Презентация Microsoft Office PowerPoint.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 15
 THE MONETARY AND CREDIT POLICY OF THE NATIONAL BANK OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN AND ITS INFLUENCE ON THE FINANCIAL MARKET Done by: Aimanova Aruana
THE MONETARY AND CREDIT POLICY OF THE NATIONAL BANK OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN AND ITS INFLUENCE ON THE FINANCIAL MARKET Done by: Aimanova Aruana
 Content Introduction…………………………………. 3 Chapter I. Theoretical aspects of monetary policy of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan. 1. 1. Theoretical bases of monetary policy…………………. . 5 1. 2. Goals and objectives of the monetary policy………………. . . 7 1. 3. The main tools of monetary policy…………………. . . 9 Chapter II. Analysis of the dynamics of the monetary policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan 2. 1. The main directions of the monetary policy………………. . . 13 2. 2. Analysis of the current antiinflation policy of price stability in the Republic of Kazakhstan in 2012………………………………. . 15 Chapter III. Problems and ways to improve monetary policy in Kazakhstan 3. 1. The main challenges of monetary policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan at the contemporary stage of development……………………. . . 18 3. 2. Ways to solve problems related to the economic estimations…………………………………. . . . 20 Conclusion………………………………. . . ……. 24 List of references……………………………. . . . 26 Appendix…………………………………. . 27
Content Introduction…………………………………. 3 Chapter I. Theoretical aspects of monetary policy of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan. 1. 1. Theoretical bases of monetary policy…………………. . 5 1. 2. Goals and objectives of the monetary policy………………. . . 7 1. 3. The main tools of monetary policy…………………. . . 9 Chapter II. Analysis of the dynamics of the monetary policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan 2. 1. The main directions of the monetary policy………………. . . 13 2. 2. Analysis of the current antiinflation policy of price stability in the Republic of Kazakhstan in 2012………………………………. . 15 Chapter III. Problems and ways to improve monetary policy in Kazakhstan 3. 1. The main challenges of monetary policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan at the contemporary stage of development……………………. . . 18 3. 2. Ways to solve problems related to the economic estimations…………………………………. . . . 20 Conclusion………………………………. . . ……. 24 List of references……………………………. . . . 26 Appendix…………………………………. . 27
 Monetary Policy For each country monetary and credit policy is an integral part of government economic policy aimed at combating with inflation to maintain the rate of the national currency and the normal conditions of the market. Monetary policy is a tool of "fine tuning" of economic conditions. Fundamental objective of monetary policy is helping the economic system to achieve such a level of production which is characterized by full employment and lack of inflation.
Monetary Policy For each country monetary and credit policy is an integral part of government economic policy aimed at combating with inflation to maintain the rate of the national currency and the normal conditions of the market. Monetary policy is a tool of "fine tuning" of economic conditions. Fundamental objective of monetary policy is helping the economic system to achieve such a level of production which is characterized by full employment and lack of inflation.
 Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan Real growth of GDP during 2011 accounted for 7. 5%. Agriculture, trade, and communication sectorsbecame the leaders in terms of growth rates of the physical volume. the Kazakhstan’s export promoted the increase in the foreign trade volumes. proficit of US$ 13. 6 bln. (or 7. 3% of GDP). Foreign direct investments amounting to US$ 13. 1 bln. by the end of 2011.
Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan Real growth of GDP during 2011 accounted for 7. 5%. Agriculture, trade, and communication sectorsbecame the leaders in terms of growth rates of the physical volume. the Kazakhstan’s export promoted the increase in the foreign trade volumes. proficit of US$ 13. 6 bln. (or 7. 3% of GDP). Foreign direct investments amounting to US$ 13. 1 bln. by the end of 2011.
 Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan By the end of 2011 the annual inflation was at 7. 4% (in December 2010 – 7. 8%). The major reasons for acceleration of inflation in 2011 were caused by a number of problems and factors among which the unstable situation in the global commodity markets, growth of world prices for raw materials and food, inefficient pricing mechanism, and low competition in certain markets of goods and services appeared to be the most significant ones.
Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan By the end of 2011 the annual inflation was at 7. 4% (in December 2010 – 7. 8%). The major reasons for acceleration of inflation in 2011 were caused by a number of problems and factors among which the unstable situation in the global commodity markets, growth of world prices for raw materials and food, inefficient pricing mechanism, and low competition in certain markets of goods and services appeared to be the most significant ones.
 Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan By the end of 2011 the reserve money expanded by 10. 3%, and growth rates of the money supply accounted for 15. 0%, which is lower than nominal growth rates of the economy. So by the end of 2011 the volume of credits amounted to KZT 8. 8 trln. , having increased by 15. 7% over the year. Credits in the domestic currency increased by 29. 6% to KZT 5681. 6 bln. , and in foreign currency – decreased by 3. 4% to KZT 3099. 7 bln.
Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan By the end of 2011 the reserve money expanded by 10. 3%, and growth rates of the money supply accounted for 15. 0%, which is lower than nominal growth rates of the economy. So by the end of 2011 the volume of credits amounted to KZT 8. 8 trln. , having increased by 15. 7% over the year. Credits in the domestic currency increased by 29. 6% to KZT 5681. 6 bln. , and in foreign currency – decreased by 3. 4% to KZT 3099. 7 bln.
 Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan During 2011 the volume of deposits of residents increased by 14. 3% to KZT 8385. 4 bln. , where deposits of legal entities increased by 10. 2%, and deposits of individuals – by 24. 1%. During 2011 foreign currency deposits increased by 2. 8% to KZT 2629. 7 bln. , and deposits in the national currency – by 20. 5% to KZT 5755. 7 bln.
Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan During 2011 the volume of deposits of residents increased by 14. 3% to KZT 8385. 4 bln. , where deposits of legal entities increased by 10. 2%, and deposits of individuals – by 24. 1%. During 2011 foreign currency deposits increased by 2. 8% to KZT 2629. 7 bln. , and deposits in the national currency – by 20. 5% to KZT 5755. 7 bln.
 Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan By the end of 2011 the annual inflation was within the target range of 7. 4%. At the beginning of the year, the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan made the decision to increase the official refinancing rate from 7. 0% to 7. 5% from March 9, 2011. Since May 31, 2011 the ratios of minimum reserve requirements for banks have been raised from 1. 5% to 2. 5% on domestic liabilities and from 2. 5% to 4. 5% on other liabilities.
Analysis of the current antiinflation policy in the Republic of Kazakhstan By the end of 2011 the annual inflation was within the target range of 7. 4%. At the beginning of the year, the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan made the decision to increase the official refinancing rate from 7. 0% to 7. 5% from March 9, 2011. Since May 31, 2011 the ratios of minimum reserve requirements for banks have been raised from 1. 5% to 2. 5% on domestic liabilities and from 2. 5% to 4. 5% on other liabilities.
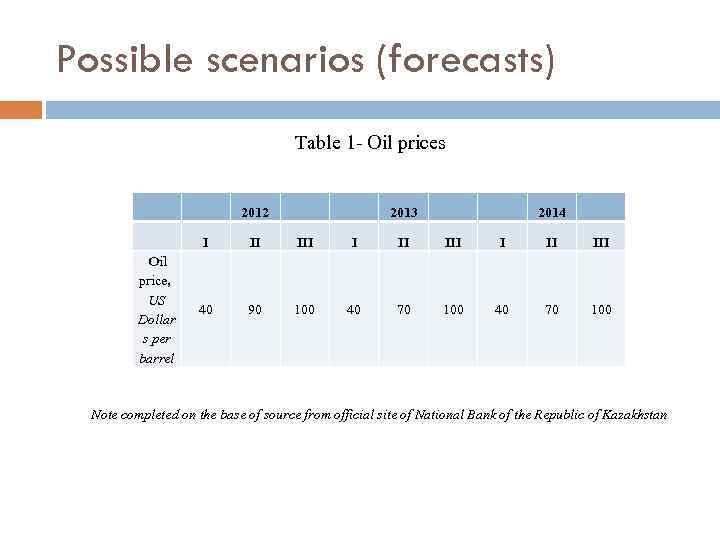 Possible scenarios (forecasts) Table 1 - Oil prices 2012 2013 2014 I Oil price, US Dollar s per barrel II III III 40 90 100 40 70 100 Note completed on the base of source from official site of National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Possible scenarios (forecasts) Table 1 - Oil prices 2012 2013 2014 I Oil price, US Dollar s per barrel II III III 40 90 100 40 70 100 Note completed on the base of source from official site of National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan
 Scenario 1 The worst case scenario of the balance of payments takes into account a significant reduction in the export of goods by 45. 1% to US$ 43. 1 bln. in 2012 and its subsequent growth by 2. 2% to US$ 44. 1 bln. in 2014 as compared to 2012. The import of goods is also expected to reduce during the forecast period as a result of a slowdown in the growth rates and decreased revenues in the economy, by 23. 4% to US$ 30. 4 bln. in 2012 with its subsequent minor growth to US$ 31. 3 bln. in 2014.
Scenario 1 The worst case scenario of the balance of payments takes into account a significant reduction in the export of goods by 45. 1% to US$ 43. 1 bln. in 2012 and its subsequent growth by 2. 2% to US$ 44. 1 bln. in 2014 as compared to 2012. The import of goods is also expected to reduce during the forecast period as a result of a slowdown in the growth rates and decreased revenues in the economy, by 23. 4% to US$ 30. 4 bln. in 2012 with its subsequent minor growth to US$ 31. 3 bln. in 2014.
 Scenario 2 With the world price of oil at US$ 90 per barrel in 2012 and US$ 70 in 2013 -2014, a positive trade balance is expected to be within US$ 20 -26 bln. , which will be partially offset by revenue payouts to foreign investors. In general, the current account is expected to be in the range between (-)1. 5% and (+)0. 5% of GDP in the forecast period.
Scenario 2 With the world price of oil at US$ 90 per barrel in 2012 and US$ 70 in 2013 -2014, a positive trade balance is expected to be within US$ 20 -26 bln. , which will be partially offset by revenue payouts to foreign investors. In general, the current account is expected to be in the range between (-)1. 5% and (+)0. 5% of GDP in the forecast period.
 Scenario 3 The current account proficit will be within the range of 2. 0 -4. 0% of GDP in 2012 -2014. The National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan believes that the third scenario of the development of the Kazakh economy is most likely to be implemented. Based on these assumptions, monetary policy measures for 2012 have been developed.
Scenario 3 The current account proficit will be within the range of 2. 0 -4. 0% of GDP in 2012 -2014. The National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan believes that the third scenario of the development of the Kazakh economy is most likely to be implemented. Based on these assumptions, monetary policy measures for 2012 have been developed.
 Threats As before, the major risks of acceleration of inflation are underdeveloped domestic competitive market environment, high monopolization of the market, poorly developed trade infrastructure as well as unstable situation in the global commodity markets. As for the global commodity markets, economic interests of Kazakhstan are primarily dependent on the world oil prices and, accordingly, fuel and lubricants. The latter have a double impact on the inflation rate – both indirect impact through prices for fuel and lubricants and through prices for other goods and services whose costs invariably include the cost of fuel and lubricants.
Threats As before, the major risks of acceleration of inflation are underdeveloped domestic competitive market environment, high monopolization of the market, poorly developed trade infrastructure as well as unstable situation in the global commodity markets. As for the global commodity markets, economic interests of Kazakhstan are primarily dependent on the world oil prices and, accordingly, fuel and lubricants. The latter have a double impact on the inflation rate – both indirect impact through prices for fuel and lubricants and through prices for other goods and services whose costs invariably include the cost of fuel and lubricants.
 Possible solutions Was carried out an analyze of the existing drawbacks in the system of monetary regulation, which include high inflation, currency issue under the amount of gold reserves, non-functioning system of refinancing and a huge foreign debt. During the search for solutions of existing problems were identified further possible prospects of monetary policy, which include the reduction of refinancing and extension issue without regard to the amount of gold reserves. These measures have to run refinancing mechanism, through which it is supposed to expand its lending to the real sector in order to diversify the economy. Besides, this will be reflected on increasing of competition and reducing of imports dependence and a corresponding reduction of inflation.
Possible solutions Was carried out an analyze of the existing drawbacks in the system of monetary regulation, which include high inflation, currency issue under the amount of gold reserves, non-functioning system of refinancing and a huge foreign debt. During the search for solutions of existing problems were identified further possible prospects of monetary policy, which include the reduction of refinancing and extension issue without regard to the amount of gold reserves. These measures have to run refinancing mechanism, through which it is supposed to expand its lending to the real sector in order to diversify the economy. Besides, this will be reflected on increasing of competition and reducing of imports dependence and a corresponding reduction of inflation.
 Thank you for attention!
Thank you for attention!


