7983bb32f08851ca0339a9a6c58a9c9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 The Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix
 Marketing Defined Marketing refers to all of the business activities necessary to establish and maintain positive relationships with one’s customers • Marketing encompasses each of the steps involved in the delivery of goods and services from producer to consumer • Ultimate goal of marketing is to sell the products produced by businesses and to effectively manage a business’s brands • Marketing includes research & development, distribution, advertising, promotion and sales •
Marketing Defined Marketing refers to all of the business activities necessary to establish and maintain positive relationships with one’s customers • Marketing encompasses each of the steps involved in the delivery of goods and services from producer to consumer • Ultimate goal of marketing is to sell the products produced by businesses and to effectively manage a business’s brands • Marketing includes research & development, distribution, advertising, promotion and sales •
 Marketing Mix • Most famous phrase in marketing • Sometimes known as the ‘four Ps' • Marketing mix consists of price, place, product and promotion
Marketing Mix • Most famous phrase in marketing • Sometimes known as the ‘four Ps' • Marketing mix consists of price, place, product and promotion
 The Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix
 The Marketing Mix - Price • There are many strategies available when pricing a product
The Marketing Mix - Price • There are many strategies available when pricing a product
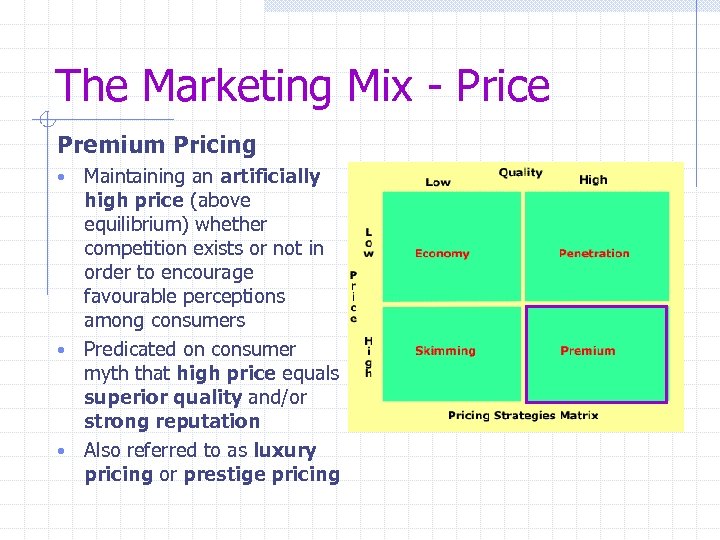 The Marketing Mix - Price Premium Pricing Maintaining an artificially high price (above equilibrium) whether competition exists or not in order to encourage favourable perceptions among consumers • Predicated on consumer myth that high price equals superior quality and/or strong reputation • Also referred to as luxury pricing or prestige pricing •
The Marketing Mix - Price Premium Pricing Maintaining an artificially high price (above equilibrium) whether competition exists or not in order to encourage favourable perceptions among consumers • Predicated on consumer myth that high price equals superior quality and/or strong reputation • Also referred to as luxury pricing or prestige pricing •
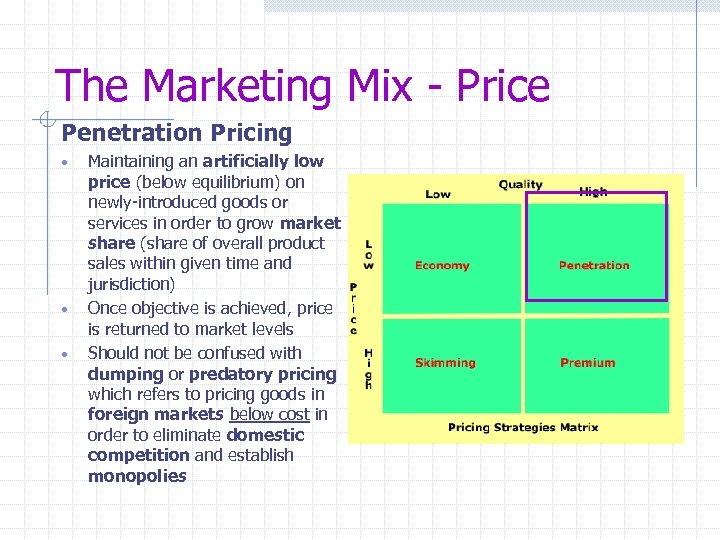 The Marketing Mix - Price Penetration Pricing • • • Maintaining an artificially low price (below equilibrium) on newly-introduced goods or services in order to grow market share (share of overall product sales within given time and jurisdiction) Once objective is achieved, price is returned to market levels Should not be confused with dumping or predatory pricing which refers to pricing goods in foreign markets below cost in order to eliminate domestic competition and establish monopolies
The Marketing Mix - Price Penetration Pricing • • • Maintaining an artificially low price (below equilibrium) on newly-introduced goods or services in order to grow market share (share of overall product sales within given time and jurisdiction) Once objective is achieved, price is returned to market levels Should not be confused with dumping or predatory pricing which refers to pricing goods in foreign markets below cost in order to eliminate domestic competition and establish monopolies
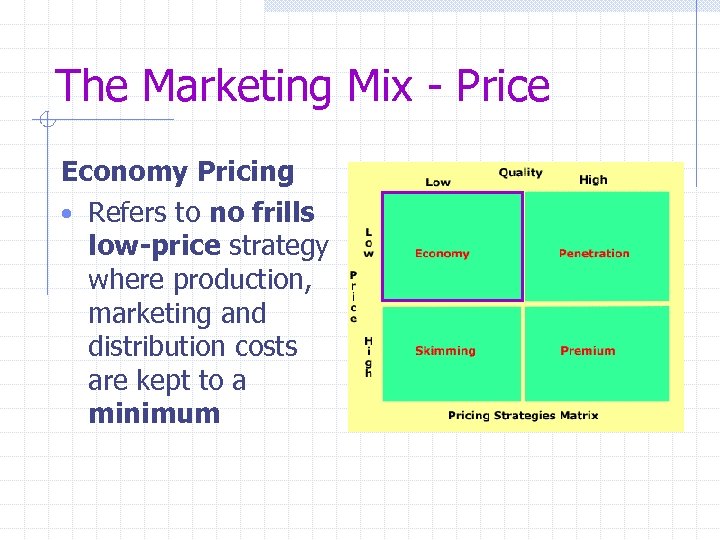 The Marketing Mix - Price Economy Pricing • Refers to no frills low-price strategy where production, marketing and distribution costs are kept to a minimum
The Marketing Mix - Price Economy Pricing • Refers to no frills low-price strategy where production, marketing and distribution costs are kept to a minimum
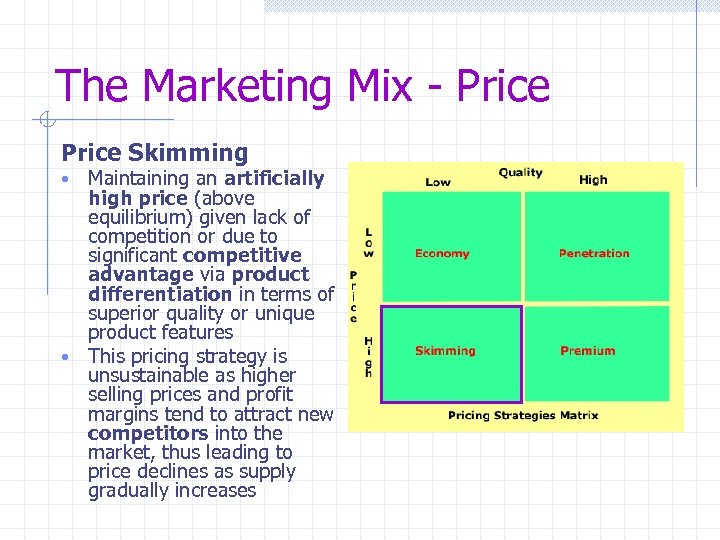 The Marketing Mix - Price Skimming Maintaining an artificially high price (above equilibrium) given lack of competition or due to significant competitive advantage via product differentiation in terms of superior quality or unique product features • This pricing strategy is unsustainable as higher selling prices and profit margins tend to attract new competitors into the market, thus leading to price declines as supply gradually increases •
The Marketing Mix - Price Skimming Maintaining an artificially high price (above equilibrium) given lack of competition or due to significant competitive advantage via product differentiation in terms of superior quality or unique product features • This pricing strategy is unsustainable as higher selling prices and profit margins tend to attract new competitors into the market, thus leading to price declines as supply gradually increases •
 The Marketing Mix - Price Additional Pricing Strategies (i) price matching or competitive pricing which involves raising or lowering one's prices to keep pace with one's closest competitors, often with the promise of price guarantees whereby retailers match (or sometimes even beat) competitor's advertised prices on identical goods (ii) combo pricing/bundling which involves lowering one's prices when customers purchase multiple products from the same supplier, essentially a form of volume discounting (iii) loss leader pricing which involves advertising certain products at below-cost prices in order to attract customers into one's stores with the hope of selling other more profitable products to those same customers during those visits (iv) up-selling which is an attempt to sell more expensive versions of the same product to customers (v) cross-selling which is an attempt to sell additional related products to customers (vi) odd cent pricing which assumes that customers will be more interested in the same product priced at $9. 99 rather than $10 (vii) negotiated pricing which allows potential customers to bargain down the advertised price of a product during negotiations with salespersons (viii) low or interest-free pricing which permits customers to finance (borrowing) their major purchases with either no interest charges or below-market interest charges over the life of the loan agreement (ix) supersizing (a form of up-selling) which is an attempt to sell larger portions of the same product at slightly higher prices (x) everyday low prices which is an attempt to convince customers to buy products today at fixed low prices rather than wait until later for a reduced sale price that will never be offered in any event Of course one of the most reliable and traditional pricing strategies simply involves placing goods and services on sale at reduced prices for a limited period of time
The Marketing Mix - Price Additional Pricing Strategies (i) price matching or competitive pricing which involves raising or lowering one's prices to keep pace with one's closest competitors, often with the promise of price guarantees whereby retailers match (or sometimes even beat) competitor's advertised prices on identical goods (ii) combo pricing/bundling which involves lowering one's prices when customers purchase multiple products from the same supplier, essentially a form of volume discounting (iii) loss leader pricing which involves advertising certain products at below-cost prices in order to attract customers into one's stores with the hope of selling other more profitable products to those same customers during those visits (iv) up-selling which is an attempt to sell more expensive versions of the same product to customers (v) cross-selling which is an attempt to sell additional related products to customers (vi) odd cent pricing which assumes that customers will be more interested in the same product priced at $9. 99 rather than $10 (vii) negotiated pricing which allows potential customers to bargain down the advertised price of a product during negotiations with salespersons (viii) low or interest-free pricing which permits customers to finance (borrowing) their major purchases with either no interest charges or below-market interest charges over the life of the loan agreement (ix) supersizing (a form of up-selling) which is an attempt to sell larger portions of the same product at slightly higher prices (x) everyday low prices which is an attempt to convince customers to buy products today at fixed low prices rather than wait until later for a reduced sale price that will never be offered in any event Of course one of the most reliable and traditional pricing strategies simply involves placing goods and services on sale at reduced prices for a limited period of time
 The Marketing Mix - Place • Place refers to channels of distribution, or the path through which goods are moved from the manufacturer to the consumer (final user) • Goods often move through one or several intermediaries along this path, e. g. , wholesaler, retailer, importer, agent, etc.
The Marketing Mix - Place • Place refers to channels of distribution, or the path through which goods are moved from the manufacturer to the consumer (final user) • Goods often move through one or several intermediaries along this path, e. g. , wholesaler, retailer, importer, agent, etc.
 The Marketing Mix - Place There are several basic channel decisions that must be made by producers: 1. Do we employ direct or indirect channels, i. e. , direct to the consumer or indirect via a wholesaler, retailer or agent? 2. Do we employ single or multiple channels to move our goods to the consumer?
The Marketing Mix - Place There are several basic channel decisions that must be made by producers: 1. Do we employ direct or indirect channels, i. e. , direct to the consumer or indirect via a wholesaler, retailer or agent? 2. Do we employ single or multiple channels to move our goods to the consumer?
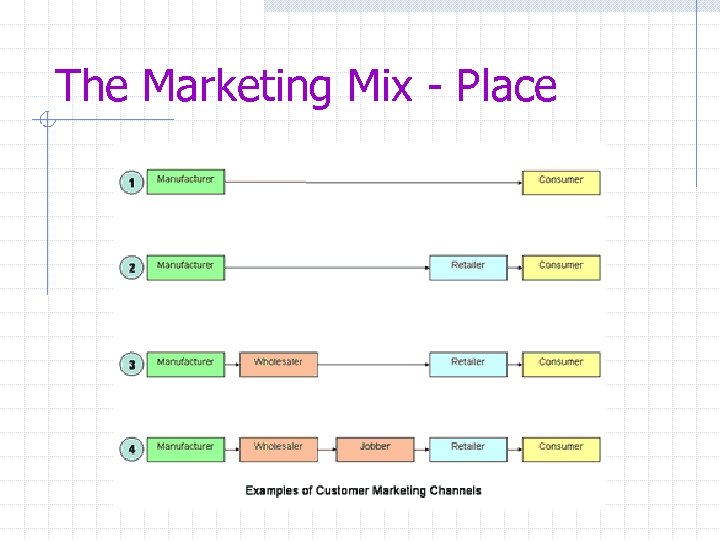 The Marketing Mix - Place
The Marketing Mix - Place
 Place - Centralized Marketing Strategy n n n This strategy focuses on the production, marketing and sale of goods and services in one country which are then exported to other countries “Think local, act global” Advantages include brand building, combined synergies and cost savings due to avoidance of duplication
Place - Centralized Marketing Strategy n n n This strategy focuses on the production, marketing and sale of goods and services in one country which are then exported to other countries “Think local, act global” Advantages include brand building, combined synergies and cost savings due to avoidance of duplication
 Place - Decentralized Marketing Strategy n n This strategy takes advantage of local production facilities, distribution centres, advertising agencies, market research firms and/or retail partnerships in foreign countries in order to target specific overseas markets Companies that employ decentralized strategies may leave all advertising, sales and promotional decisions to local sales and marketing representatives “Think global, act local” Advantages include flexibility, cultural sensitivity and shipping cost savings given proximity to foreign markets
Place - Decentralized Marketing Strategy n n This strategy takes advantage of local production facilities, distribution centres, advertising agencies, market research firms and/or retail partnerships in foreign countries in order to target specific overseas markets Companies that employ decentralized strategies may leave all advertising, sales and promotional decisions to local sales and marketing representatives “Think global, act local” Advantages include flexibility, cultural sensitivity and shipping cost savings given proximity to foreign markets
 The Marketing Mix - Product • Product refers to goods or services that satisfy consumer needs or wants • Product may possess unique features related to size, shape, colour, smell, taste, quality, design, material, variety, etc. • Marketers may increase depth of existing product line or expand number of product lines
The Marketing Mix - Product • Product refers to goods or services that satisfy consumer needs or wants • Product may possess unique features related to size, shape, colour, smell, taste, quality, design, material, variety, etc. • Marketers may increase depth of existing product line or expand number of product lines
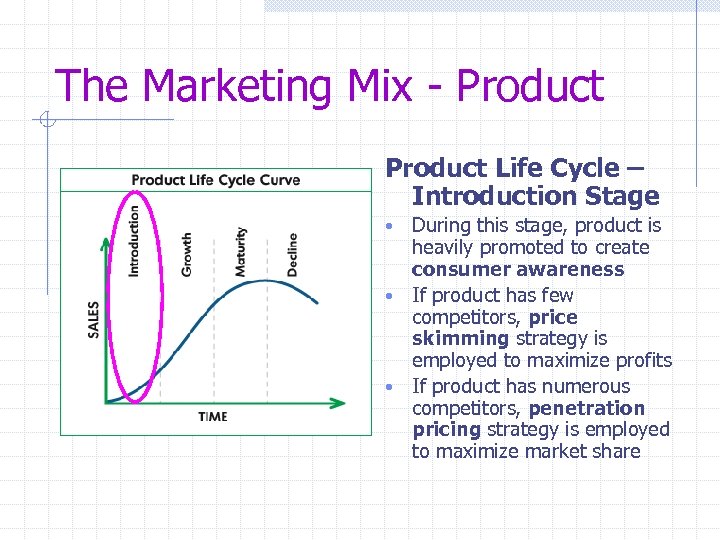 The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Introduction Stage During this stage, product is heavily promoted to create consumer awareness • If product has few competitors, price skimming strategy is employed to maximize profits • If product has numerous competitors, penetration pricing strategy is employed to maximize market share •
The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Introduction Stage During this stage, product is heavily promoted to create consumer awareness • If product has few competitors, price skimming strategy is employed to maximize profits • If product has numerous competitors, penetration pricing strategy is employed to maximize market share •
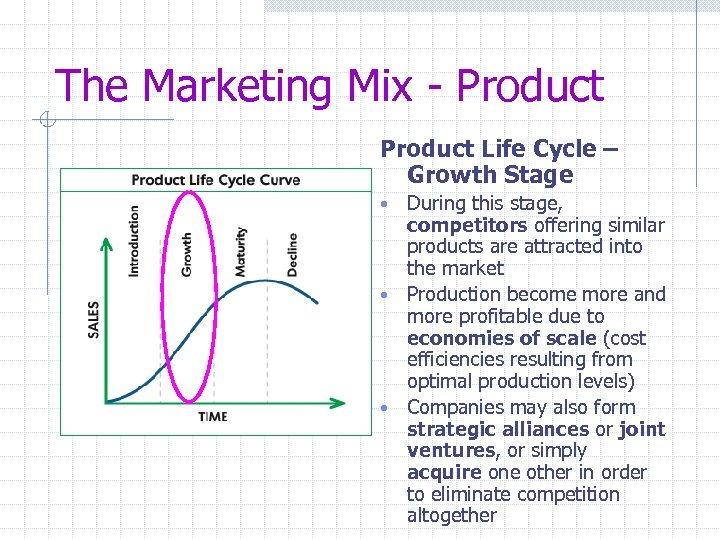 The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Growth Stage During this stage, competitors offering similar products are attracted into the market • Production become more and more profitable due to economies of scale (cost efficiencies resulting from optimal production levels) • Companies may also form strategic alliances or joint ventures, or simply acquire one other in order to eliminate competition altogether •
The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Growth Stage During this stage, competitors offering similar products are attracted into the market • Production become more and more profitable due to economies of scale (cost efficiencies resulting from optimal production levels) • Companies may also form strategic alliances or joint ventures, or simply acquire one other in order to eliminate competition altogether •
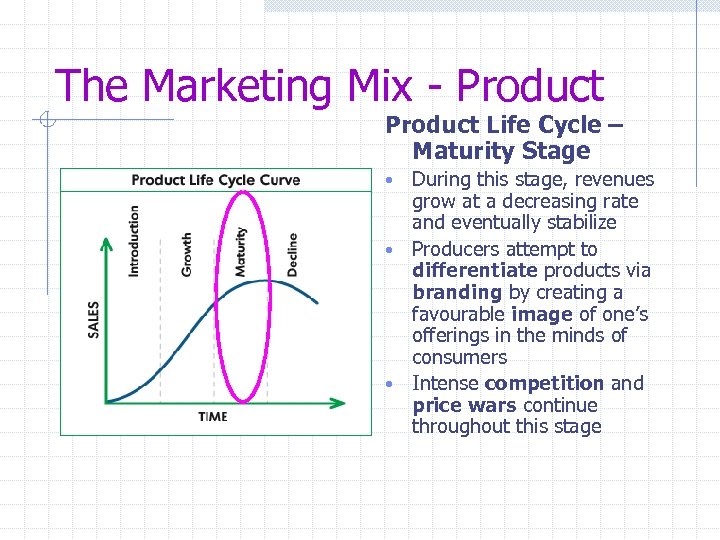 The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Maturity Stage During this stage, revenues grow at a decreasing rate and eventually stabilize • Producers attempt to differentiate products via branding by creating a favourable image of one’s offerings in the minds of consumers • Intense competition and price wars continue throughout this stage •
The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Maturity Stage During this stage, revenues grow at a decreasing rate and eventually stabilize • Producers attempt to differentiate products via branding by creating a favourable image of one’s offerings in the minds of consumers • Intense competition and price wars continue throughout this stage •
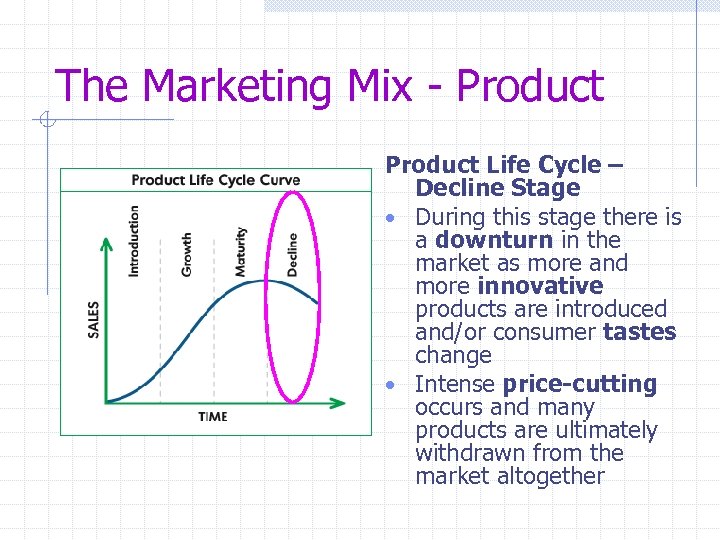 The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Decline Stage • During this stage there is a downturn in the market as more and more innovative products are introduced and/or consumer tastes change • Intense price-cutting occurs and many products are ultimately withdrawn from the market altogether
The Marketing Mix - Product Life Cycle – Decline Stage • During this stage there is a downturn in the market as more and more innovative products are introduced and/or consumer tastes change • Intense price-cutting occurs and many products are ultimately withdrawn from the market altogether
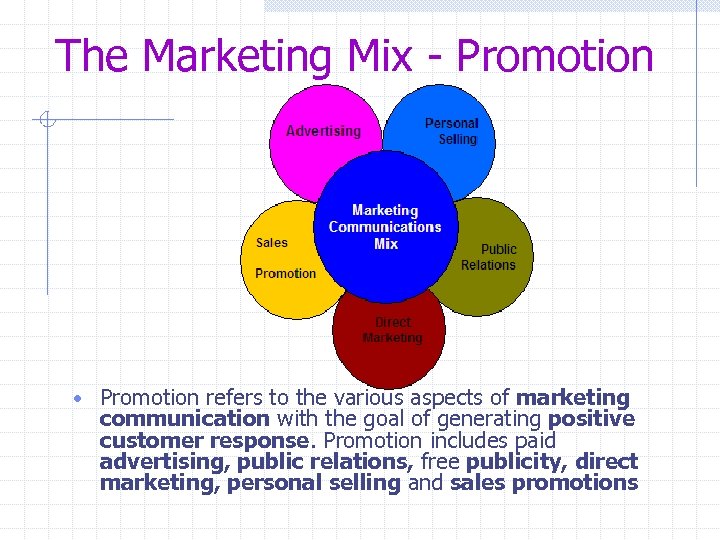 The Marketing Mix - Promotion • Promotion refers to the various aspects of marketing communication with the goal of generating positive customer response. Promotion includes paid advertising, public relations, free publicity, direct marketing, personal selling and sales promotions
The Marketing Mix - Promotion • Promotion refers to the various aspects of marketing communication with the goal of generating positive customer response. Promotion includes paid advertising, public relations, free publicity, direct marketing, personal selling and sales promotions
 Promotion – Paid Advertising • Advertising refers to paid-for promotion of commercial products using a variety of media sources directed towards particular target markets • Advertising is designed to create favourable image of company products in the minds of consumers • Examples of paid advertising includes television commercials, radio spots, newspaper and magazine ads and company websites
Promotion – Paid Advertising • Advertising refers to paid-for promotion of commercial products using a variety of media sources directed towards particular target markets • Advertising is designed to create favourable image of company products in the minds of consumers • Examples of paid advertising includes television commercials, radio spots, newspaper and magazine ads and company websites
 Promotion – Public Relations • Most large firms host public relations departments which attempt to manage the image and reputation of not only the products but also the firm itself within the larger community
Promotion – Public Relations • Most large firms host public relations departments which attempt to manage the image and reputation of not only the products but also the firm itself within the larger community
 Promotion – Publicity • Publicity refers to media promotion of firms and their products that the company did not pay for directly, e. g. , newspaper article or televised news report • Firms may attract either good or bad publicity within the media depending on the media source’s point of view
Promotion – Publicity • Publicity refers to media promotion of firms and their products that the company did not pay for directly, e. g. , newspaper article or televised news report • Firms may attract either good or bad publicity within the media depending on the media source’s point of view
 Promotion – Direct Marketing • Direct marketing allows firms to communicate directly with their customers (often against their will) and includes telemarketing, junk mail, email spam, online pop-up ads and outdoor advertising such as billboards
Promotion – Direct Marketing • Direct marketing allows firms to communicate directly with their customers (often against their will) and includes telemarketing, junk mail, email spam, online pop-up ads and outdoor advertising such as billboards
 Promotion – Personal Selling • Personal selling (or point-of-sale merchandising) refers to face-to-face salesmanship such as that seen in retail outlets between salesperson and potential customer • Ultimate goal of personal selling is to either close the deal, upsell or cross-sell to the customer
Promotion – Personal Selling • Personal selling (or point-of-sale merchandising) refers to face-to-face salesmanship such as that seen in retail outlets between salesperson and potential customer • Ultimate goal of personal selling is to either close the deal, upsell or cross-sell to the customer
 Promotion – Sales Promotions • Sales promotions are designed to increase consumer awareness and sales volumes and may include coupons, special events, free samples, contests and premiums or conditional giveaways such as BOGO offers and customer loyalty cards
Promotion – Sales Promotions • Sales promotions are designed to increase consumer awareness and sales volumes and may include coupons, special events, free samples, contests and premiums or conditional giveaways such as BOGO offers and customer loyalty cards
 The Marketing Mix Summary
The Marketing Mix Summary
 Marketing Mix – The Two Cs • The marketing mix also refers to the two Cs: consumers and competition
Marketing Mix – The Two Cs • The marketing mix also refers to the two Cs: consumers and competition
 The Marketing Mix - Consumers • Marketers must determine the demographic characteristics (e. g. , age, gender, income and education levels, etc. ) of their target market, or most typical potential consumers
The Marketing Mix - Consumers • Marketers must determine the demographic characteristics (e. g. , age, gender, income and education levels, etc. ) of their target market, or most typical potential consumers
 The Marketing Mix - Consumers • Marketers must offer significant customer value proposition, which refers to the benefits that consumers derive from the use of certain goods and services
The Marketing Mix - Consumers • Marketers must offer significant customer value proposition, which refers to the benefits that consumers derive from the use of certain goods and services
 The Marketing Mix - Competition • Marketers must also be cognizant of their direct (similar product) and indirect (discretionary income) competition
The Marketing Mix - Competition • Marketers must also be cognizant of their direct (similar product) and indirect (discretionary income) competition
 The Marketing Mix - Competition • Marketers must attempt to gain competitive advantage through (i) lower production costs per unit via economies of scale (ii) lower marketing and distribution costs (iii) product differentiation in terms of price, quality and unique features and (iv) brand equity (awareness, loyalty and insistence)
The Marketing Mix - Competition • Marketers must attempt to gain competitive advantage through (i) lower production costs per unit via economies of scale (ii) lower marketing and distribution costs (iii) product differentiation in terms of price, quality and unique features and (iv) brand equity (awareness, loyalty and insistence)
 Activity: Put the following products on the Product Life Cycle (PLC) • CD • DVD • i. Phone • i. Pad • Cell phone • Cigarettes in North America • Cigarettes in the developing world
Activity: Put the following products on the Product Life Cycle (PLC) • CD • DVD • i. Phone • i. Pad • Cell phone • Cigarettes in North America • Cigarettes in the developing world
 Activity: Put the following products on the Product Life Cycle (PLC) • MS-DOS • Play Station 3 • Fax machine • Kit-Kat and Aero chocolate bars • PC greenest shopping bag
Activity: Put the following products on the Product Life Cycle (PLC) • MS-DOS • Play Station 3 • Fax machine • Kit-Kat and Aero chocolate bars • PC greenest shopping bag
 Group Activity • You will be divided into groups of 4 • Each group will be assigned a different company from www. thetimes 100. co. uk/ • You are to list and explain the 4 Ps for each company. In addition, identify competitors and describe the typical consumer (target market) according to: income, age, gender, lifestyle, attitudes and beliefs
Group Activity • You will be divided into groups of 4 • Each group will be assigned a different company from www. thetimes 100. co. uk/ • You are to list and explain the 4 Ps for each company. In addition, identify competitors and describe the typical consumer (target market) according to: income, age, gender, lifestyle, attitudes and beliefs


