19a19e2f4622ea3eced94a068414ca82.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

The LHCb Run Control System An Integrated and Homogeneous Control System Clara Gaspar, May 2010
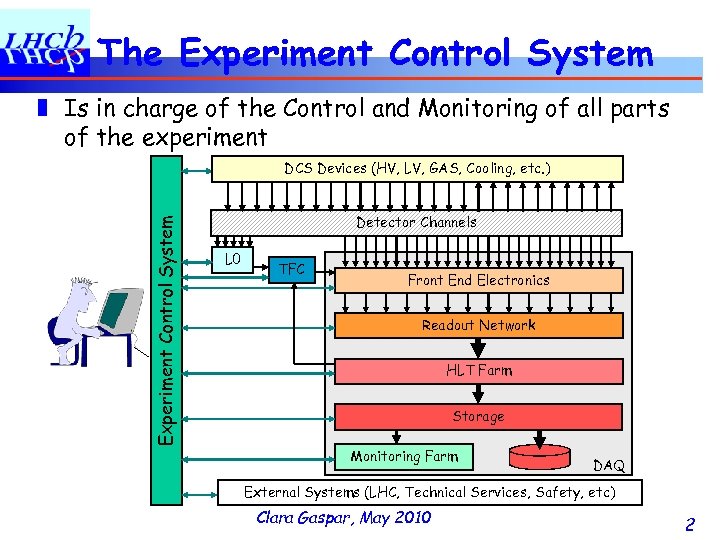
The Experiment Control System ❚ Is in charge of the Control and Monitoring of all parts of the experiment Experiment Control System DCS Devices (HV, LV, GAS, Cooling, etc. ) Detector Channels L 0 TFC Front End Electronics Readout Network HLT Farm Storage Monitoring Farm DAQ External Systems (LHC, Technical Services, Safety, etc) Clara Gaspar, May 2010 2

Some Requirements ❚ Large number of devices/IO channels ➨ Need for Distributed Hierarchical Control ❘ De-composition in Systems, sub-systems, … , Devices ❘ Local decision capabilities in sub-systems ❚ Large number of independent teams and very different operation modes ➨ Need for Partitioning Capabilities (concurrent usage) ❚ High Complexity & Non-expert Operators ➨ Need for Full Automation of: ❘ Standard Procedures ❘ Error Recovery Procedures ➨ And for Intuitive User Interfaces Clara Gaspar, May 2010 3
Design Steps ❚ In order to achieve an integrated System: ❙ Promoted HW Standardization (so that common components could be re-used) ❘ Ex. : Mainly two control interfaces to all LHCb electronics 〡Credit Card sized PCs (CCPC) for non-radiation zones 〡A serial protocol (SPECS) for electronics in radiation areas ❙ Defined an Architecture ❘ That could fit all areas and all aspects of the monitoring and control of the full experiment ❙ Provided a Framework ❘ An integrated collection of guidelines, tools and components that allowed the development of each sub-system coherently in view of its integration in the complete system Clara Gaspar, May 2010 4
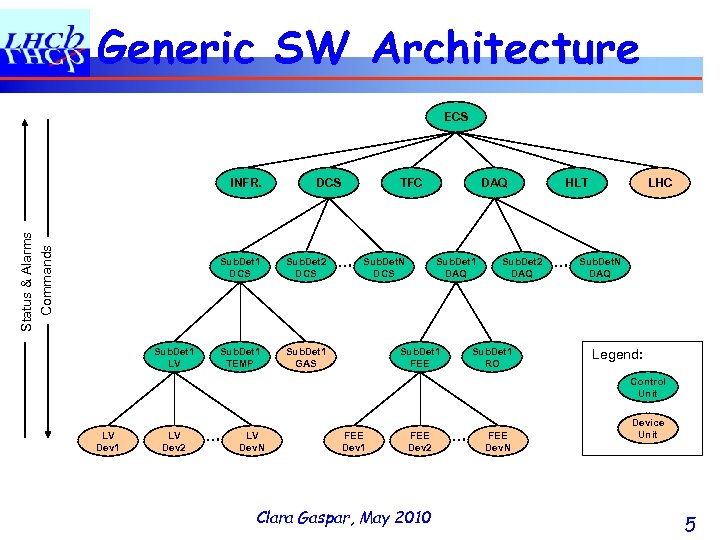
Generic SW Architecture ECS Status & Alarms Commands INFR. Sub. Det 1 DCS Sub. Det 1 LV TFC DCS Sub. Det 2 DCS Sub. Det 1 TEMP … Sub. Det. N DCS Sub. Det 1 GAS DAQ Sub. Det 1 FEE Sub. Det 2 DAQ Sub. Det 1 RO HLT … LHC Sub. Det. N DAQ Legend: Control Unit LV Dev 1 LV Dev 2 … LV Dev. N FEE Dev 1 FEE Dev 2 Clara Gaspar, May 2010 … FEE Dev. N Device Unit 5
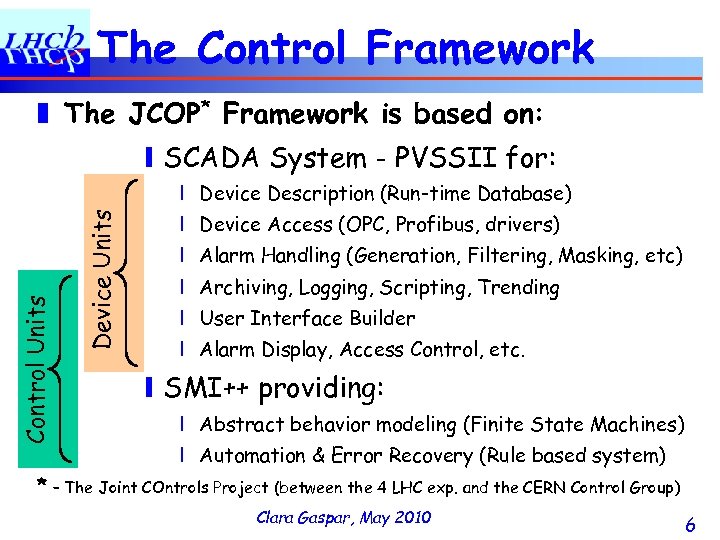
The Control Framework ❚ The JCOP* Framework is based on: ❙ SCADA System - PVSSII for: Device Units Control Units ❘ Device Description (Run-time Database) ❘ Device Access (OPC, Profibus, drivers) ❘ Alarm Handling (Generation, Filtering, Masking, etc) ❘ Archiving, Logging, Scripting, Trending ❘ User Interface Builder ❘ Alarm Display, Access Control, etc. ❙ SMI++ providing: ❘ Abstract behavior modeling (Finite State Machines) ❘ Automation & Error Recovery (Rule based system) * – The Joint COntrols Project (between the 4 LHC exp. and the CERN Control Group) Clara Gaspar, May 2010 6

Device Units Device Unit ❚ Provide access to “real” devices: ❙ The Framework provides (among others): ❘ “Plug and play” modules for commonly used equipment. For example: 〡CAEN or Wiener power supplies (via OPC) 〡LHCb CCPC and SPECS based electronics (via DIM) ❘ A protocol (DIM) for interfacing “home made” devices. For example: 〡Hardware devices like a calibration source 〡Software devices like the Trigger processes (based on LHCb’s offline framework – GAUDI) ❘ Each device is modeled as a Finite State Machine Clara Gaspar, May 2010 7
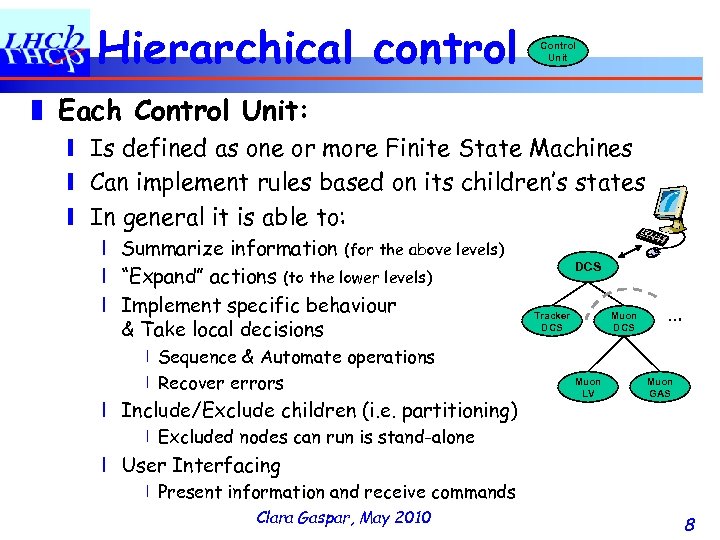
Hierarchical control Control Unit ❚ Each Control Unit: ❙ Is defined as one or more Finite State Machines ❙ Can implement rules based on its children’s states ❙ In general it is able to: ❘ Summarize information (for the above levels) ❘ “Expand” actions (to the lower levels) ❘ Implement specific behaviour & Take local decisions 〡Sequence & Automate operations 〡Recover errors ❘ Include/Exclude children (i. e. partitioning) DCS Tracker DCS Muon LV … Muon GAS 〡Excluded nodes can run is stand-alone ❘ User Interfacing 〡Present information and receive commands Clara Gaspar, May 2010 8
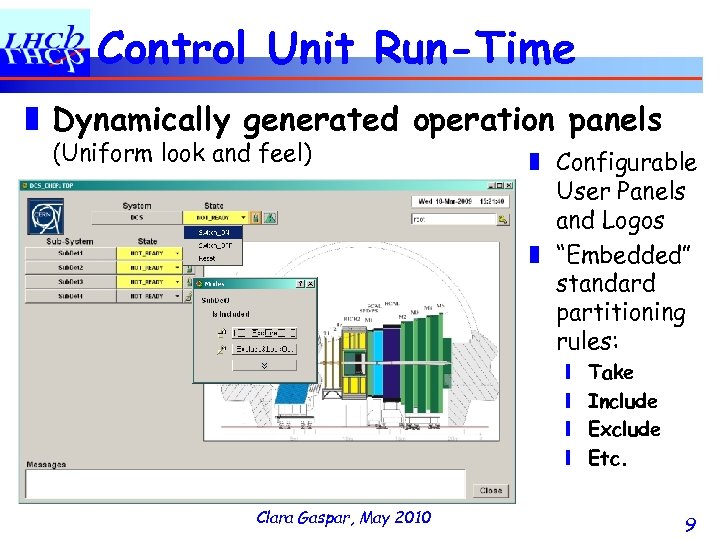
Control Unit Run-Time ❚ Dynamically generated operation panels (Uniform look and feel) ❚ Configurable User Panels and Logos ❚ “Embedded” standard partitioning rules: ❙ ❙ Clara Gaspar, May 2010 Take Include Exclude Etc. 9
Operation Domains ❚ Three Domains have been defined: ❙ DCS ❘ For equipment which operation and stability is normally related to a complete running period Example: GAS, Cooling, Low Voltages, etc. ❙ HV ❘ For equipment which operation is normally related to the Machine state. Example: High Voltages ❙ DAQ ❘ For equipment which operation is related to a RUN Example: Readout electronics, High Level Trigger processes, etc. Clara Gaspar, May 2010 10
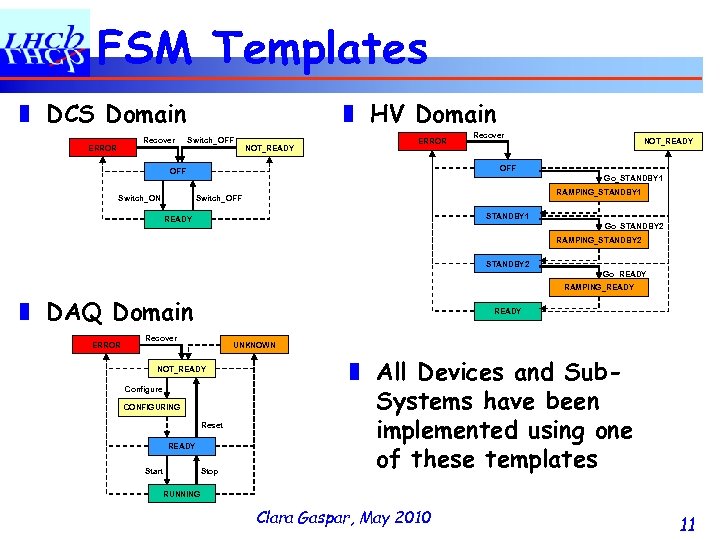
FSM Templates ❚ DCS Domain Recover ERROR ❚ HV Domain Switch_OFF NOT_READY ERROR NOT_READY OFF Switch_ON Recover Go_STANDBY 1 RAMPING_STANDBY 1 Switch_OFF STANDBY 1 READY Go_STANDBY 2 RAMPING_STANDBY 2 Go_READY RAMPING_READY ❚ DAQ Domain ERROR READY Recover UNKNOWN NOT_READY Configure CONFIGURING Reset READY Start Stop ❚ All Devices and Sub. Systems have been implemented using one of these templates RUNNING Clara Gaspar, May 2010 11
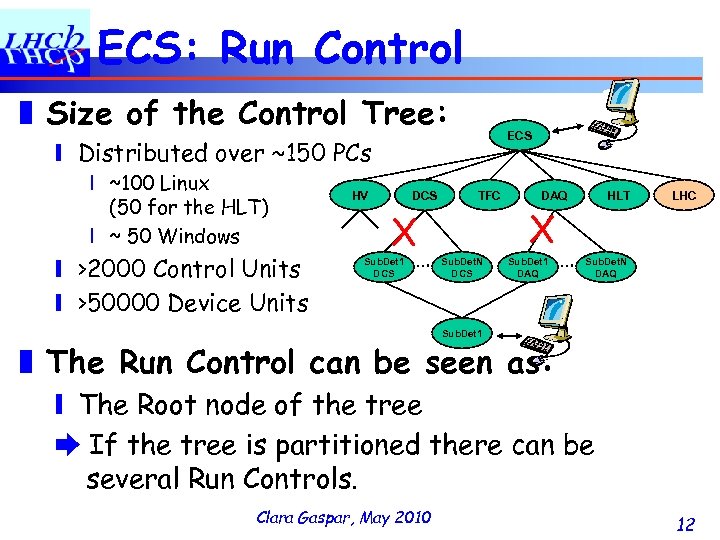
ECS: Run Control ❚ Size of the Control Tree: ECS ❙ Distributed over ~150 PCs ❘ ~100 Linux (50 for the HLT) ❘ ~ 50 Windows ❙ >2000 Control Units ❙ >50000 Device Units HV DCS TFC X Sub. Det 1 DCS … Sub. Det. N DCS DAQ X Sub. Det 1 DAQ … HLT LHC Sub. Det. N DAQ Sub. Det 1 ❚ The Run Control can be seen as: ❙ The Root node of the tree ➨ If the tree is partitioned there can be several Run Controls. Clara Gaspar, May 2010 12
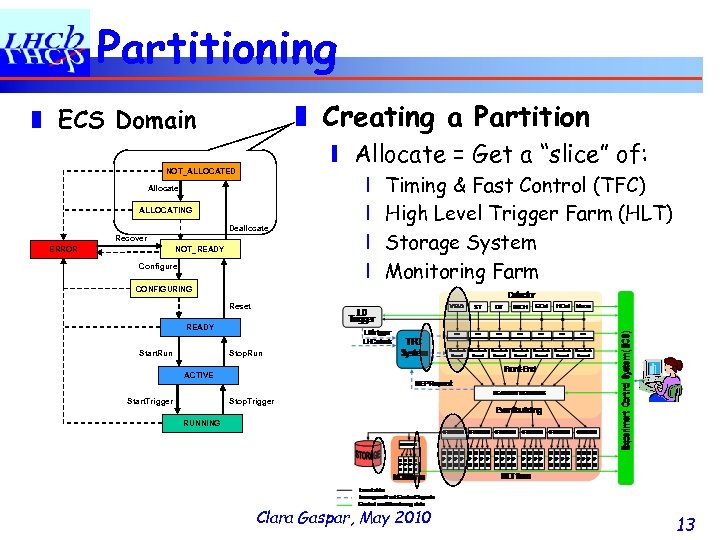
Partitioning ❚ Creating a Partition ❚ ECS Domain ❙ Allocate = Get a “slice” of: NOT_ALLOCATED Allocate ALLOCATING Deallocate Recover NOT_READY ERROR Configure ❘ ❘ Timing & Fast Control (TFC) High Level Trigger Farm (HLT) Storage System Monitoring Farm CONFIGURING Reset READY Start. Run Stop. Run ACTIVE Start. Trigger Stop. Trigger RUNNING Clara Gaspar, May 2010 13
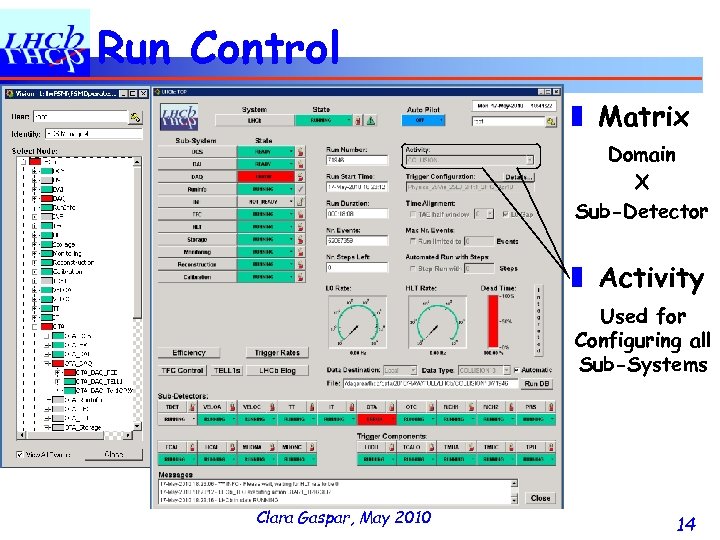
Run Control ❚ Matrix Domain X Sub-Detector ❚ Activity Used for Configuring all Sub-Systems Clara Gaspar, May 2010 14
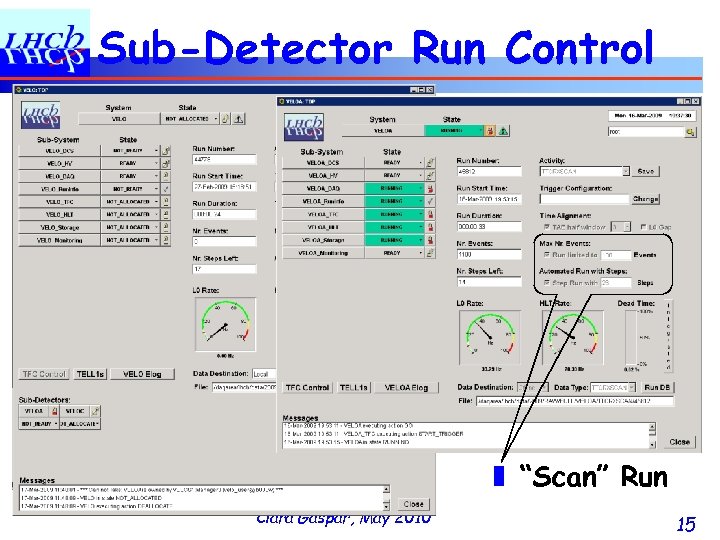
Sub-Detector Run Control ❚ “Scan” Run Clara Gaspar, May 2010 15
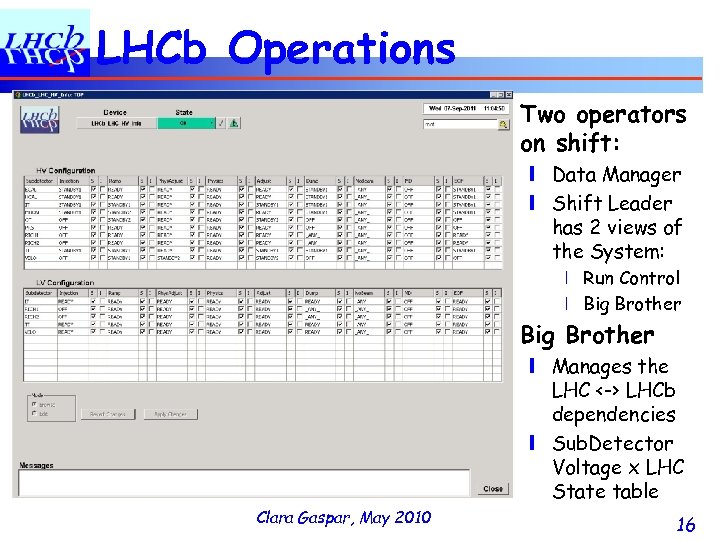
LHCb Operations ❚ Two operators on shift: ❙ Data Manager ❙ Shift Leader has 2 views of the System: ❘ Run Control ❘ Big Brother ❚ Big Brother ❙ Manages the LHC <-> LHCb dependencies ❙ Sub. Detector Voltage x LHC State table Clara Gaspar, May 2010 16
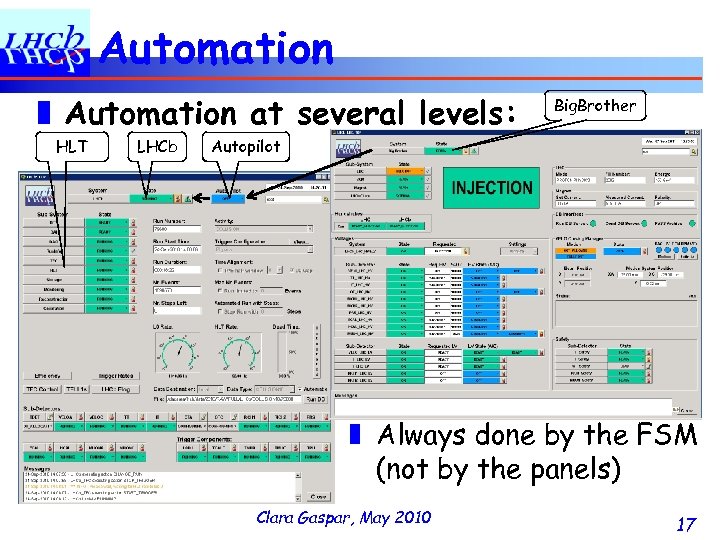
Automation ❚ Automation at several levels: HLT LHCb Big. Brother Autopilot ❚ Always done by the FSM (not by the panels) Clara Gaspar, May 2010 17
Conclusions ❚ LHCb has designed and implemented a coherent and homogeneous control system ❚ The Run Control allows to: ❙ Configure, Monitor and Operate the Full Experiment ❙ Run any combination of sub-detectors in parallel in standalone ❙ Can be completely automated (when we understand the machine) ❚ Some of its main features: ❙ Sequencing, Automation, Error recovery, Partitioning ➨ Come from the usage of SMI++ (integrated with PVSS) ❚ It’s being used daily for Physics data taking and other global or sub-detector activities Clara Gaspar, May 2010 18
19a19e2f4622ea3eced94a068414ca82.ppt