7973b732ad4a8dacad54e2c1b904e2db.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 The Linked Exchange Rate system of Hong Kong 1
The Linked Exchange Rate system of Hong Kong 1
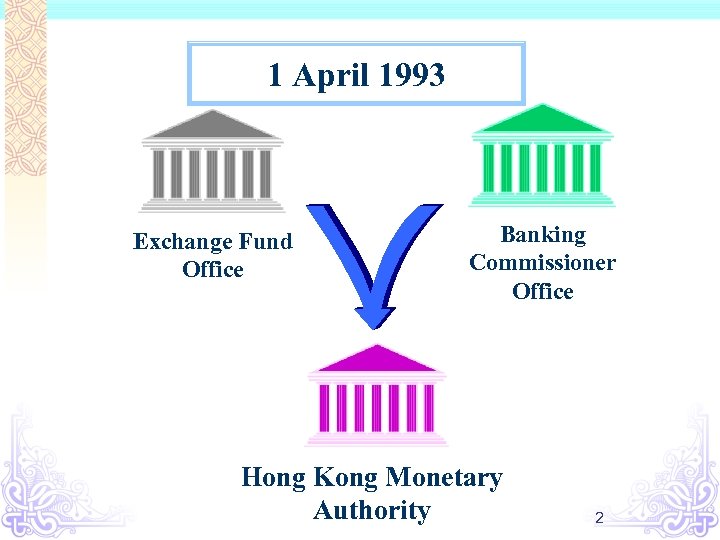 1 April 1993 Exchange Fund Office Banking Commissioner Office Hong Kong Monetary Authority 2
1 April 1993 Exchange Fund Office Banking Commissioner Office Hong Kong Monetary Authority 2
 Main Functions v Keeping the Hong Kong dollar stable v Managing the Exchange Fund in a sound and effective way v Promoting the safety and stability of Hong Kong’s banking system v Developing Hong Kong’s financial infrastructure 3
Main Functions v Keeping the Hong Kong dollar stable v Managing the Exchange Fund in a sound and effective way v Promoting the safety and stability of Hong Kong’s banking system v Developing Hong Kong’s financial infrastructure 3
 Monetary Policy Objective Currency stability, defined as a stable external exchange value of the currency of Hong Kong, in terms of its exchange rate in the foreign exchange market against the US dollar, at around HK$7. 80 to US$1. 4
Monetary Policy Objective Currency stability, defined as a stable external exchange value of the currency of Hong Kong, in terms of its exchange rate in the foreign exchange market against the US dollar, at around HK$7. 80 to US$1. 4
 Importance of Exchange Rate Stability v Hong Kong is a small and highly-open economy v As an international trading centre, external trade equals to 4 times GDP v As an international financial centre, exchange rate volatility affects capital allocation decision of foreign investors 5
Importance of Exchange Rate Stability v Hong Kong is a small and highly-open economy v As an international trading centre, external trade equals to 4 times GDP v As an international financial centre, exchange rate volatility affects capital allocation decision of foreign investors 5
 US Dollar as the Anchor Currency v US dollar is the most commonly used currency for international trade and financial transactions v US is Hong Kong’s second largest trading partner v Business cycle synchronisation between Hong Kong and the US is the highest 6
US Dollar as the Anchor Currency v US dollar is the most commonly used currency for international trade and financial transactions v US is Hong Kong’s second largest trading partner v Business cycle synchronisation between Hong Kong and the US is the highest 6
 Historical Background v In 1982 -83, Sino-British talk on the resumption of Hong Kong's sovereignty after 1997 triggered a confidence crisis, leading to sharp depreciation of the Hong Kong dollar v In response, the HK Government established the Linked Exchange Rate system on 17 October 1983 v A currency board system 7
Historical Background v In 1982 -83, Sino-British talk on the resumption of Hong Kong's sovereignty after 1997 triggered a confidence crisis, leading to sharp depreciation of the Hong Kong dollar v In response, the HK Government established the Linked Exchange Rate system on 17 October 1983 v A currency board system 7
 Currency Board system v Monetary Base fully backed by foreign exchange reserves v Components of Monetary Base: v Currency in circulation v Aggregate Balance v Exchange Fund Bills and Notes 8
Currency Board system v Monetary Base fully backed by foreign exchange reserves v Components of Monetary Base: v Currency in circulation v Aggregate Balance v Exchange Fund Bills and Notes 8
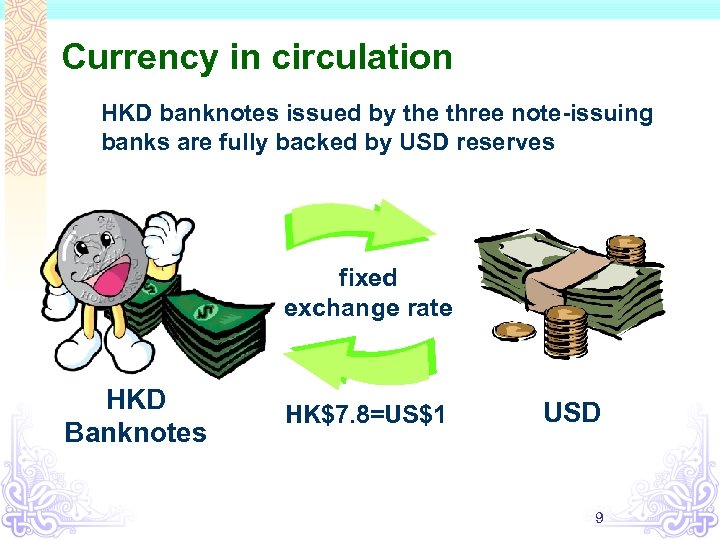 Currency in circulation HKD banknotes issued by the three note-issuing banks are fully backed by USD reserves fixed exchange rate HKD Banknotes HK$7. 8=US$1 USD 9
Currency in circulation HKD banknotes issued by the three note-issuing banks are fully backed by USD reserves fixed exchange rate HKD Banknotes HK$7. 8=US$1 USD 9
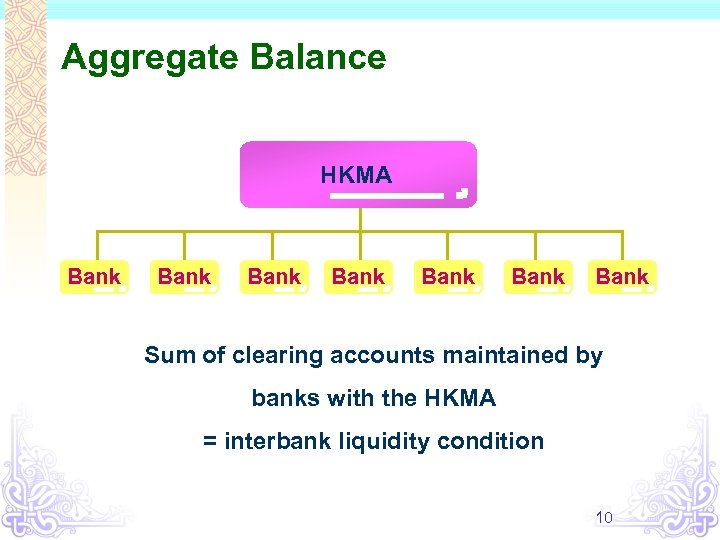 Aggregate Balance HKMA Bank Bank Sum of clearing accounts maintained by banks with the HKMA = interbank liquidity condition 10
Aggregate Balance HKMA Bank Bank Sum of clearing accounts maintained by banks with the HKMA = interbank liquidity condition 10
 Exchange Fund Bills and Notes v Direct and unconditional obligations of the HK Government under the Exchange Fund Account v Introduced in March 1990 v Tenors of the Bills are 91, 182 and 364 days, while those of the Notes are 2, 3, 5, 7, 10 and 15 years 11
Exchange Fund Bills and Notes v Direct and unconditional obligations of the HK Government under the Exchange Fund Account v Introduced in March 1990 v Tenors of the Bills are 91, 182 and 364 days, while those of the Notes are 2, 3, 5, 7, 10 and 15 years 11
 How does the Linked Exchange Rate system operate? 12
How does the Linked Exchange Rate system operate? 12
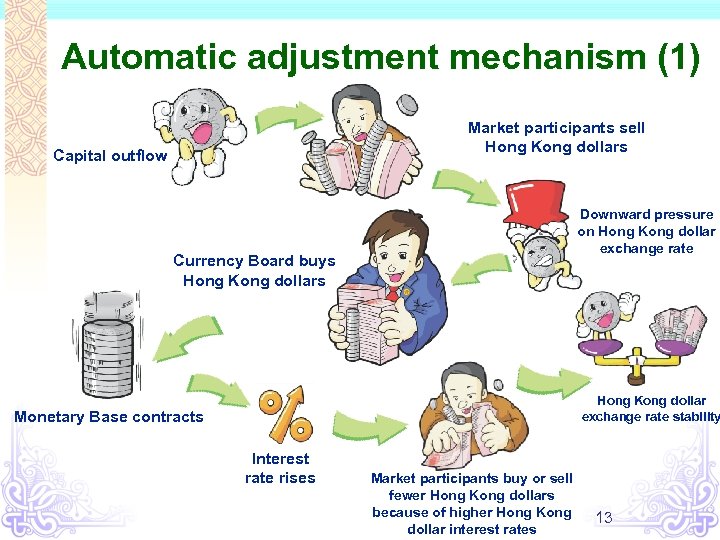 Automatic adjustment mechanism (1) Market participants sell Hong Kong dollars Capital outflow Downward pressure on Hong Kong dollar exchange rate Currency Board buys Hong Kong dollar exchange rate stability Monetary Base contracts Interest rate rises Market participants buy or sell fewer Hong Kong dollars because of higher Hong Kong dollar interest rates 13
Automatic adjustment mechanism (1) Market participants sell Hong Kong dollars Capital outflow Downward pressure on Hong Kong dollar exchange rate Currency Board buys Hong Kong dollar exchange rate stability Monetary Base contracts Interest rate rises Market participants buy or sell fewer Hong Kong dollars because of higher Hong Kong dollar interest rates 13
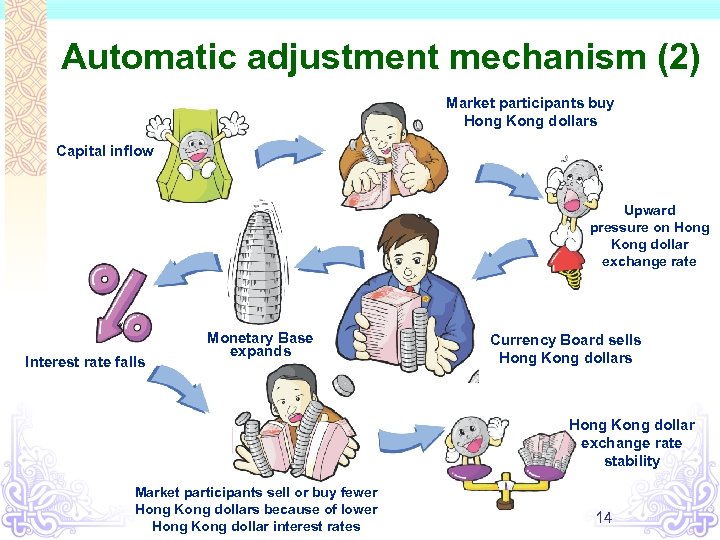 Automatic adjustment mechanism (2) Market participants buy Hong Kong dollars Capital inflow Upward pressure on Hong Kong dollar exchange rate Interest rate falls Monetary Base expands Currency Board sells Hong Kong dollars 6 Market participants sell or buy fewer Hong Kong dollars because of lower Hong Kong dollar interest rates Hong Kong dollar exchange rate stability 14
Automatic adjustment mechanism (2) Market participants buy Hong Kong dollars Capital inflow Upward pressure on Hong Kong dollar exchange rate Interest rate falls Monetary Base expands Currency Board sells Hong Kong dollars 6 Market participants sell or buy fewer Hong Kong dollars because of lower Hong Kong dollar interest rates Hong Kong dollar exchange rate stability 14
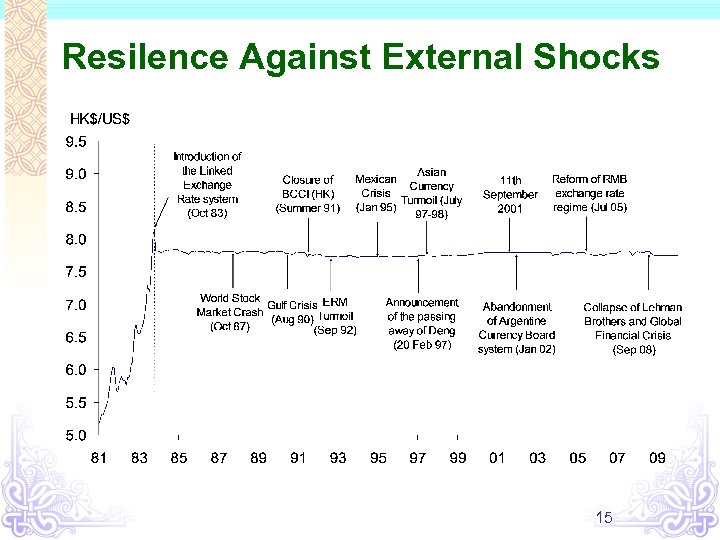 Resilence Against External Shocks 15
Resilence Against External Shocks 15
 Reform measures v September-1998 ( seven measures ) v May-2005 ( three refinements) 16
Reform measures v September-1998 ( seven measures ) v May-2005 ( three refinements) 16
 Background on seven technical measures in 1998 Market concerns: v Asian financial crisis v Rumours of renminbi devaluation, market scepticism on the commitment to the Link v A lot of Hong Kong dollar short- selling activities, tight interbank liquidity and high interest rate volatility 17
Background on seven technical measures in 1998 Market concerns: v Asian financial crisis v Rumours of renminbi devaluation, market scepticism on the commitment to the Link v A lot of Hong Kong dollar short- selling activities, tight interbank liquidity and high interest rate volatility 17
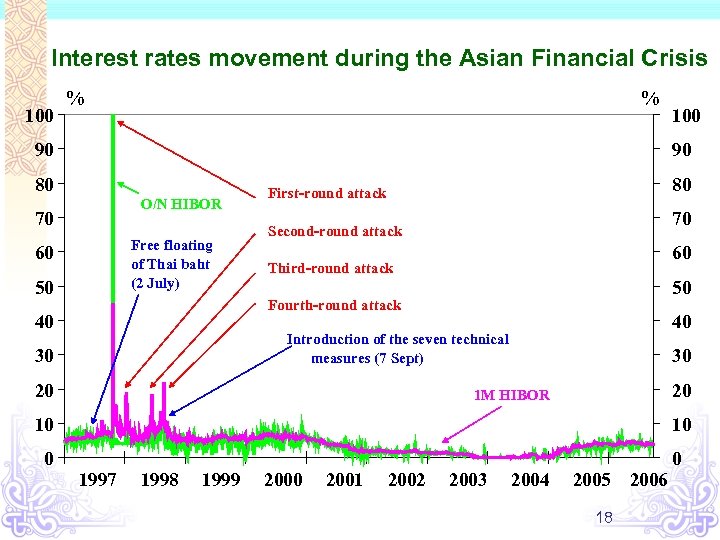 Interest rates movement during the Asian Financial Crisis 100 % % 90 100 90 80 O/N HIBOR 70 Free floating of Thai baht (2 July) 60 50 80 First-round attack 70 Second-round attack 60 Third-round attack 50 Fourth-round attack 40 40 Introduction of the seven technical measures (7 Sept) 30 20 1 M HIBOR 10 10 0 0 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 18 2006
Interest rates movement during the Asian Financial Crisis 100 % % 90 100 90 80 O/N HIBOR 70 Free floating of Thai baht (2 July) 60 50 80 First-round attack 70 Second-round attack 60 Third-round attack 50 Fourth-round attack 40 40 Introduction of the seven technical measures (7 Sept) 30 20 1 M HIBOR 10 10 0 0 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 18 2006
 Seven technical measures Introduced in September 1998 to strengthen the Currency Board arrangement Seven technical measures Convertibility Undertaking Discount Window 19
Seven technical measures Introduced in September 1998 to strengthen the Currency Board arrangement Seven technical measures Convertibility Undertaking Discount Window 19
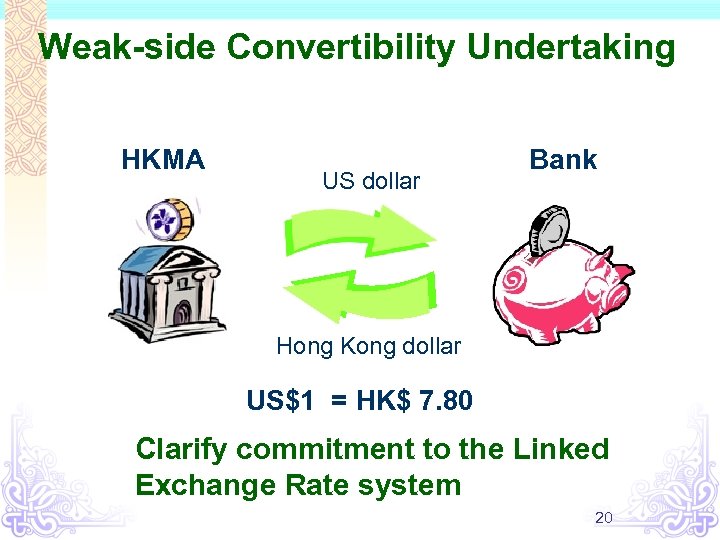 Weak-side Convertibility Undertaking HKMA US dollar Bank Hong Kong dollar US$1 = HK$ 7. 80 Clarify commitment to the Linked Exchange Rate system 20
Weak-side Convertibility Undertaking HKMA US dollar Bank Hong Kong dollar US$1 = HK$ 7. 80 Clarify commitment to the Linked Exchange Rate system 20
 Discount Window Bank HKMA Banks can use Exchange Fund paper as collateral to arrange repo agreement with the HKMA for liquidity management (4: 30 p. m. daily) Avoid excessive interest rate volatility and allows orderly adjustment 21
Discount Window Bank HKMA Banks can use Exchange Fund paper as collateral to arrange repo agreement with the HKMA for liquidity management (4: 30 p. m. daily) Avoid excessive interest rate volatility and allows orderly adjustment 21
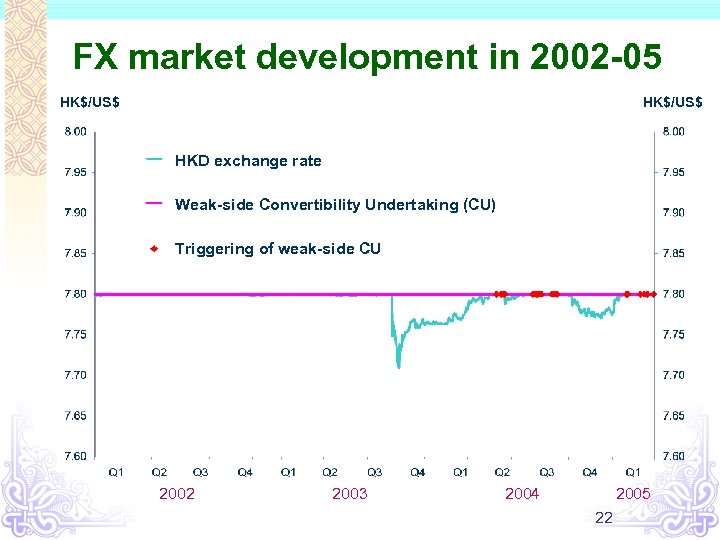 FX market development in 2002 -05 HK$/US$ HKD exchange rate Weak-side Convertibility Undertaking (CU) Triggering of weak-side CU 2002 2003 2004 2005 22
FX market development in 2002 -05 HK$/US$ HKD exchange rate Weak-side Convertibility Undertaking (CU) Triggering of weak-side CU 2002 2003 2004 2005 22
 Background on three refinements in 2005 v Expectations on renminbi appreciation v Hong Kong’s economic recovery v Depreciation of the US dollar 23
Background on three refinements in 2005 v Expectations on renminbi appreciation v Hong Kong’s economic recovery v Depreciation of the US dollar 23
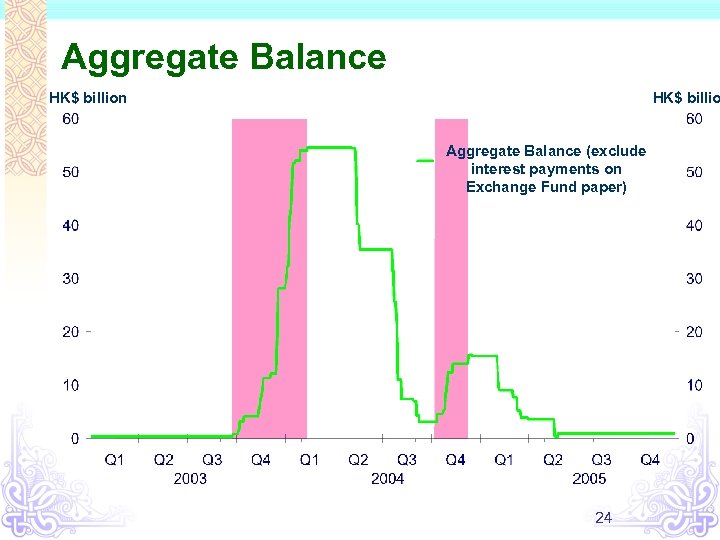 Aggregate Balance HK$ billion HK$ billio Aggregate Balance (exclude interest payments on Exchange Fund paper) 24
Aggregate Balance HK$ billion HK$ billio Aggregate Balance (exclude interest payments on Exchange Fund paper) 24
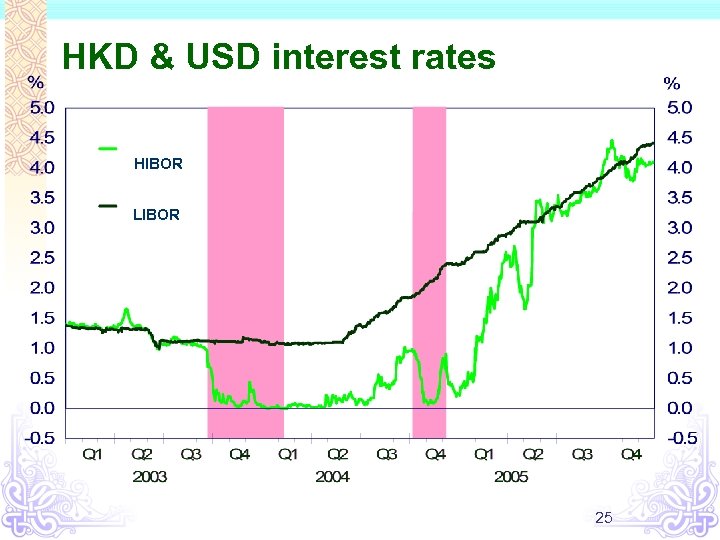 HKD & USD interest rates HIBOR LIBOR 25
HKD & USD interest rates HIBOR LIBOR 25
 Impact of easy monetary conditions v Risk of inflation and formation of asset bubble v Destabilising effect associated with realignment of HKD interest rates with USD rates 26
Impact of easy monetary conditions v Risk of inflation and formation of asset bubble v Destabilising effect associated with realignment of HKD interest rates with USD rates 26
 Three refinements Strong-side Convertibility Undertaking Weak-side Convertibility Undertaking Convertibility Zone 27
Three refinements Strong-side Convertibility Undertaking Weak-side Convertibility Undertaking Convertibility Zone 27
 Three refinements (1) The HKMA undertakes to buy US dollar from banks at HK$7. 75/US$1 28
Three refinements (1) The HKMA undertakes to buy US dollar from banks at HK$7. 75/US$1 28
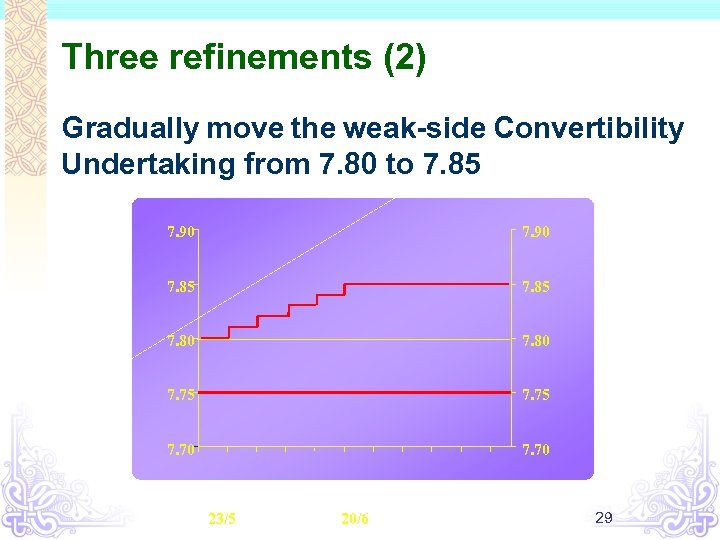 Three refinements (2) Gradually move the weak-side Convertibility Undertaking from 7. 80 to 7. 85 7. 90 7. 85 7. 80 7. 75 7. 70 23/5 20/6 29
Three refinements (2) Gradually move the weak-side Convertibility Undertaking from 7. 80 to 7. 85 7. 90 7. 85 7. 80 7. 75 7. 70 23/5 20/6 29
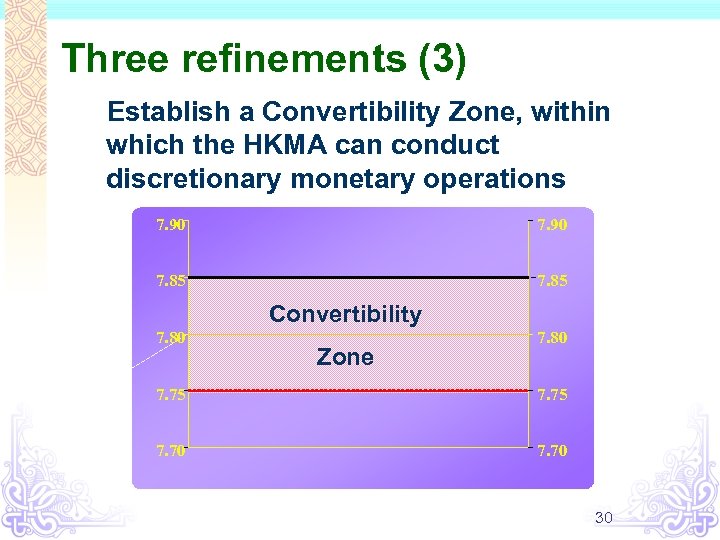 Three refinements (3) Establish a Convertibility Zone, within which the HKMA can conduct discretionary monetary operations 7. 90 7. 85 Convertibility 7. 80 Zone 7. 80 7. 75 7. 70 30
Three refinements (3) Establish a Convertibility Zone, within which the HKMA can conduct discretionary monetary operations 7. 90 7. 85 Convertibility 7. 80 Zone 7. 80 7. 75 7. 70 30
 Effects of the three refinements v Remove uncertainty about appreciation potential of the Hong Kong dollar v HKD interest rates closer to USD rates v Strengthen the operation of the Linked Exchange Rate system 31
Effects of the three refinements v Remove uncertainty about appreciation potential of the Hong Kong dollar v HKD interest rates closer to USD rates v Strengthen the operation of the Linked Exchange Rate system 31
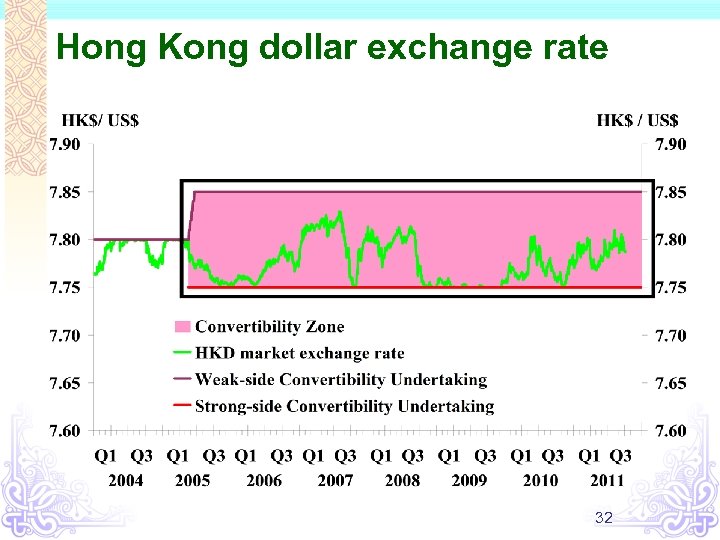 Hong Kong dollar exchange rate 32
Hong Kong dollar exchange rate 32
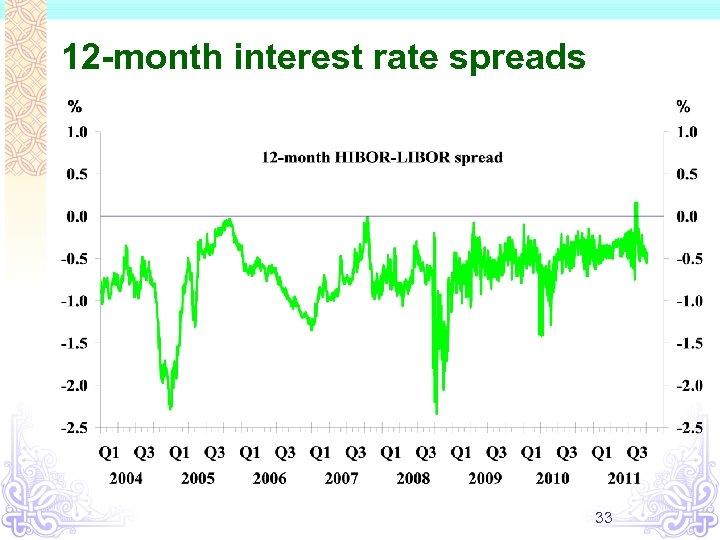 12 -month interest rate spreads 33
12 -month interest rate spreads 33
 Conclusion v The Linked Exchange Rate system is a cornerstone for maintaining economic stability v Economic underpinnings v Ample forex reserves v Flexible economic structure v Prudent fiscal policy stance v Sound banking system 34
Conclusion v The Linked Exchange Rate system is a cornerstone for maintaining economic stability v Economic underpinnings v Ample forex reserves v Flexible economic structure v Prudent fiscal policy stance v Sound banking system 34


