c8e3f9e67703d92b786acc503ddd346f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

The Legislative Branch

Where is Congress? U. S. Capitol Building Washington, D. C.

Legislative Vocabulary bicameral: two house legislature caucuses: meetings of party leaders to determine party policy or to choose the party’s candidates for public office bill: proposed law being considered by a lawmaking body quorum: minimum number of people needed to conduct business constituents: the people who a representative represents
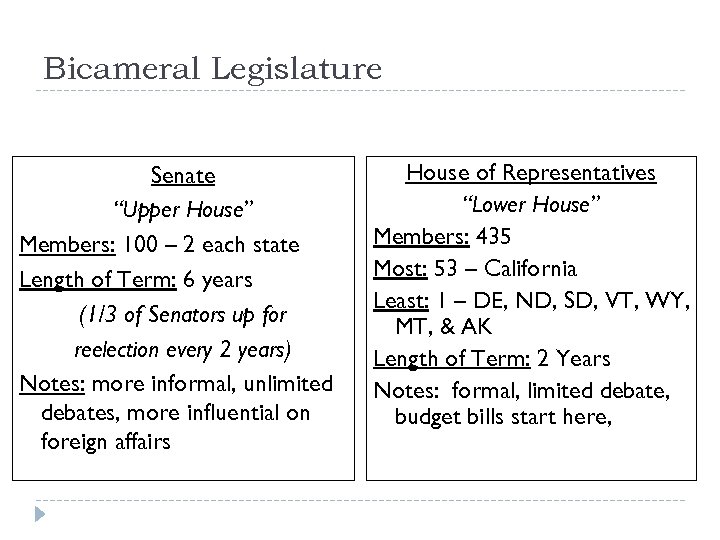
Bicameral Legislature Senate “Upper House” Members: 100 – 2 each state Length of Term: 6 years (1/3 of Senators up for reelection every 2 years) Notes: more informal, unlimited debates, more influential on foreign affairs House of Representatives “Lower House” Members: 435 Most: 53 – California Least: 1 – DE, ND, SD, VT, WY, MT, & AK Length of Term: 2 Years Notes: formal, limited debate, budget bills start here,

What to call them? Senators: Those elected to the Senate Representatives: Those elected to the House Honorable: Prefix given to Representatives Congressmen, Congresswomen: Person elected to either the Senate or House

House of Representatives 435 members Originally 1 for ever 30, 000 That would mean over 10, 000 representatives today! # set in 1913 Every ten years a census is taken Census – population count After a census; seats in the House of Representatives are apportioned based on population Every state is guaranteed at least one seat Redistricting – redrawing district lines; occurs when a state gains or loses seats
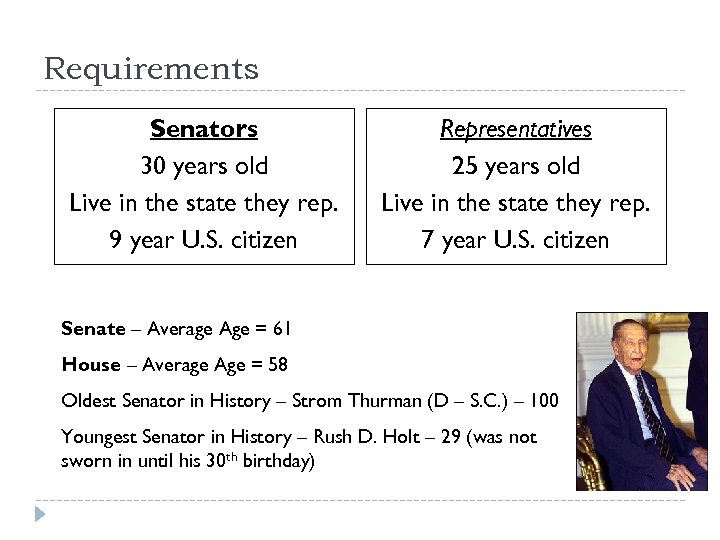
Requirements Senators 30 years old Live in the state they rep. 9 year U. S. citizen Representatives 25 years old Live in the state they rep. 7 year U. S. citizen Senate – Average Age = 61 House – Average Age = 58 Oldest Senator in History – Strom Thurman (D – S. C. ) – 100 Youngest Senator in History – Rush D. Holt – 29 (was not sworn in until his 30 th birthday)

AL Districts and Congressmen Richard Shelby Jeff Sessions Mike Rogers

Non-voting members District of Columbia Puerto Rico Guam American Samoa Northern Mariana Islands U. S. Virgin Islands They can serve on committees; but can not vote
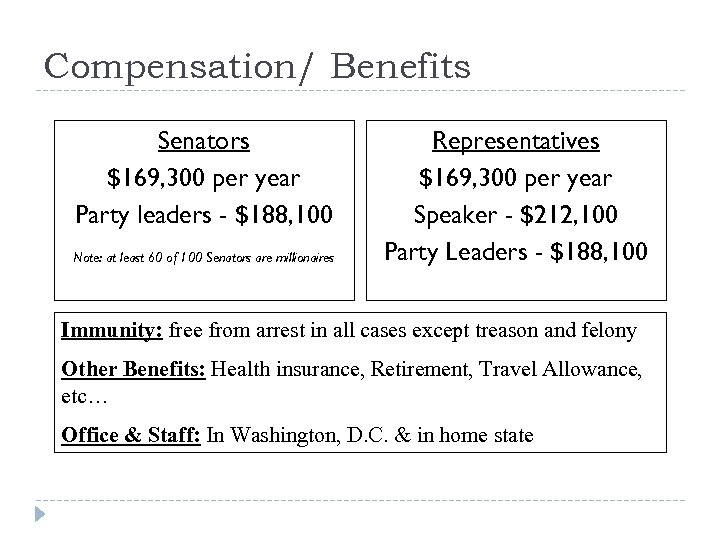
Compensation/ Benefits Senators $169, 300 per year Party leaders - $188, 100 Note: at least 60 of 100 Senators are millionaires Representatives $169, 300 per year Speaker - $212, 100 Party Leaders - $188, 100 Immunity: free from arrest in all cases except treason and felony Other Benefits: Health insurance, Retirement, Travel Allowance, etc… Office & Staff: In Washington, D. C. & in home state
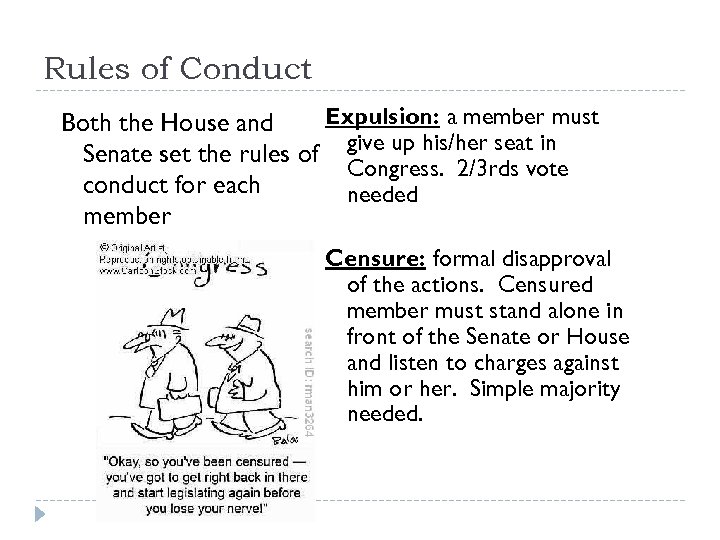
Rules of Conduct Expulsion: a member must Both the House and Senate set the rules of give up his/her seat in Congress. 2/3 rds vote conduct for each needed member Censure: formal disapproval of the actions. Censured member must stand alone in front of the Senate or House and listen to charges against him or her. Simple majority needed.
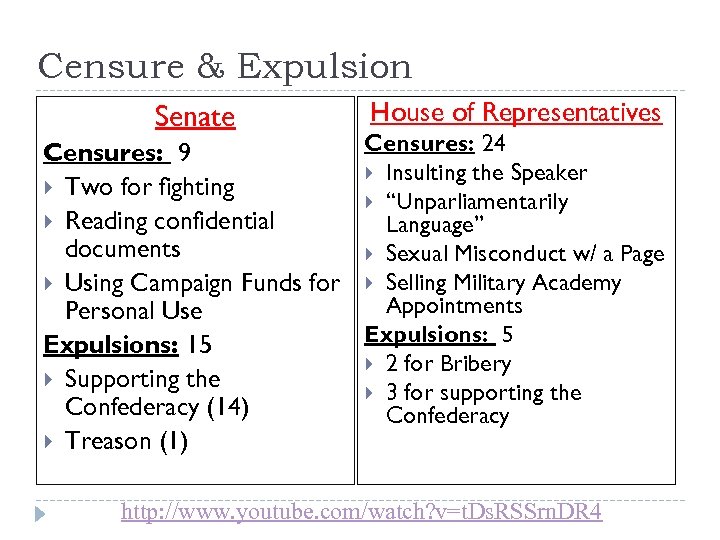
Censure & Expulsion Senate House of Representatives Censures: 24 Censures: 9 Insulting the Speaker Two for fighting “Unparliamentarily Reading confidential Language” documents Sexual Misconduct w/ a Page Using Campaign Funds for Selling Military Academy Appointments Personal Use Expulsions: 5 Expulsions: 15 2 for Bribery Supporting the 3 for supporting the Confederacy (14) Confederacy Treason (1) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=t. Ds. RSSrn. DR 4

Senate Chamber

House of Representatives
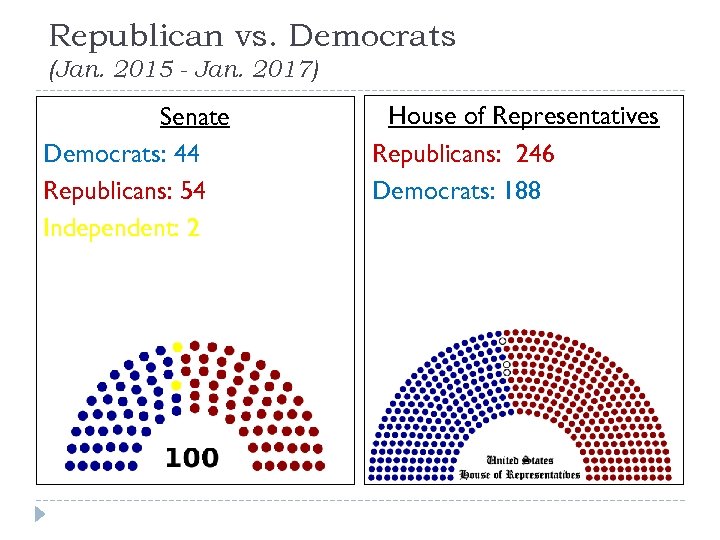
Republican vs. Democrats (Jan. 2015 - Jan. 2017) Senate Democrats: 44 Republicans: 54 Independent: 2 House of Representatives Republicans: 246 Democrats: 188
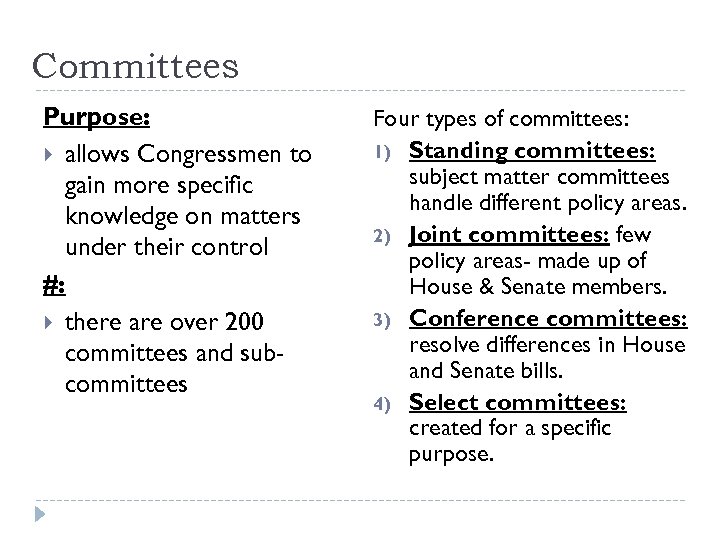
Committees Purpose: allows Congressmen to gain more specific knowledge on matters under their control #: there are over 200 committees and subcommittees Four types of committees: 1) Standing committees: subject matter committees handle different policy areas. 2) Joint committees: few policy areas- made up of House & Senate members. 3) Conference committees: resolve differences in House and Senate bills. 4) Select committees: created for a specific purpose.

Examples of Committees Senate Energy Wildlife Children’s Health African Affairs Retirement and Aging Finance Crime and Drugs Homeland Security Green Jobs National Parks House Livestock and Dairy Air and Land Forces Budget Higher Education Europe Elections Domestic Policy Highways Railroads

Example: How are Committees Used? Example: House Committee on Oversight and Government Reform Task: investigate the problem with steroids and professional athletes

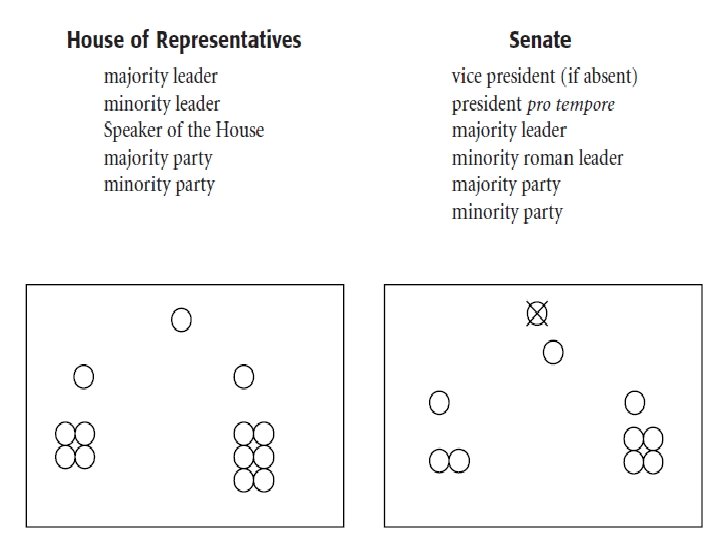
Who’s Who in the House of Rep?

Speaker of the House Role: Leader of the majority party sets agenda for his/her political party Third in line (after V. P. ) for Presidential succession. Who: Paul Ryan (R-WI)

House Majority Leader Role: Leader of the majority party (2 nd to Speaker of the House) scheduling legislation for floor consideration planning the daily, weekly, and annual schedules working to advance the goals of the majority party. Who: Kevin Mc. Carthy (R – California)

House Majority Whip (Not Mandated by the Constitution) Role: Assists Speaker of the House & Majority Leader to gather support for proposed bills Who: Steve Scalise (R – Louisiana)

House Minority Whip (Not Mandated by the Constitution) Role: assists the minority leader in coordinating the party caucus in response to proposed legislation Who: Steny Hoyer – (D – Maryland)

House Minority Leader Role: Leader of the minority party in the House; set agenda his/her party Who: Nancy Pelosi (D) California

Sergeant-at-Arms of the House Role: responsible for security of the House wing of the Capitol maintain order in the House safety of guests and tourists Who: Paul D. Irving

Chaplain of the U. S. House Role: open each session of Congress with a prayer pastor of the House Who: Fr. Patrick J. Conroy

Who’s Who in the Senate?

President of the Senate Role: Preside over the Senate to cast deciding votes in a case of a tie (only happened 242 times) Who: Vice President of the United States Joe Biden

President Pro Tempore Role: replace V. P when not present maintain order in the Senate Who: most senior member of the majority party Orin Hatch (R –Utah) serving in the Senate since 1977 Also: 3 rd in line for presidential succession

Senate Majority Leader Role: chief spokesman for the majority party in the Senate set agenda and direction of political party Who: Mitch Mc. Connell (R Kentucky)

Senate Minority Leader Role: chief spokesman for the minority party in the Senate help set agenda and direction of party Who: Harry Reid (D – Nevada)

Senate Majority Whip (Assistant Minority Leader) Role: gather votes on majority party issues 2 nd ranking party leader in the Senate Who: John Cornyn III (R – Texas)

Senate Minority Whip (Assistant Minority Leader) Role: gather votes for minority party issues 2 nd ranking party leader in the Senate Who: Richard Durbin (D – Illinois)

Sergeant-at-Arms of the Senate Role: the law enforcer of the U. S. Senate responsible for security on and around the building Who: Frank J. Larkin

Chaplain of the U. S. Senate Role: open each session of the Senate with a prayer Pastor of the Senate Who: Barry Black First African-American Chaplain Seventh Day Adventist Selected by simple majority in the Senate

Congressional Pages Who: Appointed H. S. Juniors Non-partisan federal employees Responsibilities Tending to the personal needs of Congressmen while on the floor Managing the phones Ringing bells for votes

Joint Sessions What: when both members of the House and Senate get together When: Counting Electoral Votes State of the Union Address
c8e3f9e67703d92b786acc503ddd346f.ppt