THE LIVER Hawler Medical University College of Medicine












10634-the+liver+fourth+year+_-_file_sharing_and_storage_made_simple.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 THE LIVER Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Surgery 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 1 Dr. Husen Ibrahim Taha, MSc., MRCS Fourth Year Medical college Nov. 2013
THE LIVER Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Surgery 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 1 Dr. Husen Ibrahim Taha, MSc., MRCS Fourth Year Medical college Nov. 2013
 List if Contents Objectives Introduction Anatomy Acute and Chromic Liver Diseases Investigations of Liver Management of Liver Infections, Cirrhosis, and Tumors. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 2
List if Contents Objectives Introduction Anatomy Acute and Chromic Liver Diseases Investigations of Liver Management of Liver Infections, Cirrhosis, and Tumors. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 2
 Objectives To Understand Anatomy of liver Signs of Chronic and Acute liver diseases Investigations of Liver Management of Liver trauma and Diseases 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 3
Objectives To Understand Anatomy of liver Signs of Chronic and Acute liver diseases Investigations of Liver Management of Liver trauma and Diseases 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 3
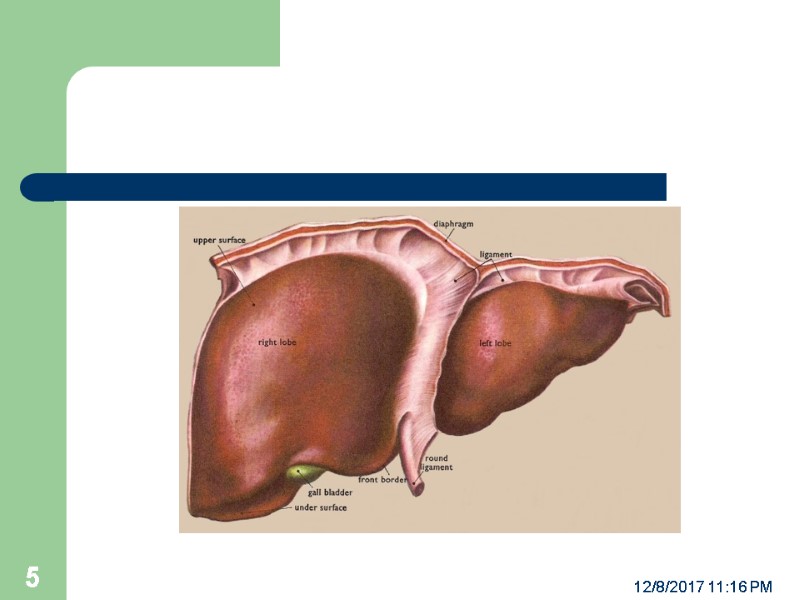
 ANATOMY The Liver is the largest solid organ, 1.5 kg in adults Has a thin capsule Covered by visceral peritoneum only in bare area Has two triangular Lig, and falciform lig. And lesser omentum It has a dual blood supply: 80% Portal, 20% hepatic artery Arterial anatomical variations may present. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 4
ANATOMY The Liver is the largest solid organ, 1.5 kg in adults Has a thin capsule Covered by visceral peritoneum only in bare area Has two triangular Lig, and falciform lig. And lesser omentum It has a dual blood supply: 80% Portal, 20% hepatic artery Arterial anatomical variations may present. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 4
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 5
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 5
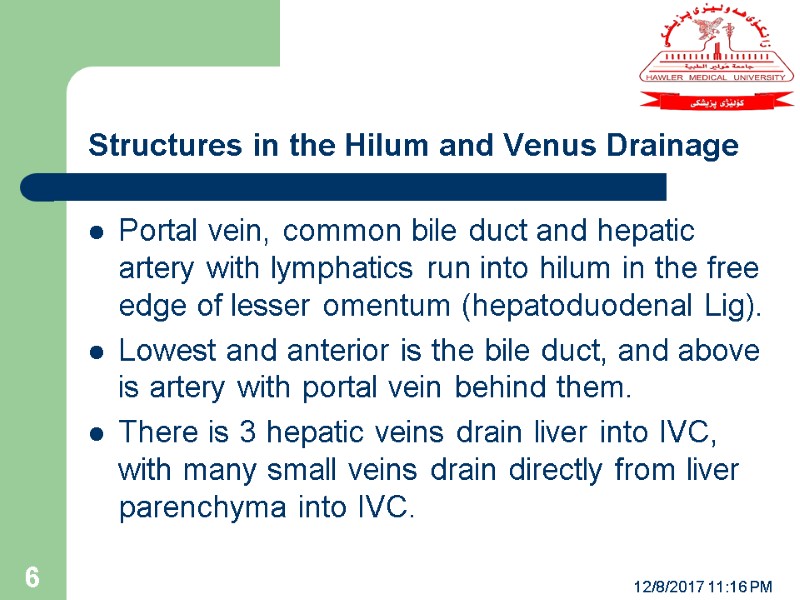
 Structures in the Hilum and Venus Drainage Portal vein, common bile duct and hepatic artery with lymphatics run into hilum in the free edge of lesser omentum (hepatoduodenal Lig). Lowest and anterior is the bile duct, and above is artery with portal vein behind them. There is 3 hepatic veins drain liver into IVC, with many small veins drain directly from liver parenchyma into IVC. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 6
Structures in the Hilum and Venus Drainage Portal vein, common bile duct and hepatic artery with lymphatics run into hilum in the free edge of lesser omentum (hepatoduodenal Lig). Lowest and anterior is the bile duct, and above is artery with portal vein behind them. There is 3 hepatic veins drain liver into IVC, with many small veins drain directly from liver parenchyma into IVC. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 6
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 7
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 7
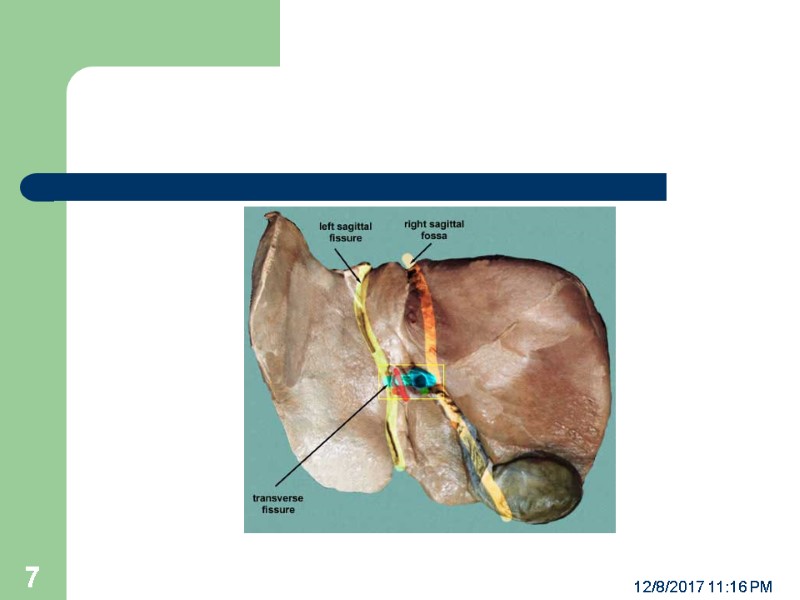
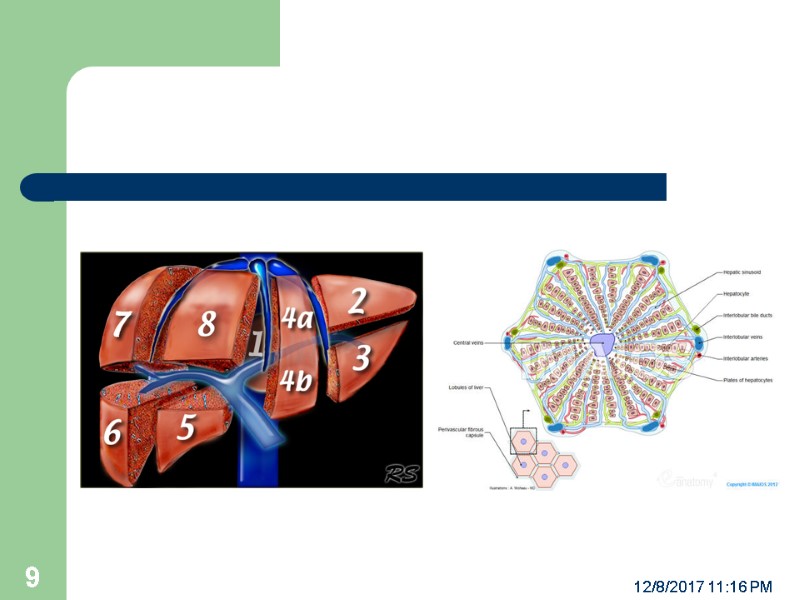
 THE INTERNAL ANATOMY OF LIVER The liver has 8 segments Each segment can be viewed as a functional unit with its own blood supply and bile duct. The understanding of these divisions facilitate surgical resection of liver for tumors, trauma and infection. The hepatic Lobule is the functional unit within the liver segment. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 8
THE INTERNAL ANATOMY OF LIVER The liver has 8 segments Each segment can be viewed as a functional unit with its own blood supply and bile duct. The understanding of these divisions facilitate surgical resection of liver for tumors, trauma and infection. The hepatic Lobule is the functional unit within the liver segment. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 8
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 9
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 9
 Embryology 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 10 The liver is a foregut structure Develops from an endodermal bud from 2nd part of duodenum making liver cells and bile ducts Liver endothelium develops from the vitelline duct and umbilical vein Supporting connective tissue, hemopoetic cells and Kupfer cells from mesnchyla cells of septum traversum
Embryology 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 10 The liver is a foregut structure Develops from an endodermal bud from 2nd part of duodenum making liver cells and bile ducts Liver endothelium develops from the vitelline duct and umbilical vein Supporting connective tissue, hemopoetic cells and Kupfer cells from mesnchyla cells of septum traversum
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 11
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 11
 FUNCTIONS OF LIVER 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 12 Maintain core body tept. pH balance and correction of lactic acidosis Synthesis of clotting factors Glucose metabolism Urea formation and protein catabolism Bilirubin formation from heam. Drug and hormone metabolism Removal of gut endotoxins and foreign antigens
FUNCTIONS OF LIVER 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 12 Maintain core body tept. pH balance and correction of lactic acidosis Synthesis of clotting factors Glucose metabolism Urea formation and protein catabolism Bilirubin formation from heam. Drug and hormone metabolism Removal of gut endotoxins and foreign antigens
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 13 Bilirubin 5-17 umol/L Alkaline Phosphatase ALP 35-130 IU/L Aspartate transaminase AST (sGOT) 5-40 IU/L Alanine transaminate ALT (sGPT) 5-40 IU/L Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase GGT 10-48IU/L Albumen 35-50 gm/L Prothrombine time II, VII, IX and X 12-16 s
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 13 Bilirubin 5-17 umol/L Alkaline Phosphatase ALP 35-130 IU/L Aspartate transaminase AST (sGOT) 5-40 IU/L Alanine transaminate ALT (sGPT) 5-40 IU/L Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase GGT 10-48IU/L Albumen 35-50 gm/L Prothrombine time II, VII, IX and X 12-16 s
 IMAGING THE LIVER 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 14 Ultrasound and Doppler US CT Scan MRI MRCP ERCP PTC Angiography Nuclear medicine Laparoscopy and Laparoscopic US
IMAGING THE LIVER 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 14 Ultrasound and Doppler US CT Scan MRI MRCP ERCP PTC Angiography Nuclear medicine Laparoscopy and Laparoscopic US
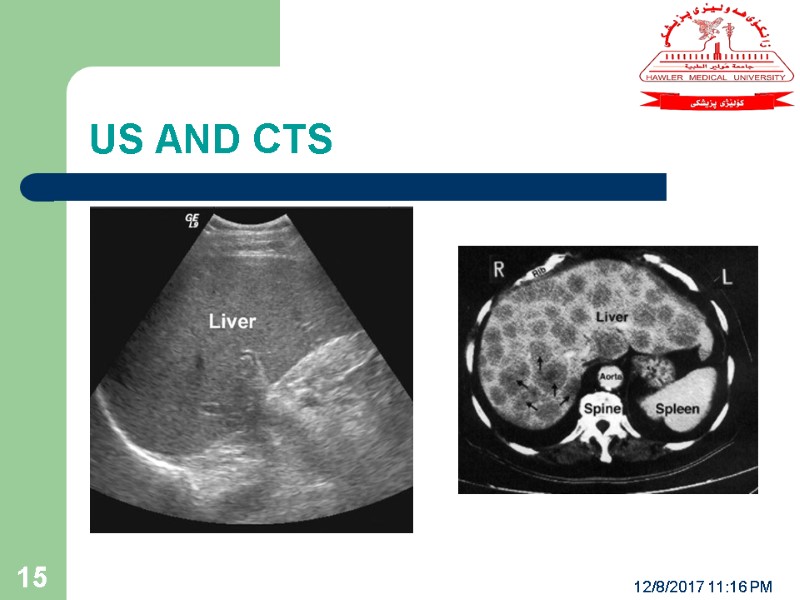
 US AND CTS 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 15
US AND CTS 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 15
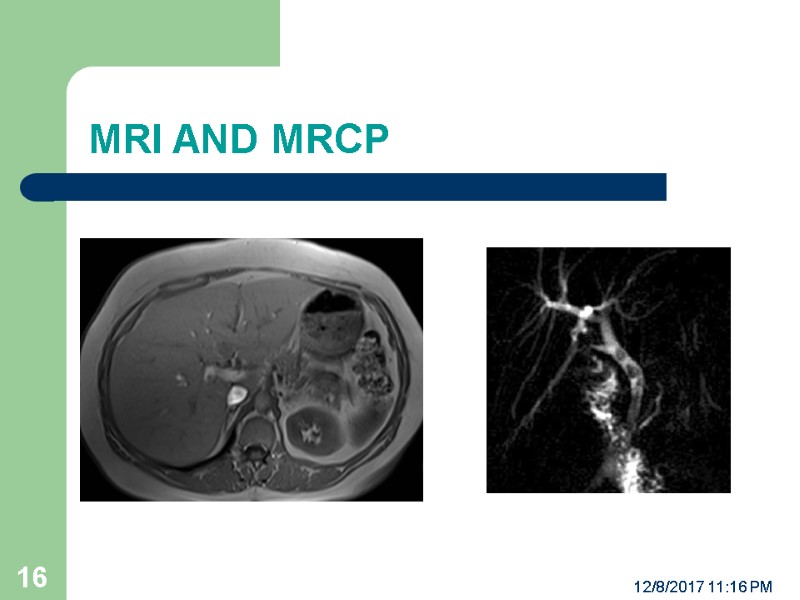
 MRI AND MRCP 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 16
MRI AND MRCP 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 16
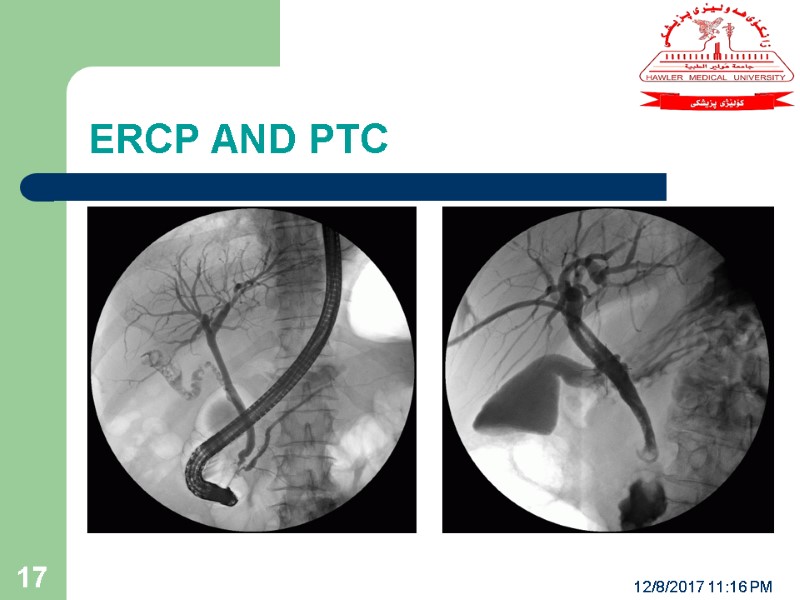
 ERCP AND PTC 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 17
ERCP AND PTC 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 17
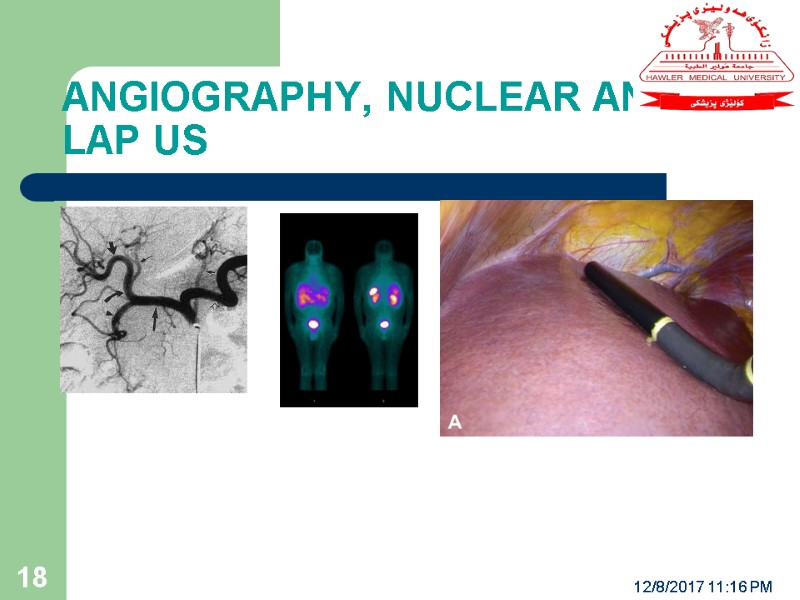
 ANGIOGRAPHY, NUCLEAR AND LAP US 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 18
ANGIOGRAPHY, NUCLEAR AND LAP US 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 18
 ACUE LIVER FAILURE 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 19 Early stage-No signs When sever damage-jaundice, neurological signs Liver flap. Confusion . Coma
ACUE LIVER FAILURE 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 19 Early stage-No signs When sever damage-jaundice, neurological signs Liver flap. Confusion . Coma
 Causes of Acute Liver Failure 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 20 Viral hepatitis Drugs: halothabe, INH, NSAD,antidepressant Paracetamole Mushroom poisoning Shock and Multiorgan Failure Acute Budd-Chiari Syndrome Wilson disease Faty liver of Pregnancy
Causes of Acute Liver Failure 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 20 Viral hepatitis Drugs: halothabe, INH, NSAD,antidepressant Paracetamole Mushroom poisoning Shock and Multiorgan Failure Acute Budd-Chiari Syndrome Wilson disease Faty liver of Pregnancy
 Management of Acute Liver Failure 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 21 Mortality >50% Well balanced fluid therapy Acid base and blood glucose monitoring Dialysis if renal failure Ventilation Treatment of cerebral edema Vigorous treatment of infections Liver transplantation
Management of Acute Liver Failure 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 21 Mortality >50% Well balanced fluid therapy Acid base and blood glucose monitoring Dialysis if renal failure Ventilation Treatment of cerebral edema Vigorous treatment of infections Liver transplantation
 Criteria for Liver Transplantation 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 22 Paracetamole induced: pH<7.3 irrespective of encephalopathy, or PT>100s+serum creatinine>100umole/L+grade 3-4 encephalopathy Non-paracetamole induced: PT>100s or any of the following 3: 1.Age<10>40, 2.aetilogy Non-A, Non-B, halotahne or idiosyncratic drug reaction, 3. .7 days jaundice before encephalopathy, 4. PT>50s, 5. Milirubin>100 umol/L
Criteria for Liver Transplantation 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 22 Paracetamole induced: pH<7.3 irrespective of encephalopathy, or PT>100s+serum creatinine>100umole/L+grade 3-4 encephalopathy Non-paracetamole induced: PT>100s or any of the following 3: 1.Age<10>40, 2.aetilogy Non-A, Non-B, halotahne or idiosyncratic drug reaction, 3. .7 days jaundice before encephalopathy, 4. PT>50s, 5. Milirubin>100 umol/L
 Chronic Liver disease-Features 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 23 Lethargy and weakness-early Fever might be due to liver infl or infection Jaundice later and indicate severity Waisting Hyperdynamic circulation Encephalopathy-imapired memmory, flapping tremor Portal hypertension: ascitis, esophageal varices, splen Skin: spider nevi, palmar erythema, easy bruising Coagulopathy-easy bruising
Chronic Liver disease-Features 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 23 Lethargy and weakness-early Fever might be due to liver infl or infection Jaundice later and indicate severity Waisting Hyperdynamic circulation Encephalopathy-imapired memmory, flapping tremor Portal hypertension: ascitis, esophageal varices, splen Skin: spider nevi, palmar erythema, easy bruising Coagulopathy-easy bruising
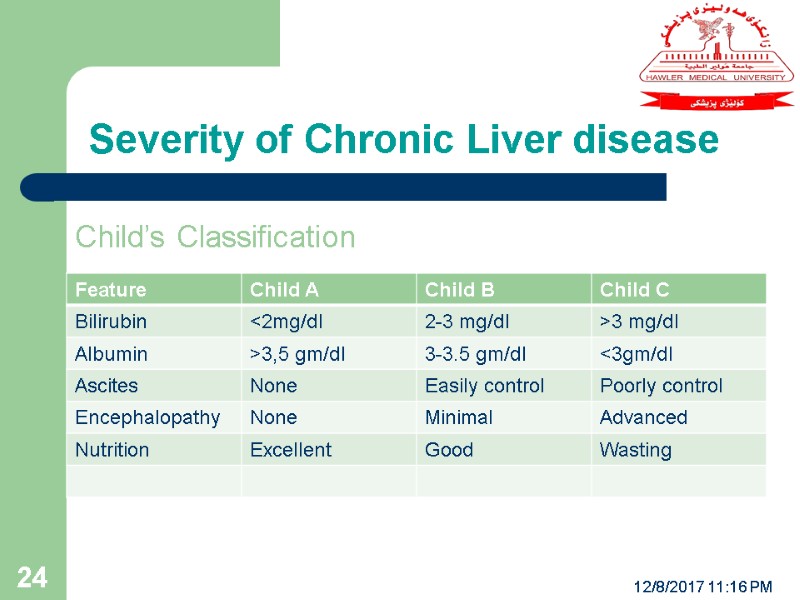
 Severity of Chronic Liver disease 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 24 Child’s Classification
Severity of Chronic Liver disease 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 24 Child’s Classification
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 25 Cause: Echinococcus Granulosus This parasite present in dog intestine Eggs ingested-larva through portal vein to liver or any other organ making Cysts The cysts contains active daughter cysts if rupture each make a new cyst Hydatid Disease of Liver
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 25 Cause: Echinococcus Granulosus This parasite present in dog intestine Eggs ingested-larva through portal vein to liver or any other organ making Cysts The cysts contains active daughter cysts if rupture each make a new cyst Hydatid Disease of Liver
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 26 Abdominal mass, or discomfort Acute abdomen after rupture from trivial trauma or spontaneous Rupture into biliary tree –obstructive jaundice Presentation of Hydatid of Liver
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 26 Abdominal mass, or discomfort Acute abdomen after rupture from trivial trauma or spontaneous Rupture into biliary tree –obstructive jaundice Presentation of Hydatid of Liver
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 27 History Physical examination Ultrasound: Multiloculted cyst CT scan Serology: antibody to hydatid by ELISA Diagnosis
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 27 History Physical examination Ultrasound: Multiloculted cyst CT scan Serology: antibody to hydatid by ELISA Diagnosis
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 28 Rupture and anaphylactic shock and dissemination Jaundice Pressure symptoms Rupture into the chest Infection: usually leads to dead daughter cysts Complications of untreated
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 28 Rupture and anaphylactic shock and dissemination Jaundice Pressure symptoms Rupture into the chest Infection: usually leads to dead daughter cysts Complications of untreated
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 29 Medical: Albendazoel, and Mebendazole Surgery: Removal of Cyst The cysts is injected by hypertonic saline to kill daughter cysts prior to removal to prevent possibility of dissemination if ruptured. Rupture into biliary tract treated endoscopically prior to cyst removal Calcified cysts are usually dead and can be followed by U/S Treatment
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 29 Medical: Albendazoel, and Mebendazole Surgery: Removal of Cyst The cysts is injected by hypertonic saline to kill daughter cysts prior to removal to prevent possibility of dissemination if ruptured. Rupture into biliary tract treated endoscopically prior to cyst removal Calcified cysts are usually dead and can be followed by U/S Treatment
 Ascending Cholangitis Duct stones are the commonest cause Fever, rigor, jaundice, tender hepatomegally Diagnosed: U/S: dilated ducts, abnomal LFT, and positive blood cultures It is a medical emergency: rehydration+broad spectrum antibiotics (cephalosporins) Endoscopic or percutaneus drainage Sphinterotomy and stone removal 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 30
Ascending Cholangitis Duct stones are the commonest cause Fever, rigor, jaundice, tender hepatomegally Diagnosed: U/S: dilated ducts, abnomal LFT, and positive blood cultures It is a medical emergency: rehydration+broad spectrum antibiotics (cephalosporins) Endoscopic or percutaneus drainage Sphinterotomy and stone removal 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 30
 Pyogenic Liver Abscess Idiopathic, diabetes, immunocompressed Anerexia, malaise, fever, abd. Pain U/S and CT: multiloculated cystic mass, confirmed by aspiration for culture. A source for infection especially in colon should be sought. Broad spectrum antibiotic +metronidazole Percutaneus aspiration under U/S guide.. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 31
Pyogenic Liver Abscess Idiopathic, diabetes, immunocompressed Anerexia, malaise, fever, abd. Pain U/S and CT: multiloculated cystic mass, confirmed by aspiration for culture. A source for infection especially in colon should be sought. Broad spectrum antibiotic +metronidazole Percutaneus aspiration under U/S guide.. 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 31
 Amoebic Liver Abscess Caused by Entameba Histolytica, spread by feco-oral The parasite reaches liver via portal vein. Presents with fever and riger. Diagnosed by finding the parasite from stool and liver lesion U/S: is important to detect liver abscess Treatment metronidazole 750 mg three times If not responded further assessment needed 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 32
Amoebic Liver Abscess Caused by Entameba Histolytica, spread by feco-oral The parasite reaches liver via portal vein. Presents with fever and riger. Diagnosed by finding the parasite from stool and liver lesion U/S: is important to detect liver abscess Treatment metronidazole 750 mg three times If not responded further assessment needed 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 32
 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 33 Hemangiomas: Commonest Hepatic Adenoma: Rare Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: sulfur colloid scan needed to distinguish from malignant and adenoma Hepatoceluar carcinoma: U/S, AFP Cholangiocarcinoma- primary sclerosing choangitis, calrolis disease…gall stones Klatskin tumors: Liver Tumors
12/8/2017 11:16 PM 33 Hemangiomas: Commonest Hepatic Adenoma: Rare Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: sulfur colloid scan needed to distinguish from malignant and adenoma Hepatoceluar carcinoma: U/S, AFP Cholangiocarcinoma- primary sclerosing choangitis, calrolis disease…gall stones Klatskin tumors: Liver Tumors
 Thank you 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 34
Thank you 12/8/2017 11:16 PM 34

