0cd3a18d4fb30fee5cacc140c16525e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 The Middle Ages The Medieval Era: 500 – 1500 CE
The Middle Ages The Medieval Era: 500 – 1500 CE
 Review: Fall of Roman Empire
Review: Fall of Roman Empire
 Feudalism POLITICAL DECENTRALIZATION: No single monarch strong enough to rule all of Europe. Developed because of constant invasions Feudalism = the system of rule by local lords who were bound to a king by ties of loyalty. Feudal Contract – Rules that grew out of customs and traditional practices between Lord and Vassals Why Feudal Contract? • • Governments ceased to be able to defend their subjects WEALTH = LAND
Feudalism POLITICAL DECENTRALIZATION: No single monarch strong enough to rule all of Europe. Developed because of constant invasions Feudalism = the system of rule by local lords who were bound to a king by ties of loyalty. Feudal Contract – Rules that grew out of customs and traditional practices between Lord and Vassals Why Feudal Contract? • • Governments ceased to be able to defend their subjects WEALTH = LAND
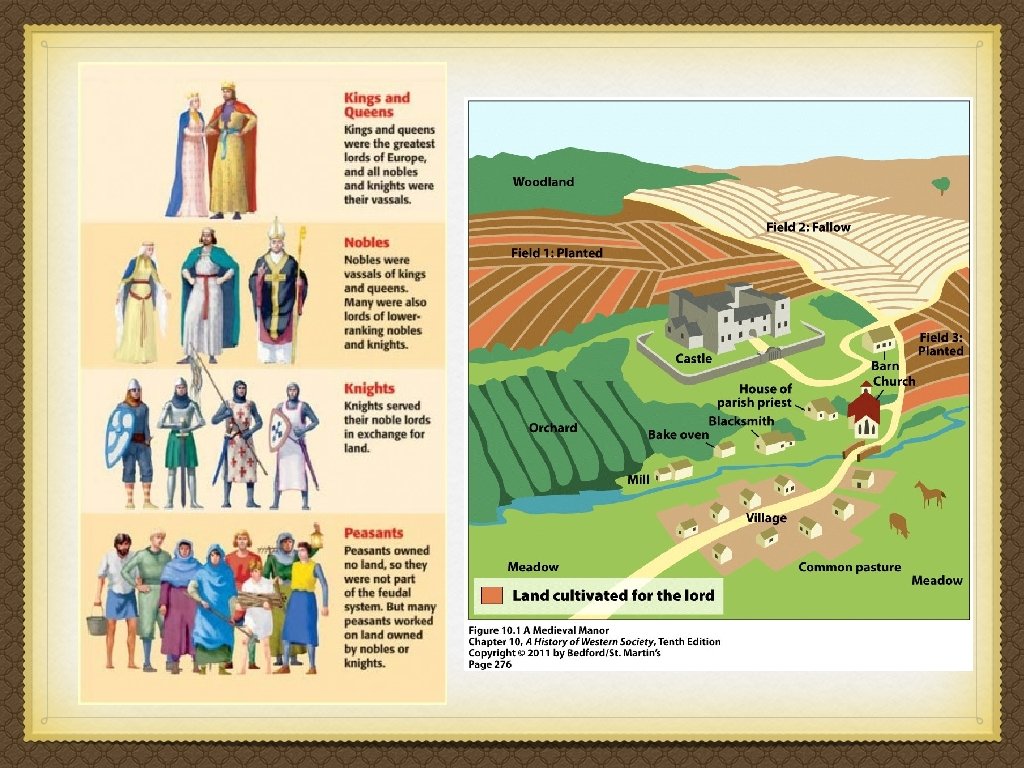
 Structure of Feudal Society • King owns all the land. Fief = estate • King divides his land amongst the Vassals. • Vassals divided their land with the Knights. • In return, the Knights and Vassals owed loyalty and service to the King. • Peasants & Serfs worked the land. • King (Lord) • Vassals (Lesser Lords/Nobles) • Knights (Mounted Warriors) • Peasants/Serfs
Structure of Feudal Society • King owns all the land. Fief = estate • King divides his land amongst the Vassals. • Vassals divided their land with the Knights. • In return, the Knights and Vassals owed loyalty and service to the King. • Peasants & Serfs worked the land. • King (Lord) • Vassals (Lesser Lords/Nobles) • Knights (Mounted Warriors) • Peasants/Serfs
 Difference between Serfs and Peasants? • Both peasants and serfs were considered to be “common people, ” making up 90% of the population. • Peasants sometimes owned their own business or small plot of land. Most were uneducated and unskilled. • Serfs were bound to the land. They were almost like slaves. They could not be bought and sold, but they could not leave their land without permission. Their land could be bought and sold. The land all the food they grew belonged to the noble. A serf’s job was whatever the noble told them it was (baker, famer, blacksmith, etc. ) A serf could buy their freedom if they could get the money, but that was almost impossible since they were uneducated and unskilled.
Difference between Serfs and Peasants? • Both peasants and serfs were considered to be “common people, ” making up 90% of the population. • Peasants sometimes owned their own business or small plot of land. Most were uneducated and unskilled. • Serfs were bound to the land. They were almost like slaves. They could not be bought and sold, but they could not leave their land without permission. Their land could be bought and sold. The land all the food they grew belonged to the noble. A serf’s job was whatever the noble told them it was (baker, famer, blacksmith, etc. ) A serf could buy their freedom if they could get the money, but that was almost impossible since they were uneducated and unskilled.
 Feudalism & the Manor = Village & surrounding land administered by a King (Lord). Chivalry = code of conduct for knights. Knights were supposed to be virtuous, loyal (to lord), just (to the peasants), gentlemen (toward women).
Feudalism & the Manor = Village & surrounding land administered by a King (Lord). Chivalry = code of conduct for knights. Knights were supposed to be virtuous, loyal (to lord), just (to the peasants), gentlemen (toward women).
 The Rise of Feudalism
The Rise of Feudalism
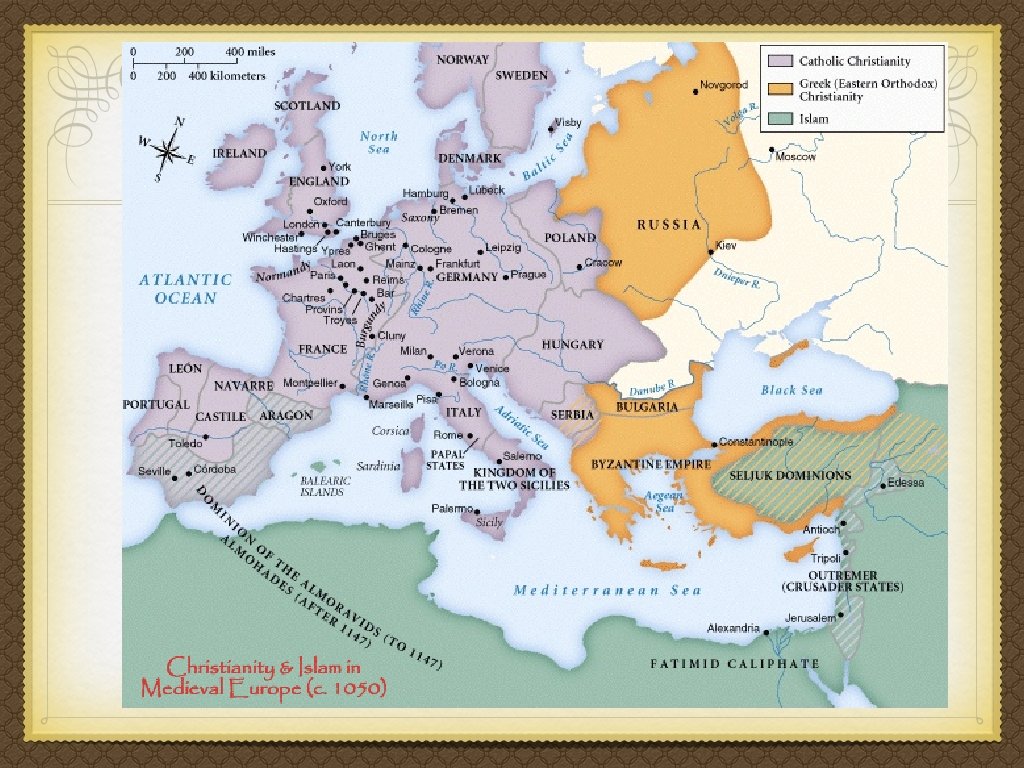
 The Role of Christianity Unified Europe, politically & culturally Great Schism, 1054: Split Church in two; Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodox Theological Differences: Among others, the role of the Pope. Eastern Orthodox is ruled by the Byzantine emperor, not the Pope. Provided feeling of cohesion Church hierarchy very powerful Owned land, collect taxes/tithes
The Role of Christianity Unified Europe, politically & culturally Great Schism, 1054: Split Church in two; Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodox Theological Differences: Among others, the role of the Pope. Eastern Orthodox is ruled by the Byzantine emperor, not the Pope. Provided feeling of cohesion Church hierarchy very powerful Owned land, collect taxes/tithes
 Role of the Church Determine heresy = belief or opinion contrary to religious doctrine Excommunicate Crusades = Military Expeditions against enemies of the Church Holy Inquisition = intense religious questioning to preserve religious community. Education/institutions Sacraments – seven rites that offered the only route to eternal life
Role of the Church Determine heresy = belief or opinion contrary to religious doctrine Excommunicate Crusades = Military Expeditions against enemies of the Church Holy Inquisition = intense religious questioning to preserve religious community. Education/institutions Sacraments – seven rites that offered the only route to eternal life
 The Crusades Purposes of Crusades: • convert nonbelievers to Catholicism • crush heretical Christian movements • resist attacks by foreigners who were not Christian (especially Muslims) Why would you want to go on a Crusade? • To obey God’s will or to achieve salvation • To carve out a kingdom of your own in Palestine • To avoid taxes and debts at home
The Crusades Purposes of Crusades: • convert nonbelievers to Catholicism • crush heretical Christian movements • resist attacks by foreigners who were not Christian (especially Muslims) Why would you want to go on a Crusade? • To obey God’s will or to achieve salvation • To carve out a kingdom of your own in Palestine • To avoid taxes and debts at home
 The Crusades
The Crusades
 Role of Church in Crusades
Role of Church in Crusades
 Charlemagne Ruled the Kingdom of Franks, which was the strongest power in western Europe (768 – 814), during the Golden Age. Most powerful Christian ruler 800 CE – crowned Holy Roman Emperor Extended borders, fought Muslims, encouraged learning, ran an efficient government
Charlemagne Ruled the Kingdom of Franks, which was the strongest power in western Europe (768 – 814), during the Golden Age. Most powerful Christian ruler 800 CE – crowned Holy Roman Emperor Extended borders, fought Muslims, encouraged learning, ran an efficient government
 Culture/Achievements • Dante – Poet. Wrote the Divine Comedy, which combined poetry, theology and history. • Chaucer – Poet. Wrote the Canterbury Tales, which was about ordinary people on a pilgrimage telling stories about their lives. • Thomas Aquinas – Scholar. Believed reason and logic could be used to support Christian faith. • Scholasticism = new school of thought. • Vernacular = everyday language.
Culture/Achievements • Dante – Poet. Wrote the Divine Comedy, which combined poetry, theology and history. • Chaucer – Poet. Wrote the Canterbury Tales, which was about ordinary people on a pilgrimage telling stories about their lives. • Thomas Aquinas – Scholar. Believed reason and logic could be used to support Christian faith. • Scholasticism = new school of thought. • Vernacular = everyday language.
 Byzantium Crossroads between Christian Europe and Islamic Middle East Constantinople (Istanbul, Turkey): joined Mediterranean Europe, Middle East, China, India, East Indies (Due to Silk Road and sea trade routes) Superior to rest of Europe in terms of economy and culture Period of decline beginning in 11 th century
Byzantium Crossroads between Christian Europe and Islamic Middle East Constantinople (Istanbul, Turkey): joined Mediterranean Europe, Middle East, China, India, East Indies (Due to Silk Road and sea trade routes) Superior to rest of Europe in terms of economy and culture Period of decline beginning in 11 th century
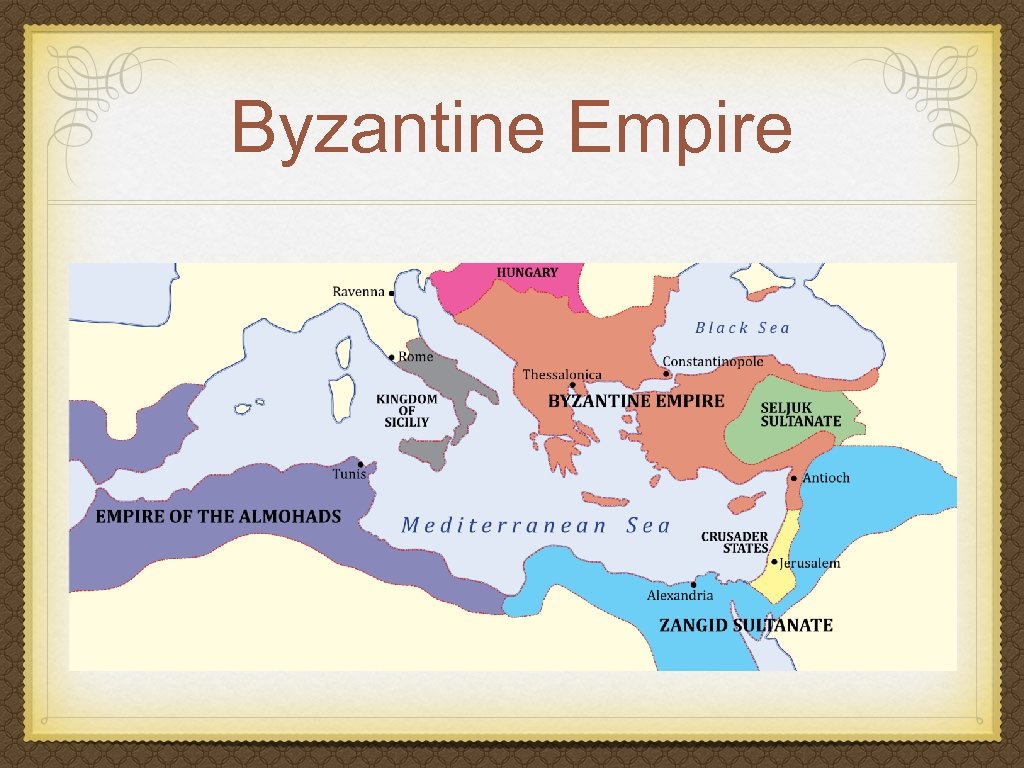 Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
 Muslim Faith • Muhammad = founder of Islam • Koran = holy book of Islam • 5 Pillars = Basic duties of Islam • Belief in Allah • Prayer 5 x a day • Almsgiving to poor • Fast during Ramadan • Pilgrimage to Mecca • Caliph = successor to Muhammad, religious and political leader of Islam
Muslim Faith • Muhammad = founder of Islam • Koran = holy book of Islam • 5 Pillars = Basic duties of Islam • Belief in Allah • Prayer 5 x a day • Almsgiving to poor • Fast during Ramadan • Pilgrimage to Mecca • Caliph = successor to Muhammad, religious and political leader of Islam
 Other Key Terms/Ideas • Guilds = associations of merchants or artisans that governed the town. • Charter = written documents that guaranteed rights. • Domesday Book = book of property that could be taxed. • Common Law = accepted legal principles that applied to everyone throughout the land. • Justinian’s Code = Summarization of existing Roman law. Principles of justice that helped shape legal systems in Western Europe & Americas. • Averoes – philosopher who sought to prove that there was no conflict between the Islamic faith and reason.
Other Key Terms/Ideas • Guilds = associations of merchants or artisans that governed the town. • Charter = written documents that guaranteed rights. • Domesday Book = book of property that could be taxed. • Common Law = accepted legal principles that applied to everyone throughout the land. • Justinian’s Code = Summarization of existing Roman law. Principles of justice that helped shape legal systems in Western Europe & Americas. • Averoes – philosopher who sought to prove that there was no conflict between the Islamic faith and reason.
 Other areas of Stress • More and longer wars • Hundred Years’ War = 1337 – 1453, France vs. England. France wanted English Kings who rule lands in France, gone. • Reconquista = Crusades launched by Spain. • Black Death/ Bubonic Plague - reached Europe in 1347, from China, Killed 1/3 of Western Europe’s population.
Other areas of Stress • More and longer wars • Hundred Years’ War = 1337 – 1453, France vs. England. France wanted English Kings who rule lands in France, gone. • Reconquista = Crusades launched by Spain. • Black Death/ Bubonic Plague - reached Europe in 1347, from China, Killed 1/3 of Western Europe’s population.
 The Black Death (Rats)
The Black Death (Rats)


