7ead5fefa8ed8d1221cdb2432c0e53dd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH Inside Congress CIVICS Mr. Hensley SRMHS

Two Types of Representatives • Representatives (House) serve for 2 years, must be 25 years old and live in their district • Senators (Senate): serve for six years, must be 30 years old and resident of their state • House: very political and very partisan • Senate: more laid back and bi-partisan

Personal and Committee Staff • Personal staff report directly to the Congressperson that hired them • They schedule meetings, answer mail both in DC and at home • May be multiple offices that need to be staffed • Committee staff are experts in their field – report directly to the Committee chair

Support Services • Library of Congress – one of the biggest libraries in the world • Congressional Research Service – researches any topic, tracks bills • General Accounting Office (GAO) – investigates spending and monitors efficiency • Congressional Budget Office (CBO) – estimates costs and plans spending

Duties of a Congressperson • Make law (pass bills) – the basic job • Casework – help constituents with problems big and small • Help the district by passing laws that result in federal funds being spent in the district • Dark side: “pork barrel”


Legislative Powers • Taxing and spending – the “power of the purse”, can make policy by cutting off $$$ (“Ways and Means”) • Regulating Commerce – can pass laws to monitor, control business • Foreign Relations – can declare war, approve treaties, pass resolutions

Non-legislative Powers • Check on executive branch– can defeat appointments, over-ride vetoes etc. • Impeachment Power– both federal judges and the President • Oversight Ability - can start or stop investigations into any topic of concern

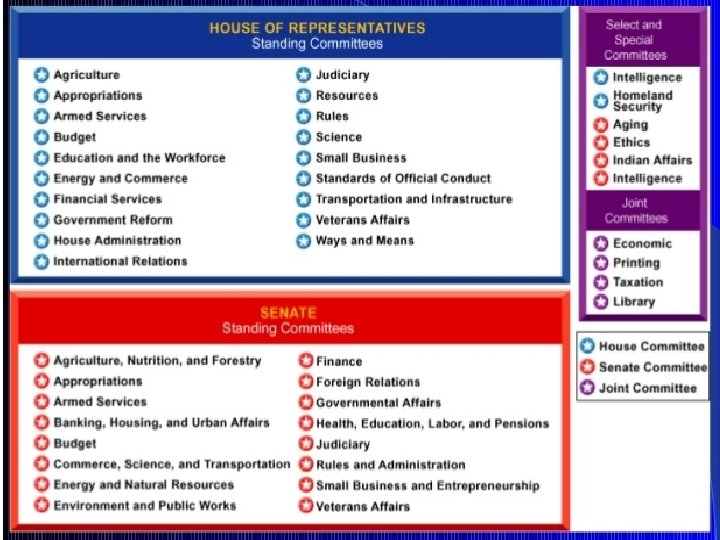
Committees • Both the Senate and the House have about 15 major committees that are subject-based • Each committee is broken down into several subcommittees • Bills get sent to the appropriate committee • Most bills get stuck there

Speaker of the House • Leader of his party in the House – controls committee assignments • Determines which bills go to which committee • Schedules debates on the House floor • Second in line for the Presidency • Tenure is two years (one session of Congress)

Senate President Pro Tempore • In charge of the Senate during normal sessions • Recall that the VP is President of Senate and can cast a tie-breaking vote • Senior member of Majority Party (by tradition) • Has less power than Speaker (fewer committee assignments) • Third in line for Presidency

Majority and Minority Leaders • Each party has a leader in each chamber of Congress – a Majority and Minority leader • Spokesperson for the party, its public face • “Whips” are the second-incommands for each party • In charge of discipline, of getting party members to vote the “party line”

Quorums and Sessions • Each Congress is broken up into 2 year-long sessions • Congress is in session about half the time (and all of August) • Each two year Congress is numbered sequentially (115 th on now) • Quorum means enough people on hand to do business – House Rule is 218, Senate is 51
7ead5fefa8ed8d1221cdb2432c0e53dd.ppt