7219b307d0461d739b838d64a70d668d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 The Middle East How can cultural differences cause conflict?
The Middle East How can cultural differences cause conflict?
 The Arab-Israeli conflict
The Arab-Israeli conflict
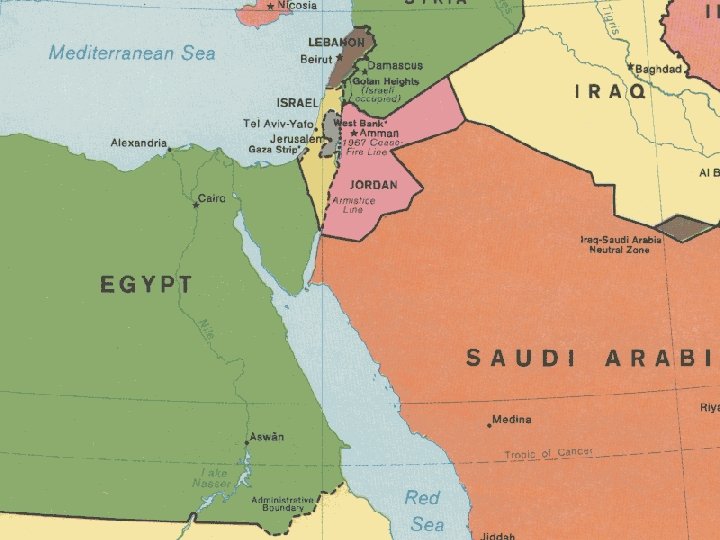
 Geography. l l l l Israel is a small but developed country on land to the East of the Mediterranean sea. It has its own religion –Judaism- and is a recently formed country-1948. It is surrounded by Muslim (Arabic) countries on three sides-Egypt, Lebanon, Palestine, Jordan, and Syria. It has a powerful friend in the USA. The land itself is fertile –if you have water. There are major cities- Jerusalem, Haifa, Tel Aviv. The land has a long history of war and bloodshed.
Geography. l l l l Israel is a small but developed country on land to the East of the Mediterranean sea. It has its own religion –Judaism- and is a recently formed country-1948. It is surrounded by Muslim (Arabic) countries on three sides-Egypt, Lebanon, Palestine, Jordan, and Syria. It has a powerful friend in the USA. The land itself is fertile –if you have water. There are major cities- Jerusalem, Haifa, Tel Aviv. The land has a long history of war and bloodshed.
 Jerusalem • Jerusalem is an ancient city that has been fought over for thousands of years. • It is important for Christians, Muslims and Jews. Each group is highly suspicious of the other. • Conflict has been violent and each group lives uneasily guarding its own space. • Jerusalem is also a modern city and an economic centre of Israel.
Jerusalem • Jerusalem is an ancient city that has been fought over for thousands of years. • It is important for Christians, Muslims and Jews. Each group is highly suspicious of the other. • Conflict has been violent and each group lives uneasily guarding its own space. • Jerusalem is also a modern city and an economic centre of Israel.
 Israel-the people. Because of its location, and long history, Israel has a large mixture of peoples. They are different faiths, appearance, skin colour etc.
Israel-the people. Because of its location, and long history, Israel has a large mixture of peoples. They are different faiths, appearance, skin colour etc.
 So what is the problem? l l The land called ‘Israel’ is also called ‘Palestine’. The local people of this land were Muslim Arabs. They were called Palestinians because the land was called ‘Palestine’. After World War II, Jewish people were escaping Europe. Many owned nothing and had stepped straight out from Hitler’s death camps. The United Nations allowed them to seek refuge in the land of their ancestors- Israel.
So what is the problem? l l The land called ‘Israel’ is also called ‘Palestine’. The local people of this land were Muslim Arabs. They were called Palestinians because the land was called ‘Palestine’. After World War II, Jewish people were escaping Europe. Many owned nothing and had stepped straight out from Hitler’s death camps. The United Nations allowed them to seek refuge in the land of their ancestors- Israel.
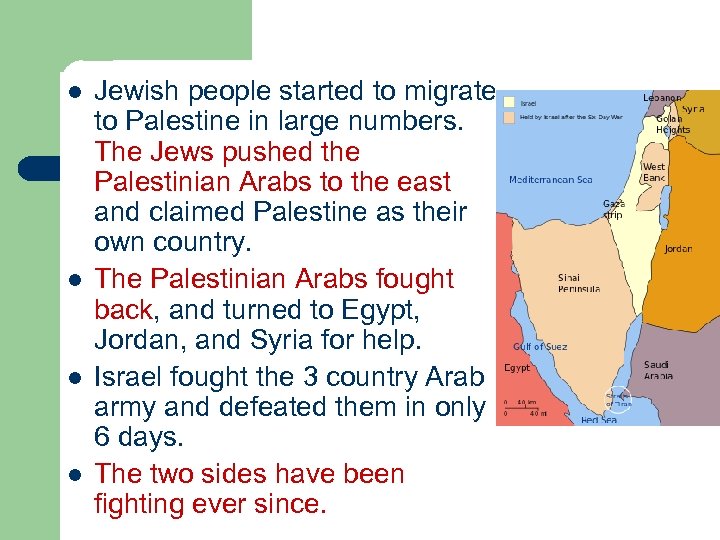 l l Jewish people started to migrate to Palestine in large numbers. The Jews pushed the Palestinian Arabs to the east and claimed Palestine as their own country. The Palestinian Arabs fought back, and turned to Egypt, Jordan, and Syria for help. Israel fought the 3 country Arab army and defeated them in only 6 days. The two sides have been fighting ever since.
l l Jewish people started to migrate to Palestine in large numbers. The Jews pushed the Palestinian Arabs to the east and claimed Palestine as their own country. The Palestinian Arabs fought back, and turned to Egypt, Jordan, and Syria for help. Israel fought the 3 country Arab army and defeated them in only 6 days. The two sides have been fighting ever since.
 The Middle Eastern Governments l l l l Democracy Republic Autocracy Monarchy Dictatorship Oligarchy Theocracy
The Middle Eastern Governments l l l l Democracy Republic Autocracy Monarchy Dictatorship Oligarchy Theocracy
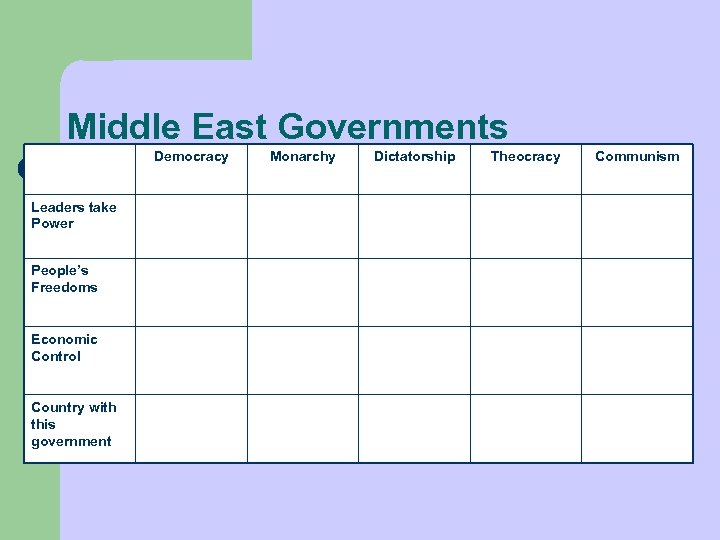 Middle East Governments Democracy Leaders take Power People’s Freedoms Economic Control Country with this government Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism
Middle East Governments Democracy Leaders take Power People’s Freedoms Economic Control Country with this government Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism
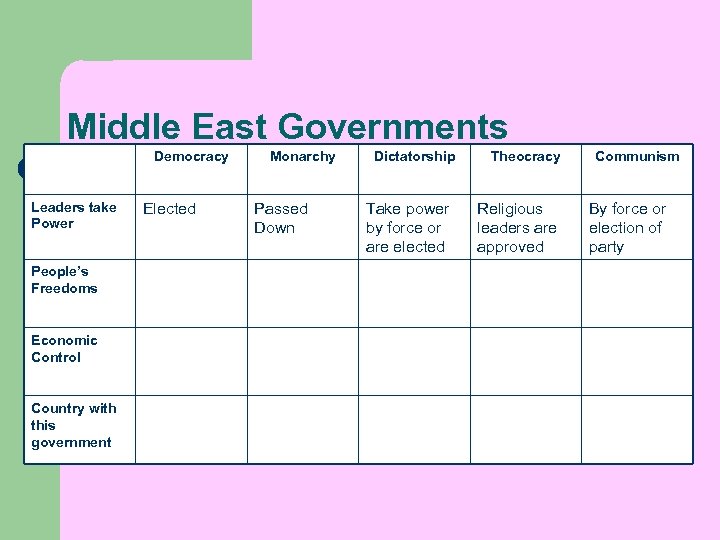 Middle East Governments Democracy Leaders take Power People’s Freedoms Economic Control Country with this government Elected Monarchy Passed Down Dictatorship Take power by force or are elected Theocracy Religious leaders are approved Communism By force or election of party
Middle East Governments Democracy Leaders take Power People’s Freedoms Economic Control Country with this government Elected Monarchy Passed Down Dictatorship Take power by force or are elected Theocracy Religious leaders are approved Communism By force or election of party
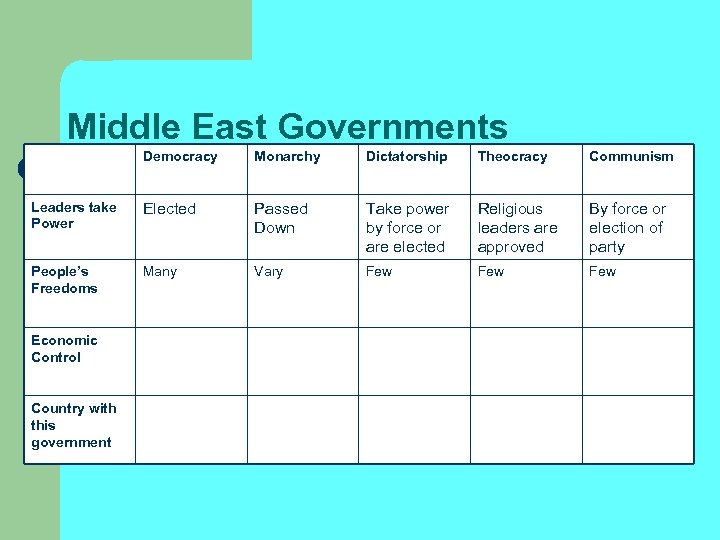 Middle East Governments Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism Leaders take Power Elected Passed Down Take power by force or are elected Religious leaders are approved By force or election of party People’s Freedoms Many Vary Few Few Economic Control Country with this government
Middle East Governments Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism Leaders take Power Elected Passed Down Take power by force or are elected Religious leaders are approved By force or election of party People’s Freedoms Many Vary Few Few Economic Control Country with this government
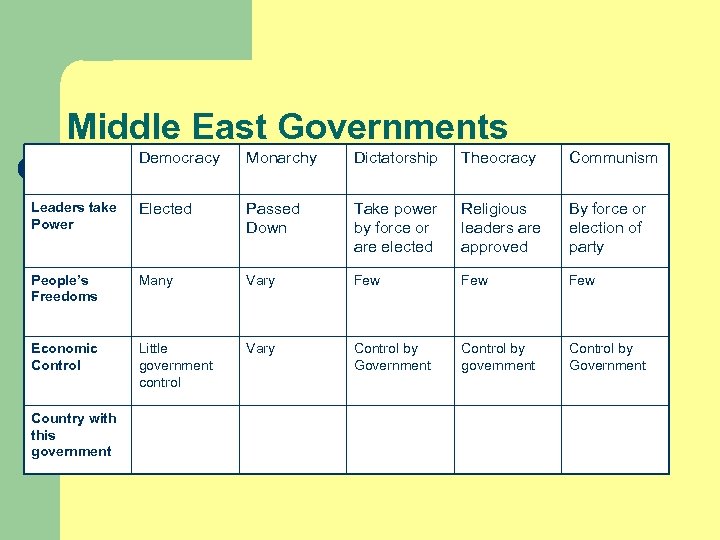 Middle East Governments Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism Leaders take Power Elected Passed Down Take power by force or are elected Religious leaders are approved By force or election of party People’s Freedoms Many Vary Few Few Economic Control Little government control Vary Control by Government Control by government Control by Government Country with this government
Middle East Governments Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism Leaders take Power Elected Passed Down Take power by force or are elected Religious leaders are approved By force or election of party People’s Freedoms Many Vary Few Few Economic Control Little government control Vary Control by Government Control by government Control by Government Country with this government
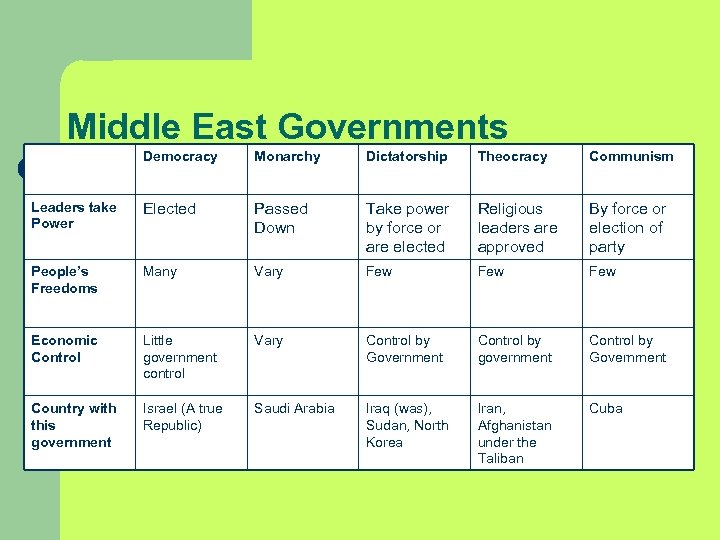 Middle East Governments Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism Leaders take Power Elected Passed Down Take power by force or are elected Religious leaders are approved By force or election of party People’s Freedoms Many Vary Few Few Economic Control Little government control Vary Control by Government Control by government Control by Government Country with this government Israel (A true Republic) Saudi Arabia Iraq (was), Sudan, North Korea Iran, Afghanistan under the Taliban Cuba
Middle East Governments Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Theocracy Communism Leaders take Power Elected Passed Down Take power by force or are elected Religious leaders are approved By force or election of party People’s Freedoms Many Vary Few Few Economic Control Little government control Vary Control by Government Control by government Control by Government Country with this government Israel (A true Republic) Saudi Arabia Iraq (was), Sudan, North Korea Iran, Afghanistan under the Taliban Cuba
 Israel l Parliamentary Democracy. l The president is head of state and serves in a primarily ceremonial role. l The prime minister is the head of government.
Israel l Parliamentary Democracy. l The president is head of state and serves in a primarily ceremonial role. l The prime minister is the head of government.
 Israel – Becoming the leader l l President is elected by the Parliament. The President nominates the Prime Minister from a member of the parliament. (following a vote of confidence from the Knesset).
Israel – Becoming the leader l l President is elected by the Parliament. The President nominates the Prime Minister from a member of the parliament. (following a vote of confidence from the Knesset).
 Israel – Role of Citizen l Citizens over 18 can vote for members of the unicameral legislature called the Knesset.
Israel – Role of Citizen l Citizens over 18 can vote for members of the unicameral legislature called the Knesset.
 Israel – Personal Freedoms l Freedom of Speech – Yes l Freedom of the Press - Yes
Israel – Personal Freedoms l Freedom of Speech – Yes l Freedom of the Press - Yes
 Checking for Understanding Select the correct answer A. Israel is a parliamentary democracy. B. President is elected by the Knesset (parliament). True or False
Checking for Understanding Select the correct answer A. Israel is a parliamentary democracy. B. President is elected by the Knesset (parliament). True or False
 Saudi Arabia l Islamic Absolute Monarchy. l King Abdullah bin Abdul Aziz Al Saud is the current King of Saudi Arabia and Head of the House of Saud.
Saudi Arabia l Islamic Absolute Monarchy. l King Abdullah bin Abdul Aziz Al Saud is the current King of Saudi Arabia and Head of the House of Saud.
 Saudi Arabia – Becoming the Leader l The right of succession is hereditary (passed down through the family). l A newly established council selects a successor among the crown princes of the Saudi royal family. l The King’s power is limited by Islamic law and he must build consensus among religious leaders and other influential Saudis.
Saudi Arabia – Becoming the Leader l The right of succession is hereditary (passed down through the family). l A newly established council selects a successor among the crown princes of the Saudi royal family. l The King’s power is limited by Islamic law and he must build consensus among religious leaders and other influential Saudis.
 Saudi Arabia – Role of Citizen l The role of the citizen in Saudi Arabia is to obey the King.
Saudi Arabia – Role of Citizen l The role of the citizen in Saudi Arabia is to obey the King.
 Saudi Arabia – Personal Freedoms l Freedom of Speech – No l Freedom of the Press - No l There are no voting rights or official political parties in this country.
Saudi Arabia – Personal Freedoms l Freedom of Speech – No l Freedom of the Press - No l There are no voting rights or official political parties in this country.
 Checking for Understanding Select the correct answer 1. The right of succession is hereditary (passed down through the family). 2. The role of the citizen in Saudi Arabia is to obey the King. True or False
Checking for Understanding Select the correct answer 1. The right of succession is hereditary (passed down through the family). 2. The role of the citizen in Saudi Arabia is to obey the King. True or False
 Iran l Iran is a theocratic republic with a presidential system. l The government of Iran is based on Islamic law. l The Supreme Leader of Iran, who is a religious leader, is the chief of state and has final say on all matters. l The Supreme Leader is commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
Iran l Iran is a theocratic republic with a presidential system. l The government of Iran is based on Islamic law. l The Supreme Leader of Iran, who is a religious leader, is the chief of state and has final say on all matters. l The Supreme Leader is commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
 Iran – Becoming the Leader l The Supreme Leader is selected by the Council of Experts. l The Council of Experts, as well as the legislature and president, are elected by popular vote. l While the president is head of government, he may be removed by the Supreme Leader at any time.
Iran – Becoming the Leader l The Supreme Leader is selected by the Council of Experts. l The Council of Experts, as well as the legislature and president, are elected by popular vote. l While the president is head of government, he may be removed by the Supreme Leader at any time.
 Iran – Role of Citizen l l There is universal suffrage (voting) for everyone over 18. The role of the citizen in Iran is to obey the Supreme Leader.
Iran – Role of Citizen l l There is universal suffrage (voting) for everyone over 18. The role of the citizen in Iran is to obey the Supreme Leader.
 Iran – Personal Freedoms l l Freedom of Speech – No Freedom of the Press - No
Iran – Personal Freedoms l l Freedom of Speech – No Freedom of the Press - No
 Checking for Understanding Circle the correct answer 1. Iran is a theocratic republic with 2. The Supreme Leader is selected a presidential system. by the Council of Experts. True or False
Checking for Understanding Circle the correct answer 1. Iran is a theocratic republic with 2. The Supreme Leader is selected a presidential system. by the Council of Experts. True or False
 Activity l Write two short personal narratives. – – In the first narrative assume the role of a Jew during the Jewish immigration into Palestine between 1918 and 1948. In the second narrative assume the role of a Palestinian during the Jewish immigration into Palestine between 1918 and 1948.
Activity l Write two short personal narratives. – – In the first narrative assume the role of a Jew during the Jewish immigration into Palestine between 1918 and 1948. In the second narrative assume the role of a Palestinian during the Jewish immigration into Palestine between 1918 and 1948.


