 The Life of Mammals
The Life of Mammals
 Mammals (class Mammalia) are a clade of warm-blooded amniotes. Among the features that distinguish them from the other amniotes, the reptiles and the birds, are hair, three middle ear bones, mammary glands in females, and a neocortex (a region of the brain). The largest group of mammals, the placentals, have a placenta which feeds the offspring during pregnancy.
Mammals (class Mammalia) are a clade of warm-blooded amniotes. Among the features that distinguish them from the other amniotes, the reptiles and the birds, are hair, three middle ear bones, mammary glands in females, and a neocortex (a region of the brain). The largest group of mammals, the placentals, have a placenta which feeds the offspring during pregnancy.
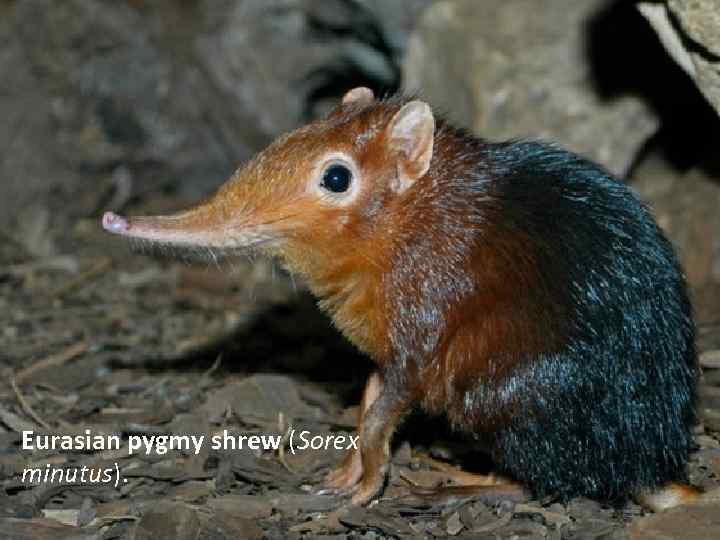 Eurasian pygmy shrew (Sorex minutus).
Eurasian pygmy shrew (Sorex minutus).
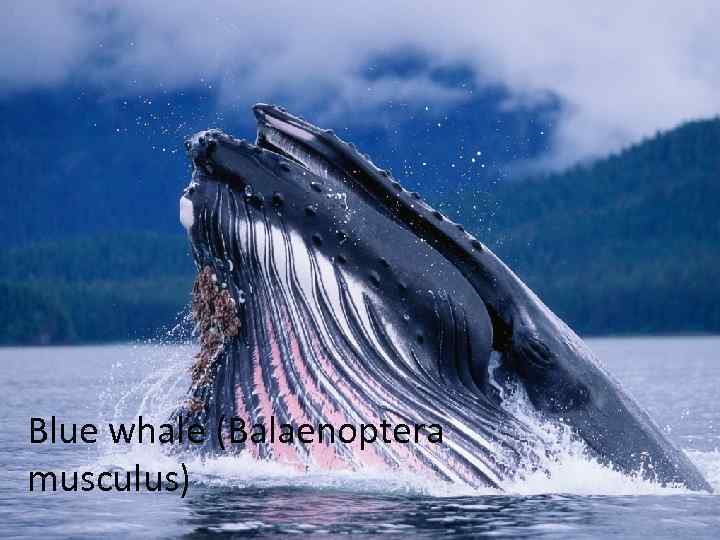 Blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus)
Blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus)
 Geographic Range Mammals can be found on all continents, in all oceans, and on many oceanic islands of the world.
Geographic Range Mammals can be found on all continents, in all oceans, and on many oceanic islands of the world.
 Habitat Regions: • temperate • tropical • subtropical • polar
Habitat Regions: • temperate • tropical • subtropical • polar
 Terrestrial Biomes
Terrestrial Biomes
 Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus)
Tundra Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus)
 Taiga Eurasian elk (Alces alces)
Taiga Eurasian elk (Alces alces)
 Desert Lesser Egyptian Jerboa (Jaculus jaculus)
Desert Lesser Egyptian Jerboa (Jaculus jaculus)
 Savanna Aardvark (Orycteropus afer)
Savanna Aardvark (Orycteropus afer)
 Rainforest Philippine Tarsier (Tarsius syrichta)
Rainforest Philippine Tarsier (Tarsius syrichta)
 Mountains Аrgali, or the mountain sheep (Ovis ammon)
Mountains Аrgali, or the mountain sheep (Ovis ammon)
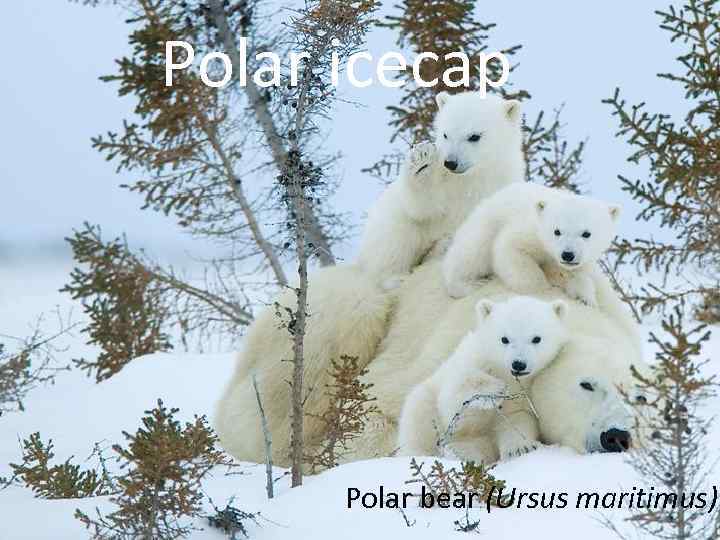 Polar icecap Рolar bear (Ursus maritimus)
Polar icecap Рolar bear (Ursus maritimus)
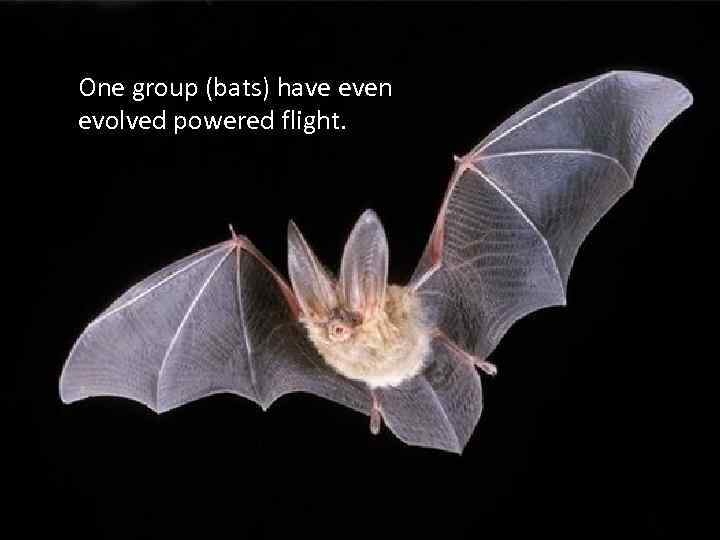 One group (bats) have even evolved powered flight.
One group (bats) have even evolved powered flight.
 Aquatic Biomes
Aquatic Biomes
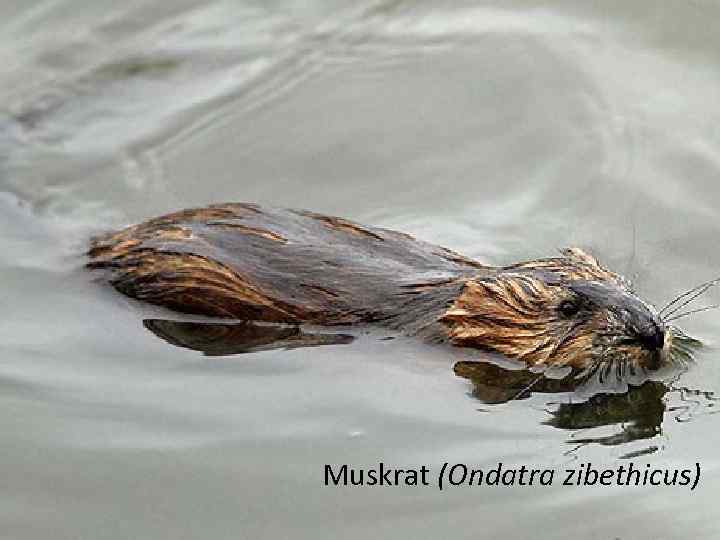 Muskrat (Ondatra zibethicus)
Muskrat (Ondatra zibethicus)
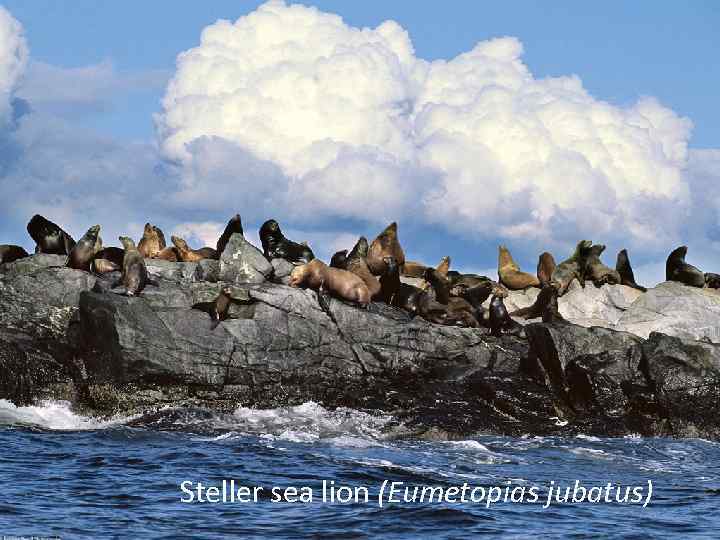 Steller sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus)
Steller sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus)
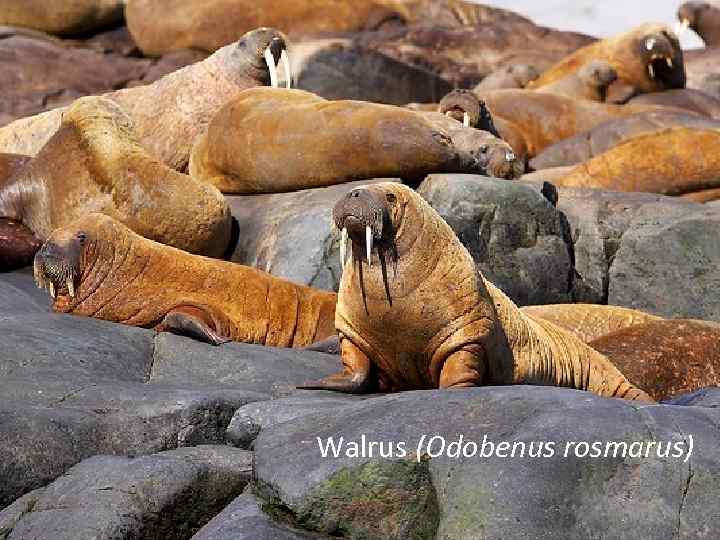 Walrus (Odobenus rosmarus)
Walrus (Odobenus rosmarus)
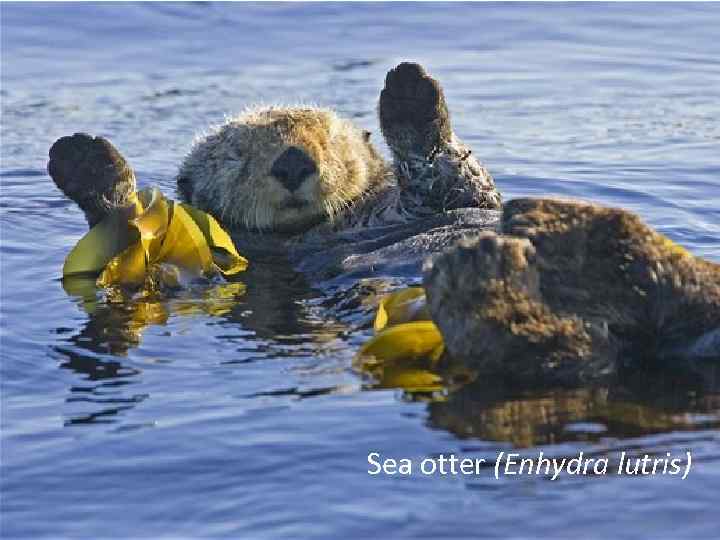 Sea otter (Enhydra lutris)
Sea otter (Enhydra lutris)
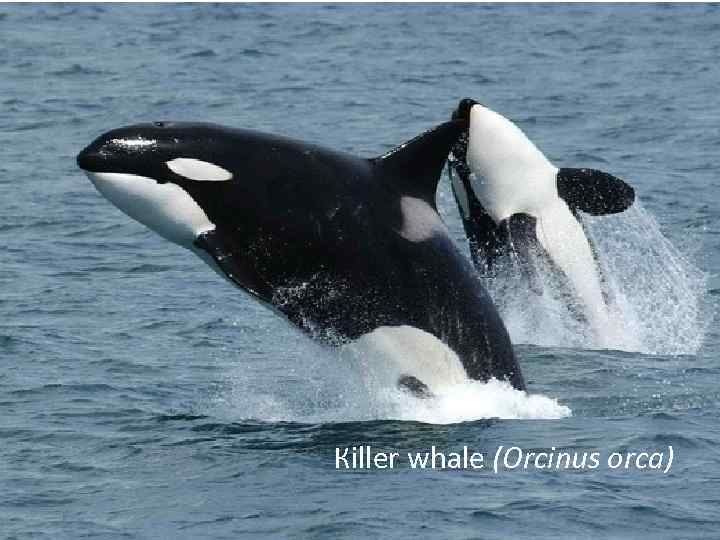 Кiller whale (Orcinus orca)
Кiller whale (Orcinus orca)
 Development
Development
 Monotremes Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus)
Monotremes Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus)
 Short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus)
Short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus)
 Marsupials (Metatheria) Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus)
Marsupials (Metatheria) Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus)
 Placental mammals (Eutheria)
Placental mammals (Eutheria)
 Reproduction
Reproduction
 Mating System • • • monogamous polyandrous polygynandrous (promiscuous) eusocial
Mating System • • • monogamous polyandrous polygynandrous (promiscuous) eusocial
 polygynous Plains zebra (Equus quagga)
polygynous Plains zebra (Equus quagga)
 monogamous European beaver (Castor fiber)
monogamous European beaver (Castor fiber)
 polyandrous Goeldi's marmoset or Goeldi's monkey (Callimico goeldii)
polyandrous Goeldi's marmoset or Goeldi's monkey (Callimico goeldii)
 polygynandrous Common chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes)
polygynandrous Common chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes)
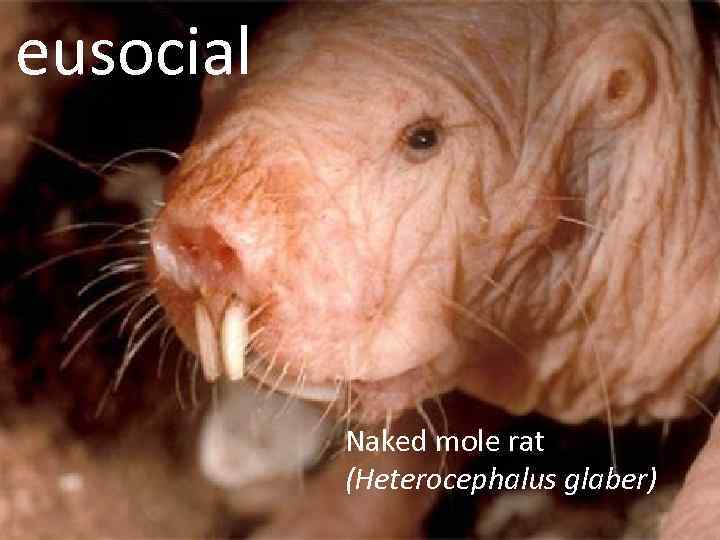 eusocial Naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber)
eusocial Naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber)
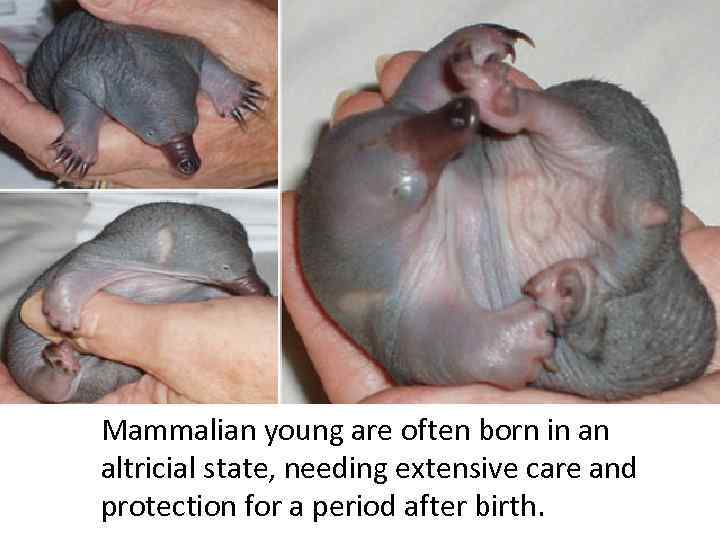 Mammalian young are often born in an altricial state, needing extensive care and protection for a period after birth.
Mammalian young are often born in an altricial state, needing extensive care and protection for a period after birth.
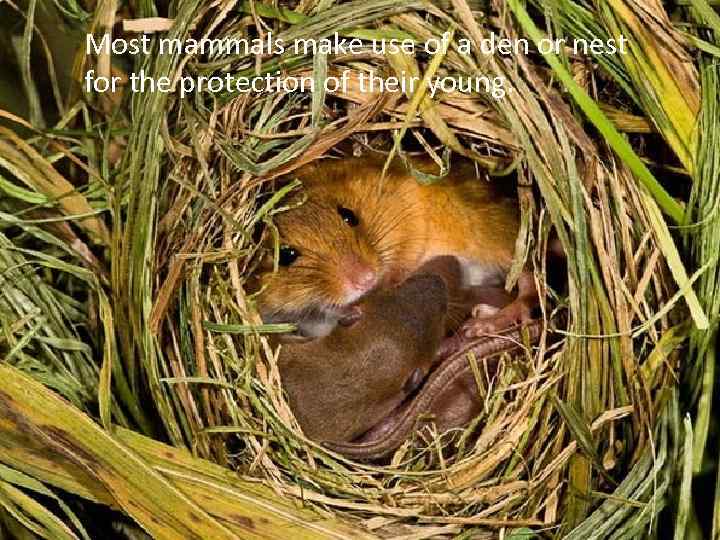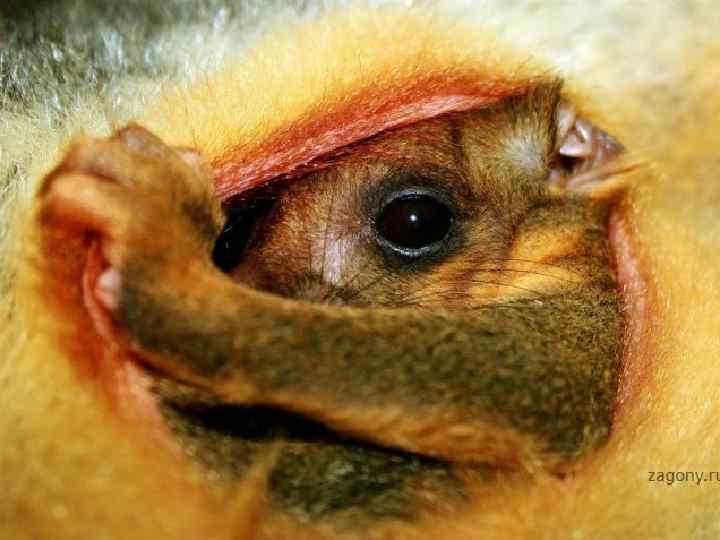
 Most mammals make use of a den or nest for the protection of their young.
Most mammals make use of a den or nest for the protection of their young.
 Some mammals, however, are born well-developed and are able to locomote on their own soon after birth.
Some mammals, however, are born well-developed and are able to locomote on their own soon after birth.
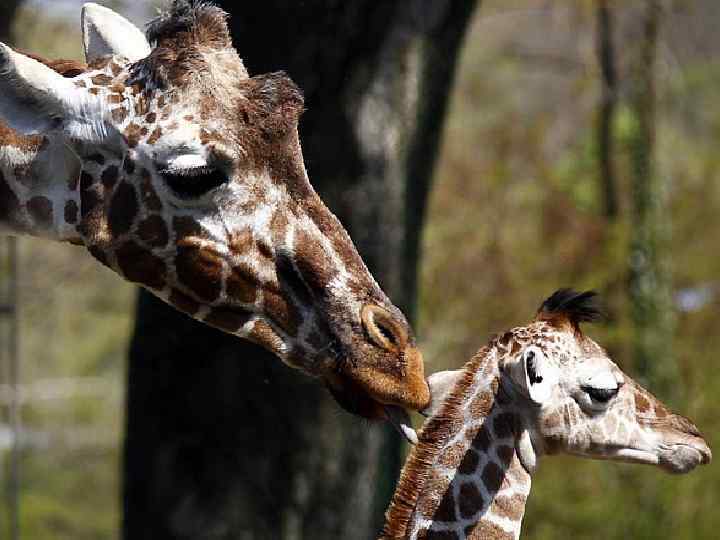
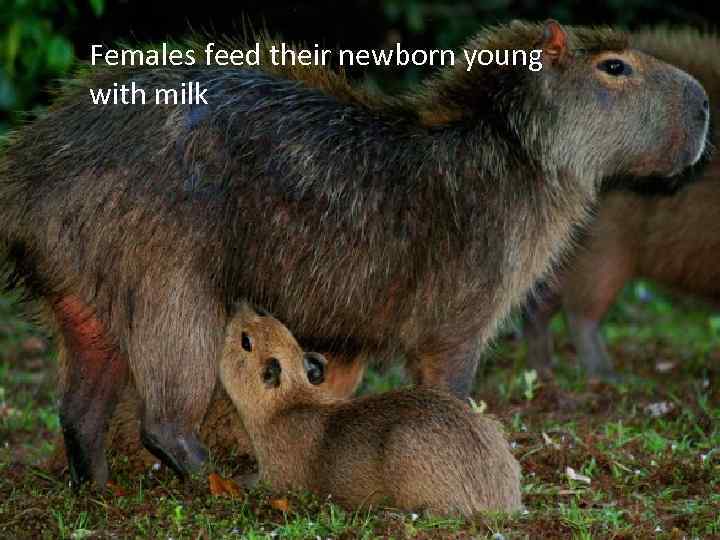
 Females feed their newborn young with milk
Females feed their newborn young with milk
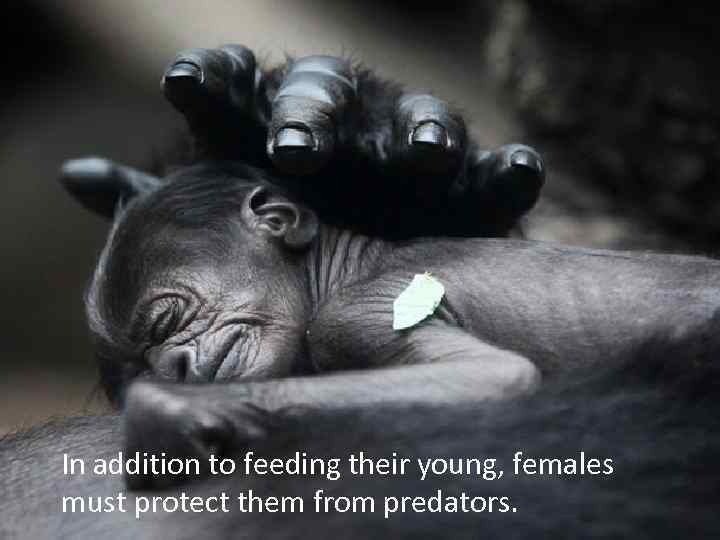 In addition to feeding their young, females must protect them from predators.
In addition to feeding their young, females must protect them from predators.
 Lifespan / Longevity Mammalian lifespans range from one year or less to 70 or more years in the wild. Bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) may live more than 200 years.
Lifespan / Longevity Mammalian lifespans range from one year or less to 70 or more years in the wild. Bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) may live more than 200 years.
 Food Habits As a group, mammals eat an enormous variety of organisms. Mammals eat both invertebrates and vertebrates (including other mammals), plants (including fruit, nectar, foliage, wood, roots, seeds, etc. ) and fungi. Being endotherms, mammals require much more food than ectotherms of similar proportions. Mammals can be:
Food Habits As a group, mammals eat an enormous variety of organisms. Mammals eat both invertebrates and vertebrates (including other mammals), plants (including fruit, nectar, foliage, wood, roots, seeds, etc. ) and fungi. Being endotherms, mammals require much more food than ectotherms of similar proportions. Mammals can be:
 Carnivores (e. g. , species within Carnivora)
Carnivores (e. g. , species within Carnivora)
 Herbivores (e. g. , Artiodactyla)
Herbivores (e. g. , Artiodactyla)
 Omnivores
Omnivores
 Locomotion styles are diverse. Mammals may:
Locomotion styles are diverse. Mammals may:
 swim
swim
 run
run
 fly
fly
 burrow
burrow
 climb
climb
 Sociality Social behavior varies considerably as well. Some mammals live in groups of tens, hundreds, thousands or more individuals. Other mammals are generally solitary except when mating or raising young.
Sociality Social behavior varies considerably as well. Some mammals live in groups of tens, hundreds, thousands or more individuals. Other mammals are generally solitary except when mating or raising young.
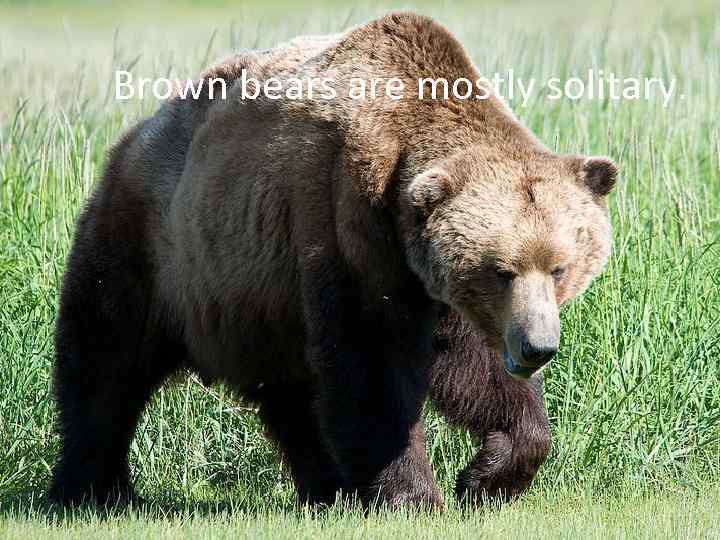 Brown bears are mostly solitary.
Brown bears are mostly solitary.
 A meerkat (Suricata suricatta) clan often contains about 20 meerkats, but some superfamilies have 50 or more members.
A meerkat (Suricata suricatta) clan often contains about 20 meerkats, but some superfamilies have 50 or more members.
 Numerous wildebeest during The Great Migratio
Numerous wildebeest during The Great Migratio
 Activity patterns among mammals also cover the full range of possibilities. Mammals may be: • diurnal - active during the day • nocturnal - active during the night • crepuscular - active at dawn and dusk
Activity patterns among mammals also cover the full range of possibilities. Mammals may be: • diurnal - active during the day • nocturnal - active during the night • crepuscular - active at dawn and dusk
 Communication and Perception • • Sensory modalities in mammals: olfaction hearing tactile perception vision
Communication and Perception • • Sensory modalities in mammals: olfaction hearing tactile perception vision




 Ecosystem Roles The ecological roles, or niches, filled by the nearly 5000 mammal species are quite diverse. There are predators and prey, carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores, species that create or greatly modify their habitat and thus the habitat and structure of their communities.
Ecosystem Roles The ecological roles, or niches, filled by the nearly 5000 mammal species are quite diverse. There are predators and prey, carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores, species that create or greatly modify their habitat and thus the habitat and structure of their communities.
 In part because of their high metabolic rates, mammals often play an ecological role that is disproportionately large compared to their numerical abundance. Thus, many mammals may be keystone predators in their communities or play important roles in seed dispersal or pollination. The ecosystem roles that mammals play are so diverse that it is difficult to generalize across the group. Despite their low species diversity, compared to other animal groups, mammals have a substantial impact on global biodiversity.
In part because of their high metabolic rates, mammals often play an ecological role that is disproportionately large compared to their numerical abundance. Thus, many mammals may be keystone predators in their communities or play important roles in seed dispersal or pollination. The ecosystem roles that mammals play are so diverse that it is difficult to generalize across the group. Despite their low species diversity, compared to other animal groups, mammals have a substantial impact on global biodiversity.


