7857a46a23cd328bda7146577ff2abe8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

The ‘MIMO Junior’ 11 n outdoor Bridging CPE A new outdoor bridging device giving connections up to 300 Meg 1
What is 11 n Wi. Fi • MIMO M(tx) x N(rx) antenna • Spatial Multiplexing – Multiple Spatial Streams multiplexed onto single channel split over multiple antenna • Space-Time Block Coding – same stream over several antenna • Transmit Beamforming – signal steering by altering the phase • 40 MHz channels – Limited on 2. 4 GHz – 11 non-overlapping channels on Band B 5 GHz • Improved Coding Schemes – Reduced Guide Interval – Block Ack – Frame Aggregation • Theoretical throughput of 100 -140 Mbps – 11 g typically 24 Mbps – 11 n tested by us at over 80 Mbps 2

The MIMO-JNR • • • 2. 4 GHz ISM or 5 GHz UNII bands Dual Polarization 8 d. Bi antenna for 2. 4 Ghz version or 13 d. Bi for 5 GHz version. Acts as two separate antenna Alignment Tools Passive Po. E (24 V) 11 n Draft 2. 0 PHY rates up to 300 Mbps – True TCP 83 Mbps • 7 Operating Modes – – – Access Point Client Wireless Routing Client Gateway Wireless Adapter Mode Transparent Client 3
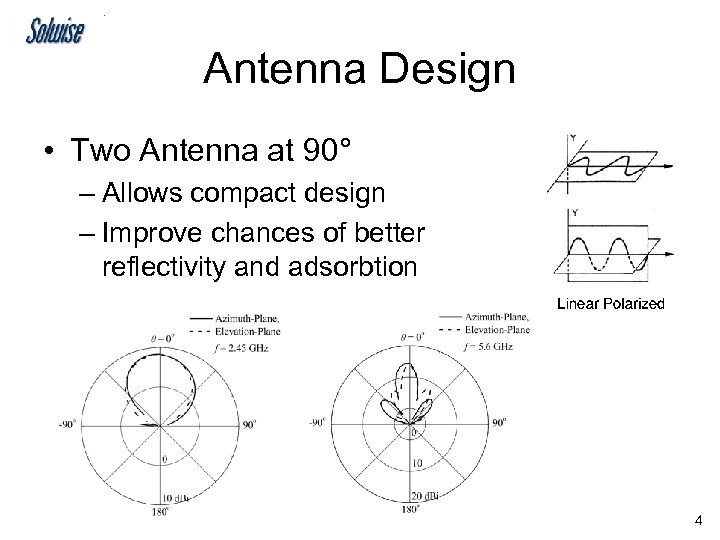
Antenna Design • Two Antenna at 90° – Allows compact design – Improve chances of better reflectivity and adsorbtion 4

Configuring the MIMO-JNR 5
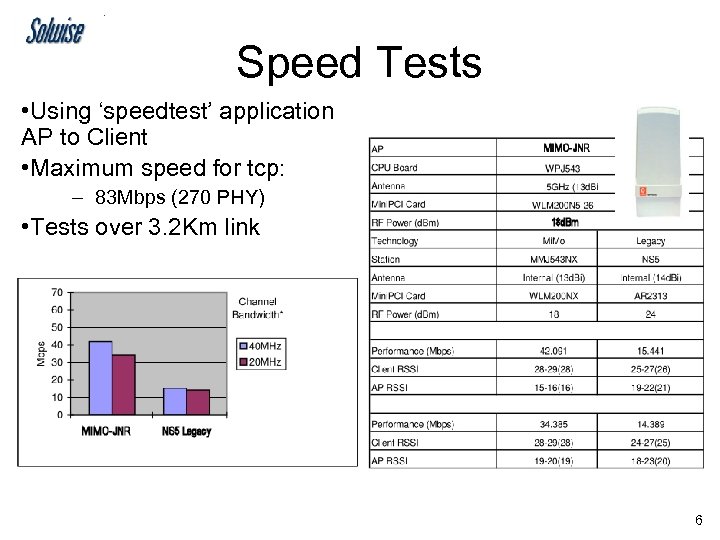
Speed Tests • Using ‘speedtest’ application AP to Client • Maximum speed for tcp: – 83 Mbps (270 PHY) • Tests over 3. 2 Km link 6
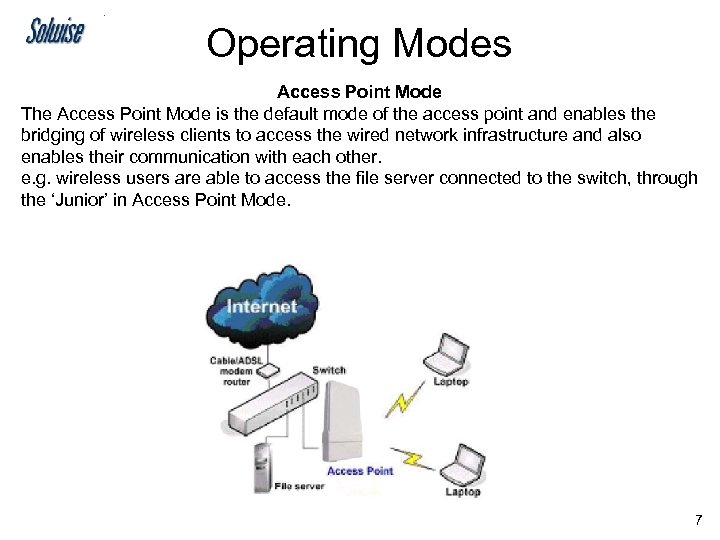
Operating Modes Access Point Mode The Access Point Mode is the default mode of the access point and enables the bridging of wireless clients to access the wired network infrastructure and also enables their communication with each other. e. g. wireless users are able to access the file server connected to the switch, through the ‘Junior’ in Access Point Mode. 7
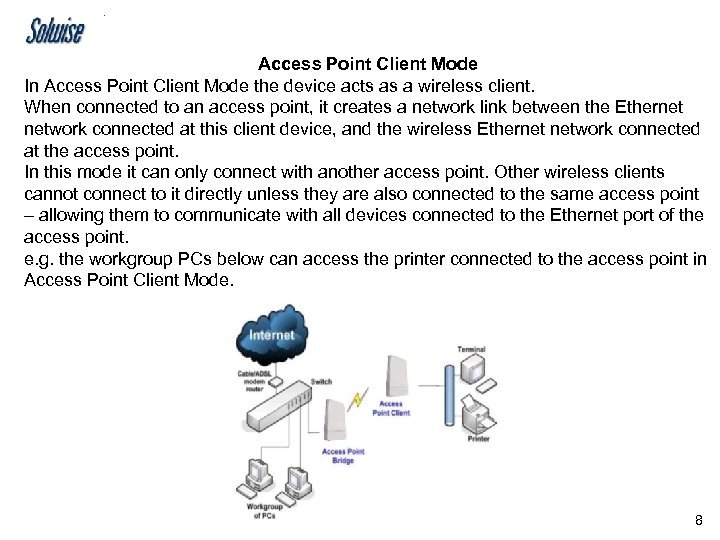
Access Point Client Mode In Access Point Client Mode the device acts as a wireless client. When connected to an access point, it creates a network link between the Ethernet network connected at this client device, and the wireless Ethernet network connected at the access point. In this mode it can only connect with another access point. Other wireless clients cannot connect to it directly unless they are also connected to the same access point – allowing them to communicate with all devices connected to the Ethernet port of the access point. e. g. the workgroup PCs below can access the printer connected to the access point in Access Point Client Mode. 8

Wireless Routing Client Mode In Wireless Routing Client Mode the Ethernet port of the access point may be used to connect with other devices on the network while Internet access would be provided through wireless communication with a wireless ISP. 9
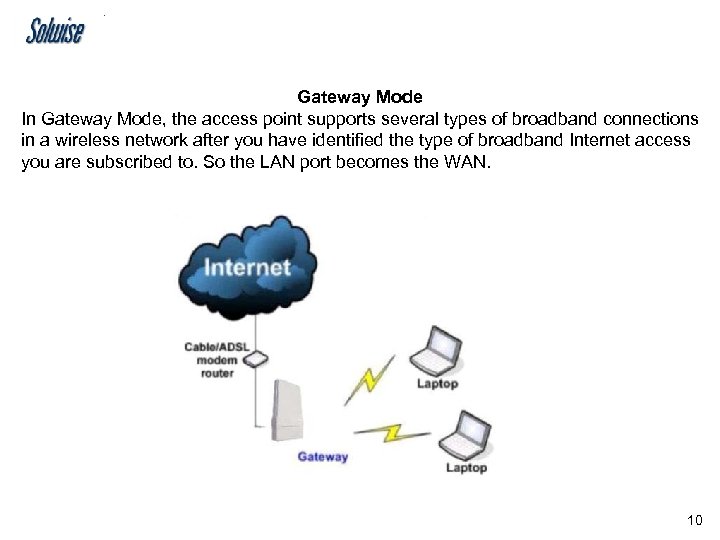
Gateway Mode In Gateway Mode, the access point supports several types of broadband connections in a wireless network after you have identified the type of broadband Internet access you are subscribed to. So the LAN port becomes the WAN. 10
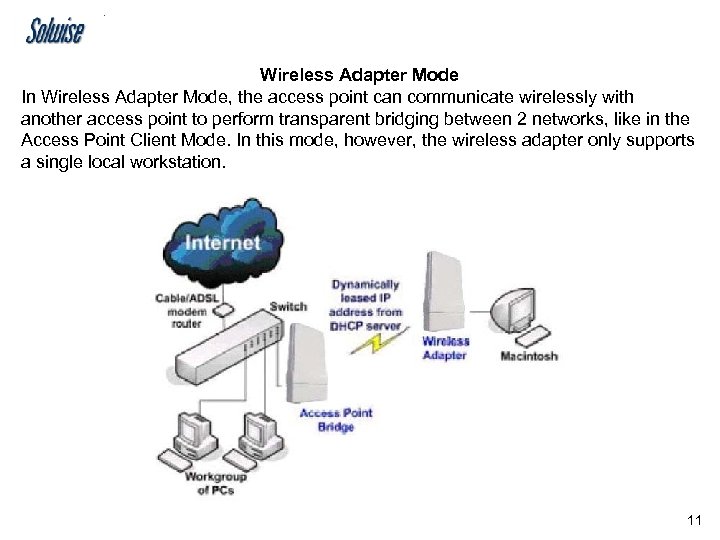
Wireless Adapter Mode In Wireless Adapter Mode, the access point can communicate wirelessly with another access point to perform transparent bridging between 2 networks, like in the Access Point Client Mode. In this mode, however, the wireless adapter only supports a single local workstation. 11
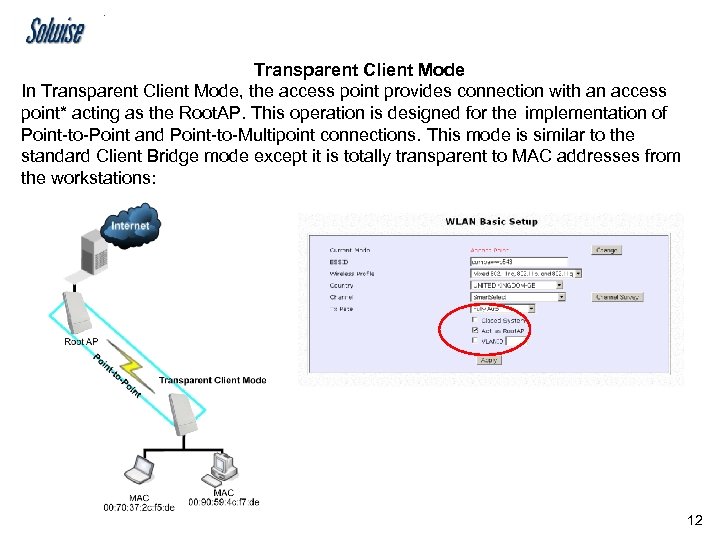
Transparent Client Mode In Transparent Client Mode, the access point provides connection with an access point* acting as the Root. AP. This operation is designed for the implementation of Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint connections. This mode is similar to the standard Client Bridge mode except it is totally transparent to MAC addresses from the workstations: 12

Repeater Mode The Junior also supports a built-in Repeater Mode to extend the range, and allows you to extend the network over a greater distance. In Repeater Mode, the access point acts as a relay for network signals on the network by regenerating the signals it receives, and retransmitting them to extend the range of the existing network infrastructure. Note when using a repeater setup then the main AP needs to have Root. AP enabled. 13

Presented by Steve Mace © Solwise 2009 Solwi se ® 14
7857a46a23cd328bda7146577ff2abe8.ppt