs) nowadays last day of the reserve maintenance period ØStructural operations De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Main refinancing operations (MROs): ØOpen for all banks with a minimum reserve requirement (cf US system of primary dealers) ØInterest rate on MROs is main ECB interest rate ØMain source credit extension Eurosystem ØVariable rate tender (opposite to fixed rate tender) ØMarginal rate few base points above min. bidrate De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Main refinancing operations (MROs): ØOpen for all banks with a minimum reserve requirement (cf US system of primary dealers) ØInterest rate on MROs is main ECB interest rate ØMain source credit extension Eurosystem ØVariable rate tender (opposite to fixed rate tender) ØMarginal rate few base points above min. bidrate De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
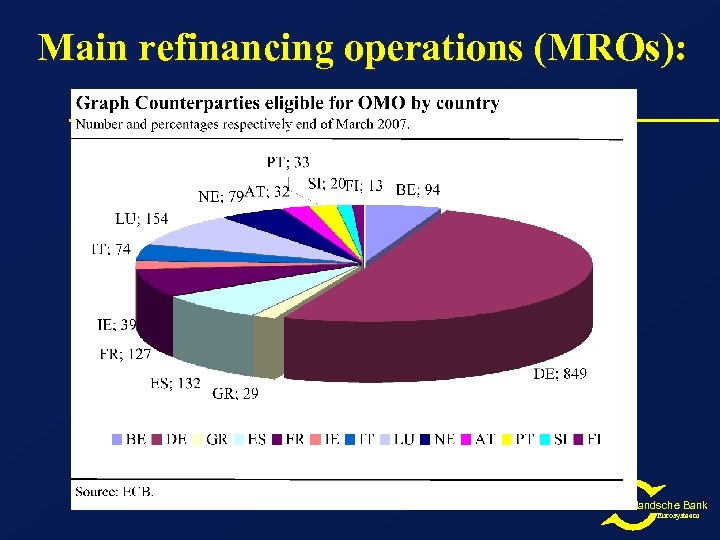 Main refinancing operations (MROs): De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Main refinancing operations (MROs): De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Long term refinancing transactions (LTROs): ØLiquidity providing ØMonthly auction via variable rate tender ØThree month maturity De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Long term refinancing transactions (LTROs): ØLiquidity providing ØMonthly auction via variable rate tender ØThree month maturity De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Long term refinancing transactions (LTROs): ØReverse transactions ØPre-announced 50 billion euro size each ØParticularly designed for smaller banks ØAmount allotted is sufficient to balance supply and demand De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Long term refinancing transactions (LTROs): ØReverse transactions ØPre-announced 50 billion euro size each ØParticularly designed for smaller banks ØAmount allotted is sufficient to balance supply and demand De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Fine-tuning operations (FTOs): ØSmooth out effects on interest rates of unexpected liquidity fluctuations ØLiquidity providing or liquidity absorbing ØAd hoc basis and regular basis i. e. last day of a reserve maintenance period De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Fine-tuning operations (FTOs): ØSmooth out effects on interest rates of unexpected liquidity fluctuations ØLiquidity providing or liquidity absorbing ØAd hoc basis and regular basis i. e. last day of a reserve maintenance period De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Fine-tuning operations (FTOs): ØShort-term basis ØTender or bilateral operation ØSelected group of fine-tuning counterparties De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Fine-tuning operations (FTOs): ØShort-term basis ØTender or bilateral operation ØSelected group of fine-tuning counterparties De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Structural operations: ØLiquidity-providing or liquidity-absorbing ØConducted on an ad hoc basis (never used yet) ØMaturity not standardised ØTender or bilateral operations De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Structural operations: ØLiquidity-providing or liquidity-absorbing ØConducted on an ad hoc basis (never used yet) ØMaturity not standardised ØTender or bilateral operations De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Types of open market operations: ØReverse transactions ØOutright transactions ØForeign exchange swaps ØCollection of fixed-term deposits ØIssuance of ECB debt certificates De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Types of open market operations: ØReverse transactions ØOutright transactions ØForeign exchange swaps ØCollection of fixed-term deposits ØIssuance of ECB debt certificates De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Stabilizing money market interest rates: ØFine-tuning instruments ØAveraging facility on the reserve requirements ØStanding facilities De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Stabilizing money market interest rates: ØFine-tuning instruments ØAveraging facility on the reserve requirements ØStanding facilities De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Standing facilities : Deposit facility overnight liquidity absorption at relatively low (official) interest rate floor for market rates normally no restrictions Marginal lending facility overnight liquidity provision at relatively high (official) interest rate ceiling for market rates normally no restrictions except collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Standing facilities : Deposit facility overnight liquidity absorption at relatively low (official) interest rate floor for market rates normally no restrictions Marginal lending facility overnight liquidity provision at relatively high (official) interest rate ceiling for market rates normally no restrictions except collateral De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
 Standing facilities : General: ØProviding / absorbing liquidity at the discretion of banks/at the initiative of counterparties ØLimiting maximum interest volatility ØSignal general stance of monetary policy De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Standing facilities : General: ØProviding / absorbing liquidity at the discretion of banks/at the initiative of counterparties ØLimiting maximum interest volatility ØSignal general stance of monetary policy De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
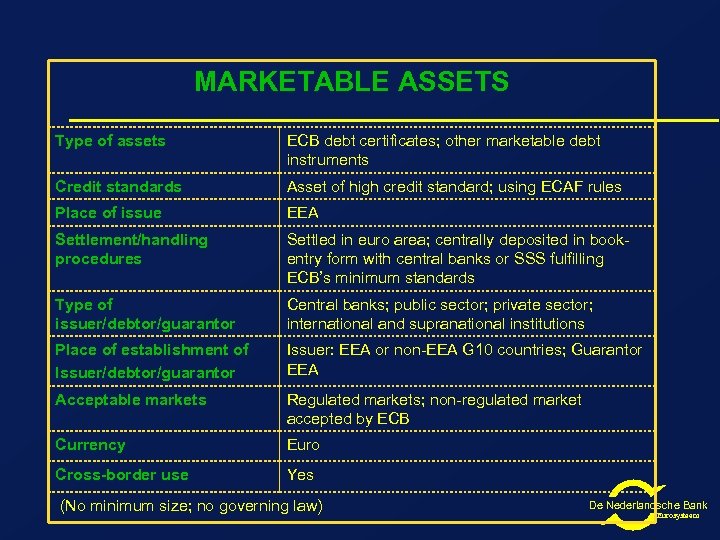 MARKETABLE ASSETS Type of assets ECB debt certificates; other marketable debt instruments Credit standards Asset of high credit standard; using ECAF rules Place of issue EEA Settlement/handling procedures Settled in euro area; centrally deposited in bookentry form with central banks or SSS fulfilling ECB’s minimum standards Type of issuer/debtor/guarantor Central banks; public sector; private sector; international and supranational institutions Place of establishment of Issuer/debtor/guarantor Issuer: EEA or non-EEA G 10 countries; Guarantor EEA Acceptable markets Regulated markets; non-regulated market accepted by ECB Currency Euro Cross-border use Yes (No minimum size; no governing law) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
MARKETABLE ASSETS Type of assets ECB debt certificates; other marketable debt instruments Credit standards Asset of high credit standard; using ECAF rules Place of issue EEA Settlement/handling procedures Settled in euro area; centrally deposited in bookentry form with central banks or SSS fulfilling ECB’s minimum standards Type of issuer/debtor/guarantor Central banks; public sector; private sector; international and supranational institutions Place of establishment of Issuer/debtor/guarantor Issuer: EEA or non-EEA G 10 countries; Guarantor EEA Acceptable markets Regulated markets; non-regulated market accepted by ECB Currency Euro Cross-border use Yes (No minimum size; no governing law) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
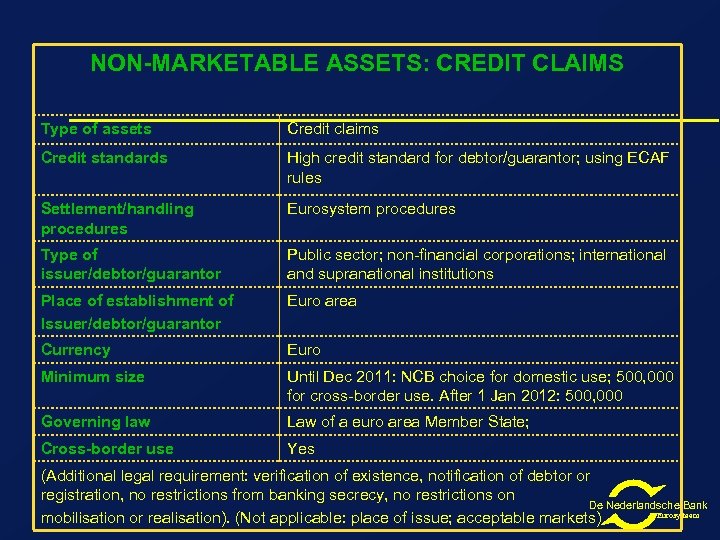 NON-MARKETABLE ASSETS: CREDIT CLAIMS Type of assets Credit claims Credit standards High credit standard for debtor/guarantor; using ECAF rules Settlement/handling procedures Eurosystem procedures Type of issuer/debtor/guarantor Public sector; non-financial corporations; international and supranational institutions Place of establishment of Issuer/debtor/guarantor Euro area Currency Euro Minimum size Until Dec 2011: NCB choice for domestic use; 500, 000 for cross-border use. After 1 Jan 2012: 500, 000 Governing law Law of a euro area Member State; Cross-border use Yes (Additional legal requirement: verification of existence, notification of debtor or registration, no restrictions from banking secrecy, no restrictions on De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem mobilisation or realisation). (Not applicable: place of issue; acceptable markets)
NON-MARKETABLE ASSETS: CREDIT CLAIMS Type of assets Credit claims Credit standards High credit standard for debtor/guarantor; using ECAF rules Settlement/handling procedures Eurosystem procedures Type of issuer/debtor/guarantor Public sector; non-financial corporations; international and supranational institutions Place of establishment of Issuer/debtor/guarantor Euro area Currency Euro Minimum size Until Dec 2011: NCB choice for domestic use; 500, 000 for cross-border use. After 1 Jan 2012: 500, 000 Governing law Law of a euro area Member State; Cross-border use Yes (Additional legal requirement: verification of existence, notification of debtor or registration, no restrictions from banking secrecy, no restrictions on De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem mobilisation or realisation). (Not applicable: place of issue; acceptable markets)
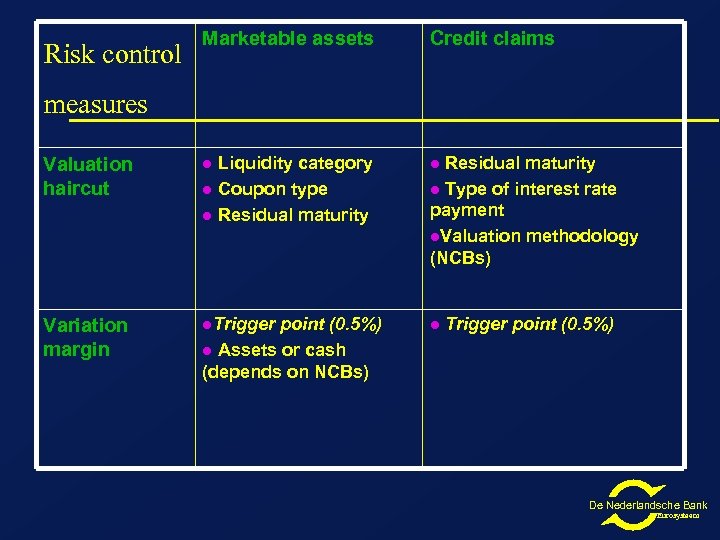 Risk control Marketable assets Credit claims measures Valuation haircut l Liquidity category l Coupon type l Residual maturity l Variation margin l. Trigger l point (0. 5%) l Assets or cash (depends on NCBs) Residual maturity l Type of interest rate payment l. Valuation methodology (NCBs) Trigger point (0. 5%) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem
Risk control Marketable assets Credit claims measures Valuation haircut l Liquidity category l Coupon type l Residual maturity l Variation margin l. Trigger l point (0. 5%) l Assets or cash (depends on NCBs) Residual maturity l Type of interest rate payment l. Valuation methodology (NCBs) Trigger point (0. 5%) De Nederlandsche Bank Eurosysteem


