da72a5aaa8a26fd4bd8699a5f78d0a96.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15


The Legislative Branch The US Congress Created by Article I n Bicameral n Upper House – Senate n Lower House – House of Representatives n n Leaders Senate – VP / President Pro Tempore n House – Speaker of the House n

Requirements and terms of service n Senate: n Term: Senators serve unlimited 6 year terms, elected by popular vote (**note: The original Constitution called for Senators to be elected by the state legislatures, the 17 th amendment changed this to a popular vote) n n Requirements: Senators must be over 30, 9 year citizens of the US and a resident of the state House of Representatives: n n Term: Representatives serve unlimited 2 year terms, elected by popular vote Requirements: Representatives must be over 25, 7 year citizens of the US and a resident of the state

Representation n Senate: n n Representation: Each state has 2 Senators House of Representatives: n Representation: Each state's number of representatives is proportional to population. The number of Representatives is fixed at 435 and division among the states is determined by the census (population count) conducted ever 10 years as required by the Constitution.

The Executive Branch The President Created by Article II n Consists of n The President n His Advisors n All Federal Agencies and their heads. n

Special powers & Responsibilities n Judicial Grant pardon (forgiving an individual of his/her crime(s)) n Grant amnesty (forgiving a group of people of a specific class of crime) n

Requirements and terms of service n Terms: President serves a maximum of 2 terms of 4 years (**note: the original Constitution allowed of unlimited terms of service, this was revised by the 22 nd amendment in 1951) n Requirements: President (or Vice-President) must over 35, a natural born citizen and a 14 year resident of the United States.

The Judicial Branch The Supreme Court n n n Created by Article III Composed of the Supreme Court and all of the lower federal courts as created by Congress The most significant power of the judicial branch is that of judicial review, first stated by Chief Justice John Marshall in the 1803 case of Marbury vs. Madison, but not expressly granted the court by the Constitution.

Jurisdiction (Supreme Court) The Supreme Court hears cases of appeal from lower federal and state courts n The Supreme Court has original jurisdiction (may hear a case first) in cases involving a state vs. state matter or a branch vs. branch matter n

Requirements and terms of service n n Terms: Judges serve for life, they are nominated by the president and approved by the Senate but may be removed by an impeachment proceeding Requirements: There are no specific requirement for judgeship in the Constitution

Article IV n Relations between the states. n Citizenship, extradition etc. Rules about new states. n Guarantees each state a republican government, protection from invasion and domestic violence n
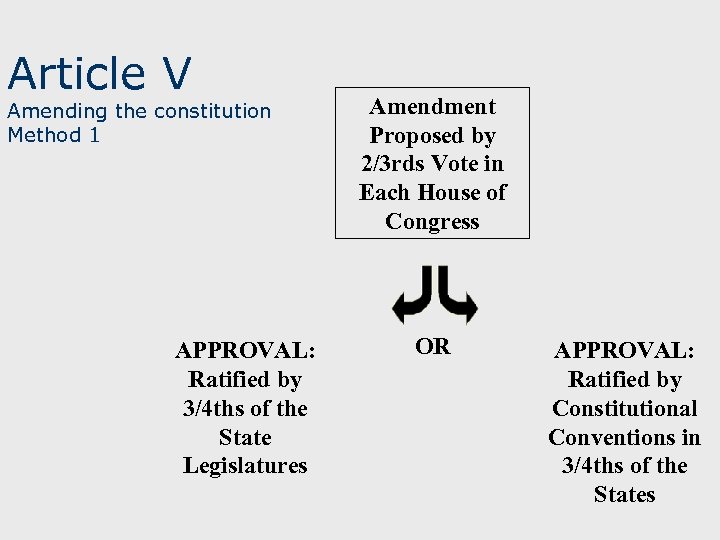
Article V Amending the constitution Method 1 APPROVAL: Ratified by 3/4 ths of the State Legislatures Amendment Proposed by 2/3 rds Vote in Each House of Congress OR APPROVAL: Ratified by Constitutional Conventions in 3/4 ths of the States
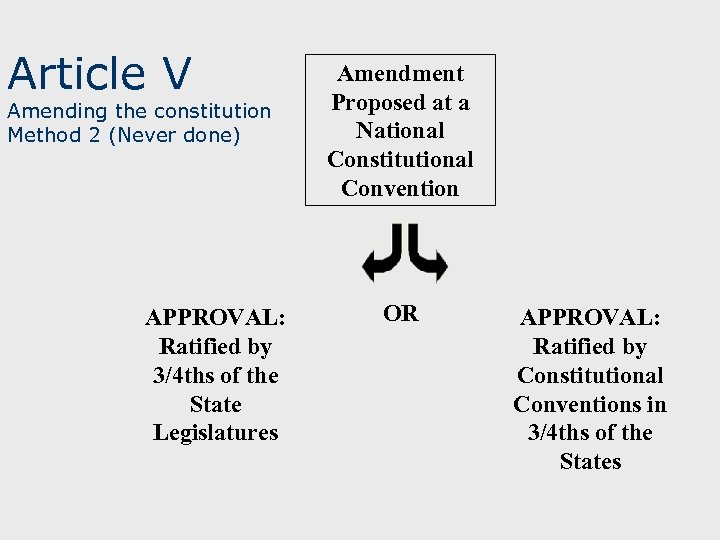
Article V Amending the constitution Method 2 (Never done) APPROVAL: Ratified by 3/4 ths of the State Legislatures Amendment Proposed at a National Constitutional Convention OR APPROVAL: Ratified by Constitutional Conventions in 3/4 ths of the States

Article VI n Sets the federal government as the supreme law of the land

Article VII n States that 9 states must ratify the constitution in order for it to take effect
da72a5aaa8a26fd4bd8699a5f78d0a96.ppt